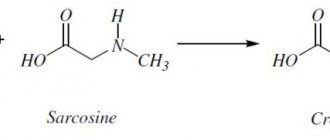
Creatine
Sergey Sidoruk 03/31/2019 no comments
2
How to take creatine while cutting
5 (100%) 1 vote
One of the best and most effective sports supplements is creatine monohydrate. This substance stimulates the growth of muscle mass, increasing endurance and human potential. In addition, it has several other functions that can be useful in burning subcutaneous fat, as a result of which the body acquires the appropriate relief. At the same time, the question remains open about whether it is possible to drink creatine while cutting.
What is creatine?
This is a natural substance that has nothing to do with doping. Creatine is a nitrogen-containing compound (also called non-protein nitrogen) that is involved in energy metabolism.
This substance is found in many foods, but is destroyed by high temperatures during cooking. The human body also produces it through the kidneys and liver. The main suppliers are amino acids: arginine, glycine, methionine. On average, muscle tissue contains 90-140 g of a substance that is consumed every day and is not always restored in the required quantity with food intake. Metabolism of this substance occurs in muscle tissue and nerve fibers. It quickly penetrates the muscles and is absorbed by the body, providing the necessary amount of amino acids required to strengthen skeletal muscles. Girls need creatine as an accelerator of ATP resynthesis and metabolism.
Top 7 rating: which company is better
- Optimum Nutrition - Creatine powder. Creatine produced by Optimum Nutrition is considered one of the best. It constantly ranks top in various ratings and sales. This creatine powder contains no unnecessary additives and consists entirely of creatine monohydrate. Has proven itself well among professional athletes. The price corresponds to the quality;
- Ultimate Nutrition - 100% Micronized Creatine Monohydrate . Creatine from this manufacturer differs from its analogues in its structure. The manufacturer paid attention to the size of the granules and made them micronized. During production, creatine goes through an additional grinding stage. The finished product, which consists of 100% creatine monohydrate, is easily and completely absorbed by the body, especially in combination with juice or other sweet drink;
- Dymatize - Creatine micronized . This creatine also has a micronized structure. There are no shortcomings in the product. This is the perfect combination of price and quality. For little money - high-quality creatine monohydrate without additives;
- MusclePharm – Creatine . This creatine complex has proven itself to be excellent among athletes around the world. The manufacturer offers a patented product, it includes: creatine monohydrate, creatine AAB, malate and two more formulas from MP. The exact recipe is not disclosed and does not make it possible to analyze the theoretical effect on the body. This is a high quality product. Among the disadvantages are the packaging volume of 300 g, and the price is almost twice as high as its analogues;
- Universal Nutrition - Creatine Powder . This is ordinary high quality creatine monohydrate, without additives. Has no disadvantages. The price of the product is acceptable;
- Scitec Nutrition – Attack . This is a creatine complex belonging to the matrix type. It contains a number of additives that complement each other and increase effectiveness. The mixture includes several types of creatine, monohydrate, arginine, ALA, R-ALA, etc. The components contribute to the rapid delivery of creatine to the muscles, which gives endurance when performing strength exercises. The company has released a good product, but it is quite expensive. It is suitable for people who have poor absorption of pure creatine monohydrate;
- BioTech - 100% Creatine Monohydrate . This is the most affordable creatine monohydrate. Some people are concerned about it because of the low price, but in vain. In fact, this is a high quality product without third-party impurities.
Mechanism of action
During a training session, muscle tissue loses up to 2 g of substance, which can cause slow muscle shrinkage. Creatine is a source of energy that helps muscles recover faster and get less tired from exertion.
With large energy expenditures, the body begins to take energy reserves from additional sources: muscles, adipose tissue. Muscle tissue gives in more easily, so it is the one that suffers first when losing weight. With the correct intake of amino acids, this will not happen and the muscles will remain intact, and the process of rapid fat breakdown will begin. During exercise, the body uses creatine as an energy supplier without depleting tissue.
