Why physical therapy?
Many people assume that painkilling injections will cure osteochondrosis. Yes, the pain will be eliminated for a while, but no more. The problem is that the vertebrae and their functionality need to be restored . This is why exercise therapy exists; special exercises will help slow down the degenerative processes occurring in the spine, improve tissue nutrition, create a natural muscle corset, eliminate muscle spasms and relieve pain for a long time.
Main reasons
Painful sensations in the sacrum
- lumbosacral radiculitis (particular discomfort will be experienced during coughing or sneezing);
- osteochondrosis;
- the presence of a hernia in the lower back (this disease can also be accompanied by pain in the pelvic area);
- general weakness of the spinal muscles;
- the presence of an inflammatory process in soft tissues (in the pelvic area);
- urolithiasis:
- kidney inflammation.
By the way, the lumbar region often also hurts in women who are pregnant. In this case, such a reaction of the body is more than natural, and you definitely shouldn’t be afraid of it. This is all due to the fact that the baby may simply be positioned incorrectly and rest his head against the back of the pelvis. All this usually goes away without outside intervention, after 3-5 days.
Requirements for conducting classes
You should know the basic requirements:
- Exercise therapy can be performed only after pain has been relieved.
- During an exacerbation, only the simplest exercises are possible.
- Once remission occurs, exercise should become regular.
- Exercises must be performed smoothly. Soreness is a signal to stop the exercise.
- The loads increase gradually - amplitude and number of repetitions.
- Breathe evenly and calmly.
- The first classes should be carried out only under the supervision and control of a specialist.
- Clothes must be breathable.
- Before starting exercises, they are agreed with your doctor.
What should you not do if you have lower back problems?
Forbidden:
- Start classes with maximum loads.
- During the acute period, do exercises only in bed.
- Do painful exercises.
- For protrusions and hernias, twisting, running and jumping, lying leg press, any barbell lifting, and standing exercises are contraindicated.
Methodological recommendations for motor mode in the second (subacute) period
With a decrease in pain, the possibilities of using special and general developmental exercises increase. During this period, in addition to exercises that increase the strength of the abdominal muscles and hip extensor muscles, exercises that focus the lumbar spine (No. 7,8,10,11,13,15, 22,23) become important.
When choosing both special and general developmental exercises, it is important to ensure that they do not increase lumbar lordosis. Painful sensations are a signal to change the structure of the exercise (towards easier) or to eliminate it.
At the end of the second period, you should gradually include exercises that increase the strength of the back muscles. Exercises No. 7,6,9 and 10 can be performed in a circular system 2-3 times. They are the most important. Increase the number of repetitions of special exercises to 15-50 times. The pace of the exercises can be gradually increased. We should remind you once again: exercise should not cause pain!
Preparation rules
Exercise therapy is prescribed by the attending physician after a comprehensive examination. It starts with simple preparation:
- It is better to plan to perform the complex in the first half of the day, no earlier than 1.5 hours before or after meals.
- Start any activity with a warm-up - it will help warm up the whole body and prepare the muscles and heart for the load.
- For exercise, prepare a thick cushion under your knees. Its height should be such that the thigh and lower leg are perpendicular.
- It is useful to keep a diary to monitor the exercises performed and the results achieved.
Lesson plan, general rules
Exercises for osteochondrosis vary in stages and complexity. It is necessary to strictly follow the lesson plan without mixing different complexes.
The blocks go in stages:
- The first stage is carrying out exercise therapy in the acute period. Exercises should be extremely simple and slow.
- The second stage is the subacute period. There is less pain and more stress.
- The third stage is remission. The pain has passed and it’s time to connect complex programs.
Equipment and inventory
Clothing should not restrict movement; usually it is a cotton T-shirt or T-shirt, tights or shorts.
In cold weather, to avoid hypothermia, you can wear woolen items. Required equipment:
- fitball;
- Swedish wall;
- gymnastic mat;
- cushion under the knees.
Rules for performing gymnastics
After a medical examination and treatment prescription, patients should begin preparing for exercise therapy. Loading the body without prior preparation is unacceptable.
Certain rules must be followed:
- The patient should feel comfortable during the sessions. The training room should be spacious and well ventilated. During the warm season, you can exercise outside.
- For exercise therapy, you need to choose comfortable clothes and suitable shoes.
- You should eat at least one and a half to two hours before classes. Food should be light and quickly digestible. It's hard to exercise on a full stomach. But you can’t live without food at all – you need energy to carry out the workload.
- During the lesson, the load must be distributed rationally. The peak of effort should occur in the middle part of the session.
- Movements must be performed smoothly, without jerking.
