Photo: pinterest.com Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) is a unique compound that contains cobalt. The component is involved in hematopoiesis, normalizes metabolism, and stimulates the functioning of the nervous system.
Cyanocobalamin is prescribed to prevent anemia, improve the condition of hair, nails and skin. The drug is used for stomatitis, unbalanced (vegetarian) diet, neuralgia, cerebral palsy, radiculitis, hepatitis, pancreatitis.
Cyanocobalamin belongs to the category of biological components containing cobalt. Therefore, when asked what else vitamin B12 is called, doctors answer that its second name is cobalamin. Vitamin B12 is called cyanocobalamin and Castle's extrinsic factor. Other designations:
- Hydroxocobalamin
- Cobamamide
- Methylcobalamin.
Structural formula of Cyanocobalamin.
Photo: yandex.ru The most common name is cyanocobalamin. It is in this form that the compound enters the body.
Many people don’t know whether pyridoxine is vitamin B6 or B12? Pyridoxine is actually a type of adermin (B6). The substance stimulates metabolic processes, improves protein absorption, blood cell synthesis and distributes glucose throughout the cells.
The component is highly soluble in water. It is an odorless, crystalline powder with a dark red color. B12 is a unique element containing cobalt atoms. And the chemical interaction of carbon and metal is the only compound that is not repeated in living nature. Cyanocobalamin is produced by archaea and bacteria. The production of cyanocobalamin by chemical method is a very complex process. A small amount, insufficient to meet the daily requirement, is synthesized by the intestinal microflora. The element accumulates in the liver.
Why does the body need vitamin B12?
The main functions of vitamin B12 are stimulation of metabolic processes in cells, hematopoietic effect. The substance is involved in a number of biological processes:
- formation of nucleic acids, choline, creatine, methionine;
- activation of growth and development of the child’s body;
- stimulation of protein, lipid, carbohydrate metabolism;
- improvement of processes of saving and energy consumption;
- vascular protection;
- formation of red blood cells, hemoglobin;
- restoration of liver function.
Why else does the body need vitamin B12? Neurologists know. Doctors say that cyanocobalamin neutralizes the effects of harmful chemical compounds that affect the nervous system and increase the risk of heart or vascular disease.
Interesting fact! William Parry Mary and George Mike received the Nobel Prize in 1934. Scientists received a prestigious award for the discovery of the therapeutic effect of cyanocobalamin.
Why does the body need vitamin B12? Photo: heaclub.ru
Diseases for which vitamin B12 is used
- anemia (iron deficiency, posthemorrhagic, malignant);
- cerebral palsy;
- liver dysfunction (hepatitis, Botkin's disease, cirrhosis);
- normocytic anemia in children;
- radiculitis;
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- alcoholic delirium;
- migraine;
- Down syndrome;
- psoriasis.
Cyanocobalamin-based drugs are used for anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency or poisoning. Other indications are causalgic syndrome, sun allergy, atopic dermatitis, radiation sickness, chronic gastritis or pancreatitis.
Functions performed in the body
B12 plays the following roles in the body:
- Participates in hematopoiesis.
- Participates in the process of transmethylation.
- Transports hydrogen atoms.
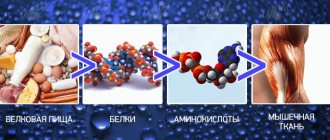
- Promotes the formation of the essential amino acid methionine (regulates protein metabolism).
- Participates in the formation of creatine, choline (a derivative of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine) and nucleic acids.
- Improves the functioning of the nervous system and liver. B12 helps conduct electrical impulses by building the myelin sheath of nerves.
- Has a mild analgesic effect.
- Activates folic acid.
- Affects the functioning of the blood coagulation system (activates prothrombin and thromboplastin). This is important for bleeding.
- Promotes healing of damaged skin and mucous membranes. This is achieved by stimulating cell division.
- Participates in lipid metabolism.
Benefits of Vitamin B12
Few people know why the female body needs vitamin B12. But the role of cyanocobalamin is very important. When a woman receives the daily dose of the substance, she becomes dizzy, weak, and her hair condition improves. Vitamin B12 is good for hair - it gives it shine, volume, prevents fragility and thinning.
Cyanocobalamin relieves muscle weakness, shortness of breath, improves vision, and facilitates menopause. The substance is used to eliminate pallor and bruises on the skin, improve memory and mood. For men, vitamin B12 deficiency is dangerous for the development of heart disease and muscle weakness. The substance improves sleep, calms the nervous system, and helps to quickly adapt to a new daily routine.
