Due to high stress, the knee joint often undergoes age-related deformation. However, often the problem does not arise because of the years lived. Damage to the osteoarticular surfaces as a result of injuries, sprains, ruptures and microtears of muscles are the most relevant situations for knee damage. The treatment process is far from quick, since therapy is carried out conservatively and surgically. But any treatment option requires exercises to strengthen the knee joint. Exercise therapy not only promotes speedy rehabilitation after surgery for any ailments, but also helps strengthen muscles and stabilize the ligamentous apparatus of the lower extremities.
The knee joint is most often affected because it has a large range of motion.
Therapeutic effect
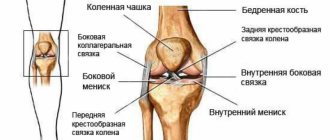
The muscles and ligaments of the entire lower limb take part in the work of the knee. The main task of the knee joint is to extend, flex and rotate the tibia relative to the thigh. They are especially effective when the hip joint is in a bent position. On the side of the lower leg, the sartorius and gastrocnemius muscles are involved in the process of active movements, and rotational actions in a bent state are achieved due to tension in the tibial fascia. The maximum number of connections of muscle fibers and ligaments are located in the popliteal fossa. It is this segment that is impacted by isometric gymnastics - modern exercises for developing the knee joint after surgery.
Movement in the knee is a complex process that involves the work of many anatomical structures of the limb. Damage to any part of the chain leads to events leading to the formation of diseases of the knee joint.
Physical therapy (physical therapy) alone cannot cure any of the joint diseases. But it helps strengthen ligaments and muscles, which provides benefits during complex conservative therapy or after surgery. Exercise therapy effectively facilitates leg movements with arthrosis, which is especially important for older people. Regular muscle exercises increase their physical endurance and tendons become elastic. Videos of exercises for the treatment of arthrosis can be viewed in publicly available sources.
Knee replacement in the Czech Republic: guarantees, prices, rehabilitation, reviews and statistics.
Find out more
Complete outline of exercise therapy sessions for medial meniscopathy
Physiotherapy exercises for injury - meniscal tears - can protect you from surgical intervention. The lesson notes below are compiled for patients who have damage to the internal (medial) meniscus. It will include not only exercises for the knee joint after a meniscus injury.
Knee pain causes a person to step on their foot incorrectly. As a result, the natural curves of the arches of the feet begin to change, and posture is disrupted. Therefore, the warm-up includes movements to prevent flat feet, and special exercises for the knees in a lying position will correct the spine.
Warm-up
Bringing your heels together and spreading them out while raising your toes
Warm-up is carried out in the following order:
- One palm lies on the stomach, the other on the chest. Inhalation and exhalation with the stomach alternates with inhalation and exhalation with the chest - 30-60 seconds.
- Movements with the chin: “pendulum”, outlining circles parallel and perpendicular to the floor in front of you – 6-8 times.
- Shoulder circles – 8 forward and 8 back.
- Rotations at the wrist, fingers clenched into a fist (thumb inside) - 10 times.
- Circles with the pelvis clockwise and counterclockwise (hands on the belt) - 10 times.
- The palms rest on the chest under the armpits, fingers pointing forward. As you inhale, move your pelvis back. As you exhale, return it to place by turning the tailbone. Dosage – 30-60 seconds.
- Stand on one leg and draw circles with the outstretched toes of the other – 8 times clockwise and 8 counter-clockwise. Make movements with the other leg.
- Place your feet slightly narrower than your shoulders. Slowly rise on your toes, try to bring your heels together, and smoothly return back. Repeat 6 times. Then do 6 raises on your toes, but do not bring your heels together, but separate them from each other (pictured above).
- "Crawler soles." You need to move forward without lifting your feet from the floor - by bending/extending the soles. First, bend your fingers, “clinging” to the floor, the arch bends, the heels move forward. Then, standing on your heels, straighten the sole, straightening your toes and pushing them forward. Do the movements until you get tired, rest and repeat again.
