The benefits and harms of this sport
Arm wrestling will strengthen your joints, and the stiffness of the ligaments decides who wins the fight. Your hand will have a real iron grip. In this sport, many exercises are aimed at developing grip strength. Gripping fingers will improve your climbing skills. It will be easier for you to carry heavy objects (lifting furniture to the fifth floor).
Arm wrestlers win thanks to correct technique and explosive muscle power. Those athletes who manage to react in time to the judge’s command immediately find themselves in an advantageous position, so the reaction speed of arm wrestlers is crucial.
By practicing arm wrestling, you will increase your speed, explosiveness and reaction speed. Arm wrestling will strengthen your character, you will be able to endure and not give up in difficult times.
During a fight, the wrists, elbows and shoulders, ligaments and muscles of the hands experience colossal overloads. The most common injuries in arm wrestling:
- Shoulder muscle avulsions and tears.
- Sprains and tears of the elbow and shoulder ligaments and injuries to these joints.
- Fractures of the humerus.
Arm wrestling is a very traumatic sport, so before you start wrestling on your arms, strengthen them with regular training and special isometric exercises for 1-2 months. To avoid injuries, devote most of your training, especially at the initial stage, to strength training and strengthening of ligaments, regimen and proper nutrition. And sparring with a partner should be done no more than once a week.
Pros and cons of arm wrestling
Arm wrestling training strengthens the body and character. By practicing this sport, you will significantly improve your explosive strength and reaction speed. Such skills will be useful both in competitions and in everyday life. For example, when carrying heavy loads. In addition, your perseverance in achieving your goal can only be envied. Arm wrestling has virtually no age restrictions. If you are healthy and full of strength, go for it!
The disadvantages of arm wrestling are, of course, injuries. Fractures, dislocations, sprains, ruptures - the arsenal of injuries in this sport is truly rich. In order not to experience the downside of this type of dispute, it is necessary to train regularly, strengthen the ligamentous-articular apparatus, observe a rest and nutrition regime, and also not to violate the technique of performing wrestling techniques.
Contraindications
Arm wrestling training is aimed primarily at strengthening the arms and hands, both muscles and joint-ligamentous apparatus. If you experience pain during exercise, you should stop immediately. Do not engage in arm wrestling if you have injuries to the shoulder, elbow and wrist joints, or if you have chronic and inflammatory diseases of the joints of the hands (arthritis, arthrosis, dislocations, torn ligaments).
Be careful when exercising if you have high blood pressure or heart disease, or better yet, consult your doctor first.
Do not exercise if you are poisoned or sick - such training will not lead to anything good. First, you need to undergo proper treatment and fully recover, and only then start training.
The role of ligaments and tendons in arm wrestling
I have always been amazed by the amazing ignorance of the majority of arm wrestlers in matters relating to the tendon-ligament apparatus. Firstly, ligaments are constantly confused with tendons. Secondly, they attribute some amazing qualities to the ligaments. Based on the thickness of the tendons, they confidently declare a genetic predisposition to arm wrestling.
Constantly puzzled by the question of how to pump up the ligaments. The list of these absurdities can be continued for a long time. And I have been observing this in arm wrestling for more than 20 years. It seems that most armwrestlers have never opened an anatomy textbook in their lives. But no, it opened. The same athletes are well aware of the pronator teres and quadratus muscles, the supinator muscle, and the functions of the brachioradialis muscle. That is, those anatomical points about which the average gym goer has a very vague idea. So why is there such ignorance about ligaments and tendons? Honestly, I don't know.
I hope that my article will allow you to better understand the role of the tendon-ligamentous apparatus in arm wrestling and force you to reconsider the generally accepted provisions.
Ligaments
Ligaments are connective tissue cords, the strength of which is increased by the fact that their constituent fibers do not run parallel, but have a cross and oblique course. Some of the ligaments, such as the iliofemoral or long plantar ligaments, can withstand tensile loads of several hundred kilograms. (M.F. Ivanitsky). Ligaments are built from dense connective tissue rich in collagen fibers. The elastin content in ligaments is higher than in tendons, so they are more extensible. Some ligaments are capable of increasing their length by 20-40% when stretched, while tendons are capable of stretching only 2-5% (Shah et al., 1977).