Vitamin B12 in the human body. Photo: semanticscholar.org
Implications for athletes
The role of cobalamin for athletes cannot be overestimated, because with its deficiency:
- The level of hemoglobin drops, therefore, the supply of oxygen to the muscles deteriorates;
- the functions of the nervous system are disrupted, and therefore neuromuscular transmission;
- the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and the synthesis of necessary enzymes and vitamins are disrupted.
All these violations are incompatible with the concept of health, and even more so with intense physical activity. It is necessary to monitor your diet and well-being, and at the first signs of cobalamin deficiency, check its level in the blood. Vegetarians and other categories of people at risk should be especially careful in this regard. They need to monitor their vitamin B12 levels regularly.
Release forms
Often the element cyanocobalamin is produced in the form of a solution. It is believed that in this form it is better absorbed. Vitamin B12 ampoules contain 200 mcg or 500 mcg of the base component. One bottle contains 1 ml of product. Vitamin B12 injections are given intravenously, subcutaneously intramuscularly. Vitamin B12 tablets - name of the drugs:
- Century;
- Doctor's Best;
- Sundown Naturals;
- Country Life;
- MRM;
- Now Foods, Methyl;
- Solgar;
- Superior Source;
- Vegan B12 - Deva;
- Methylcobalamin - Natural Factors.
Vitamin B12 tablets are also produced by domestic companies. Recommended - Vitaxon, Neovitam, Neurobex, Milgamma, Neurobion. In addition to tablets and solution, cyanocobalamin is available in the form of chewable tablets, sprays, and rectal suppositories. Other forms are lollipops, fortified liquid in bottles.
Contraindications and side effects
Contraindications to the use of cyanocobalamin in the form of a solution are:
- intolerance;
- thromboembolism;
- erythremia (excessive production of red blood cells by the bone marrow);
- erythrocytosis.
Negative effect: pain in the heart area.
The following undesirable effects are possible when using cyanocobalamin:
- tachycardia;
- excitation;
- pain in the heart area;
- urticaria (rare).
When using combined vitamin preparations, allergies in the form of rash and itching, sweating, dyspepsia (indigestion) and nausea are possible.
Vitamin B12 deficiency
If an adult receives less than 3 mcg of cyanocobalamin per day, then we can talk about a lack of vitamin B12. It is noteworthy that deficiency often occurs due to the body’s inability to fully absorb it.
Vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms, the causes and treatment of which must be determined by a doctor, are caused by helminthiasis and the presence of foreign microbes in the ileum, where cyanocobalamin should be absorbed. It is poorly absorbed due to a lack of calcium, dysfunction of the stomach or pancreas, and an excess of ascorbic acid.
Causes of vitamin B12 deficiency. Photo: ortocure.ru
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- poor appetite;
- nervousness;
- personality degradation;
- stool disorder;
- pallor and yellowing of the skin;
- backache;
- depression;
- redness of the tongue;
- muscle numbness;
- malaise;
- photosensitivity.
Lack of vitamin B12 - other symptoms in adults - ulcers on the corners of the mouth, increased fatigue, difficulty walking. Other signs include itching, burning, redness of the eyes or tachycardia, shortness of breath that occurs with minimal physical activity. Cyanocobalamin is found in animal products. Accordingly, deficiency of the substance is more often diagnosed in vegetarians.
A lack of vitamin B12 contributes to the development of pernicious anemia, the breakdown of amino acids, and intoxication. Deficiency provokes brain damage, causes schizophrenia, anemia, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Lack of the substance leads to damage to mitochondria, which increases the likelihood of infection with deadly bacteria - fecal enterococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Problems and interactions with vitamin B12
The absorption of vitamin B12 may be difficult if a person was or is an alcoholic or a smoker. In addition to alcohol and nicotine, long-term use of antibiotics can also reduce the GI tract's ability to absorb and use vitamin B12. People taking medications that reduce stomach acid production should talk to their doctor about taking vitamin B12 supplements.
Potassium supplements can also reduce the absorption of vitamin B12, so if you take large amounts of potassium in supplement form, you should monitor for possible vitamin B12 deficiency. Dietary potassium should not cause a problem, but very high amounts can cause vitamin B12 deficiency.
Tags: Vitamin B12
- Related Posts
- What is calcium pyruvate? Everything you need to know
- Can Thermogenic Fat Burners Help You Burn Fat?
- Melatonin: benefits and harms, use, dosage
« Previous entry
Excess vitamin B12
When using large doses of cyanocobalamin, its toxicity was not detected. But in the presence of individual intolerance, excess vitamin B12 promotes mutation of DNA cells and increases the risk of developing heart failure and pulmonary edema. Other consequences include a predisposition to blood clots and prostate or lung cancer in men. Other signs of hypervitaminosis are urticaria, anaphylaxis.
