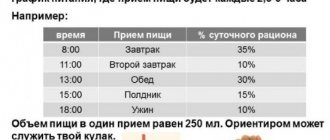
Working out is extremely important for building a beautiful body and gaining muscle mass. But the second pillar of any fitness and sport is proper (that is, complete and balanced) nutrition. And in nutrition, a special role is played by the competent selection of products according to their components - first of all, according to BZHU (proteins-fats-carbohydrates). And fish, which many of us neglect, considering it some kind of uninteresting product (such as “cat food”), or, on the contrary, too pretentious (“shark fin soup”), is in fact an extremely useful product, especially for those engaged in sports or fitness.
What makes fish exceptionally healthy?
High protein content
Fish actually contains from 7 to 23% protein, on average 15-22%. The champions in protein content are such fish species as tuna (22.7%), chum salmon (22%), pink salmon (21%), salmon (20%), and small saury (20%). Even fish such as halibut, burbot, pike perch, perch, carp, whitefish, mackerel, horse mackerel contain 18-19% protein. As we know, protein is extremely important for muscle growth. Not only will its deficiency cause the body to simply lack the building material to create muscles, but amino acids (especially BCAA) inhibit catabolism after training and speed up recovery. Therefore, the amount of protein in the diet for anyone who wants to build muscle should be about 2 g per kilogram of body weight, and about 25-30% of the daily caloric intake.
Fish protein is of very high quality in amino acid composition - it almost exactly corresponds to the “ideal” protein (only it contains less histidine). Therefore, it can more than replace meat and eggs in the diet.
Tuna recipes for bodybuilders
Let's look at recipes for popular dishes that include tuna, which are in demand among bodybuilders.
Mediterranean tuna salad
To prepare it you will need the following ingredients:
- Pasta - 4 cups;
- Canned tuna - 2 cans;
- Finely chopped tomatoes - 2 pcs;
- Finely chopped cucumber - 0.5 cups;
- Sweet pepper - 0.5 cups;
- Boiled chilled broccoli - 0.5 cups.
For the salad you need to prepare the filling, and for this you will need:
- Apple cider vinegar - 0.5 tbsp. l.;
- Olive oil - 1.5 tbsp. l.;
- Grated cheese - 1 tbsp. l.;
- Crushed garlic - 1 tsp;
- Dried basil - 1 tsp;
- Salt, pepper and seasonings are added to taste.
Preparation: Mix the first six ingredients in a bowl. Products intended for dressing should be mixed in another bowl. After this, you need to pour the salad with dressing and place it in the refrigerator.
Ideal fat composition
Fish can be fatty or lean. Of course, fatty fish is much higher in calories, so for those who are concerned about being overweight, it is better to choose lean fish species (crucian carp, pollock, navaga, burbot, river perch, blue whiting, pike perch, cod, tuna, pike, hake). For example, the energy value of fatty eel (30.5% fat) is 333 kcal, slightly less fatty herring and salmon (19.5 and 15.1%, respectively) are 242 and 219 kcal. Against 70-75 kcal in pollock, blue whiting and cod (0.7, 0.9 and 0.6% fat).
But a very important nuance is that fish oil is very healthy, unlike other animal fats. It consists slightly more than entirely of unsaturated fatty acids (in particular, it contains more than 70% oleic acids). It also contains up to 25% omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, which protect the heart and blood vessels, as well as vitamins A and D, which improve vision and the condition of bone and connective tissue.
Paradoxically, PUFAs in fish oil not only do not contribute to the gain of fat mass, but on the contrary, they activate fat metabolism and lead to a decrease in the thickness of the fat layer.
Therefore, anyone who is trying to gain muscle mass can eat fatty fish without any restrictions. Champions in Omega-3 content are mackerel, herring, tuna, trout and salmon.
Attention!
Humanity manages to ruin everything it touches. Today, sea waters are contaminated with heavy metals such as lead and mercury. Therefore, eating fish from such waters can cause poisoning. Therefore, scientists strongly do not recommend eating large fish. Such fish live long and their meat is literally saturated with heavy metals. The most harmful are shark, swordfish, albacore tuna and king mackerel.
The American Dietetic Association stated that in our time, consuming no more than 400 grams of fish per week can be “safe”. Children - half as much, and pregnant women should completely exclude fish from their diet.
Athletes love tuna very much. But don’t even think about buying a jar that says “albacore tuna”! This fish can “feed” heavy metals so that you will restore your health for many years. But small types of tuna are much safer to eat.
The ideal choice for the modern athlete is salmon. It is high in protein and omega 3 fats.
Nutrient table
What did you eat before? Sprats and herring? Finally put an end to your denseness! And we will present to your attention a list that represents a whole pantheon of fish. You can choose what suits you - depending on your tastes and your geographical location. So, proper nutrition for muscle growth:
- Atlantic mackerel contains 342 calories, 44 g protein, 20 g fat and 4.4 g omega 3 fats.