- Alternating legs, quickly touch the heel to the buttock. After 50 times (25+25), bend deeply forward, the forearms of the hands are connected and placed on the top of the head, the palms grab the opposite elbows. Repeat the cycle 2 times.
Main part of the lesson
Table 1 - Exercises in a standing position:
| Image | Explanation |
| We remain in position 1 for as long as possible – up to 2.5 minutes. Lift your heels as far off the floor as possible, but do not bend your knees beyond a 90-degree angle. After a static hold, which develops the strength of the quadriceps muscles, stand for 10-15 seconds in compensating pose 2. Dosage – 2-3 times. |
| Place your feet as wide as possible, turn your toes outward, bend your knees, hold your hands as comfortable as possible (fragment of photo 1). Rise up onto your toes and take 10 short steps (without letting your heels touch the floor) forward and 10 back. Straighten your legs, relax. Do 3 approaches, then bend over (fragment 2) and stand there for 15 seconds. |
| In pose 1, do not bend your knees more than 90 degrees, do not lift your heels off the floor, lean your back on the wall, holding a brick or book, you must stand for 90 seconds. After which we give the muscles a rest and “sit” for another 90 seconds. After which we lie down in pose 2. You can move your legs and make vibration movements. You need to lie down for 2-3 minutes. |
Naturally, the indicated temporary dosage will not be immediately feasible for everyone. Start doing exercises with the time that is available, and gradually build it up, adding a few seconds every day.
Table 2 – Supports and lying asanas:
| Image | Explanations |
| In the indicated position, raise one leg low above the floor, and draw circles clockwise and counterclockwise with your outstretched fingers. Do 10-14 circles in each direction. After resting for a couple of seconds, perform the movements with the other leg. |
| Place the rubber band behind your foot and pull your leg toward you (1). Then move your leg outward (2), and then inward (3). Try not to lift your shoulders and pelvis off the floor. Repeat the movement with the other leg. The number of repetitions of the cycle is 2-3 times. |
| This asana can be done dynamically only if the emphasis on the knees does not cause pain. While performing the movements, try to keep your heel as close to your buttock as possible. Make 10 backward movements with your leg, and then freeze for 20 seconds in position 2. Repeat the same with the other leg. |
| To begin, bring the side plank fixation to 90 seconds. The hold must be done in both directions. Then gradually make the exercise more difficult. Raise your upper leg slightly and turn your shin, turning your heel up and your toes inward. You need to stand in this position for 15 seconds. |
| You need to lie in this asana for as long as you can. Recommended holding time is 30 seconds. The asana must be done in both directions. |
|
|
Movements against the resistance of an elastic band
Strengthening ligaments and muscles with tape
Do the exercises in the following order:
- Slowly pull your knee up to the level of your hip joint – 14 times.
- We move the leg diagonally forward - 14 times.
- We move our leg to the side and hold the position for 30 seconds.
- Bend the knee, trying to touch the buttock – 14 times.
- We bring the leg inwards, as far as possible - 10 times.
- We move the straight leg outward - 10 times.
- Maintaining balance while standing on the affected leg (on a pillow) – 3 times for 15 seconds.
- Knee traction in the Deadman's position, a large roller lies under the knees - 3 minutes.
Hitch
Exercises performed at the end of a physical therapy session for meniscopathy
Do asanas 1 to 4 for 30 seconds, and in position No. 5 – straight legs pressed against the wall, stay for 3-5 minutes
And in conclusion, let us remind you once again. In case of injury or chronic disease of the knee joints, it is imperative to treat them with movement. Only exercise therapy can protect against complications, disability and prosthetics.
Implementation principles
No matter how severe the injury to the knee joint, gymnastic training will always be beneficial for the patient. Physical therapy is not able to cure the affected joint, but it can improve its function, as well as stabilize blood flow and activate muscle tone before surgery. There are two sets of knee exercises.
Of these, 1 part of the training is intended to facilitate movements and relieve pain during conservative treatment. It also serves as an excellent help in preparing the patient for various operations, especially endoprosthetics. And part 2 of the training complex is used for rehabilitation after traumatic ligament damage, as well as to speed up walking in the postoperative period.
The main rules of therapeutic exercises are presented below.