The function of ligaments is to strengthen the joints. They are not connected to muscles and, accordingly, do not take any part in muscle contraction. Therefore, it is basically impossible to download the bundle. At the same time, an increase in protein synthesis occurs in the ligaments under the influence of growth hormone (GH). Therefore, by performing exercises in static dynamics, and it is this mode that promotes maximum secretion of GH, we increase the concentration of growth hormone in the blood, and from the general bloodstream some of the hormones will be absorbed by the tissue of the ligaments. So, regular training without any specialization is enough for the ligaments to maintain their condition.
Constant tensile stress on the ligaments does not lead to their training, but to overstretching. And this process is irreversible. Former athletes - swimmers, representatives of rhythmic gymnastics and other sports that require increased flexibility from athletes, upon completion of their careers, often suffer from loose joints and the spine. They have only two options: either have surgery to remove part of the ligament, or continue strength training for the rest of their lives. Then the muscles take on the function of stabilizing the joints. But as soon as you stop training, muscle tone drops and joints begin to fly out again.
Wrestlers often experience habitual shoulder dislocation. Some of them even got used to adjusting it themselves. This is nothing more than a hyperextension of the ligaments of the shoulder joint and can only be cured by surgery.
Elbow joint
The elbow joint is a fairly strong joint. Stability is provided by the shape of the trochlear glenohumeral joint, the annular ligament, the radial collateral ligament, and the fan-shaped ulnar collateral ligament. With any technical variant used in arm wrestling, the main movement is shoulder pronation, performed in a static mode. Accordingly, during the struggle, a force will always be applied to the joint in the direction of its supination, turning the bones of the forearm out of the joint. It would seem that the restraining role of the medial ligaments of the joint should be decisive, but this is not entirely true.
Firstly, the joint is significantly strengthened by tense muscles, both the muscles of the forearm, attached to the medial epicondyle of the humerus, and the flexors of the forearm, which, although they apply force perpendicular to the acting force, the strong tension of the flexors, balanced by the counteracting force of the partner, helps stabilize the joint and reduces the load on the ligamentous apparatus in any direction of applied force. That is, first of all, the load falls not on the ligaments, but on the muscles and tendons, especially the forearms.
Therefore, diseases and injuries of the medial ligaments of the forearm are extremely rare, while diseases and injuries of the tendons are much more common. For example, the well-known medial epicondylitis, golfer's elbow. This is an inflammation of the tendons attached to the medial epicondyle of the humerus, the following muscles: pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum superficialis.
Familiar muscles? All of them play an important role in the fight and it is their tension that significantly removes the load from the ligaments and takes the blow. Secondly, the strength of the elbow joint is quite high and even if muscle tone decreases, for example, in a wrestling position in a dangerous position, when the shoulder in the frontal plane comes forward of the grip, it is not the ligament rupture that occurs, but a screw fracture of the humerus - the most common injury in arm wrestling . So the strength of the ligaments is not the limiting link, unlike the strength of the tendons. Constantly fighting in a dangerous position during training may not lead to a fracture, but it will lead to overstretching of the medial ligaments and subsequent destabilization of the joint, the consequences of which I have already written about.
Tendons
Tendons are the connective tissue part of muscles through which they are attached to bones. The tendon consists of compact parallel bundles of collagen fibers, between which are rows of fibrocytes. As already mentioned, tendons are stronger and less tensile than ligaments. The main functional significance of tendons is that, by fixing the places of attachment of muscles to bones, they ensure the transmission of muscle forces to bone levers.
Despite the fact that tendons are directly involved in muscle work, they themselves do not have contractile elements and are, by and large, simply cables connecting muscles to bones, and they do not have a significant effect on the force exerted. Imagine that you are about to pull a friend's stuck car out of the mud. You customize your car and attach a tow rope to the cars.
So, you can pull the car out only if the power of your car is capable of creating the force necessary for this. Whether you use one cable or hang five, it doesn’t matter. If one cable is strong enough to withstand the required force, then there is no need to add others. The same goes for muscle work. The tendon is the same cable, and the muscle is the towing machine. The width and strength of the tendon does not provide any advantages, since the traction force is created only by the myofibrillar apparatus of the muscles. Although a reservation should be made here. A wide and strong tendon indirectly indicates a large number of muscle fibers, and this is an indicator of genetic talent for strength sports.
But strength is determined not by the number of fibers in the working muscle, but by the number of myofibrils. Muscle fiber (MF) can increase its diameter by 5 times due to an increase in the number of myofibrils. And an athlete with a relatively small number of hypertrophied CFs will have more myofibrils than an athlete with a large number of CFs, but of average size. And although the first tendon will be thinner, it will have an advantage in strength.