- Herring contains 346 calories, 40 grams of protein, 20 grams of fat and 3.6 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Atlantic salmon contains 350 calories, 38 grams of protein, 22 grams of fat and 3.4 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Chinook salmon contains 392 calories, 44 grams of protein, 22 grams of fat and 3 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Salmon juice contains 368 calories, 46 g protein, 18 g fat, 2.4 g omega 3 fats.
- Canned salmon contains 232 calories, 40 grams of protein, 8 grams of fat and 2 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Sardines contain 354 calories, 42 grams of protein, 20 grams of fat and 2 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Shark contains 260 calories, 42 grams of protein, 10 grams of fat and 1.8 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Flounder contains 324 calories, 46 grams of protein, 14 grams of fat and 1.6 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Canned white tuna contains 218 calories, 40 grams of protein, 6 grams of fat and 1.4 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Swordfish contains 264 calories, 44 grams of protein, 8 grams of fat and 1.4 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Seabass contains 210 calories, 40g protein, 4g fat and 1.4g omega 3 fat.
- Halibut contains 238 calories, 46 grams of protein, 6 grams of fat and 1 gram of omega 3 fat.
- Crabs contain 174 calories, 34 g protein, 4 g fat and 1 g omega 3 fat.
- Lobsters contain 244 calories, 44 grams of protein, 4 grams of fat and 1 gram of omega 3 fat.
- Tuna contains 244 calories, 52 grams of protein, 2 grams of fat and 0.8 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Oysters contain 278 calories, 32 grams of protein, 8 grams of fat and 0.8 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Canned light tuna contains 198 calories, 44 g protein, 2 g fat, 0.6 g omega 3 fat.
- Shrimp contain 168 calories, 36 g protein, 2 g fat and 0.6 g omega 3 fat.
- Haddock contains 190 calories, 42 g protein, 1.6 g fat and 0.4 g omega 3 fat.
- Catfish contains 258 calories, 32 g protein, 14 g fat and 0.4 g omega 3 fat.
- Tilapia contains 218 calories, 44 grams of protein, 4 grams of fat and 0.4 grams of omega 3 fats.
- Cod contains 178 calories, 38 grams of protein, 2 grams of fat and 0.2 grams of omega 3 fat.
- Mahi Mahi contains 186 calories, 40 grams of protein, 2 grams of fat and 0.2 grams of omega 3 fats.
We present to your attention several recipes for not only tasty, but also healthy fish dishes for athletes.
Roast fish
For 4 servings: 2 tablespoons olive oil, 2 grated garlic cloves, 1/2 onion, 1 chopped carrot, 1/2 tablespoon ground black pepper, 4 tomatoes cut into pieces and 400 g fish fillet (cod, flounder or peksha).
Heat the oil in a deep, thick saucepan, add the onion and garlic and cook until the ingredients soften. Then add the tomato pieces and carrots. Sprinkle it all with pepper and bring to a boil. Then reduce the heat and simmer for 5 minutes. Add fish fillet pieces to the pan and cook for 7-10 minutes.
- 1 serving of this dish contains 175 calories, 30 g of protein, 6 g of carbohydrates and 3 g of fat.
Grilled salmon
Makes 2 servings: 1 cup plain yogurt, 2 tablespoons chopped coriander (or other seasoning to taste), 2 minced garlic cloves, 2 tablespoons crushed mint, 1/2 teaspoon ground black pepper and 2 pieces of salmon (each approx. 180 g each).
In a deep bowl, mix yogurt, chopped coriander, garlic, crushed mint and pepper. Partially pour the resulting liquid mass back into another cup (1/4 volume). Place salmon pieces into the resulting mixture, cover with a lid and refrigerate for 15 minutes. Then place the salmon on the grill and cook for 7-10 minutes. The fish only needs to be turned over once! Pour the remaining mixture over the cooked fish.
- 1 serving of this dish contains 336 calories, 36 g of protein, 4 g of carbohydrates and 20 g of fat.
Grilled cod
For 2 servings: 1/2 cup lemon juice, 1/2 cup zest, 2 tablespoons mustard, 1 tablespoon dry herb to taste, 1/4 spoon black pepper, 2 tablespoons olive oil, 2 pieces halibut fillet 180 g each.
Combine lemon juice, zest, mustard, seasoning and black pepper in a deep bowl. Pour in olive oil. After mixing the resulting mass, place the fish fillet in a bowl and turn over several times. Place the dish in the refrigerator for half an hour. Preheat the oven and place the fish pieces on a baking sheet. Cook the top and bottom sides for 5-7 minutes.
- 1 serving of this dish contains 269 calories, 33 g of protein, 47 carbohydrates and 10 g of fat.
Minerals
For the full functioning of the body, especially those experiencing increased stress, various micro- and macroelements are also necessary. Fish is also rich in these components. Particularly important is the presence of zinc in it, which is necessary for the production of testosterone. It is unnecessary to remind you what an important role this hormone plays in the process of muscle growth.
Another important substance is iodine, which is also found in fish (mostly in sea fish). Iodine is necessary for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland and its deficiency leads to serious diseases. Therefore, eating sea fish is very healthy. True, in order to protect yourself from iodine deficiency, seaweed is more suitable (it contains just a lot of iodine), but fish also makes its contribution.