- Regular use. Using any exercise once will not bring any benefit. In addition, when performed dynamically on an untrained knee, it can lead to further impairment of active movements. The first part of the exercises must be performed for at least 3 months, and after surgery on the knee joint - before independent, easy manipulations in the endoprosthetic joint.
- Gradual increase in loads. Exercising too intensely will lead to ligament rupture and muscle strain.
- You can't overdo it. With regular training, 30-40 minutes a day is enough for the full effect of gymnastics.
- Monitoring by medical staff. The beginning of any training is carried out under the supervision of a doctor or exercise therapy instructor. In the postoperative period, the condition of the leg is monitored by rehabilitation specialists, who develop an individual complex of therapeutic effects of dosed physical activity.
- Symmetry. Even if only one joint is affected, both should work fully. This will ensure uniform blood flow and facilitate movement in both limbs.
- Strictly no pain. If exercises cause serious discomfort, you should stop using them. Only an experienced specialist will give further instructions on physical activity. A little pain is not an obstacle to exercise, since straightening the muscles and increasing the range of motion in the injured knee is impossible without it.
Every patient suffering from pathology in the knee joint is recommended to use a set of therapeutic exercises. For mild injuries, training will help to quickly restore the functioning of the joint; for severe injuries, it will ensure the success of postoperative rehabilitation. Although exercise therapy cannot completely cure a knee, it can improve the condition of all muscles and tendons involved in movement.
Techniques of Pavel Evdokimenko
The main focus of author's gymnastics is to improve the functional condition of the knees. Pavel Evdokimenko’s technique is excellent for complete assistance in the conservative treatment of arthrosis, as well as for preoperative preparation of the patient. The essence of the classes is static and dynamic training of the muscles and tendons responsible for the functioning of the joint. The slow cycle alternates with the fast one, which ensures maximum participation of the entire lower limb in the treatment process.
Doctor Evdokimenko.
The static part involves fixing the leg in a certain position, which maintains muscle shape in tension. Dynamic exercises provide adequate blood flow and the necessary elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus.
Below are typical healing movements proposed by Pavel Evdokimenko.
- Knee extension.
You will need a chair for this exercise. Starting position – sitting with your feet on the floor. The essence of the exercise is slow extension of the knee joint followed by fixation. The leg should be held in an extended state for up to 1 minute, then slowly return to its original position. For the effect, 2 static workouts per day are enough. Then the exercise should be repeated in dynamic mode with a multiplicity of up to 15 times. You can use one leg and put pressure on the other. - Lying knee extension.
Quite simple but effective physical training. Starting position – lying on your back. Both legs are bent at the knees and the heel is pressed to the floor. It is necessary to raise your leg, straightening it at the knee joint. Hold in this state for 2 minutes, then slowly lower. After 2 static exercises, repeat 15 times in dynamic mode with each lower limb. Perform with both legs. - Asymmetrical movements.
The starting position is lying on the floor, the right leg is bent at the knee joint, the left leg is extended. It is necessary to alternately change the position of the leg - straighten the right leg and bend the left leg at the same time. Then the bent leg must be lifted off the floor and held suspended for up to 2 minutes. In dynamic mode, repeat the exercise up to 20 times. Hands along the body. - Raising your toes. The exercise does not directly develop the knee joint, but is necessary to strengthen the calf muscles, which play a critical role in the movement of the joint. The workout is simple - standing on your feet, heels pressed to the floor, you need to rise onto your toes. Maintain this position for as long as possible. Then repeat in dynamic mode up to 15 times.
Even regular use of Pavel Evdokimenko’s technique is not able to heal the joint. But it is excellent as preoperative preparation, which will allow the patient to quickly recover after endoprosthetics.
For arthrosis of the knee joint
With age, degenerative changes occur in the knee - the joint space narrows, the amount of synovial fluid decreases, the range of active movements decreases - this is how osteoarthritis occurs, which most often affects people over 50 years of age. Conservative methods can only slow down its progression, but only surgery can radically eliminate the problem. However, the exercise therapy complex facilitates the condition of patients in any situation. On the one hand, gymnastics helps reduce pain and facilitate movements, on the other hand, it helps prepare for surgery and recovery after it. Therefore, when the knee joint is damaged, physical therapy will help all people.
