Daily physical therapy exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis are the most effective way to treat it. At the initial stage of the disease, regular exercise often allows you to completely stop taking medications. By strengthening the back muscles, the patient’s well-being quickly improves - pain in the thoracic region and stiffness of movement disappear. A physical therapy doctor is present at the first classes and tells you how to do the exercises correctly and dose the load.
In what cases can exercises help with thoracic osteochondrosis?
Neurologists and vertebrologists refer patients with thoracic osteochondrosis to a physical therapy doctor immediately after eliminating severe pain. The stage of the pathology does not matter. But it must be taken into account by the physical therapy doctor when compiling a set of exercises. The more pronounced the damage to the intervertebral discs and vertebrae, the more carefully the physical activity is dosed.
Physical therapy exercises, as a method of therapy, are especially useful for already developed complications of thoracic osteochondrosis. Doing exercises and daily exercises help get rid of shortness of breath, pain in the heart, a sore feeling and a “coma” in the throat. It is also recommended for patients with progressive osteochondrosis extending to the cervical discs.
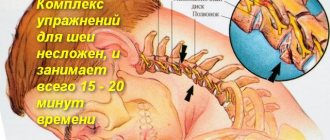
The pictures show a decrease in the gap between the vertebrae in the thoracic region.
Contraindications and side effects
Contraindications to exercise therapy for cervical osteochondrosis include:
- Bad feeling.
- Impaired cerebral blood flow.
- Acute pain in the neck and shoulders.
- Muscle compression, spasms (how to relieve muscle spasm during SCH?).
- Hernia.
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Ankylosing spondylitis.
- Cervical osteochondrosis of the 3rd degree.
- Spondylopathy.
What loads can cause harm?
Despite all the advantages of therapeutic exercises, it is worth noting those exercises that can harm the patient , further worsen his condition and increase pain.
Such exercises include physical activity that is aimed at straightening the back.
Training effectiveness
Daily exercises help increase the range of motion in the thoracic spine and eliminate muscle spasms. And after performing stretching exercises, the distance between adjacent discs and vertebrae increases. They stop squeezing the spinal roots, which allows you to avoid the risk of acute, piercing pain. What positive changes are still happening:
- surges in blood pressure, panic attacks, and dizziness, often caused by pinched vertebral arteries, disappear;
- the muscles of not only the thoracic region, but also the entire back, as well as the neck and shoulder girdle are strengthened;
- ventilation of the lungs improves, which allows patients not to worry about pain when taking a deep breath;
- blood circulation in the area of vertebral structures affected by osteochondrosis is accelerated, nutrient reserves are replenished;
- Correct posture is formed and the physiological curves of the spine are restored.
Physical therapy exercises are indicated not only for patients with osteochondrosis. They are recommended for people who are at risk of premature disc failure. As a rule, their work involves staying in one body position for a long time.
Experts' opinion
Doctors advise against sleeping on large pillows; it is advisable to use an orthopedic cushion. After treatment of the acute form, it is recommended to visit the bathhouse and sauna, and sign up for the pool.
You also need to avoid hypothermia. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate ; the transition from one stage to another occurs very quickly.
What does Doctor Shishonin say?
According to Dr. Shishonin, simple exercises can cope with various problems, improve well-being and restore tone to the neck muscles. Dr. Shishonin has developed a set of exercises aimed at treating and preventing both cervical osteochondrosis and other neck problems. You can learn about the features of performing Dr. Shishonin’s gymnastics with SHOC from our material.
We invite you to watch a video containing Dr. Shishonin’s opinion on osteochondrosis:
We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the principle of action of gymnastics by Alexandra Bonina and Vladimir Butrimov for cervical osteochondrosis.
General rules of therapeutic exercises
Only compliance with all the rules of therapeutic exercises will help achieve the expected result. This is due to irreversible changes in the discs and vertebrae that have already occurred in the thoracic region. It is necessary to dose the loads so that strengthening the back muscles does not cause even greater destruction of the vertebral structures. The following medical recommendations should be followed:
- warm up before training and stretch after it;
- increase physical activity gradually as you build up your muscle corset;
- completely eliminate any sudden movements that provoke microtrauma of the discs;
- exercise every day, and skip workouts only because you feel unwell.
During classes, you need to listen to the sensations that arise. Pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness become signals to stop training. And if certain movements lead to a pleasant feeling of muscle stretching, then they need to be done more often - in 2, and sometimes in 3 approaches.