A much more important indicator is not the width of the tendon, but the distance from the place of its attachment to the axis of rotation of the joint. It is not for nothing that since ancient times people have been spoken about people of heroic build and about sinewy people who are not inferior to them in strength. Stringy means that the tendons are clearly visible under the skin, which is possible when they are removed from the joint. Such people exert much less muscular effort when performing a certain motor action than their less gifted rivals. Therefore, do not be surprised that, having a smaller diameter of the working muscle, they are able to develop greater strength. Laws of mechanics!
So remember, if a skinny guy in training easily deals with more massive opponents, his ligaments or tendons are not stronger, and the attachment points of the tendons are further from the axis of rotation of the joint.
The myth about the exceptional role of tendon strength in the development of strength came from the great circus athlete and wrestler Alexander Zass, a truly cult figure in strength sports. Many are familiar with his statements: Muscles by themselves cannot lift a horse, but tendons can.
Some people with thin legs are stronger than people with thick legs - Why? Because the power lies in the tendons, in those invisible hard tissues that are second in density only to bones. Without tendons, a person would turn into jelly. But the tendons need to be trained. From my experience, one can be convinced that a large man does not necessarily have to be strong, but a man of modest build does not have to be weak.
I don't believe in big muscles unless there's real big tendon power next to them. You can see physical fitness enthusiasts who have quite large muscles. But what good are they if there is no powerful foundation - developed tendons. They are unable to fully utilize the strength of their muscles during an actual test of strength. And therefore their power is only an illusion.
Tendons increase their strength best when their power is applied to some almost immovable object. They become stronger from resistance than from movement.
But all these speculations of the great athlete have no scientific basis. Strength is determined solely by the development of the muscle component. In no way do I want to diminish the greatness of Zass. On the contrary, I consider him one of the greatest athletes of all time and I plan to write a series of articles about him and his training system. But Zass was not a scientist, was not a doctor, and did not even have a higher education.
He developed his system based on his own experience and experiments. Zass had unique genetics, precisely in terms of the large distance from the point of attachment of the tendons to the axis of rotation of the joints, which allowed him to show outstanding strength results with a fairly modest muscle mass. By the way, he inherited genetics from his father. He easily broke horseshoes without any training.
From the point of view of sports adaptology, isometric Zass gymnastics does not have any advantage for the development of tendons over dynamic training, although it is quite effective for increasing strength. Tendon growth occurs along with myofibril hyperplasia.
Myofibrils grow in 10-14 days, and their end parts entering the tendon take 50-90 days. With a properly organized training process, the growth of myofibrils is always accompanied by thickening of the tendons. Unfortunately, in sports such a process is practically impossible. Shock loads and wrestling from the start injure the tendons, and they take about 50 days to recover. But not a single athlete will stop developmental training for such a period.
As a result, injuries accumulate and the tendon wears out. This is especially noticeable when taking anabolic steroids. AS act on the contractile part of the muscle, while growth hormone acts to a greater extent on the connective part. But the growth of the connective tissue of the tendon is much slower than the growth of muscles, and when using shock loads, plyometric exercises, and sparring from the start, the tendon wears out and tears. It must be said that there is no such thing as a tendon rupture. The rupture always occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the bone.
In 2012, my distal biceps tendon was torn off during competition. The next morning they performed surgery and placed him on a titanium anchor. The operating surgeon showed me the pictures. I was amazed at how worn, thin and fibrous my tendon was. The doctor said that all athletes have a similar picture. The reality of big sport is that no one gives time for tendons to recover. Nobody can afford a two-month break in the season, and injuries accumulate and tendons wear out.
The tendon becomes loose and the ends of the collagen threads scratch the walls of the tendon sheath. Hence the constant aching pain. In order for these protruding threads to die off and be destroyed, the load must be stopped or significantly reduced, otherwise this sluggish inflammatory process will continue. In this case, treatment with nitric oxide using the air-plasma device “Plazon” helps best (more information about this can be found in my article “NO-therapy in the treatment of sports injuries.” ZhM No. 9).
Unlike ligaments, tendons can be trained. As I already said, growth hormone plays the most important role in connective tissue protein synthesis. Somatropin is absorbed from the general bloodstream by active tissues. Blood vessels penetrate the tendons from the side of the muscle belly and from it GH penetrates into the tendon tissue.