With grade 2 gonarthrosis, intense movements are required to maximally strengthen the muscles and ligaments. With the help of therapeutic exercises, it is necessary to delay the progression of the disease and prolong the joy of full functioning of the knee joint. Below are the most relevant exercises for intense knee development.
- Pendulum.
Starting position – sitting on a chair. The legs should hang down freely, so it is important to choose its height so that the heels do not touch the floor. It is necessary to make rhythmic movements in the “back and forth” direction. The number of repetitions is not important, but it is advisable to spend at least 15 minutes training for each leg. You can use a tourniquet to increase the load. - Bending backwards. Starting position – standing, with emphasis on the wall. The essence of the exercise is to bend the knee with intense movements, but the heel is facing in the direction opposite to the support. The frequency is also not important; the training time is at least 10 minutes.
No emphasis? Lie down on the floor.
- "Running while sitting." Starting position: on a chair, feet pressed to the floor. The essence of the training is alternately or simultaneously raising and lowering the lower limbs bent at the knees. It turns out to be a kind of running, only in a sitting position. Completion time: at least 10 minutes.
A chair with a back is better.
- Squats.
This widespread exercise is excellent for grade 2 knee arthrosis. The main goal is not the strength of the training, but the maximum flexion of the knee joints under the weight of the body. The frequency of repetitions depends on physical capabilities - optimally up to 15 times. You can hold onto a support and do half squats.
With grade 3 arthrosis, it will not be possible to restore movement in the knee joint. Further progression is inevitable, so the exercises are aimed at strengthening the muscles and ligaments responsible for activity in the joint. Exercise therapy in this situation is necessary for preoperative preparation for endoprosthetics.
The most relevant exercises are presented below:
- Mini squats.
Gentle bending of the legs under the influence of the muscles of the thigh and legs. The essence of the exercise is small squats until the knees are bent. Then slowly return to the starting standing position. You should perform up to 15 repetitions. Maintain an even body position. - Light swaying of the legs.
A high chair is needed so that the lower limbs can hang freely. The essence of the exercise is to grab the thigh 5 cm above the knee and rub it back and forth. At the same time, move the knee joint with pendulum-like movements. The task is not in the number of repetitions, but in the intensity of massaging the thighs with your hands. The goal of the training is to improve venous outflow from the injured knee. A tourniquet will help. - Hitting your heels. A useful exercise for stabilizing the ligamentous apparatus. Its essence is simple - while sitting on a chair, alternately tap your heels on the floor, but so that the vibration is felt in the knee. Duration – 10 minutes per day.
- Pinwheel. Starting position – sitting on a chair or standing. The goal of the workout is to develop the muscles of the thigh and lower leg. The essence of the exercise is to perform rotational movements in the knee joint with the greatest possible amplitude. A full-fledged “pinwheel” will not work, since the changes with arthrosis of the 3rd degree are great. But 10-15 minutes a day is enough to strengthen muscle tissue not only in the legs, but also in the thighs.
Training for grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint should begin from the moment the prospect of surgical treatment appears. Even with the planned endoprosthetics after 3 months, regular exercise helped a lot for quick recovery after surgery.
Knee replacement in the Czech Republic: guarantees, prices, rehabilitation, reviews and statistics.
Find out more
Rehabilitation complex of exercise therapy after surgery on the posterior cruciate ligament of the knee
We would like to immediately draw your attention to the fact that the exercises presented below, strengthening the ligaments of the knee joint and muscles, are selected specifically for the rehabilitation of the posterior cruciate ligament. For its antagonist or lateral collateral ligaments, other exercises are needed.
Moreover, the presented rehabilitation exercise therapy after a ruptured knee ligament is designed for patients under the age of 40, athletes or people with good physical fitness. However, older patients, if they succeed, can adopt all or some of the exercises, but perform them with a small number of repetitions and long (up to 1 minute) pauses for rest. Jumping is contraindicated for old people.