With the correct schedule of exercise and nutrition, the body will spend not only the energy obtained from food, but also the fat layer to restore muscle fiber. In order for excess weight to go away, you need to regularly load your body to burn calories.
The substance has a cumulative effect and requires regular use. It acts in a complex manner, but its main function is to maintain phosphocreatine reserves in muscle tissue. This substance is the main source of strength and helps:
- increasing endurance;
- decrease in myostatin levels.
- increase in anabolic hormones;
- increasing the level of water content in cells;
- reducing the level of protein breakdown;
Creatine also helps: stabilize heart function, improve the condition of blood vessels and the central nervous system, and help preserve joints and tendons during intense training. Without frequent physical activity, non-protein nitrogen has no effect on the body and does not by itself help in weight loss.
When losing weight
Taking creatine increases performance and endurance, promotes muscle growth, which makes it possible to train longer and more intensely. The larger and stronger the muscles, the more energy they will expend, which means that fat tissue will be burned quickly.
The desired effect can be achieved only if you follow the rules on how to take creatine monohydrate
You need to understand that taking creatine without training will not give any results, because burning fat tissue requires spending a lot of energy.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among professional athletes, the non-protein supplement is very popular because it is not a steroid. The content of the right amino acids nourishes the body even during severe cutting and preparation for competitions. In addition, creatine helps:
- reduce blood cholesterol levels;
- increase muscle mass without increasing fat tissue;
- reduce the likelihood of developing coronary disease;
- remove inflammatory processes after minor tissue tears;
- protect the nervous system from lack of oxygen;
- improve the contractile function of the heart muscle;
- for men, increase testosterone levels;
- avoid muscle atrophy;
- increase energy reserves during drying;
- reduce inflammation in arthritis;
The main disadvantage of a creatine supplement is that it retains water in the body. On the one hand, this helps muscle growth and protects the body from overheating during intense exercise, but on the other hand, it makes life more difficult for those who are prone to swelling. When you stop taking it, the fluid goes away quickly, but in some cases it is necessary to take a course of urinary medications.
This situation may affect the functioning of the kidneys, so before starting to use the supplement, it is recommended to consult a doctor and, if necessary, undergo tests.
Regular consumption can lead to calcium being washed out of the bones along with the liquid, which will lead to their fragility.
The saga of CREATINE.CH-4. Safety Issues and Benefits of Creatine
Home ▸ Articles ▸ Sports supplements ▸ Creatine ▸ The saga of CREATINE.CH-4. Safety Issues and Benefits of Creatine
Is creatine safe?
Numerous scientific experiments confirm the safety of creatine supplements, even in large dosages. A British study conducted by the University of Nottingham Medical School found that people consuming 20g of creatine monohydrate daily for five days followed by 5g of creatine daily for six weeks experienced no negative responses. The researchers concluded that "even significant dietary supplementation with creatine monohydrate poses no apparent health risk in youth or adults."
Still, in rare cases, some undesirable effects may occur.
Creatine and the gastrointestinal tract
Gastrointestinal disorders are the most common problem when taking creatine: loss of appetite, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, nausea, flatulence. To eliminate disorders of the digestive system, it is necessary to change the time of taking creatine in relation to food. That is, if you take creatine after meals, try doing it on an empty stomach, and vice versa. If this does not have an effect, reduce the dosage. Try changing the liquid in which you dissolve creatine. Replacing the creatine with a different brand of supplement may also help.
Creatine and dehydration
In addition to digestive problems, relatively common complaints associated with taking creatine are: thirst, mental lability, drowsiness, dizziness. All this can be considered manifestations of dehydration. To prevent these disorders, you need to maintain the correct water regime and drink up to 3 liters of water per day.