After the basic GH release exercise, it is necessary to perform tendon strengthening exercises. This is achieved by volumetric training work of low intensity. It is desirable that the movements be performed with the maximum possible amplitude for a given joint and in all directions. (Zatsiorsky V.M., Seluyanov V.N., Arunin A.S. 1981). This is the kind of training and work in static dynamics that should be followed in case of injuries and pain in the tendons.
A story about tendons would be incomplete without telling us that when performing fast movements we can still use the elastic properties of tendons. They provide an increase in working effect due to the use of additional (non-metabolic) mechanical energy. Elastic deformation of tendons and excited muscles when they are stretched by an external force leads to the accumulation of a certain tension potential in their substance, which, with the onset of contraction, is used as a significant force additive to the traction force of the muscles, increasing the power of their contraction.
The greater the contribution of such a strength additive to the movement, the higher its working effect (you can read more about this in my article-interview with V.N. Seluyanov “Elastic deformation in strength sports” ZhM No. 9). But in circus strength acts and in arm wrestling, the energy of elastic deformation is practically not used. It is used primarily in running, jumping and throwing. That is, in speed-strength sports. There it gives a significant increase.
Conclusions:
- Tendon thickness and strength do not provide a strength advantage.
- The thickness of the tendon only indirectly indicates a predisposition to the manifestation of force, suggesting a large number of MVs.
- The distance from the place of attachment of the tendon to the axis of rotation of the joint is the main criterion for endowment.
- Tendon training is only required to reduce injury.
- The tendons are best affected by low-intensity volumetric training after a basic exercise in static dynamics to increase the secretion of GH and training in a static dynamic mode.
- Ligaments do not participate in muscle work
- Ligament strength is not a limiting factor in arm wrestling
- Ligaments do not require specialized training, but are systematically strengthened during the normal training process.
Thus, the role of ligaments in arm wrestling is greatly exaggerated.
Author: Andrey Antonov. Based on materials from Iron World.
Arm wrestling technique
Hook wrestling
Before starting, press your shoulder and elbow tightly to your chest. At the referee's command, immediately bend your hand with your palm facing you and pull your forearm towards you, reducing the angle at the elbow joint. If you managed to do all this, feel free to take down your opponent, he is at a disadvantage. Throughout the movement, keep your elbow tight to your body and fight with your whole body, not just your arm. This method is popular among competitors with developed biceps.
To prevent themselves from being overcome by a hook technique, athletes strengthen their wrists to effectively resist bending of the wrist. And they pull their arm towards themselves, trying to increase the angle at the opponent’s elbow joint.
Overhead fighting system
In this method, you need to bend your opponent's wrist so that your hand is higher. Extend the fingers on your opponent's hand, bring your wrist higher and take your opponent down. This method is more often used by athletes who have long forearm.
Often, when wrestling over the top in competitions, the grip breaks, in order to prevent this situation from happening again, the judges tie the opponents’ hands with a belt.
Fighting sideways
The athlete strives, without changing the angle, to put the opponent down with a lateral force, while the role of the fingers is almost completely absent. When wrestling to the side, the strength and speed of the athlete play a decisive role. This method is used with tied hands. It is important when starting to not let your opponent twist your wrist.
Professional athletes must master all these techniques and be able to effectively resist them; for this they need to strengthen:
- Fingers and wrist.
- Forearm.
- Biceps.
- Upper back.
- It is imperative to improve the antagonist muscles - triceps, pectoral and deltoids.
Particular attention should be paid to strengthening the ligaments, for this you need to use exercises using isometric tension (holding a load with your fingers, hanging on a bar with bent arms, holding a heavy dumbbell on your biceps).
Technique
To understand how to arm wrestle correctly, you first need to master the technique. The battle is divided into three parts:
- starting;
- gaining an advantage;
- implementation.
In order to take part in the competition, you must meet the following conditions:
- Externally, the athlete should look neat and wear sports clothing.
- Your hands should be completely free of any clothing items.
- The athlete’s hands must comply with hygienic conditions: nails are trimmed and free of fungus, and washed before sparring.
- When wearing clothing that has a manufacturer's logo on it, this point should be agreed upon in advance with the competition organizers.
Hook wrestling
When fighting with the top hook, the opponent's wrist is bent. During combat, flexion occurs due to the flexor pollicis, as well as the flexor carpi radialis.