- In the process of performing a set of exercises, you need to listen to the sensations. If pain occurs, exercises are replaced with more gentle ones or the exercises are stopped completely.
- Classes must be regular.
Training complexes
The total duration of time when performing exercises is no more than 20 minutes.
Regularity of execution is important; it is advisable to increase the number of repetitions of exercises to 12-15. Any complex is preceded by a warm-up:
- tilts in different directions;
- spreading your arms in different directions;
- circular movements of the shoulders.
Permissible load in the acute stage
All loads are general strengthening and gentle. At this stage, all exercises are performed as carefully as possible. Even with minor pain, the activity stops immediately. In an acute condition, exercises should only be performed in the presence of an instructor.
The number of repetitions is adjusted according to how you feel, but not less than 8 times. It is useful to complete the complexes with diaphragmatic breathing. Since the whole complex is short, it can be repeated in the morning and evening.
Ten exercises
The starting position of all exercises is lying down. If the lesson is carried out on a bed, the mattress should be orthopedic.
- A bolster under bent knees. Flexion and extension of the feet and fingers.
- Take turns bending and unbending your legs, sliding them along the surface of the mat.
- Breaststroke - with hands.
- Lateral leg abductions and return in turn.
- Legs are straight. Alternately raising your legs up, the toe “looking” at the floor.
- Pull your legs towards your stomach, helping yourself with your hands.
- Alternately, move your knees to the sides - “frog”.
- Rotate the feet at the ankle clockwise and counterclockwise.
- Bend and straighten your elbows, do not hold your breath. Legs are straight.
- Vacuum - retraction of the abdomen.
Subacute stage
Provides improvement in general condition, reduction of pain and a slight increase in load. The goal is already changing - strengthening the muscle corset. It is a good idea to undergo physical therapy during this period.
Seven exercises
TOP 7 exercises for the subacute period:
- Lying on your back with bent knees, do half bridges.
- From the same position, as you exhale, tighten your stomach and raise your head, and while inhaling, relax.
- Without changing position, strain your buttocks with a delay of 10 seconds. Relaxation while inhaling.
- Lying on your back, pull your heel as close to your buttock as possible and hold it for 5-6 seconds.
- From the same position, do half-bridges with a delay of 10 seconds, relax as you exhale.
- Standing on all fours and without lifting your palms from the bed, sit on your heels with your buttocks.
- From the same position, perform the “good and evil cat” exercise - arch and bend your back.
In stable condition
There are no restrictions regarding the complex at this stage. Even going to group classes can be helpful.
However, you can also exercise at home; it is advisable to choose exercises with weights. It is the power loads that will allow you to develop the muscles to support the spine and strengthen the lower back.
Charging during remission
- Lying on your back, alternately bend and straighten your knees.
- From the same position, pull your heel as close to your buttock as possible and hold it for 5-6 seconds.
- Alternately raise your straight arms behind your head and back.
- Move your legs alternately to the sides.
- Alternately raise and change legs, with one bent at the knee, the other straight - like riding a bicycle.
- From a lying position, do half-bridges with a delay of 10 seconds, relax as you exhale.
- Cross your arms over your chest. Do head and shoulder lifts while tensing your abdominal muscles.
- From the same position, strain your buttocks with a delay of 10 seconds. Relaxation while inhaling.
- Raise both legs and pull them towards your chest, holding them with your hands. Exposure – up to 10 seconds.
- Standing on all fours and without lifting your palms from the bed, sit on your heels with your buttocks.
- Standing on all fours, straighten opposite arms and legs, maintaining balance for 5 seconds.
- Half-cobra - arms to the sides, a cushion under the stomach. Raise your head and shoulders with a delay of 3-4 seconds. Keep your head straight.
- Take a deep breath, slowly raise your legs and pelvis, stay in this position, lower yourself and exhale. Don't throw your head back!
Workout without twisting
All exercises are performed from a lying position:
- Bend your knees, do half-bridges as you inhale, and relax as you exhale.
- Hold in the half-bridge for 10 seconds, lower as you exhale. 3-4 times.
- Pull the spine in different directions - tailbone down. The top of the head is up. Pull your legs towards your stomach one by one and return them with a delay.
- Bend and pull your legs towards your stomach, clasp them with your arms and sway for a few seconds.
- Lying in airplane pose on your back, bend your knees and spread your legs apart, opening your hips.
With twisting
Twisting exercises:
- Lying on your back in airplane pose, raise your legs and bend your knees at a right angle. Lower your bent legs alternately to the sides, do not straighten your knees.
- Stretch out on the mat. Hands behind head. Pull your legs vertically towards you for several breathing cycles and gently lower them.
