For the beauty of skin and hair, the coordinated functioning of the whole body, and the normalization of hormonal levels, a person needs to receive many useful nutrients. One of them is pantothenic acid - a B vitamin. This substance is actively used in various branches of medicine: dermatology, cosmetology, gastroenterology, and even in surgery. In this article you will learn about the physicochemical properties and biological role of acid, signs of deficiency and excess of the substance, and receive information about various ways to use pantothenate for beauty and health.
— 46%
Jarrow Formulas, Pantothenic Acid B5, 500 mg, 100 Veggie Caps
873 ₽ from 471 ₽
More details
general information
The first mention of the substance dates back to 1933, when American biochemist John Williams isolated a previously unknown nutrient from yeast. The active compound was named vitamin B5. Research into the molecule continued, and in 1940, chemists from the German company Merck isolated the substance in its pure form and studied in detail the structure and chemistry of the bonds. Later, vitamins B5 began to be called pantothenic acid. The name comes from a Greek word that means “omnipresent,” as the compound has been found in many animal and plant foods.
Vitamin B5 continued to be studied in 1953, when scientists discovered coenzyme A, an essential component of almost all biochemical reactions in cells. This coenzyme is synthesized with the participation of pantothenate and the amino acid cysteine. After this discovery, doctors became interested in the properties of vitamin B5 and began to actively use it for medical purposes.
Natural springs
If there is a lack of pantothenic acid in the body, it is enough to diversify your daily diet with food ingredients such as soybeans, brewer's yeast, green peas, apples, buckwheat, rice bran, white wheat bread, peanuts, champignons, cocoa powder, barley, flax seeds , cauliflower, asparagus, avocado, dates, dried apricots, broccoli, rye bread, garlic, pumpkin, potatoes, onions and tomatoes.
Particular attention to the listed ingredients should be paid to people who are professionally involved in sports, as well as those people who are prone to individual episodes of developing colds.
You can buy vitamins in Odintsovo at any time. It is important to remember that a diet rich in carbohydrates impairs the absorption of pantothenic acid. Canning and heat treatment of products containing vitamin B5 leads to a loss of the volume of this element in an amount of 50% or more of the original amount. During the freezing process, the amount of vitamin B5 in food ingredients is reduced by 34%.
Chemical properties
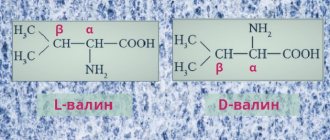
According to the chemical formula, the nutrient is derived from the amino acid beta-alanine and pantoic acid.
In its pure form, pantothenic acid has a light yellow color. The melting point of the molecule is about 80°C. Unlike other amides, the compound quickly reacts with cold acetic acid, ethyl alcohol, and water. Vitamin B5 is almost insoluble in organic solvents and ethers. When water is added to pantothenate, sodium and calcium salts are formed. In alkaline and acidic environments the formula is unstable; at a neutral pH value the substance is relatively stable. A derivative of pantothenic acid called pantethine is a highly active disulfide substance that is formed during the reaction with cysteamine. When the carboxyl group in the vitamin molecule is replaced by an alcohol group, panthenol is synthesized, which also has beneficial properties and is used in medicine.
Precautions and contraindications
There are no restrictions on taking vitamin B5 supplements as such. They are well tolerated by the body.
Sofia Sokolova
Pharmacist. Author of articles on the site
Ask a Question
Possible contraindications include hypervitaminosis and hemophilia. It has been noted that pantothenic acid can increase the period of blood clotting. Such changes pose a serious danger in this disease.
During pregnancy and lactation, taking supplements is not prohibited. However, you should still consult a doctor before using them.
Biological role
Most of the beneficial effects of pantothenic acid are realized through the formation of coenzyme A. This compound is necessary for all reactions of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism. It changes the biochemistry and speed of metabolic processes, activates other enzymes of the human body.
Vitamin B5 has the following beneficial properties:
- Anti-inflammatory activity. Vitamin B5 affects the activity of the adrenal cortex, enhances the production of the most important hormones - glucocorticoids. Adrenal hormones have powerful anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects.
- Prevention of arthritis, heart disease, gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Maintaining the functioning of the nervous system. Pantothenic acid stimulates the conversion of the vitamin-like substance choline into acetylcholine, which is the main neurotransmitter. A sufficient daily intake of pantethine helps prevent senile dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
- Immune activation. Vitamin B5 affects the key cells of the immune system - lymphocytes, enhances the production of antibodies and provides effective protection against various bacteria.