Warm-up
Physical therapy for any pathology requires preparing muscles for stress.
Pinching of the nerve roots between the deformed vertebrae will lead to severe pain and hospitalization.
Warm-up is carried out according to general rules and has no special features worth attention. Example of some movements:
- body/head tilts;
- circular movements of the body/head/limbs;
- flexion/extension of the body/limbs/head;
- swings of the upper/lower limbs;
- walking in place;
- lunges forward on the right/left leg.
Before performing the exercises, you should warm up.
The number of executions is variable, but not less than 3–5 for each. Number of approaches: 2. The combination of movements is individual.
A set of exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
The first classes do not last longer than 15-20 minutes. The back muscles must adapt to the loads that arise, so first you need to perform the simplest exercises. If there is no discomfort and increased mobility of the thoracic region, you can increase the training time to 30-40 minutes. And the exercise therapy doctor will include complex exercises in the treatment complex, but also more effective for osteochondrosis.
Sitting on a chair
Patients with thoracic osteochondrosis will need a chair, not a stool. When performing some exercises, you need to focus on its back:
- sit in such a way that your shoulders and upper back are pressed tightly against the back of the chair. Try to bend back, arching your lower back, and then slightly lean forward;
- sit up straight, put your hands on your shoulders. Try to lift them, resisting with your palms.
The number of approaches is from 5 to 10. Such exercises are often used for combined cervicothoracic osteochondrosis.
Lying on your back
For thoracic osteochondrosis of 2-3 degrees of severity, you will need a small pillow for exercise, which should be placed slightly above the lower back. What exercises are most effective:
- Bend your legs at the knees, rest your feet on the floor. Raise your shoulders, trying to keep your neck motionless;
- straighten your legs, spread your arms to the side. Raise one hand, place it behind the chest, trying to bring it as close as possible to the floor surface;
- straighten your legs, place your arms arbitrarily and, without using them, try to roll over first on one side, then on the other.
Repeat the exercises 10-15 times. As your muscles strengthen, you should stop using the pillow.
On all fours
It is convenient to do therapeutic exercises in a standing position on all fours on a thick gymnastics mat. For thoracic osteochondrosis, the following exercises are usually included in the complex:
- round your back, lowering your chin, and then bend it, raising your head up;
- sit down without lifting your hands from the floor, stretch your lower back, and take the starting position of your body. Then straighten your legs, focusing on your hands, and bend well again.
Perform exercises 7-10 times. Hold in the position of maximum tension of the back muscles for 10-20 seconds.
For two
Paired gymnastic exercises are convenient to perform during training sessions conducted by a physical therapy doctor. At home, you should use the help of a family member. What exercises are most useful for damage to the thoracic discs and vertebrae:
- sit down, spread your legs wide, rest your feet on the ground. Hold hands, bend forward and backward in turn;
- press your backs together, grab with your elbows. Perform shallow bends without straining your back muscles too much;
- stand with your backs to each other. Pass an object, such as a ball, first from the right and then from the left.
Repeat exercises 10 times. The effect of training is greater if the partner is approximately the same height and weight.
Complex for stretching the back muscles
After completing the main complex, you must definitely do stretching exercises to strengthen, increase muscle elasticity, and adapt to subsequent loads:
- sit on a chair, or better yet, on a stool, wrap your arms around your chest, as if hugging yourself. Try to continue placing your hands behind your back;
- stand up, press your legs together, bend over, trying to touch your forehead to your knees;
- lie down, bend one leg and cross it behind the other, trying to touch the floor with your knee. Repeat the exercise in the opposite direction.
The number of approaches is arbitrary. When performing stretches, only pleasant sensations usually arise, so you can repeat them up to 20 times.
Respiratory
Patients with thoracic osteochondrosis often breathe shallowly, which reduces the mobility of the costovertebral and sternocostal joints. The following exercises will help increase the volume of air when inhaling:
- sit up straight and wrap a narrow towel or scarf around your lower chest. While stretching the fabric with your hands, take deep breaths. At the maximum point of tension, hold your breath for 5 seconds;
- sit down, raise your hands, clasping your fingers. Inhale deeply to tighten your abdominal muscles. As you exhale, bend first to one side, then to the other. Inhale again and stretch upward.
At the initial stage of training, you need to do the exercises about 5 times due to the high likelihood of dizziness. Gradually the number of approaches should be increased to 10-15.