Creatine and cramps
Some athletes report the appearance of cramps while taking creatine. Scientists have suggested that this may be related. There are a wide variety of physiological explanations for this phenomenon. One of the most popular is based on the fact that it is associated with an overload of muscle cells with creatine, leading to excessive hydration. If this were true, then the same thing would happen to athletes after carbohydrate loading. Since a large amount of glycogen accumulates in the muscles, according to the law of osmosis, water begins to flow intensively into the muscle.
In theory, such water oversaturation can lead to leaching of calcium and potassium from the muscles (dilution). Normal concentrations of calcium and potassium are necessary for muscle contraction, but in a state of dilution the relative concentrations of these ions decrease, which can lead to impaired muscle contractility. This mechanism sufficiently explains the pathogenesis of muscle spasms, but one problem arises: most cramps occur during and after training, that is, when the muscle tissue is not in a state of water oversaturation. Therefore, this theory should be questioned.
In contrast, a clinical study shows that creatine use is not associated with cramping. This study followed 16 men who took creatine or a placebo. Under certain hydration conditions, local spasm and tension were reported in both groups, but "nothing else that could be associated with creatine use." Two other studies were conducted at Arkansan State University and found that using creatine in 61 athletes during training camps had no effect on the cause of muscle cramps, injury or disease. These athletes used 15-25g/day during the loading phase, and later 5g/day during the plateau phase.
It follows that the key to the problem of cramps is poor physical fitness. This theory is confirmed by the fact that cramps in the athletes studied were mainly observed at the beginning of the season, and by the end they practically disappeared. Acclimatization to hot and humid climates and dehydrating weather conditions are also important. All these factors cause disturbances in the electrolyte balance of the body, and, as a result, seizures occur. The use of creatine leads to greater fluid losses due to increased training intensity, and therefore electrolyte disturbances are more pronounced.
To avoid such a disorder, try to consume more fluid (up to 3 liters per day), and also take microelements in the form of vitamin-mineral complexes.
Creatine and acne
Creatine is not a direct cause of acne. However, there are indirect factors that can provoke their appearance.
First, dehydration is a direct side effect of using creatine. According to the law of osmosis, the fluid of the vascular bed and tissues goes into the muscles following creatine. This can lead to the appearance of acne by reducing the water saturation of the skin. Dehydrated skin loses its ability to utilize toxins and fats, and local resistance also decreases, all of which are factors predisposing to acne.
Secondly, taking creatine with quickly digestible carbohydrates such as juices, glucose, honey and other sugar-containing foods. Simple carbohydrates, in turn, cause the release of insulin into the blood. And insulin causes not only an increase in the size of the sebaceous glands, which leads to their blockage and inflammation. Sugar is a breeding ground for microbes, which also cause inflammation.
Thirdly, as a result of more intense training, there is an increase in the level of anabolic hormones, in particular testosterone, which increase the secretion of the sebaceous glands, and thereby contribute to the formation of acne.
What should I do if acne occurs while taking creatine? You can continue taking it, but take more fluid (more than 2 liters per day), and also avoid mixing creatine and simple carbohydrates. Of course, this will reduce the effectiveness of creatine to some extent, but this reduction is not so significant as to sacrifice aesthetic beauty. In this case, it is best to take creatine after a meal, when insulin and insulin-like factor 1 (IGF-1) levels are high enough to allow creatine to be transported across the intestinal lining.
Creatine and kidneys
Today, scientists are less and less inclined to believe that creatine can cause primary kidney damage, although there are anecdotal reports that have documented kidney damage such as interstitial nephritis. Creatine causes changes in urine concentration ratios; delayed side effects can affect the tubular apparatus of the kidneys, where primary urine is formed, and also accelerate stone formation. Experiments on mice revealed an acceleration in the growth of cysts in polycystic kidney disease (polycystic kidney disease in humans occurs with a frequency of 1 person per 1000 population). Therefore, patients with diagnosed kidney disease are advised to avoid taking creatine supplements.