- Normalization of lipid profile. The nutrient regulates the rate of formation and breakdown of fatty acids, reduces the deposits of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels. Due to this, blood flow in the arteries improves and the load on the heart decreases.
- Regenerative properties. Vitamin B5 promotes rapid healing of wounds and other skin damage without scarring. The compound also accelerates the recovery of erosions of the mucous membranes.
Metabolic pathways
When pantothenic acid B5 is taken orally into the human body, it is absorbed through the small intestine. In the blood, most of the substance is in a free state, and small amounts are bound to erythrocyte proteins. It is excreted from the body in the form of hydrolyzed pantothenate products along with urine (about 2.5 mg per day). The compound can be synthesized in the large intestine with the participation of Escherichia coli bacteria, but such pantothenic acid, unlike exogenous one, is practically not absorbed into the bloodstream, so it has no medical significance.
All about vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid, calcium pantothenate)
Calcium salt of D-(+)-pantothenic acid – calcium pantothenate
Description
Pantothenic acid gets its name from the Greek "pantothene", meaning "everywhere", due to its extremely wide distribution. Pantothenic acid, entering the body, is converted into pantethine, which is part of coenzyme A, which plays an important role in the processes of oxidation and acetylation. Coenzyme A is one of the few substances in the body that is involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Vitamin B5 is necessary for the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, amino acids, the synthesis of vital fatty acids, cholesterol, histamine, acetylcholine, and hemoglobin. Pantothenic acid is sensitive to heat; almost 50% of the vitamin is lost during heat treatment.
Sources
| vegetable | animals | synthesis in the body |
| Peas, yeast, hazelnuts, green leafy vegetables, buckwheat and oatmeal, cauliflower. | Liver, kidneys, heart, chicken, egg yolk, milk, fish roe. | Produced in significant quantities by E. coli. |
Pantothenic acid [D(+)a, g-dioxy-b, b-dimethylbutyryl-b-alanine] is widely distributed in nature.
The content of vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) in Argo dietary supplements: Beauty Natural, Longevity, Bogatyrskoe salad oil, Poly Vitabeas (vitamins), Multi-Complex, Nettle extract, Cocktail “Grace”, “Energy”, Nutricons
Action
The most important property of vitamin B5 is its ability to stimulate the production of adrenal hormones - glucocorticoids, which makes it a powerful tool for treating diseases such as arthritis, colitis, allergies and heart disease. It plays an important role in the formation of antibodies, promotes the absorption of other vitamins, and also takes part in the synthesis of neurotransmitters. Pantothenic acid is involved in fatty acid metabolism. It normalizes lipid metabolism and activates redox processes in the body. Pantothenic acid has a significant hypolipidemic effect, apparently due to inhibition of the biosynthesis of the main classes of lipids that form low and very low density lipoproteins in the liver.
Daily requirement
Recommended daily intake of vitamin B5 by age in the United States (mg)
| Infants | Children | Men | Women | ||||||||||||||
| Age | 0-1/2 | 1/2-1 | 1-3 | 4-6 | 7-10 | 11-14 | 15-18 | 19-24 | 25-50 | > 51 | 11-14 | 15-18 | 19-24 | 25-50 | > 51 | pregnant women | nursing |
| USA | 2 | 3 | 3-4 | 3-4 | 4-5 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 | 4-7 |
The need for vitamin B5 increases with heavy physical activity, as well as in breastfeeding women.
Symptoms of hypovitaminosis
Vitamin deficiency can be caused by low levels of protein, fat, vitamin C, B vitamins in food, diseases of the small intestine with malabsorption syndrome, as well as long-term use of many antibiotics and sulfonamides. Symptoms of hypovitaminosis:
- fatigue
- depression
- sleep disorder
- increased fatigue
- headache
- nausea
- muscle pain
- burning, tingling, numbness of toes
- burning, excruciating pain in the lower extremities, mainly at night
- redness of the skin of the feet
- dyspeptic disorders
- duodenal ulcers
With pantothenic deficiency, the body's resistance to infection decreases, and acute respiratory diseases often occur.
Indications
Calcium pantothenate is used as a medicine. Indications for use are:
- various pathological conditions associated with metabolic disorders
- polyneuritis, neuralgia, paresthesia
- eczema
- bronchitis (acute and chronic), bronchial asthma
- allergic reactions (dermatitis, hay fever, etc.)