In acute form of pathology
During a relapse of thoracic osteochondrosis, acute pain occurs in the area of damaged discs. Any sudden, awkward movement can intensify it. Therefore, doctors often do not recommend exercising during the acute period. If the pain is moderate, then the following exercises are allowed:
- Lie on your stomach, stretch your arms to the side. Take a deep breath, slightly raise your head and arms. Stay in this position for 5 seconds, exhale, take the starting position;
- turn on your back, put your hands behind your head, stretch, straining the muscles of your back, neck, and shoulder girdle;
- lie on your stomach, stretch your arms along your body, relax. Try to bring your shoulder blades together only by tensing your muscles, and not by moving your arms or shoulders.
If osteochondrosis worsens, you can repeat the exercises no more than 5 times. In this case, movements should be smooth, slightly slow, without jerking.
Features of gymnastics for a herniated disc
Treatment of a hernia with exercises promotes the formation of adaptive mechanisms that are aimed at establishing physiological balance in the affected segment of the spine. Exercises allow you to prevent further progression of the disease, accelerate resorption processes, which lead to resorption or a significant reduction in the size of the hernial protrusion. Physical activity accompanies the main therapy, treatment regimen, diet and other measures prescribed by the doctor and, when performed correctly, leads to:
- pain reduction;
- elimination of other symptoms (tingling, headaches, numbness in the back, limbs, etc.);
- restoration of spine flexibility;
- increasing overall tone and mood. And the right motivation, as we know, only contributes to the treatment of the disease.
There are separate sets of exercises for each part of the spinal column. Depending on the stage and severity of the disease, classes are conducted in gentle, therapeutic and training modes. The first two lead to mobilization and stretching of the spine, as well as relaxation of muscle tissue. The third is aimed at stabilizing the spinal column.
Rules for performing exercises for spinal hernia:
All techniques, their combination, number of repetitions must be selected by a doctor! With a sudden or incorrect movement, pinching of the nerve roots or even rupture of the fibrous ring of the damaged disc may develop. It is advisable to learn therapeutic exercises in a rehabilitation department under the guidance of a physical therapy instructor, and at a minimum, consult with your doctor to see if certain techniques can be performed in your particular case.
- Any techniques that require sudden movements, high-amplitude bending from a standing position, jumping, significant rotational movements of the body, deep squats, heavy lifting and strong twisting of the spinal column, as well as running are unacceptable.
- Classes are held regularly, every day, in a pre-ventilated room, preferably on the floor on a special gymnastic mat.
- All techniques are performed at a slow pace, smoothly and carefully, monitoring the condition and any sensations: dizziness, numbness, tingling and pain indicate that the exercise is performed incorrectly or is contraindicated in a particular case. If you experience slight pain after the first day of training, you should lie on your back on a flat surface and relieve your back.
- The load and range of motion increase gradually.
- Technically difficult exercises should not be attempted the first time. The spine should become more flexible, and this is only possible after 1-2 months of training.
- Each exercise, unless otherwise indicated, is repeated 5-10 times.
- After class you should not be very tired. If this occurs, you need to reduce the duration of exercise therapy and the number of repetitions.
- In addition to the complex, additionally during the day, provided you feel well and have an adequate reaction of the body, the following are recommended:
- morning exercises in the form of a 10-minute warm-up;
- short warm-ups and unloading of the spinal column every 2 hours;
- unloading the back before bed (calm walk, swimming, Strelnikova breathing exercises).
How can you quickly achieve a therapeutic effect? It is difficult to answer this question; even in mild cases, treatment can last from six months to several years. In any case, there is no need to hope for an instant cure (much less believe in dubious methods and healers who promise to get rid of a hernia in a week). This is a long process that requires patience and perseverance from the patient.
Stretching after exercise
During the period of remission, stretching after the main workout is successfully replaced by hanging on a horizontal bar or crossbar for 5-10 minutes. You can also do the following exercises:
- sit sideways, spread your legs slightly, place your hands on your knees. Try to lean towards the back. When performed correctly, the exercise should tighten the lateral muscles of the back. Repeat movements in the other direction;
- in a sitting position with a straight back, inhale deeply, bending back, trying to bring your shoulder blades as close as possible. Stay in this position for 5 seconds, and while exhaling, return to the starting position;
- standing on all fours, place your hand under your stomach and pull it to the side, performing a twist. Repeat the exercise in the opposite direction.
Strengthening the spinal muscles is facilitated by alternate and then simultaneous lifting of the arms and legs while lying on the stomach.