Creatine and diabetes
In theory, creatine may affect insulin secretion. This is relevant for people with diabetes or suffering from hypoglycemic conditions. When consuming creatine, you should monitor your blood sugar levels, as adjustments to your glucose-lowering medication regimen may be necessary.
Creatine and allergies
Allergic reactions to creatine are occasionally possible: rash, itching, shortness of breath. In this case, it is better to stop using creatine.
Pros of Creatine
Having analyzed in detail the main side effects of creatine, I would like to counterbalance this with a much more impressive list of key positive effects and advantages:
- dietary supplementation with creatine has a positive effect on reducing total cholesterol, triglycerides and very low-density lipoproteins in plasma (cardiovascular protection);
- creatine may have anti-inflammatory effects in acute inflammation, local irritation, and chronic inflammatory conditions (eg, arthritis);
- taking creatine/phosphocreatine has a protective effect on the central nervous system during ischemia and hypoxic conditions (with a lack of oxygen);
- Nutritional supplementation with creatine is used to treat diseases that cause muscle wasting, creatine depletion, and neuromuscular disorders;
- Creatine is being investigated for possible benefits in inhibiting the growth of certain types of tumors in mammals. Some studies suggest that creatine may have some anti-cancer activity;
- supplementing the diet with creatine has a positive effect on the athletic performance of vegetarians;
- in chronic heart failure, the level of creatine in the heart tissue decreases; Supplementing patients with such symptoms with creatine increases the amount of energy-rich phosphocreatine in skeletal muscle and, consequently, strength and endurance. In 50 patients undergoing heart valve replacement surgery, creatine supplementation reduced arrhythmia by 75%. People suffering from chronic heart failure have also used this supplement in doses of 20 grams per day to increase their exercise capacity;
- taking creatine monohydrate powder or capsules at a dose of about 20 g/day leads to an increase in phosphocreatine in the muscles and an increase in explosive strength (speed-strength qualities);
- taking chemically pure creatine increases body weight due to an increase in caliperometric indicators of muscle mass;
- Creatine phosphate is extremely poorly absorbed in the stomach. The introduction of phosphocreatine into the blood helps to improve and restore the contractile function of the heart muscle, but actually has little effect on the growth of muscle mass;
- complexes of creatine monohydrate with proteins or B vitamins do not have any significant advantages compared to preparations of pure creatine monohydrate;
- No adverse side effects have been detected from taking supraphysiological (i.e., more than 2 g/day) doses of creatine monohydrate.
Creatine: gender and age limits
Creatine consumption is associated, as a rule, with the male half of the population in the age range from 18 to 35 years. Scientific studies conducted in groups with this composition clearly confirm both the effectiveness of creatine and its safety. However, the effects of creatine on children, the elderly and women have been studied much less. Theoretically, there is no good reason to believe that the underlying mechanism of action of creatine differs depending on age or gender. However, minor differences may occur and the details and reasons for these will be discussed below.
Creatine and children
Is creatine safe for young people is one of the questions that comes up most often on forums. Many scientists agree that it is better to postpone the use of creatine until after puberty. This is mainly due to the fact that the long-term effects of taking creatine supplements have not yet been well studied. In other words, if long-term side effects of creatine exist, then young athletes using it in their training will be susceptible to these adverse reactions to a greater extent than adults. Moreover, a previously unknown mechanism of the effect of creatine on cellular metabolism and anabolism was recently discovered, and it is not yet known whether the danger of such a mechanism for children can be completely denied.
On the other hand, should children go beyond their natural strength limits at all? Let me remind you that creatine supplements, first of all, increase the strength of muscle contraction during a short period of physical activity. Given this, some experts are concerned that excessive mechanical loads on an incompletely formed skeleton can lead to deformations and displacements of bone elements.