- trophic ulcers, burns
- toxicosis of pregnant women
- hyperthyroidism
- tuberculosis
- circulatory failure
- chronic liver diseases
- chronic pancreatitis
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of non-infectious nature (gastroduodenitis, etc.)
- hypomotor intestinal dyskinesia
In surgery, calcium pantothenate is used to eliminate intestinal atony after operations on the gastrointestinal tract. Calcium pantothenate is used in the complex therapy of withdrawal syndrome in patients with alcoholism. Vitamin B5 has shown its effectiveness in large doses (up to 10 g per day) in the treatment of acne (acne).
Dosages
Calcium pantothenate is used orally, intramuscularly or intravenously. Orally, adults are prescribed 0.1-0.2 g 2-4 times a day; children from 1 to 3 years old - 0.005-0.1 g, from 3 to 14 years old - 0.1-0.2 g 2 times a day. The daily dose for adults is 0.4-0.8 g, for children - 0.1-0.4 g. In dermatology, vitamin B5 is used in large doses: in adults 1.5 g per day, in children 0. 1-0.3 g 2-3 times a day.
Safety
Calcium pantothenate is well tolerated. When taken orally, dyspeptic symptoms are possible; with intramuscular injections - pain.
Interaction
Calcium pantothenate increases the effectiveness of cardiac glycosides. Reduces the toxic effect of streptomycin and other anti-tuberculosis drugs. Vitamin B5 is necessary for the normal absorption and metabolism of folic acid.
Daily requirement of vitamin B5
Since the active substance has many beneficial effects on the human body, it is very important to ensure sufficient intake. Daily Values for a nutrient may vary slightly among countries.
In Russia, the following nutrient dosages are generally accepted for people of different ages (table):
| Age | Amount of B5, mg |
| Children under 1 year | 1-1,5 |
| Children 1-3 years old | 2,5 |
| Children 3-11 years old | 3 |
| Children 11-14 years old | 3,5 |
| Girls 14-18 years old | 4 |
| Boys 14-18 years old | 5 |
| Adults | 5 |
The need for acid increases in women during pregnancy and breastfeeding, since part of the nutrient is spent on the needs of the fetus. During pregnancy, doctors advise taking 6 mg of the vitamin per day, and during lactation – 7 mg.
To accurately determine the content of pantothenic acid in the blood, a highly specific chromatographic analysis is performed. To obtain a reliable result, you should not eat, drink, or smoke 2 hours before the test.
Normal values are in the range of 0.2-1.8 μg/ml. The analysis allows us to detect even subclinical hypovitaminosis B5, which is accompanied by scant and nonspecific symptoms.
Indications for the use of vitamin B5 in ampoules
Additional intake of pantothenic acid is indicated:
- Pregnant and lactating women;
- People over 55 years of age;
- People who abuse alcohol;
- With increased physical activity;
- For those who have been under stress for a long time;
- People suffering from debilitating chronic diseases such as regional enteritis, celiac disease, sprue.
In addition, taking vitamin B5 in ampoules has been shown to be beneficial for people consuming vitamin-deficient or low-calorie foods and those with increased nutritional needs.
Vitamin B5 in food
The substance is found in many foods, especially milk and dairy products, meat, and meat by-products.
Table: “Content of pantothenic acid per 100 g of products”
| The product's name | Amount of vitamin, mg |
| Sunflower seeds | 6,5-7 |
| Liver (beef) | 6-6,5 |
| Egg yolk | 3-6 |
| Milk | 3,2-3,5 |
| Buckwheat | 2,5 |
| Tomatoes | 2 |
| Soybeans | 1,8 |
| red fish | 1,5-1,6 |
| Beef | 1-1,5 |
| Beans, lentils | 0,9 |
| Cauliflower | 0,9 |
| Mackerel | 0,8 |
| Chicken meat | 0,7 |
Please note that pantothenic acid is a thermolabile compound - it is destroyed when exposed to high temperatures. Therefore, during heat treatment of products, up to 50% of the active substance is lost. Vitamin B5 is partially destroyed when acids (vinegar) are added to food, canned, or frozen.
Food Sources of Vitamin B5
Food sources of calcium pantothenate (mg/100 g):
- Soybean – 6.8;
- Pork kidneys – 3;
- Beef liver – 6.8;
- Pork liver – 5.8;
- Beef kidneys – 3.8;
- Chicken eggs – 1.3;
- Beans – 1.2;
- Split peas – 2.3;
- Sardine, chum salmon – 1.
