Creatinine is the end product of the metabolism of creatine, a compound that is responsible for normal muscle contractility and energy metabolism. The substance belongs to the end products of creatine metabolism and is excreted by the kidneys, and therefore is considered an important indicator of the efficiency of the entire excretory system.
Deviations are clearly considered as signs of pathology. How dangerous and severe it is is being investigated by doctors of two specialties: nephrologists and endocrinologists. It is important not to miss the moment and start treatment, since all pathological processes are definitely dangerous.
Therapy depends on the original cause of the increase in the indicator. As a rule, etiotropic correction is prescribed. Aimed at combating the primary culprit factor.
What does blood creatinine mean?
Creatinine is a nitrogenous substance based on creatine (a nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid) that provides muscles with energy. Creatinine is synthesized in the pancreas, liver and kidneys in the amount necessary for muscle tissue to contract.
It is excreted from the body in the urine, so the quality of glomerular filtration of the kidneys is judged by creatinine clearance. Normal GFR (glomerular filtration rate) in men averages about 125 ml per minute, in women – 110 ml/min. The higher the GFR (clearance), the less creatinine is excreted in urine.
The human body needs about 2% creatinine every day. This is a constant because a person’s muscle mass is stable. Creatinine concentration is correlated by gender and age. If it does not go beyond the age norm, then kidney function is not impaired. Deviations in any direction indicate renal failure of varying severity.
Composition and properties of creatine
This natural protein consists of several components. In tandem, they create a product that helps you quickly build muscle mass and increase your physical abilities.
So, creatine contains arginine, glycine and methionine. Individually, they have very useful properties. But together these three substances do incredible things. In particular, if you want to gain muscle mass. Not all preparations based on it have this composition and properties of creatine. Some manufacturers produce creatine with the addition of many vitamins and microelements.
Blood creatinine levels in adults and children
The level of creatinine in the blood is determined by the volume of muscle mass. Since laboratory test data in different clinics may differ from each other, when performing a creatinine test, they are guided by reference values. They depend on gender and age. Creatinine norms for men, women and children are presented in the table.
| Age | Norm, µmol/l |
| Children | |
| Newborns | 22-87 |
| Up to a year | 15-37 |
| up to 15 years | 25-80 |
| Men | |
| Up to 50 years | 70-125 |
| Over 50 | 65-110 |
| Women | |
| Up to 50 years | 55-100 |
| Over 50 | 50-105 |
There are also standards for patients living with one kidney: from 175 units (in women) to 185 (in men). In older people with many concomitant pathologies and poor nutrition, the indicators may be significantly lower than the generally accepted norm. But exceeding the reference values in children by up to 200 units or in adults (without gender differences) by up to 400 clearly indicates pathology.
Are there any side effects of creatine?
The vast majority of medications have a number of indications, contraindications, and, of course, some side effects. This also applies to creatine.
It is worth noting that the side effects of this substance can only appear due to exceeding the norm of creatine. The most common ones include:
- diarrhea;
- mild nausea;
- general weakness.
You can avoid such unpleasant consequences of taking creatine by carefully following the instructions. It should also be taken with plenty of liquid.
Reasons for the increase
The only physiological reason for an increase in creatinine in the blood is voluntary nutrition with dietary supplements with a high concentration of creatinine for artificial muscle growth and super-endurance. As a rule, we are talking about athletes. In other cases, an increase in endogenous creatinine is a reason for further examination, since it may indicate, first of all, a pathology of the urinary system against the background of kidney injuries, ischemia or a tumor of the organ, or urinary tract.
In addition, increased levels of the substance according to the results of a hemorenal test are characteristic of burns or bruises. A high level of creatinine can be a sign of dehydration (dehydration) of the body, internal bleeding of any location.
We must not forget that high creatinine in men, women, and children can indicate a latent ongoing process in the kidneys and be the only indicator of impending danger. Biochemical screening allows you to make a correct diagnosis in a timely manner, select adequate therapy, and prevent complications.
Will creatine harm your health?
This is the first question that arises among people who want to “build” a beautiful body. Everyone is afraid, everyone is worried and is looking for an answer to this question. However, you need to independently research the pros and cons of taking the drug, the properties and composition of creatine.