When sparring with a low hook, after the match has begun, the emphasis is on supinating the opponent's hand.
The middle hook is a classic variation of this technique, in which the initial movements involve both twisting and supinating the opponent’s hand.
Overhead fighting system
There are many variations of overhead wrestling. The most typical type of wrestling is considered to be one in which the athlete, after the judge’s command, makes a pull movement toward himself and moves the grip in his direction, while the working angle remains unchanged.
All movements are carried out diagonally towards oneself and to the side until the sparring opponent’s hand crosses the plane of the roller or touches it. A very important point is how to work with the body: the athlete’s hand should be positioned statically, and all movements should be carried out by moving the body and the arm along with it.
Also of no small importance is the ratio of the athlete’s lateral ligament and the strength of the forearm muscles, which determines how much the athlete will fight with a stretch or a lateral movement, and also affects the direction of the attack. The more pressure is applied to the side, the greater the strength the lateral ligament will have.
Fighting sideways
When installing, the athlete’s finger is positioned as close as possible to the phalanx of the opponent’s index finger, while pressure must be applied to it at the same time.
Using circular movements to the side, you should simultaneously pull the opponent’s fingers towards you. The elbow will move sideways to the outer edge of the armrest. With the wrist bent, the opponent's hand should be pressed against the side pad.
Exercises that arm wrestlers use to prepare
- The standing biceps curl is an effective exercise that develops the biceps, back and forearms. Do not perform the lift in full amplitude - try not to extend your arm more than 1200. To strengthen your forearm, do this movement with a thick bar, or put elastic bands on the bar to increase its diameter.
- Lifting the barbell onto the wrist - take the barbell, place your forearms on the bench, palms facing up, bend your hands towards you, lifting the barbell. The exercise can be performed with one hand and using a long barbell, this will additionally load the pronator and supinator muscles.
- Lifting a kettlebell with a hand with two hands - put your forearms on the bench and take the kettlebell, palms facing each other, thumb facing up, lift the kettlebell by bending and straightening your wrist.
- Deadlifts using a hook or overhead pull-down can be performed both on an arm wrestling table and while standing. The movement repeats that performed during wrestling. We take the handle and pull it to the chest. The arm remains tense throughout the entire exercise, keeping the elbow pressed to the body. It is advisable to use a large diameter handle of the exercise machine to strengthen grip strength (arm wrestler’s handle).
- Dumbbell lift for the brachioradialis muscle on the Scott bench. We take a dumbbell with a hammer grip and perform lifts, extending the arm in incomplete amplitude no more than 1000 - 1200 at the lowest point. You can use a lower block for this exercise.
- Work out the wrist and biceps with a rubber band or resistance band, using different angles and simulating wrestling.
- Training pronation (twisting the hand with the thumb towards you) and supination on a block using a strap.
- Holding large weights with your fingers, and lifting with your fingers.
- Hold a dumbbell on the biceps with a right angle at the elbow joint.
- Pull-ups – This exercise will strengthen not only your biceps, but also your latissimus dorsi muscles. For arm wrestling, it is useful to perform explosive pull-ups not at full amplitude, when at the top point the palms come off the bar, and at the bottom point the elbows do not straighten completely.
- Hanging on the bar with bent arms with a right angle at the elbow joint.
Exercises for the shoulder girdle:
- Standing barbell and dumbbell presses.
- Swing dumbbells through the sides.
- Dumbbell swings for the rear deltoid.
Barbell presses, bench presses and dips are needed to strengthen the triceps, chest and deltoid muscles; these movements are basic and contribute to the production of testosterone, which is needed to increase muscle mass. Barbell squats and deadlifts are good for these purposes. Performing these exercises once a week will help you quickly build arm muscles and increase strength.
Once a week you need to spar with a partner to practice the correct technique. Beginners should spar once every two weeks. See the video below for an example of a workout.
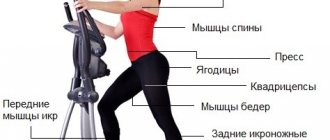
What muscles work in arm wrestling
To the question: “What muscles work for arm wrestling?” – professionals, without thinking twice, answer: “That’s it!” And this is not a joke. During power sparring, most of the muscles are tensed. By not paying proper attention to a certain part of your body, you not only become vulnerable, but also risk serious injury. We must not forget that this is also an extremely traumatic sport. However, there are a number of muscle groups that should be strengthened first if you decide to take up arm wrestling.