Thus, creatine supplements can be safely used only after puberty. The onset and pace of puberty are determined by the interaction of constitutional factors and environmental influences. The age range of puberty is subject to wide individual fluctuations and (taking into account acceleration processes) fits into the period: for girls - from 8-9 to 16-17 years, for boys - from 10-11 to 19-20 years. In girls, the end of sexual development can be considered the moment at which the regular menstrual cycle begins. In boys, it is not possible to clearly record the moment, so one should focus on secondary sexual characteristics. By the time they are fully formed, you can safely start taking creatine.
Creatine and the elderly
Muscle phosphocreatine levels decline with age, partly explaining the decline in strength and susceptibility to fatigue that is commonly seen in older adults. Creatine supplements can reverse these unwanted age-related changes. This opinion is supported by several modern studies that have demonstrated improvements in health and strength in people over 50 years of age who consumed creatine. It is also important that the effectiveness of creatine supplements increases with age.
Oddly enough, after age 70, the effectiveness of creatine supplements begins to decline sharply. This may be due to a concomitant decrease in endogenous anabolic hormones, a selective reduction in the number of type 2 muscle fibers, which are the main consumers and implementers of the action of creatine.
However, there is no need to worry as this can be easily avoided through regular exercise. An active lifestyle will maintain high levels of anabolic hormones, which will prevent the loss of type 2 muscle fibers.
In addition, it was found that creatine prevents the development of certain mental and neurodegenerative diseases of old age, reduces the risk of coronary heart disease, and improves DNA methylation. Many scientists pay a leading role in aging to the reduction in the activity of DNA methylation.
Still, it must be remembered that creatine in rare cases may slightly increase blood pressure. Hypertension is a pressing problem in older people, so be sure to monitor your blood pressure levels when you start taking creatine supplements.
Creatine and women
Several scientific studies have been devoted to examining the effects of creatine on the female body at different levels of physical fitness. These studies showed that although creatine increases strength in women, the effect is less than in men participating in the same studies. Creatine supplements had a more pronounced effect on them, which is explained by higher testosterone levels.
Thus, creatine can be recommended to women, especially when losing weight. When losing weight, creatine supplements will increase the intensity of your workouts, and, therefore, speed up the process of fat destruction. In addition, creatine will preserve muscle mass as much as possible, which begins to be actively lost during fasting. From this it becomes clear that creatine is useful not only for gaining muscle mass, but also for creating a beautiful female figure.
Who needs creatine?
1. Creatine for athletes
The main benefit of creatine is associated with enhancing short-term athletic performance, such as sprinting, cycling sprints, strength sports and weightlifting. Creatine is suitable for sports that require jumping, acceleration or finishing dashes. During the snatch phase, the intensity of the load is so great that creatine phosphate (phosphocreatine) is also used as an energy source. Supplementing athletes with creatine may also provide benefits when high-intensity exercise is alternated with lower-intensity exercise or rest. Team sports such as basketball, football, hockey, as well as combat sports, tennis, athletics and sprinting are also characterized by short, explosive muscle contractions, followed by short periods of rest or recovery periods.
Creatine appears to help maintain a high level of rapid energy supply to the body. It also prevents the increase in ammonium levels in the blood plasma, which slows down physical activity.
2. Creatine for gaining muscle mass
Creatine supplements can help an athlete train harder for a longer period of time. In turn, the increased intensity of muscle training generates faster muscle growth and strength. For example, in a study conducted among iron sports enthusiasts by Conrad Earnest and his colleagues at the Cooper Southwest Medical Center and Clinic in Dallas, Texas, athletes in just one month increased their lean body mass on average when supplementing with creatine. by 1.6 kilograms.
According to the observations of one Swedish sports physiologist, creatine allows weightlifters to achieve an increase in muscle mass by 2.1 (or more) kg. Practical experiments have shown that increasing the total creatine pool can promote body weight gain. Many athletes who supplement their diet with creatine have noted an increase in water retention within muscle cells, which leads to increased cell volume. Muscle tension - so-called muscle tone - improves and the muscles respond better to physical activity. An athlete weighing 75 kg, involved in strength sports, can “grow” by 2-4 kg. After stopping supplemental creatine intake, weight gain decreases again due to increased water production. But due to better performance during training, some of the actual muscle gain remains. At the same time, in strength sports, there is an improvement in the “spring” properties of the muscles and their ability, as a result, to overcome large weights!
