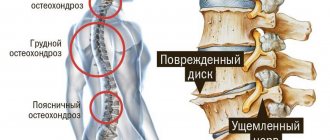
Osteochondrosis of the spine is the most common problem in people over 40 years of age. But if you take adequate measures and pay enough attention to it, the consequences can be avoided. One of the main assistants in this is physical therapy, or exercise therapy. The set of exercises for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is simple and takes only 15-20 minutes.
Rules for therapeutic exercises
The basic rules of therapeutic exercises for all parts of the spine are the same.
- Fresh air or a well-ventilated area;
- All exercises begin with a warm-up;
- Perform exercises only at the stage of remission of the disease;
- Movements should be free, so choose comfortable clothes;
- The movements are not sudden, gradually increasing in amplitude and number of times. Then you will avoid injury to ligaments and muscles;
- If you feel pain while doing exercises, stop the exercise;
- Before you start exercising and after you finish, measure your pulse. If it is elevated, then reduce the load;
- Watch your breathing while charging;
- Regularity is the most important component of successful treatment. If you do exercises from time to time, it will not give the desired effect;
- The exercises necessary for the prevention and treatment of osteochondrosis are prescribed and selected only by a specialist. Do not self-medicate, it may have the opposite effect;
Warm-up
A very important component of the entire set of exercises is warm-up. It helps to avoid injuries to muscles and joints. You need to do the warm-up slowly. First, simple arm swings are performed, then the charging elements become more complex.
- Stand up straight. Slowly, while inhaling through your nose, raise your arms up; after you have fully filled your lungs with air, lower your arms and exhale noisily through your mouth.
- To warm up the cervical spine, perform sideways head tilts and rotational movements, lowering your head to your chest and making a semicircle from one shoulder to the other.
- Then you should stretch your chest a little; to do this, stand against the wall so that your heels, buttocks, shoulder blades and the back of your head rest against it. Take 2 steps away from the wall and squeeze your shoulder blades together. Hold for 3 counts, then relax your shoulder blades and return to the wall.
- Raise your left shoulder, then your right, and then both shoulders together.
Each exercise must be done 10 times.
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis
The most common type of this disease is cervical osteochondrosis. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to this particular part of the spine and perform simple exercises. We present to your attention some of them:
Complex from a standing position
- Stand with your hands on your hips. Start turning your head left and right. 10 times.
- Then the same thing is done, only tilting the head to the right shoulder and to the left. Perform 10 times.
- Begin smooth rotational movements with your head, describing a semicircle. 10 times.
- Place your palm against your forehead and press it into your palm. At the same time, the neck muscles should tense. Do it 3 times.
- Rest and press the back of your head into your palm so that the neck muscles also tense. 3 times.
- Do the same procedure with your palm, pressing on your right and left temple. 3 times.
Complex from a lying position
Starting position for the complex: lying on your back, legs straight, arms along the body.
- From the starting position (IP), slightly raise your head and hold in the position for about 5 seconds. To lower the head. Repeat 3 times.
- Place your hands on your shoulders and perform rotational movements with your elbows in both directions 4 times. Repeat 3 times.
- From I.P. lift one leg and bend it at the knee. Then switch legs. We simulate walking in place while lying down. Perform 3 times for 30 seconds.
- Raise your arms above you and alternately pull them towards the ceiling, while lifting your shoulder blade off the floor. For each hand 6 times.
- Extend your arms to the sides and up while inhaling. As you exhale, lift your knee and pull it towards your chest. Don't lift your head off the floor. Repeat the exercise 5 times.
- Lying on your back, place your hands on your waist. As you inhale, raise your legs and bend your knees. As you exhale, straighten your knees and relax your legs. Do it 5 times.
- While in I.P. bring your shoulder blades together and press them to the floor. Hold the position for 3 counts. Must be completed 5 times.
Complex from a sitting position
Sit on a hard chair. This is your IP.
- While sitting in a chair, press your left hand onto your left knee for 3 seconds. We do the same exercise with the right hand. Then we press on our knees with both hands. We do it 5 times.
- Pull your left shoulder towards your left ear. Let's hold for 3 seconds. Let's do the same exercise with the right shoulder. Then we try to pull both shoulders towards our ears. 5 approaches each.
- We perform rotational movements with the left shoulder, then with the right, and then with both shoulders. 7 times for each shoulder.
- Raise your legs by slightly bending your knees. Exercise "bicycle".
- As you inhale, spread your arms, and as you exhale, clasp your shoulders with your hands.
- Sit on the left side of the chair. We perform the following exercises:
6.1 Raise and lower the left hand;
- Move your hand back and forth, as if sawing wood;
- We perform circular movements with our hands clockwise, then counterclockwise;
- Raise your hand up, throw it down and shake.
6.2 Move to the right side of the chair and perform the same complex.
- Sit upright in a chair. As you inhale, raise your arms up. Grasp your knees as you exhale. Repeat 3 times.
The entire set of exercises is performed slowly until slight pain is felt.
Features and signs of the disease
Osteochondrosis of the spine in the lumbar region is perhaps the most common disease of the spinal column. It usually develops in men and women over the age of 30, but recently it has become younger and affects younger people. With osteochondrosis, there is degradation of the tissues of the intervertebral discs, a reduction in the space between the vertebrae and a gradual disruption of the functioning of the spinal cord roots. Due to the fact that they can be pinched by segments of the spine, the main symptom of the disease appears - periodic or constant pain. Then other signs begin to develop - muscular-tonic, neurodystrophic, etc.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
How does the disease develop? Due to an incorrectly distributed load on the spine, the intervertebral discs begin to be compressed, the quality of metabolic processes in them gradually deteriorates, fluid loss occurs, and then a decrease in elasticity is noted. Gradually, the so-called fibrous ring (one of the elements of the disc) is destroyed and as a result, pinched nerve endings occur, which immediately sends a signal to the brain about a problem - the person begins to feel pain.