- Extend your arm and leg on one side alternately. As you exhale, turn your head and knees in different directions.
- Standing on your knees, lower your pelvis alternately, on one side and the other of your legs, stretch your arms in front of you.
- Tilt your head to your knee - sit on the floor, spread your legs wide. Bend one leg at the knee so that the heel rests on the groin, the knee as close to the floor as possible. Slowly reach towards the straight leg, and turn the body towards the bent one.
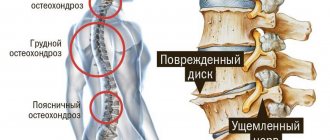
Characteristics of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region
Intervertebral discs are made of cartilage tissue that tends to lose moisture over time. A decrease in their height is possible, and as a result, further degenerative changes. Tissue affected by osteochondrosis absorbs worse, becomes hard, expands to the sides and puts pressure on nerve endings. Regular aching pain occurs in the lumbar region.
An acute attack can occur due to the following reasons:
- overexertion due to heavy lifting;
- hypothermia;
- serious stress.
The reasons that provoke osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region are as follows:
- hereditary predisposition;
- spinal injuries;
- flat feet and scoliosis;
- lack of physical activity;
- excess weight;
- age-related changes.
Symptoms of this disease increase slowly. Therefore, osteochondrosis is most often diagnosed at the second stage. The disease provokes limitation of mobility. When sitting, turning, bending, pain occurs. The pain may radiate to the leg and be sharp or aching. There may be short-term pain, like an electric shock, reaching the heel. The nerve roots are affected, and both a decrease and an increase in skin sensitivity are possible. Tendon reflexes decrease and muscles become weaker.
Osteochondrosis develops gradually and goes through four stages in total:
- Stage 1 . Initially, the violations provoke mild pain in the lower back. During physical activity, dull pain in the back and buttocks increases.
- Stage 2 . It is characterized by the destruction of the fibrous ring, the distance between the vertebrae decreases. Possible pinching of nerve endings. There are sharp pains that radiate to the outer side of the thigh and the affected side of the lower leg. During an attack, the patient bends to the healthy side and freezes paralyzed in that position. An attack can occur suddenly, even with the simplest awkward movement. The chronic course occurs 1-2 days later. The signs of the disease become different, the intensity decreases. Pain appears after standing, prolonged sitting, or bending. Painless intervals between attacks are shortened. Most often, one side of the lower back suffers from pain. As the disease progresses, endurance for prolonged physical activity deteriorates.
- Stage 3 . Due to the destruction of the fibrous ring, intervertebral hernias appear. The spine is significantly deformed, the pain becomes intense.
- Stage 4 . Due to severe spinal deformation, it is difficult for the patient to move. The pain may subside for a short time. Bone growths increase, which causes disability for the patient. In the lumbar region, only burning heat or cold may be felt. Paresthesia appears (the feeling of goose bumps running over the skin), active sweating at the time of the attack. The duration of an acute attack is about a week. Due to the progress of the disease, necrosis of vertebral cells appears, dystrophy with complete destruction.
Exercises on a fitball
A fitball is a large rubber ball that can be used to successfully perform the following exercises:
- Locust - lie on the fitball with your stomach, in this position raise your arms and legs one at a time.
- Hyperextension - hips and stomach on the ball, hands behind the head, legs extended back. As you inhale, lean forward, rounding your body. As you exhale, straighten up smoothly.
- Half bridge - back on the floor, feet on the ball at a right angle. As you exhale, raise your pelvis and straighten your legs while inhaling and lower.
- The pose is the same. Hands behind your head, legs clasping the ball. Raise it 90 degrees and lower it, alternating repetitions.
- Flugel or twist - put your feet on a fitball, your back on the floor, your arms to the sides. Roll your legs with the ball to the right and left to reach your knee to the floor.
Experts recommend that to be effective, all exercises should be completed up to 20 times .
Methods of Bubnovsky and Evdokimenko
Dr. Sergey Bubnovsky is a doctor + rehabilitation specialist; he has developed many sets of various exercises for joints, which are recognized by official medicine.
Dr. Pavel Evdokimenko is a rheumatologist and honorary academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. He has written a number of books on the problems of treating arthrosis and arthritis.
Set of exercises:
- Lying on your stomach, bend your legs alternately and reach your buttocks with your heels, holding for 10 seconds. The head is turned in the opposite direction. Relax for 5 seconds and repeat again.
- Get on all fours on the mat. Angry cat exercise – keep your back arched for 5 seconds, then relax.
- Lie on the mat, alternately pull your legs towards your stomach, helping with your hands, tense your muscles for 7 seconds, then relax.