Calcium pantothenate is also found in chicken meat, whole grains, bananas, oranges, brewer's yeast, grain sprouts, bran, broccoli, milk, lentils, avocados, and lobster.
Hypovitaminosis B5
Due to the supply of pantothenic acid and other B vitamins with many foods, deficiency of the substance occurs quite rarely. Acid hypovitaminosis can develop with dysbacteriosis, malabsorption syndrome, and helminthic infestations. Symptoms of vitamin deficiency are also observed in vegans or people who follow a strict diet to lose weight.
The main manifestations of hypovitaminosis B5:
- circadian rhythm disorders, insomnia, depression;
- decreased ability to work;
- feeling of “crawling goosebumps” throughout the body;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- hair loss and fragility;
- dryness and flaking of the skin, the appearance of rashes or acne;
- loss of appetite, nausea;
- attacks of severe pain in the legs, which are more often observed at night;
- interruptions in heart function.
With a long-term deficiency of vitamin B5, vision problems, gastritis or peptic ulcers develop. Women may experience menstrual irregularities, and adolescents may experience slower growth and physical development.
Symptoms of hypovitaminosis respond well to treatment by prescribing large dosages of pantothenate, 2-3 times higher than the standard daily intake. In severe cases, doctors use up to 30 mg of the substance per day.
Symptoms of B5 Deficiency
Since this vitamin is found in almost all foods, deficiency is extremely rare. Most people become deficient due to malnutrition and not getting enough daily calories.
However, B5 deficiency can occur in combination with a deficiency of other vitamins. The following symptoms are typical for this condition:
- prostration;
- depression, nervousness, sleep disorders;
- stomach pain, vomiting;
- muscle spasms;
- hormonal imbalances, severe toxicosis (during pregnancy).
Deficiency will also affect your appearance. Your skin will become less elastic and irritation may appear. Your hair will be dull and lifeless, and the color will not be as intense.
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC:
- Are you sure you are not deficient in B vitamins? Want to know what they contain?
- What is biotin (vitamin H), what products contain it and instructions for its use
- What is vitamin B3 (niacin) needed for and what foods contain...
The group of people who are at risk of developing B5 deficiency is large. Here are women taking contraceptives, people with severe malnutrition and frequent alcohol consumption. There are also people with impaired absorption of vitamins and minerals due to certain medications or intestinal disorders.
Excess pantothenic acid
Hypervitaminosis is an extremely rare occurrence, since pantothenate belongs to water-soluble vitamins, the excess of which is excreted in the urine. Excess acid may occur in people with chronic kidney disease, or with long-term use of B5 supplements in maximum doses. The main manifestations of hypervitaminosis are dyspeptic symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting), lack of appetite. This condition does not require specific treatment - after stopping medications with vitamin B5, all symptoms disappear on their own.
Interaction of pantothenic acid with drugs and other vitamins
Vitamin B5 is better absorbed in the presence of vitamin B1. Pantothenic acid preparations improve the effect of cardiac glycosides, increase the absorption of folic acid, vitamins B4 and B9.
Additional intake of vitamin B5 reduces the toxicity of streptomycin, drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis. The combined administration of vitamin B5 with choline, riboflavin, niacin, vitamins C and D promotes the successful treatment of obesity.
The structure of vitamin B5 is destroyed when taking antibiotics, hormonal contraceptives, and alcohol together.
[Video] Lecture by personal trainer Nikolay Ogorodov about pantothenic acid:
Where is the best place to buy
Pantothenic acid as part of medicines and nutritional supplements is sold in stationary pharmacies and various online stores. But prices for products in pharmacy chains can be inflated several times. To save money and be guaranteed to buy a high-quality dietary supplement, we recommend choosing supplements on the popular international website iHerb.
6 main advantages of purchasing on iHerb:
- The cost of goods is 35-50% less than that of other sellers, due to direct sales and the company’s high turnover.
- A huge range of medications with vitamin B5 and other nutrients from well-known pharmacological corporations from Europe and the USA.
- Lots of ratings and reviews of products from real customers from around the world.
- Various delivery methods worldwide, including free delivery to Russia.
- Fast assembly of orders and dispatch within one day after payment.
- 24-hour work of site consultants who are ready to answer any questions from customers.
Readers of our magazine who have not previously ordered products on iHerb can take advantage of a special discount offer - a -10% discount on the amount of their first purchase. To activate the discount, you need to copy the promo code AGK4375 into the column of the same name when filling out the payment information in the cart or simply follow the link.