3. Creatine for vegetarians
Since vegetarians do not consume meat, which is the main source of creatine, supplementation is especially recommended for them. And here there is a problem not only of sports achievements, but also of health.
4. Creatine for weight loss
In 1994, Anthony Almada and his colleagues conducted research at Texas Woman's University. The main goal of the research was to demonstrate that weight gain with creatine supplementation occurs solely due to an increase in lean muscle mass and that creatine supplementation leads to an increase in strength. The research results were published in the journal Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. Over the next four years, at least twenty independent university studies were conducted that showed that the use of creatine monohydrate improves training results, speed and strength performance, recovery rate and, as a result, accelerates the loss of fat reserves.
5. Creatine for fitness
You have already read about all the positive qualities of this supplement, and given its almost complete safety, you simply cannot refuse all the benefits that creatine can give a healthy person to have good physical shape, high vitality and intellectual activity.
Creatine withdrawal
Worries are in vain, since discontinuation of creatine does not cause any serious changes in the body. Creatine is not addictive or addictive. Creatine withdrawal does not lead to a significant drop in athletic performance. The only answer that can be given is a slight weight loss, which is due to the fact that the body loses excess water, which is formed when using creatine supplements. For the same reason, there is a slight decrease in muscle volume.
However, even taking into account all the losses, the results are generally superior to those obtained without the use of creatine supplements. Even long-term use of creatine does not cause metabolic changes or disruption of the synthesis of endogenous creatine.
Some scientists believe that, through a feedback mechanism, the formation of intrinsic creatine may be reduced in the near future after withdrawal, but within a short period of time it is restored to its original level. For complete safety and one hundred percent preservation of the function of endogenous creatine synthesis, it is recommended to take weekly breaks after 1-2 months of continuous use of creatine supplements.
Continuation:
The saga of CREATINE. Ch-1. History of discovery, biochemistry and physiology of creatine
The saga of CREATINE.Part 2. New forms: Ethyl Ester, Kre-Alkalyn, Serum, etc. Critical analysis
The saga of CREATINE.CH-3. Creatine with transport system
The saga of CREATINE.CH-5. Optimal dosing regimen
Contraindications
Creatine monohydrate powder is the most researched dietary supplement. Researchers in the field of biochemistry claim that it has no harmful effects on the body. But this does not exclude individual reactions to individual components.
It is not recommended to use if you have:
- allergic reactions;
- hormonal imbalances;
- asthma or difficulty breathing;
- thyroid diseases;
- pregnancy or lactation;
- chronic kidney or liver disease;
Chronic stomach diseases may worsen due to insufficient water intake while taking the supplement. Digestive disorders can lead to indigestion, cramps, intestinal colic, or persistent nausea.
In addition, people with acne often experience an increase in the number of breakouts. Such complications can only occur in the event of a sharp increase in dosage or taking expired products.
Creatine use is contraindicated for minors.
Side effects
The drug itself is safe, but side effects can be caused by the components included in the composition or by an incorrectly calculated dosage that exceeds the recommended standards.
Due to fluid retention in the muscles, swelling and dehydration of other parts of the body may occur. This can interfere with the removal of calcium from the kidneys and lead to the formation of stones. Taking the drug in large doses - up to 10 g at a time - can lead to polycystic kidney disease.
Due to the effect on muscle tissue contractions, cramps are sometimes observed; they occur not only during exercise, but also on fasting days. This side effect is observed in 4% of cases. It has been found that regular use of the drug increases the level of dihydrosterone, a powerful androgenic hormone that helps increase strength. But this hormone can trigger baldness in men prone to this problem. An increase in this hormone will not affect people with thick hair in any way; we are talking only about those who had receding hairline before taking it.