Vitamin B12 in the body. Photo: yandex.ru
Vitamin B12: Benefits, Disadvantages and Food Sources
Cobalamin
Vitamin B12 helps the normal functioning of the nervous system: it helps maintain healthy nerve cells (including those needed to transmit neurotransmitter signals) and helps form the protective covering of nerves called the myelin sheath. This means that when vitamin B12 levels are low, almost every cognitive function can suffer.
Vitamin B12 (sometimes also called hydroxocobalamin, cobalamin, cyanocobalamin, or methylcobalamin) also helps with digestion and heart health, so a deficiency can lead to both digestive problems and an increased risk of heart disease. It can be obtained from food sources, by injection, or by intramuscular injection of vitamin B12 hydroxycobalimine.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) estimates that somewhere between 1.5 and 15 percent of people in developed countries are deficient in vitamin B12 (). Other studies, such as one conducted by the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition in 2000, suggest that this number may be even higher—up to 39% of the population may be deficient in vitamin B12 ().
Animal products are the best food sources of vitamin B12, including natural dairy products, eggs, organic meat, wild fish, organic poultry and organ meats. According to the NIH, plant foods do not naturally contain vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 can be found to a certain extent in fortified plant foods such as nutritional yeast, fortified cereal products and seaweed. However, artificially added vitamin B12 to plant foods does not appear to be as well absorbed as the vitamin found in natural animal sources.
How to take vitamin B12
You cannot use cyanocobalamin on your own without a doctor’s prescription. The indication for the use of any of the dosage forms is a deficiency of vitamin B12. The established daily dosage of the substance for an adult is 3 mcg. To confirm cyanocobalamin deficiency, you need to take a blood test for vitamin B12. If the results of the study show the presence of vitamin deficiency, you need to visit a doctor to prescribe vitamin therapy.
It is important to know! Just one milligram of a cobalt-containing substance lasts a person for two years. Moreover, the liver has reserves that will be enough for 3-5 years. Vegetarians, pregnant or lactating women, and children often suffer from a lack of cyanocobalamin.
When prescribing a drug containing cyanocobalamin, the doctor is guided by the norm that should enter the body per day.
Daily value of vitamin B12
Daily requirement of Vitamin B12 for children, based on age:
- up to six months - 0.4 mcg
- from 6 months to 1 year - 0.5 mcg
- 1-3 years - 0.9 mcg
- 4-8 years - 1.2 mcg
- 9-13 years - 1.8 mcg
- Over 14 years old - 2.4 mcg
Pregnant women need to receive 2.6 mcg of cyanocobalamin per day. The norm for nursing mothers is 2.8 mcg. The instructions for the solution containing cyanocobalamin indicate that the drug can be administered to pregnant women according to indications. For such patients with vitamin deficiency, the doctor may also suggest taking dietary supplements or fortified complexes. But there is a high risk of developing an allergy to the components of the product. Therefore, it is better to get your daily requirement from animal products.
For vitamin deficiency in children accompanied by nutritional anemia, the solution is administered subcutaneously in an amount of 30 kg. The course of therapy is 15 days. For dystrophy, Down syndrome, and cerebral palsy in a child, the solution is administered subcutaneously. Dose - 15-30 mg. The drug is used every other day. The amount of solution for an adult varies depending on the type of vitamin deficiency. Dose - 30 to 500 mcg per day. The drug is administered daily or every other day. The course of treatment lasts from 15 to 40 days.
How to take vitamin B12 in tablets for adults is written in the instructions for the drug containing the component. The dosage of tablets for adults depends on the manufacturer and the amount of the product. Often, 1-4 tablets per day are enough to fill the deficiency. For vitamin deficiency in children, the dosage is no more than 1-2 tablets per day.
Contraindications
The use of B12 in dosage form is prohibited in case of severe hypersensitivity. The use of drugs is unacceptable for erythrocytosis and tense angina.
In regions where there are unsanitary conditions, even vegetarians do not experience a shortage of cyanocobalamin. This is due to the lack of processing of fruits and vegetables before consumption. Such food contains beneficial bacteria containing cyanocobalamin. Also, cyanocobalamin is not used in the presence of neoplasms, excluding megaloblastic anemia, vitamin deficiency. Other contraindications are erythremia, thromboembolism.
What foods contain vitamin B12. Photo: zen.yandex.ru
Risk factors for developing vitamin B12 deficiency
Who is most at risk for vitamin B12 deficiency? Elderly people with digestive disorders are one of the most vulnerable groups of the population. This is because older people's bodies tend to produce less stomach acid, which is necessary for the proper conversion of vitamin B12.
Since animal products are generally the best sources of vitamin B12, those who follow a vegan diet and do not consume any animal products are also likely to be deficient in this vitamin. Thus, both older adults and vegans and vegetarians are advised to take a daily vitamin B12 supplement ().