Indications and instructions for use
Instructions are required for all supplements containing pantothenic acid. It lists the following indications for the use of vitamin B5:
- hair loss;
- the presence of dermatological pathologies;
- respiratory diseases;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- neurological disorders;
- excessive physical and mental stress;
- exposure to stress;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract of non-infectious etiology;
- alcohol abuse, smoking.
The medications should be taken during meals with plenty of water.
Release form
Pantothenic acid-based supplements are available in the form of capsules and tablets. They have the optimal dosage selected. Dietary supplements are convenient and easy to use. You just need to choose the most suitable option for yourself.
Dosage
The daily requirement of vitamin B5 for an adult is only 10–15 mg . In case of its deficiency, excessive loads, exposure to stress, the body needs more of this substance. The need for it doubles during pregnancy.
The optimal dose is selected taking into account the purpose of using the product and the selected dietary supplement. Instructions are included with each supplement. It indicates the optimal dosage. As a rule, it is enough to take only 1-2 capsules or tablets .
Storage
Supplements should be stored in a dry place protected from sunlight. The expiration date of the product must be indicated on the packaging. After its expiration, taking the drug is strictly prohibited. Otherwise, instead of the expected benefit, harm may be caused to the body.
Importance for the body
Despite its popularity, not everyone knows what the features of vitamin B5 are, what this element is needed for, and what functions it performs in the body.
Pantothenic acid has a multifaceted effect:
- Improving the functioning of the adrenal glands . Scientists have proven that the intake of vitamin B5 is a guarantee of normal functioning of the adrenal glands. At the same time, a sufficient amount of coenzyme-A is produced, which prevents the occurrence of problems such as colitis, allergies and heart disease.
- Normalization of the central nervous system . Pantothenic acid accelerates the metabolism, without which the full functioning of the nervous system is impossible - hormones, mediators, neurotransmitters and others. Thanks to this, taking the element is a chance to normalize the state of the central nervous system. At the same time, it has been proven that its regular use is useful for older people, who in this way avoid Alzheimer's disease and dementia.
- Regulation of cholesterol levels . It is no secret that the action of pantothenic acid is associated with the participation of fats and fatty acids in metabolic processes. In this case, the action of vitamin B 5 is aimed at inhibiting the formation of “bad” cholesterol. As a result, “contamination” of the arteries and the appearance of growths (cholesterol plaques) are eliminated. For this reason, the benefit of the element in the fight against atherosclerosis, which is causing more and more people to die, is difficult to overestimate.
- Participation in the production of fatty acids . The role of the substance in the synthesis of fatty acids, without which not a single human body can survive, was mentioned above. They ensure the flow of metabolic processes and guarantee optimal brain activity. As a result, the deposition of excess fat in the body is eliminated. People who suffer from metabolic problems are required to take this vitamin.
- Strengthening the immune system . A sufficient amount of vitamin B 5 in the diet is a guarantee of good health. But its action is somewhat different from the work of tocopherol or retinol. The latter fight viral infections directly, through free radicals. As for the element in question, it shows strength in the synthesis of antibodies. Without a sufficient amount of pantothenic acid, the body becomes defenseless against external threats.
Considering the multifaceted effect of vitamin B 5, it is used in medicine and is prescribed in combination with medications. Indications for use are:
- eczema;
- burns;
- previous surgery;
- disruptions in the functioning of the circulatory system;
- gastrointestinal and liver diseases;
- problems with metabolic processes;
- allergy;
- respiratory system diseases;
- CNS diseases and so on.
The element has proven effective in relieving hangovers. It is also prescribed during pregnancy, with severe toxicosis.
Sources
To eliminate the problems discussed above, it is important to know where vitamin B5 is found, as well as what products supply the required amount of the element to the body. It is immediately worth noting that pantothenic acid is unstable and most of it is lost in the case of industrial processing, freezing or cooking.
Studies have shown that 30-70 percent of B5 is lost in animal sources. The volume of the useful element also decreases when canning fruits and vegetables, processing grain crops, and making fruit juices.
All sources of pantothenic acid fall into two categories:
- Vegetable - brewer's yeast, grains (oatmeal, whole wheat), green peas and cauliflower.
- Animals - beef, liver, kidneys, dairy products, eggs, caviar.
To eliminate vitamin deficiency, it is recommended to saturate your diet with fresh vegetables and fruits. In addition, it is recommended to eat fish and meat after cold smoking or in dried form.