Take before or after meals
After many studies, scientists do not give a specific answer when you can take creatine. But most advise taking the drug before meals, since food delays the passage of creatine through the gastrointestinal tract, this increases the time the drug remains in an acidic environment and leads to its damage, and also prevents rapid and complete absorption.
If the drug is taken after a meal, the conversion of creatine to creatinine is practically blocked, since food entering the stomach buffers the acidic environment. Food also promotes the production of insulin, which serves as an excellent transporter of creatine through the gastrointestinal tract.
Determining the right time to take creatine is difficult. But there is a solution. It is best to consume creatine in combination with carbohydrates and proteins. This is the best option for taking the drug.
Effect of use
The main function of the product is to increase endurance. With longer and more intense workouts, the weight loss process goes faster, and the results last a long time. The drug helps muscles recover faster, taking adipose tissue as the main source of energy.
Proper training involves not only a large number of approaches and a gradual increase in loads, but also the correct technique for performing the exercises. Rapid depletion of energy reserves makes it impossible to perform each subsequent approach correctly, which can lead to injury and not provide any effect from the load.
Increasing endurance does not only apply to one sport; this effect also manifests itself during fitness classes. Muscle growth occurs with any regular exercise.
The monohydrate substance is deposited in the tissue and attracts a large amount of liquid, which helps the fibers become more rounded and prominent. This effect is clearly visible when working on abdominal tone.
There is an opinion that monohydrate helps to gain muscle mass, but this is not true. It helps increase strength loads, which lead to increases. But without proper nutrition containing a large amount of protein, gain cannot occur.
The effect of creatine on osteoarthritis of the knee[edit | edit code]
- Neves M Jr, Gualano B, Roschel H, Fuller R, Benatti FB, Pinto AL, Lima FR, Pereira RM, Lancha AH Jr, Bonfá E. Beneficial effect of creatine supplementation in knee osteoarthritis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011 Aug;43(8):1538-43. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182118592.
| Weight loss | No |
| Study design | Double blind |
| Duration | 1-6 months |
| Number of subjects | 24 |
| Floor | female |
| Age | 45-64 |
| Physical training | overweight |
Notes for this study:
Creatine supplementation reduced knee stiffness (52%), pain (45%), and increased physical function (41%) and lower extremity muscle mass (P = 0.04).
How to take creatine monohydrate?
There are several options for taking the supplement:
Loading phase. Large doses of monohydrate are taken for 5-6 days: 5 g 4 times a day. After the cells are saturated, the dosage is reduced to 3 g once a day. This method helps to quickly achieve the desired result, but there is a risk of side effects. To avoid an overdose, a large consumption of the product is required - training should be intense and with a short time interval.
Non-loading reception phase. In this case, there is no transition from a larger amount to a smaller one; the entire cycle of taking the drug is used once a day, 5 g. This helps reduce the risks of complications from an overdose and does not require large consumption of the product as in the first case. This option is more suitable for girls who want to lose a couple of extra pounds and tighten their muscles during a gentle workout.
Constant use leads to the fact that the body itself ceases to produce creatine in the required amount, so the total duration of use can be a maximum of 2 months with a break before the start of the next cycle of 3-4 weeks.
On days when no training is planned, it is better to drink the product in the morning, because at this time of day it is best absorbed. On a training day, it is recommended to drink it after pumping the muscles.
It is not recommended to abruptly stop taking the drug. A jump in daily dosage can have a bad effect on the removal of water from the body. It is best to gradually reduce the dosage, for example, 1 g per day, then it will be easier for the body to readjust and start taking the substance only from muscle tissue.
What is the difference between creatine powder and creatine capsules?
Sports nutrition manufacturers produce creatine in powder, compressed tablet and capsule form. Each type of finished product has its pros and cons.