Other populations at higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency include smokers (as nicotine can block absorption), alcoholics, people with anemia, and people with digestive diseases such as celiac disease or Crohn's disease.
What foods contain vitamin B12
The best way to eliminate hypovitaminosis is to eat natural products that contain cyanocobalamin. Nutritionists and doctors know which foods contain vitamin B12.
The optimal amount of the element is found in beef liver (60 mcg/100 g). In second place is pork liver (26 mcg/100 g). Third place goes to octopus (20 mcg/100 g). What other foods contain vitamin B12? The element is present in seafood:
- mussels;
- cod;
- perch;
- chum salmon;
- shrimps;
- mackerel;
- herring;
- carp.
Table 1 - Vitamin B12 in foods. Photo: nic-eda.ru
Cyanocobalamin tolerates heat treatment well. Therefore, the substance remains in products even after cooking. Where else is vitamin B12 found? Cyanocobalamin is also present in beef kidneys, lamb, sour cream, turkey, eggs, broiler chickens, and cottage cheese. Other products containing the valuable element are pork, Swiss cheese, chicken heart, yogurt, cheddar, milk.
Shellfish
The edible shellfish is rich in nutrients. This shellfish is a good source of protein and contains very high concentrations of vitamin B12. You can get more than 3,130% of the RDA for vitamin B12 from just 20 small clams (190 grams) ().
Shellfish also provide the human body with a large amount of iron. 20 small clams contain almost 300% of the RDA for vitamin B12 ().
Shellfish have also been found to be a good source of antioxidants (). Interestingly, clam broth also contains a lot of vitamin B12. It was found that canned broth provides the body with 2.7-14.1 mcg of vitamin B12 for every 100 g ().
Conclusion:
A 100g serving of shellfish contains up to 99 mcg of vitamin B12, which is 1600% of the RDA.
Vitamin B12 Reviews
B12 normalizes many processes occurring in the body. Cyanocobalamin is especially useful for the nervous and hematopoietic systems. To prevent hypervitaminosis, it is better to know what cyanocobalamin contains and introduce these products into the daily menu. Vegetarians and those with nutritional deficiencies are advised to take a multivitamin that contains B12. But it is important to coordinate the use of a solution or medication with your doctor. The advantage of fortified products is an affordable price, few side symptoms, and contraindications.
Salmon
Salmon is well known for having one of the highest concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids. However, this product is also an excellent source of B vitamins.
Half a fillet (178 grams) of cooked salmon can contain more than 80% of the RDA for vitamin B12. The same serving size also provides an incredible 4,023 mg of omega-3 fatty acids ().
Along with being high in fat, salmon also contains high amounts of protein, around 40 grams in a half fillet (178 grams).
Conclusion:
Half a fillet (178 grams) of cooked salmon contains more than 80% of the RDA for vitamin B12.
Causes and symptoms of deficiency
The body excretes cyanocobalamin in bile. Its destruction takes a long time.
A lack of vitamin B12 occurs with a long-term refusal of foods containing it - meat, liver, fish, milk, eggs. The preservative E200 can also cause the destruction of cyanocobalamin.
The reason for the deficiency is a violation of its absorption in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - atrophic gastritis, enterocolitis, helminthic infestations.
Regular deficiency for 5-6 years is the cause of the development of B12 deficiency anemia. The pathological condition disrupts the formation of deoxyribonucleic acid, the metabolism of fatty acids, reduces the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin, and affects the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system. This type of anemia causes diseases of the liver, kidneys, and blood.
Other causes of B12 deficiency anemia are taking medications for seizures, birth control, and excessive consumption of foods containing yeast.
Diseases of the stomach, biliary tract, and intestines cause secondary vitamin deficiency due to a decrease in the production of cyanocobalamin by intestinal microflora.
Even with a sufficient intake of foods containing vitamin B12, it is poorly absorbed if the body does not produce enough intrinsic factor (Castle factor) - an enzyme that interacts with the inactive form of cyanocobalamin from food and converts it into the active (digestible) form.
In old age, Castle factor is practically not produced due to reduced synthesis of acids in the body. In this case, the doctor prescribes injections instead of cyanocobalamin tablets. Including acidic plant foods - berries, fruits, vegetables - in the diet helps maintain the required level of acid production in the body.
Some vitamins are antagonists. Therefore, you cannot mix vitamins B12 and B1, B2, B6, and ascorbic acid in one syringe - they are destroyed by the cobalt ion, which contains the cyanocobalamin molecule.
The following signs indicate vitamin B12 deficiency:
- increased fatigue, drowsiness, depression;
- headache, dizziness;
- irritability;
- lack of appetite;
- numbness of the limbs;
- weakening and hair loss;
- grayish or yellowish complexion.