- Lying on your back, pull your legs towards your stomach, clasping them with your arms. Tighten your muscles for 10 seconds, relax.
- Sit on a chair and slowly bend over, stretching your back. Tighten your lower back muscles for 6-7 seconds and relax as you exhale.
Efficiency
More than half of all hernia cases occur in the l4 l5 localization. The protrusion occurs between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae. Such a hernia is considered one of the most unfavorable, leading to paresis or complete paralysis.
Properly selected gymnastic exercises can get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of l4 l5 hernia and osteochondrosis, remove muscles from spasm, and strengthen a weakened spine. The range of movements depends on the stage and localization of the pathology and the age of the patient.
The following groups of exercises are prescribed:
- for relaxation – yoga, Chinese gymnastics, swimming pool exercises,
- to strengthen muscle groups,
- for stretching.
Orthopedic doctor, 12 years of experience A hernia up to 5 mm in size is treated only with exercise therapy and stretching. When the protrusion is up to 8 mm, water squats and sliding in the pool are added to the gymnastics. In 90% of patients, exercise therapy helps avoid surgery.
Timely diagnosed protrusion of l5 s1 between the last lumbar and first sacral vertebrae can be treated without surgery. Thanks to the gymnastic complex, the muscle corset is restored, pain is eliminated, and the back is strengthened. Exercises normalize weakened muscles and relieve hypertonicity and tension. Special movements restore the corset holistically and relieve overload from the spinal column.
When there is no time for a course of physical therapy
Not everyone has time to workout. In such cases, you don’t have to do the full complex, but you need to do it to feel light in the body. For this, a 5-minute complex instead of morning exercises is quite enough. It includes the basic most important exercises.
Mini-complex for problematic lower back
- Lie on your stomach and alternately bend your knees as much as possible so that someone can help hold them by the ankle for 5-7 seconds to create resistance. At the same time trying to straighten the leg.
- Next, repeat the exercise, but the role of an assistant is played by a belt or towel.
- After this, the “evil-good cat” exercise.
- Lie on your back and help yourself with your hands, pulling your knees to your chest one by one.
- Lying on your back, bend and pull your legs towards you. Next, the assistant holds the legs, and the patient tries to move them away from him.
Benefits of exercise
The course of rehabilitation gymnastics presents a scientifically based set of exercises. The patient must understand that exercise therapy is physical education therapy, so it is necessary to exercise under the guidance of an exercise therapy instructor.
To achieve results, the patient must:
- Don't rush into training.
- Follow the instructor's recommendations.
After the first lessons, results appear. But this effect is short-lived. In just a few sessions, the patient can:
- The process of restoring blood circulation in the problem area begins.
- The load on the spine will be significantly reduced.
- The synthesis of immune cells will increase, the body will be able to more actively resist infections.
- Resistance to external influences will increase, the patient will be able to withstand shocks and blows.
- The process of cell destruction will stop.
If the patient regularly engages in exercise therapy, then he will:
- The pain will begin to disappear.
- An even posture will be formed.
- The joints will become more mobile.
- Muscle tissue will grow.
- Hormonal levels will return to normal.
- There will be no swelling and inflammation in sore areas.
Prevention
Exercise therapy already prevents osteochondrosis:
- Stretching the back muscles while hanging on a horizontal bar is also useful.
- Attention should also be paid to the abs, it supports the spine.
- Swimming is useful.
- When carrying heavy objects, you should wear a corset belt; you should not lift more than 10 kg.
- Massage courses are useful once every six months.
If osteochondrosis is not neglected, you can live with it for quite a long time, even without pain. Exercise therapy will help with this, but exercises do not replace visiting a doctor and following his instructions.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine
A neurologist treats this disease. The following measures are used for diagnosis:
- palpation of the spine at the initial appointment;
- X-ray;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
Doctors prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs with analgesics. Electrophoresis with Karipazim is widely used. Diclofenac injections are given intramuscularly.
Surgical intervention is indicated in 10-12% of cases. The remaining patients receive conservative treatment. The standard in the treatment of intervertebral hernias is microdiscectomy. Thanks to the use of gentle microsurgical operations, the indications are expanded.
Methods such as endoscopic nucleotomy and laser vaporization of intervertebral discs can be used. As a result, intradiscal pressure decreases and the hernial protrusion is reduced. Plasma nucleoplasty is based on applying low temperatures along with coagulation directly into the disc. During evaporation, the resulting gases are removed using an introducer needle.
In developed countries, neurosurgeons are beginning to master such an innovative method as disc replacement. Prodisc prostheses demonstrate good results.