Forearms top this list for a reason. Their training will help you gain an iron grip and decide the outcome of the fight in a matter of seconds.
Biceps and triceps are the basis of arm wrestling. However, if you think that more attention needs to be paid to the working hand, then you are very mistaken. During a fight, a colossal load is placed equally on both limbs.
Latissimus, deltoid, pectoral and abdominal muscles . Combining them into one group is not accidental. In this case, all of them play a stabilizing role, distributing the load throughout the body.
Leg muscles . Weightlifters have a paradoxical saying: “If you want strong arms, pump up your legs!” Arm wrestling can also be characterized by this phrase. The fact is that strong legs help develop a good reaction, without which victory in this sport is often impossible to achieve. In addition, trained calves and thighs help you perform a number of basic strength exercises, including back squats and deadlifts.
You can gain a ton of muscle and still lose if you don't train your ligaments. In arm wrestling, it is not the beauty of the body that is important, but real strength, which cannot be gained without strengthening the tendons.
Home workout example
For home exercises, we will need a horizontal bar, kettlebell, dumbbell, expander, or any weight and an old towel.
We perform three sets of pull-ups for the maximum number of repetitions.
We carry out lifting loads with a towel:
- Lifting a weight from the floor onto a 4x10 hook.
- Lifting a weight from the floor to the top 4x10.
- Practicing bending the hand towards yourself 4x10-12.
- Practicing pronation and supination 4x10-12.
Exercises on the horizontal bar:
- Reverse grip pull-ups 3 sets max.
- Hanging on the bar with an angle at the elbow joint of 900 – 3 approaches for each arm.
Hold the kettlebell with your fingers for 3 sets.
Push-ups 3 sets for maximum reps.
Arm wrestling exercises
You don't have to go to the gym to train your physical strength. Here are the simplest exercises for arm wrestling at home.
Push ups
A popular and very effective arm wrestling exercise that helps strengthen the muscle groups of the arms, shoulders, back and abs. And reverse push-ups and dips are the best workouts for triceps. The main rules of classic push-ups are to avoid arching your back and not letting your chest touch the floor. We perform 10-20 repetitions for 3 approaches. Better at a fast pace.
Pull-ups
This is a great addition to the previous exercise. In addition, pull-ups help strengthen the latissimus dorsi muscles. For arm wrestling training, explosive pull-ups . With a sharp movement we raise the body up to chest level, hover in this position for a couple of seconds, then smoothly lower down. At the lowest point, do not straighten your elbows completely, holding there for a couple more seconds. We perform 3-5 repetitions in 3-4 approaches.
Pull-ups on towels
They should be highlighted especially because they also perfectly strengthen the wrist ligaments. Everything is clear with the work equipment. The main thing is to choose stronger towels and the same length. It is also necessary to hold on to them at the same level. We pull ourselves up at a slow pace. This exercise will not be easy to do at first, so don’t try to go over the bar right away. If you master these pull-ups, regular ones will be much easier for you.
Hammer curls with dumbbells
We take dumbbells with a regular grip. We extend our arms along the body, with the inside of our palms facing us. As you exhale, alternately or simultaneously raise the dumbbells to shoulder level by bending your elbows. We hold our hands in this position for 2-3 seconds. Then, while inhaling, slowly lower it back. All movements are performed at a smooth pace, without jerking. We do 3 sets of 15-20 repetitions.
Arm wrestling at home is remarkable for the ease of selecting sports equipment. Therefore, any weights of suitable shape and the same weight are suitable for the role of dumbbells. For example, a pair of heavy hammers. It is better to start with small weights - 5 kg.
Weighted wrist curls
The exercise is performed with a barbell or dumbbells. Beginners are recommended to do it with an empty bar. We sit on a chair or bench, placing our forearms on our thighs. Flexion-extension is performed only in the area of the wrist joint, since it is this area that is trained. We perform 10-15 repetitions in 3 approaches.
exercises with expanders will help you work out your forearms and hands . Classic squats (including with weights), cycling, walking up stairs and other simple exercises will help you train your leg muscles. Alexander Zass , is perfect .
An example of upper training in the gym
- Bench press 4x12.
- Standing biceps curl 4x10.
- Wrist curl with barbell 4x10-12.