Before starting to perform special movements aimed at strengthening the ligaments of the knee joint after posterior cruciate plastic surgery, it is imperative to do a 5-7 minute joint warm-up.
| Title and image | Explanations |
| Increase the depth of the squat gradually. There is no need to squat too deeply, so that the angle between the thigh and shin is sharp. |
| During execution, try to keep the supporting (operated) leg in a slightly bent position, and move the healthy leg back and slightly to the side. After a series of jumps described below, balance while standing on the floor, but stand with your “affected” side to the place where the band is attached, and move your healthy leg (with the band) clearly to the side. |
| When performing jumps from side to side, measure forward movement. At first, the zigzags of the “snake” should be short, then medium, and at the end long. After this, rest and repeat the jumping series of 3 sets, but now increase the speed. |
| After abducting the healthy leg to the side (see explanation in exercise 2), do a step-down for 3 minutes, while descending from the platform and ascending to it from the operated leg. Look down and make sure the foot is positioned correctly, do not “tilt” your knee to the side. |
| Jump around the squares on two legs clockwise. After resting, perform a series of counterclockwise jumps. Start with “3 squares” in a row, and gradually increase the number of repetitions to 10-12. |
| Place the foot of your operated leg on a platform whose height should be just below your knees. Take a slow lunge, resting your hands on your operated knee. Freeze for 5 seconds, and then for another 5 seconds make small, literally “centimeter” sways. To complete the exercise, slowly return to the starting position. |
The following are performed:
- jumping onto the step platform - forward, and then left and right side;
- long jump from the affected leg and landing on it;
- running sideways with side steps, knees bent, heels not touching the floor;
- walking backwards.
If possible, every day you should work on an exercise bike with shortened pedal arms.
On a note. Any gymnastic exercise therapy complex for damaged knee ligaments should contain several balancing positions in a standing position on the affected leg. First, they are performed while standing on the floor, and then in more complicated versions, for example, a pillow or a special platform is placed under the foot.
For gonarthrosis of the knee joint
Dystrophic processes in the knee joint will inevitably lead to depletion of cartilage tissue and a decrease in the secretion of synovial fluid. This lesion is called gonarthrosis. The disease leads to complete immobility in the joint, which makes it impossible not only to walk, but also to get out of bed. With grades 1 and 2 of gonarthrosis, physical therapy can relieve pain and improve motor capabilities. But the more the disease progresses, the less chance there is to improve the quality of life with osteoarthritis. However, for gonarthrosis of any degree, exercise therapy will help strengthen the muscular system, as well as stabilize venous and arterial blood flow. In the future, the radical operation will completely return the joy of movement to the patient, and the exercises performed before and after will sharply shorten the rehabilitation period.
The higher the degree of joint damage, the more gentle the training should be. Isometric gymnastics helps, aimed at improving blood flow in the knee. Its main advantage for gonarthrosis is the direction of its effect on the vessels and muscles directly involved in the functioning of the joint. Below are the most popular exercises.
- Shifting. Starting position – sitting on a chair. The essence of the exercise is to alternately raise the knees up due to movements in the calf muscles. With arthrosis of the 2nd degree, you can perform it at a fast pace, and with more severe lesions - slowly.
Can be performed standing.
- Knee forward.
Performed in a standing position. The essence of the training is an alternate lunge with the knee bent at a right angle forward, supporting the other leg. You can strengthen the exercise by simultaneously bending your torso back. Repeatability up to 15 times. At the end point the knee should be 90 degrees. - Alternating leg raises.
Performed while sitting on a chair. Since it is often impossible to fully straighten the leg at the joint, you can use a lighter version of the exercise. It is necessary to perform leg raises to the maximum possible extension at the knee. Multiplicity – at least 15 times for each limb. Do it slowly!
Gonarthrosis cannot be cured with exercise. Only surgery can radically change a patient’s life. However, before and after it, gymnastics is absolutely necessary for the speedy rehabilitation of the patient.
Hamstring strain
- Stand up straight. You can hold on to a wall or chair. However, it will be better if you do the exercise without support. This will not only put stress on the tendon, but also improve the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
- Slowly bend one leg at the knee, moving your foot back.