Stages of development of spinal osteochondrosis
Typically, pain occurs after physical activity that is unusual for the body. The pain may be:
- dull, radiating to the leg;
- strong and constant;
- shooting, usually manifesting itself after hypothermia;
- aggravated by the need to drag heavy objects or make sudden movements.
Pain due to osteochondrosis can be different
Prices for painkillers for back pain
Also, osteochondrosis may be accompanied by chilliness of the legs, problems with sweating, and sensory disturbances in the feet, legs, thighs, and buttocks. There may be tingling in the legs and goosebumps on the skin. The skin in places where pain is felt begins to peel off.
Usually the disease is chronic, but it can go into an exacerbation stage in case of heavy load or due to sudden movement. Cold can also trigger an acute period.
Osteochondrosis is divided into three types: cervical, lumbar, thoracic
Attention! Osteochondrosis of the lower back in an advanced form can cause the development of serious complications, often leading to loss of ability to work.
Exercise therapy during exacerbation
If the disease progresses and an exacerbation occurs, it is important to follow household rules of behavior. They include:
- Sleep and just lie only on a hard mattress;
- Place a pillow or bolster under your knees. This way you will relieve excess tension from the spine;
- Perform special exercises to relax the spinal muscles.
When performing physical exercises in moments of exacerbation, it is important to perform all exercises slowly, sitting in front of a mirror, and carefully control all your sensations.
I.P. sitting on a hard chair, legs together, hands on knees, head straight, chin parallel to the floor.
- Turn your head very slowly, first to the right and then to the left. The chin should be parallel to the floor. 3 times.
- Tilt your head to your right shoulder, then to your left. The shoulders are fixed in one position and do not rise towards the head. 3-4 times.
- Tilt your head down, resting your chin on your chest. Do not throw your head back too much when returning to IP. Do it 3 times.
- Very slowly stretch your chin to the right collarbone, then to the middle, and to the left collarbone. 4 times.
- Lower your head down so that your chin reaches your chest, slowly making movements in the shape of a semicircle from one shoulder to the other. Do it 4 times.
- Stretch your neck up, hold the position for 3 seconds, and as you exhale, return to IP.
- Rest your forehead in your palm, hold for 3 counts, then rest your head in your palm, also for 3 seconds, and rest your right and left temples in your palm for 3 seconds.
Contraindications to exercise therapy
There are very few contraindications for performing therapeutic exercises. Most often, these are not contraindications, but recommendations for limiting activities during a certain period of time. In case of osteochondrosis, it is recommended not to engage in exercise therapy during periods of exacerbation and severe pain. But there are general contraindications. These include:
- Increased body temperature;
- Severe pain in any part of the body;
- The appearance of malignant neoplasms;
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- High blood pressure;
- If the patient's mental state is impaired, exercise therapy is not prescribed;
- Bleeding or likelihood thereof;
- Blood clots;
- The presence of incurable progressive diseases.
When drawing up a course of treatment for osteochondrosis, as well as any disease that requires physical exercise, it is important for each doctor to determine the possibility of indications or contraindications for physical therapy. Therefore, the complex is compiled by a specialist in this field.
Individual approach
Before performing Bubnovsky joint gymnastics, consult your doctor.
A set of physical exercises for spinal osteochondrosis is compiled by a doctor individually. Not only the degree of osteochondrosis is taken into account, but also its localization, other existing diseases and pathologies, as well as the age and general fitness of the body.
Therefore, you should not be surprised that your individually designed lesson plan will be different from the video Set of exercises for spinal osteochondrosis posted on the Internet.
For example, not everyone can do Bubnovsky’s much-advertised set of exercises for osteochondrosis. It requires a detailed consideration, together with your treating specialist, of each movement, the number of its repetitions and the correlation of the overall physical load of the session as a whole.
Important! This warning especially applies to those who decide to perform a set of exercises with a fitball for osteochondrosis from Bubnovsky. Many movements not only require good physical preparation and safety when performing, but are also disputed by other exercise therapy specialists as therapeutic and, importantly, safe for the back and neck.
Prevention recommendations
If you approach the issue of preventing osteochondrosis wisely, then it can be avoided altogether. The basic recommendations are not complicated:
- Perform a daily complex of physical therapy;
- Take medications;
- Move more;
- Get rid of bad habits;
- Watch your diet;
- Get your health checked regularly.
Prevention is the best way to prevent a disease, but treating its consequences is quite difficult. If you consult a doctor at its first stage, follow the treatment recommendations and don’t be lazy, then you can forget about the pain in a couple of months.
Description of the pathology
Osteochondrosis is a pathology of the spinal column, during the development of which degeneration and dystrophy occur in the vertebral discs, and over time the bone itself is destroyed. The leading signs of this pathology are pain, the location of which depends on the level of the lesion. The pain is almost always accompanied by the following symptoms:
- muscle weakness;
- change in sensitivity;
- pathological changes in the functioning of internal organs.
A patient with osteochondrosis feels severe pain.
The main reason for the development of osteochondrosis is considered to be insufficient physical activity, excess weight, injuries, flat feet and uneven distribution of load forces on the spinal column. As part of therapy and preventive methods in such cases, physical therapy is used.
A well-developed plan of therapeutic exercise helps restore blood supply to the affected areas, nourish cells, improve mobility and increase the strength of the muscle frame.
And most importantly, with the help of exercise therapy it is possible to slow down bone destruction.