Additional treatment and prevention
Yoga
You need to start gradually. Do yoga for the spine about once a week for about half a month . If no pain occurs, you can increase the number of classes to 2 times a week. There are many exercises that are indicated for cervical osteochondrosis.
- Utthita Trikonasana.
- Parivritta Trikonasana.
- Vrksasana.
- Virabhadrasana I and II.
- Ardha Chandrasana and others.
You will learn how to perform these and other exercises, as well as indications and contraindications for SHOC here.
We invite you to watch a video about yoga for osteochondrosis:
Pool
Swimming can reduce stress on the spine . The positive effect of procedures in water is achieved within 40 minutes, during which time the intervertebral discs return to their places.
How to move in water?
- Go into the water up to your chest and walk in place, raising your legs higher and actively moving your arms.
- Raise your bent leg so that your knee reaches your stomach. Repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Go into the water up to your neck and spread your straight arms to the sides and lower them. Repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Place your hands on your belt. Gently arch your torso, trying to keep your shoulder blades connected together. Then round your back. Repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Leave your hands on your belt, slightly twisting your torso to the sides.
Repeat the set of exercises 3 times.
Running and fitball
Running is indicated for patients whose disease has just begun to develop. Before jogging, you should walk a little and warm up thoroughly. You need to jog.
Exercises with a fitball are suitable for rehabilitation of the thoracic and cervical regions.
Exercises with fitball
Fitball exercises help:
- tone muscles;
- improve joint mobility;
- spine stretching.
The main advantage of the exercises is that they are suitable for people with different physical fitness. The fitball is selected individually depending on the height and weight of the patient.
Horizontal bar and exercise equipment
What to do on the horizontal bar?
Exercises on the tourniquet help to stretch the spine and eliminate compression of the nerve roots. It is important to understand that with cervical osteochondrosis, these exercises can provoke a deterioration in the patient’s condition and affect the reduction of blood supply to the brain. This is due to the fact that performing a hang or half-hang leads to pinching of the fifth cervical vertebra.
Therefore, you should hang on the horizontal bar upside down, clasping the bar with your legs.
If the leg muscles are not ready for such loads, you can use safety belts. After some time, the exercises can be performed with dumbbells and turning the body to the right and left.
Use of simulators
Classes can be carried out both in the gym and at home. To treat cervical osteochondrosis, you can use various exercise machines.
- The expander develops the muscles of the arms, forearms, muscles in the thoracic and cervical region. It is a flat or tubular harness with two comfortable handles, which can be mounted on the wall or performed exercises by standing in the middle of the harness.
- Cardio equipment includes an orbitec, a treadmill and a manual rowing machine. Exercises are carried out 2-3 times a week for 30-60 minutes. Such exercises promote weight loss and improve the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
- The Evminov simulator is designed specifically for the prevention, correction and treatment of osteochondrosis in the thoracic and cervical region. It is a wooden panel equipped with movable handles.
- The Yalovitsyn swing is designed to stretch the spine. It is a wooden structure, similar to a children's swing at the ready.
Often, a gymnastic stick is used as equipment when performing exercises for the back and neck with osteochondrosis. You can read more about this here.
Contraindications for implementation
Acute, piercing pain in the back, radiating to the hips and shoulder blades, is an absolute contraindication for exercising. You should not perform exercises in the following pathological conditions:
- tachycardia, bradycardia;
- severe dizziness, loss of coordination of movements;
- high or low blood pressure;
- respiratory, intestinal infections;
- elevated body temperature.
Training should be postponed in case of exacerbation of other chronic diseases. If you have recently undergone surgery, then performing exercises is strictly prohibited.
Breathing exercises
Breathing control is very important when performing any gymnastics routine. And performing breathing exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis is allowed even during exacerbations and after operations.
One of the most effective methods of breathing exercises is Strelnikova’s gymnastics. It consists of alternating fast and strong inhalation through the nose with a slow exhalation through the mouth.
Yoga asanas
This teaching is convenient because it does not force a person to perform poses perfectly. It is enough to try, and this will be quite enough at the initial stage.
For thoracic osteochondrosis, 3 asanas will be useful:
- tadasana;
- virabhadrasana;
- bhujanasana.
Tadasana
The simplest pose. You need to take the most vertical position possible, imagining that a rope is tied to the top of your head and it is pulling your body up. If your condition allows, raise your arms vertically, pointing your fingertips at the ceiling.
Virabhadrasana
It starts with Tadasana, only you need to join the palms of your arms extended upward. Inhale deeply and jump your legs (one forward, one back) about 1.2 m wide, with your right foot pointing outward at 90° and your left foot slightly inward.