- Repeat 20 times for each leg.
If you don't have any serious knee problems, give them extra stress. To do this, do not lift your free leg, but pull the elastic band or expander with it.
For knee injury
The knee is a complex anatomical formation that consists of various types of tissue. Since it is subjected to increased load during walking, injuries are possible. When the knee joint is damaged, the bones, ligaments, blood vessels and cartilage are affected. In each specific situation, certain treatment methods are used. But in any case, exercise therapy is prescribed, which is necessary for the speedy restoration of motor activity in the joint.
When knee ligaments are torn, surgical treatment is the only option for successful treatment. Before the intervention, complete rest for the knee is required, since the degree of damage cannot be aggravated. You can begin your first exercises immediately after surgery. On day 1, active movement of the toes is allowed, and from day 2 the range of movements increases significantly. If ligaments are damaged without rupture, conservative therapy is possible with the beginning of exercise therapy from 2 days after the injury. Exercises for all tendon injuries differ significantly from osteoarticular pathologies, such as arthritis.
Knee injury is very common.
Below are relevant exercises for sprained ligaments, as well as for rupture after surgery.
- Muscle tension. Performed in bed. It is necessary to alternately tense and relax the muscles of the thigh and lower leg. This simple exercise achieves two goals at once - preventing muscle atrophy and improving blood supply to damaged ligaments.
- Ankle flexion. Performed in bed. It is necessary to bend and straighten the ankle joint towards the knee. The exercise can be performed frequently - lying in bed up to 10 times a day for 5-15 minutes.
- Circles with soles. Lying down, perform circular movements with your feet. The rotation should be done slowly, but the duration of the exercise can be increased to the maximum tolerated.
- Rolling the ball. Performed after expanding the motor mode. A treatment ball is required, which is placed between the feet. It needs to be rolled at a distance of the lower extremities spread apart across the width of the shoulders.
If the cruciate ligament is torn, surgery is also indicated. Rehabilitation exercises are similar to those used for other tendon injuries. However, it is important to carry out therapeutic exercises only under the supervision of a treating specialist or exercise therapy instructor. With uncontrolled physical activity, tendon damage can worsen, which will lead to a new operation.
Cyst on left leg.
With a Baker's cyst, synovial fluid accumulates in a capsule in the popliteal fossa. This causes pain and difficulty in bending movements in the joint. Treating it conservatively is absolutely futile; even persistent exercises will be ineffective. After surgery, exercise therapy is required to strengthen the muscles of the lower leg and thigh. But exercises are prescribed by a rehabilitation specialist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
In diseases of a dystrophic nature in the knee joint, without surgery, a complete restriction of active movements inevitably occurs. In case of contracture (stiffness), exercise therapy will help keep the muscles in working condition, that is, prevent atrophy from developing. Therapeutic physical education before surgery is used according to the isometric method, and after surgery - on the recommendation of the instructor in a gentle mode. For contracture, the only method of radical therapy is knee replacement.
Synovitis of the left knee joint.
With synovitis, the inflammatory process involves cartilage tissue. Exercise therapy is carried out only after the acute phenomena have subsided according to a gentle recovery regime with a gradual increase in loads. For bursitis, a particular variant of synovitis, treatment is carried out through surgical sanitation with the support of antibiotics. Additionally, analgesic therapy is used, which reduces the actual sensitivity of tissues to stress. Therefore, exercise therapy is prescribed after the temperature has normalized and opiates have been withdrawn. When the knee joint is dislocated, the help of a surgeon is necessary, since it usually cannot be set on its own. The first 2 days you need rest, but you can start actively moving your toes. Subsequently, the regime is expanded, and exercise therapy is carried out according to the tendon restoration regime. Rehabilitation for fractures of the knee joint bones is carried out in the same way.
In case of recurvation, which occurs more often due to a genetic defect, surgical treatment is the only alternative to return the child to the joy of full movement. In the postoperative period, recovery is carried out according to the method of Sergei Bubnovsky or isometric training techniques.