The product in capsules or tablets is convenient to take with you to the gym and can be consumed at any time. The powder analogue must be dissolved before use. The finished drink with dissolved creatine cannot be stored for a long time; it must be used within an hour. In addition, before preparation you need to measure the dosage, which creates inconvenience when taking it in the gym.
Creatine in powder form is not completely absorbed. This is due to losses when it enters the stomach, as well as partial loss as a result of incomplete digestion. Creatine in capsules enters the digestive tract without loss thanks to the capsule shell, and is absorbed almost 100%. The effectiveness of powdered creatine is much lower than its capsule counterpart.
The choice of many athletes falls on powdered creatine because of its affordable price. The costs of producing capsules are much higher, so the cost of the finished product is higher.
Since the purity of creatine depends only on the quality of the product, the main differences between creatine powder and creatine capsules are:
- ease of use;
- degree of assimilation;
- price.
Taking creatine while cutting
Cutting is the process of burning fat. Experts have not come to a clear opinion whether it is necessary to drink creatine during drying, because it retains water in the body, which is why body weight sometimes begins to grow. The dangerous point is that moisture may be retained in the muscles, and other organs will not receive sufficient water.
Not all athletes agree with this. Drying depletes the body due to a reduction in calories entering the body, and this can affect strength indicators. The drug helps maintain strength for the required type of load.
As for people who are not involved in professional sports, but simply want to stay in shape or lose weight, creatine is not recommended as a way to quickly lose weight.
The non-loading phase (which is suitable in this case) does not involve sudden jumps in the amount of the drug taken. Consistent use of one dosage will help you increase the volume of work with heavier weights and engage in cardio exercises for longer, which contribute to weight loss.
When drying
Drying is a process during which the fat layer is burned to display the full relief of the muscles. To achieve relief, you need to train hard and spend a lot of energy. And to ensure a long-term training process, taking creatine is perfect.
It must be taken carefully and not overdo it, because creatine causes fluid to accumulate in the muscles, and for a bodybuilder this is an undesirable phenomenon during cutting. However, over time, excess fluid will leave the tissues, but the muscle relief will remain.
What should I take it with?
First, you need to say that the drug comes in the form of tablets or powder. It can be mixed with many liquids, it all depends on taste preferences. Most often, the tablets are taken with non-carbonated water or juice.
As for powder, there are many more options: water, juice, yogurt, milk, kefir, fermented baked milk and coffee. The only thing you cannot mix the drug with is alcohol. Its effect on the liver in conjunction with alcohol can have an unpredictable effect on the body and lead to many disorders.
There is a separate type of taking creatine - taking it together with fat burners. The non-protein nitrogen supplement itself does not interact with other substances. Many athletes take the drug in combination with fat burners, because the former give strength for training, and the latter burn fat 2 times more effectively.
The combination of creatine and protein supplements leads to severe dehydration of the body, so you need to drink a lot of water (up to 3 liters per day).
If we talk about food products with which it is recommended to use the drug, then these are:
- lean fish;
- citrus;
- chicken's meat;
- low fat dairy products;
- porridge;
- green vegetables;
It is forbidden to drink the supplement while taking medications for stomach ulcers and gout.
Cycling
Consists of 3 stages (dosage is calculated for an athlete weighing 100 kg):
- Take 5 g of creatine in the morning after breakfast, 5 g before and the same amount within 3 hours after training. The remaining 10 g (5+5) are consumed together with a gainer - in the evening or in the morning.
- Do not take aminocarboxylic acid for three days.
Over the course of 8 weeks, 3 days of use alternate with 3 days of abstinence. At the end, it is recommended to take a 7-day break from training (non-training period). During the last 3 days of rest, you need to start taking creatine again.
The cycling scheme aims to ensure high absorption of creatine and achieve its increased concentration in myocytes, eliminating possible disruption of transport mechanisms. But many consider the scheme described above to be erroneous.