- Pull-ups with partial amplitude and a jerk at the top point, 4 sets to the maximum.
- Imitation of wrestling in a hook on a block while standing 4x10-12.
- Performing pronation on a block using a 4x10-12 strap.
- Practicing supination on a block with a 4x10-12 strap.
- Lifting a load with an armlifting handle or holding the load with your fingers for 3 approaches to the maximum.
- Triceps on the upper block 4x12.
Sets and reps
I gave an example of a training scheme for beginners; during training, you can use a different number of repetitions in a set from 15 to 2. Most of the time you need to perform movements in the range of 8-12 repetitions. Select the weight of the weights so that you can do an average of 10 repetitions until failure.
If you do 3 workouts a week, do one of them according to the scheme 15 - 12 - 8 - 6 - 4 repetitions, adding weight in each approach. Exercises should not be done to failure in order to reach the maximum in the last approach. Do this type of training no more than once a week.
If you just want to arm wrestle well, just include a few arm wrestling exercises in your bodybuilding workout once a week.
Common mistakes
It is dangerous to fight on a long or too short table; use only special tables for arm wrestling. Athletes must stand opposite each other on opposite sides of the table; only in this position can they fight.
A common mistake that causes injuries, and even fractures, is turning the head and body away from the fighting hand. It is necessary to look at the fight, and the body should be turned towards the hand.
Keep your body near the table, and press your elbow closer to your body, keeping sharp angles, this will make it easier to fight. The elbow should not be allowed to move too far away from the body; fully straightening the arm can lead to shoulder injury. Try to keep your forearm and shoulder in line.
Ripping your arm off the armrest can cause injury to your elbow; try to keep your elbow in place.
Correct positioning of the legs during a fight is very important; the front leg in front rests on the crossbar, which runs from the bottom in the middle of the table. The hind leg is set back.
Techniques and rules for holding arm wrestling matches
Often, novice athletes do not pay serious attention to the technical side of arm wrestling training at home and, as a result, get injured or even inflict them on their opponent.
Sprains and other joint injuries occur most often in arm wrestling. Fractures may also occur, although this type of injury is much less common. Injuries are most common at the initial stage of training. This is due to the fact that muscle strength increases much faster in comparison with the development of the articular-ligamentous apparatus. If you do not follow the technique, you perform unnatural movements, which causes injury. If you watch professional athletes compete, you probably know that the number of injuries there is very low. Fractures practically never occur.
The reason for this lies precisely in the high technique of movements of all participants in the competition. At the amateur level, unfortunately, the situation is completely different. There are two techniques that you can actively use during a fight. The first of them is called the “hook”. From the start of the fight, you need to tuck your working arm so that the inside of the hand is facing you. It is with this “hook” that you must catch the hand (more precisely, the wrist) of your opponent.
After this, pull your hand to the side and at the same time press it to the table. Many pro athletes believe that this technique is best suited for athletes with short fingers and forearms. This allows you to increase leverage over your opponent's hand. The second technique is to fight through the hand. From the start of the fight, you need to grab the hand higher than your opponent in order to be able to later turn his wrist. As a result, your hand should be positioned higher than the opponent's hand and it will be much easier to press it to the surface of the table. This is a significantly more complex technique in terms of technique compared to the “hook”. First of all, to use it you must have a high reaction speed. We recommend that you try both techniques first and then choose the one that suits you best.
Let's get acquainted with the basic rules, because you want to conduct full-fledged arm wrestling training at home.
- Preparing for the fight.
Opponents must take their starting positions. The shoulder joints are located parallel to the surface of the table, the hands are clasped in a “lock”, and at the same time, the phalanges of the thumbs must necessarily be located on top. Use your free hand to hold the pin. It is the preparatory stage that takes the most time, since the referee must carefully monitor the correct grip of the participants in the fight. - Start of the fight.
When the referee is sure that the grip is correct, he gives the command to be ready to start the fight, and the loan starts it. - The fight itself.
Contractions can be quite prolonged or very short. The winner of the fight is the athlete who presses the outer part of the opponent’s arm to the table. To do this, athletes use jerks and pressure on the opponent's hand.
Based on practical experience, we can give one piece of advice. If you think that you are losing the fight, do not lower your hand with a sudden movement, as this can lead to injury. Loosen your grip gradually and don't worry about defeat. No athlete can always win and you need to continue to do regular arm wrestling training at home. This will give you the opportunity to take revenge in the future.