Bend your right leg at the knee so that an angle of 90° is formed between the thigh and ankle. The chest and face “look” towards the toes of the right foot. Slowly and smoothly move your head back, feel how your spine stretches - look at your fingertips.
Change the position to symmetrical and repeat. Delay in the pose 30 – 90 seconds. Return to Tadasana with a jump, then relax. If your physical fitness is weak, skip the jump and take a wide step.
The asana promotes full opening of the chest, relieves spasm from the pectoral, neck, and shoulder muscles. A different execution of Virabhadrasana is possible.
Bhujanasana
This is a rather difficult pose (cobra pose) if performed perfectly, so start with the simplest:
- Take a sphinx pose (lying, raising yourself up and focusing on your elbows), while stretching your legs strongly, feeling the lower part of the spine stretching behind them.
- As soon as the sphinx pose becomes familiar, make it more difficult - the head and shoulders remain at the same level, but now the emphasis is on the palms, the elbows are pressed to the sides.
- Retract your shoulder blades, feel the thoracic spine.
- Now slowly straighten your arms, expanding your chest.
- If your physical fitness allows, with your arms outstretched, bend your back well in the area of the thoracic vertebrae and slowly tilt your head back. Stay for a comfortable time.
- Return to the lying position, slowly bending your arms.
Study the picture below carefully. It shows step by step how to do the cobra pose to avoid mistakes.
On a note. It has been noticed that yoga has a beneficial effect on both the body and the emotional state. In addition to the asanas described, introduce other simple poses into gymnastics and learn to concentrate, completely forgetting about the world around you. This will help over time to get rid of such consequences of osteochondrosis as VSD and panic attacks.
Symptoms
This disease is characterized by the presence of such a symptom as palpable pain in the upper back. By nature, the syndrome is divided into two types - dorsago and dorsalgia.
Upper back pain
Prices for painkillers for back pain
Table. Types of pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic part.
| View | Description |
| Dorsalgia | In this case, pain is felt in the area of the intervertebral discs. It is weakly expressed, but is felt for a long time. There are problems with mobility in the lumbar-thoracic and cervicothoracic spine. |
| Dorsago | With this nature, the pain is strong, pronounced, acute, often paroxysmal. The mobility of the back is severely limited, and there may be difficulty in inhaling and exhaling. |
In general, the symptoms of the development of pathology are pain in the chest, back, also felt in the heart and upper lateral abdomen. The syndrome intensifies during movements of almost any intensity, with deep breathing, at night. The patient may also complain of periodic numbness in the area of the shoulder blades or left arm.
Chest pain is one of the symptoms
On a note! Sometimes pain with such osteochondrosis can be confused with intercostal neuralgia, characterized by pain in the scapula area. In general, this disease is not difficult to confuse with a number of other pathologies, including gastritis, appendicitis, and renal colic. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
In the thoracic region, the spinal cord canal is very narrow. And at the slightest disturbance in this part of the back, compression of the spinal substance and pinching of nerve endings can occur. The danger is that in this way you can easily get problems with a number of internal organs - heart, kidneys, pancreas, etc.
Anatomy of the spine
Exercises with a gymnastic stick
They are considered effective for osteochondrosis of the spine of any location. They are best performed under the supervision of an instructor, but the most basic ones can be done at home:
- Take a table pose - bend forward so that your torso forms a right angle with your hips, place the stick on the floor and rest your palms on it. Now slowly, as far as your condition allows, bend in your chest, and then in your lower back. Repeat a comfortable number of times. Breathe deeply and measuredly.
- Hold the stick with your arms spread wide. Now extend them in front of you and begin to make twisting movements, as if turning a steering wheel. Repeat a comfortable number of times.
- Grab the stick behind your back with your arms bent at the elbows (your hands on your sides parallel to the floor, with your palms facing the ceiling). Tighten your shoulder blades, trying to touch them one against the other (as in similar exercises by Bubnovsky and Bonina). Then relax. Repeat as many times as is comfortable.
On a note. Exercises with a stick are an independent complex, and quite complex. Doing them on your own can lead to an aggravation of the condition, so do not experiment - seek advice from an experienced doctor-instructor.
Gymnastics plays an important role in the treatment of osteochondrosis. At the first unpleasant symptoms, consult a doctor. He will select therapy and recommend what exercises you need to do to live without pain and keep your spine flexible.