Easy to digest
Fish is much easier and easier to digest than meat and dairy products - partly due to the lack of saturated fat, and partly due to the special structure of muscle tissue, less dense and containing simpler proteins (actin, myosin, myogen, globulin). For comparison, meat contains up to 20% collagen (a rather difficult to digest connective tissue protein), and fish contains only up to 3%. Dairy products contain large quantities of casein, a protein that takes a very long time to digest. Therefore, fish (even fatty ones) is almost always easier and faster to digest than meat, quickly saturating the body with amino acids and allowing you to quickly return to active activity.
Omega 3
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in fish, and nowhere else, if we are talking about the diet of the average person. Yes, omega-3 can be found in meat, eggs and milk, but the concentration varies significantly, dozens of times. Omega-3 is found in oils, nuts, and other plant products. But our body needs fatty acids from fish and animal products, since their composition is the most complete and is absorbed better than others.
Fish oil is an element that is critically lacking in the modern human diet. Scientifically proven fact: eating fatty fish reduces the likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases. But this is the cause of death for more than 75% of people over the age of 45.
That is, if you personally, the reader, lived to be 45 years old, then the probability that you will die from heart problems is 75%. Three out of four people you know will die for the same reason.
Fish in bodybuilding is a saving element. A bodybuilder is more likely to die from heart problems than the average person. Especially if you train hard.
Speaking of wear and tear. The main harm of bodybuilding is the wear and tear on the nervous system. Healthy fat is an element that “lubricates” our nervous system and speeds up its recovery. And fish oil is three times beneficial.
Fish for a bodybuilder is not only a product for muscle growth, but also an element of maintaining and improving health.
Use these tables when choosing fish as your source of omega-3s.
Low cost and other nuances
Often fish fillets (such as hake, pollock, blue whiting, cod) can be found in stores cheaper than meat, even cheaper than chicken breast fillets. Although high-quality fish of more valuable species will, of course, be more expensive. But if you choose between chicken and fish, we recommend giving preference to fish, it will not be so fatty, easier to digest, and most likely cheaper.
Here you just need to keep in mind that some beneficial substances contained in fish (for example, PUFAs) are very sensitive to light and high temperatures, so it is advisable to cook the fish as quickly as possible and in the most gentle way possible (fried fish is the least healthy).
You should choose only fresh fish (at least fresh frozen). Under no circumstances should it be frozen. We will not go into details here about how to choose fish in a store, but we highly recommend that you think about this carefully before going to the store - and be sure to take a closer look at what you take, since low-quality fish can even cause poisoning.
If you buy half a kilo of good fish and cook it at home, you can significantly diversify your diet and enrich it with a large number of useful substances that will help you succeed in training.
Well, if you were unable to get the required daily dosage of Omega-3 PUFAs with the help of fish, you can take a closer look at such a useful supplement as Omega-3 from Be First.
Fish in bodybuilding. For what?
Including fish in your diet can bring enormous benefits due to the following properties:
- High protein content . Fish is one of the record holders for protein content, without which your muscles will not grow;
- Complete amino acid profile . Not only the quantity of protein matters, but also its quality and complete amino acid profile. Fish protein is high quality animal protein. This is exactly the compound you need for rapid muscle growth and health;
- Natural product . Natural (caught, not specially grown) fish is one of the most natural products in our latitudes. Unlike meat, it is a much cleaner product. Of course, if we are talking about natural conditions;
- Improved health . There is evidence that eating fish can improve the condition of the skin, reduce the incidence of cancer, and have a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Scientists, of course, often point us in the wrong direction, but it makes sense to trust this information. Fish is one of the oldest foods for humans. This means that our gastrointestinal tract is very well adapted to it, and this food is healthy;
- Omega-3 . The most important thing in fish. Fish oil accelerates muscle growth, promotes recovery after training, and improves the functioning of the nervous system. More on this below;
- Healthy nutrition element . Fish contains many vitamins and microelements that will benefit your health. Eating fish improves brain function and strengthens hair and nails. According to some studies, eating fish with enough omega-3 is a cure for bad skin;
- Lots of cooking variations . Even if you don't really like fish, it can add variety to your diet. Bodybuilders rely mainly on meat (usually chicken breast) and eggs, which is detrimental at least in terms of taste.
PS How to cook?
You don't need any tricks to cook fish. It is enough to take a ready-made fillet (cod, hake, pollock, trout - to your taste), cut into portions, lightly add salt (this is optional, but many cannot eat without salt), pour in lemon juice and sprinkle with spices (again, your choice – nowadays there are even ready-made sets of spices for fish), put it on a baking sheet (after laying it out with foil, baking paper, or putting the fish in a special baking sleeve) and you can splash a little water. Then place in a hot oven (180 degrees) for 20-30 minutes. Watch it yourself so it doesn't burn.
If you want something more refined, you can vary the quantity and set of spices, experiment with soaking fish in milk, pouring sour cream, etc. – there is a huge field for experimentation here. The main thing is that it will be beneficial both for muscles and for communication - after all, you can invite someone to visit you for dinner with delicious fish who, like you, appreciates sports and fish dishes.