Today there is no single scientific study on the dangers of creatine for human health. There is an opinion that it has a negative effect on the kidneys or liver function. However, the professors proved the opposite. Therefore, taking medications based on this substance can in no way harm your health. Except in cases where the recommended dose is exceeded. It is for this reason that the instructions always indicate how much creatine a particular person needs to take.
Reasons for the downgrade
Reduced creatinine levels in a biochemical blood test may be due to a sharp decrease in muscle volume due to prolonged fasting, liver pathology, or degenerative processes in the body of various origins. In addition, the clearance of creatinine in the blood decreases when the nutrition and oxygen supply to the kidneys is disrupted, neoplasms develop in them, and at the first signs of cardiovascular failure.
A decrease in creatinine in the blood can be a consequence of a protein-free diet, pregnancy, destruction of myocytes (rhabdomilliosis), or cirrhosis of the liver.
Does creatine affect hair condition?
There are rumors that this supplement negatively affects the condition of the skin, nails and hair. Some men may not pay attention to the first and second and put up with brittle nails or dry skin. But not everyone will agree to have a billiard ball hairstyle.
Scientists have conducted some research on this issue, and it has been proven that taking creatine can increase hair loss. However, not to such an extent that you go bald completely in a month. Therefore, those who have thick hair need not worry. But those who are afraid of losing extra hair should know that creatine supplements increase hair loss.
Diagnostics
The level of creatinine in the blood can be determined using several laboratory techniques. In this case, blood is drawn from a vein or finger. Basic tests:
- detailed biochemical blood analysis;
- Rehberg-Tareev hemorenal tests: determination of the concentration of endogenous creatinine by clearance;
- detection of azotemia (protein/creatinine ratio) is the main method for early diagnosis of kidney pathology.
Each of these tests is informative in itself; a combination of them is carried out in case of a questionable diagnosis or differential diagnosis.
No special preparation is required to take a creatinine test: two days before the test, avoid physical activity, and one day before the test, avoid protein foods. They drink a lot of water, but on the eve of the test, tea and coffee are prohibited.
How to take creatine correctly
Taking creatine, like other medications, requires studying the instructions for it. A preliminary consultation with a specialist is also necessary. An equally important point is a thorough study of the composition and properties of creatine in order to prevent possible allergic reactions to its components.
The standard dose of creatine preparations for an ordinary person and for a beginning athlete is 1-2 grams. For those who constantly exercise their body every day, the dose of creatine should be at least 4 grams.
How to adjust the level
Reducing creatinine levels can be achieved with medication or a strict diet, the purpose of which is to improve the functioning of the urinary system. Most often, elevated creatinine in the blood is normalized with medications:
- enterosorbents – cleanse the body of decay products, waste, toxins, microorganisms: Smecta, Enterosgel, Polysorb;
- drugs that stimulate the excretion of protein breakdown products: Chitosan, Ketosteril, Lespefan;
- diuretics – remove excess moisture from the body: Triampur, Indapamide, Spironolactone;
- antihypertensive drugs of different pharmaceutical groups: Hypothiazide, Corinitek, Concor.
Diet
Therapeutic nutrition for increased creatinine in the blood is based on the exclusion from the diet of foods that overload the kidneys:
- purines - they are part of animal proteins and stimulate additional synthesis of creatinine, uric acid, urea, which must be excreted from the body;
- phosphates are vital, but provoke a decrease in calcium concentration in the body: meat, fish, canned food and foods with preservatives.
Treatment table No. 7, 7a, 7b, which is prescribed for the treatment of nephritis, helps reduce creatinine in the blood and urine. The essence is a minimum of protein with a predominance of plant carbohydrates. A high level of creatinine in the blood requires the use of: vegetables (except potatoes), herbs, unsweetened fruits, berries, honey, nuts. In addition, the following are allowed: low-fat milk and its derivatives, cereals, vegetable soups, vegetable oil and salt-free bread.
A couple of times/week, subject to a slight increase in creatinine, you can include dietary meat, fish, potatoes, eggs (no more than three pieces) in your diet. The drinking regime is calculated together with the doctor and strictly observed.
If creatinine increases, it is forbidden to eat: fatty meats, fish, smoked foods, fried, spicy, salted foods. Baked goods, milk, strong tea and coffee should be excluded. Cooking method: steamed, boiled, stewed, in the oven.
What is better to combine taking Creatine with?
There are two benefits to taking creatine. And one concerns
- what to drink creatine with at the same time (which acts as a transport system),
and the second one
- What sports nutrition should I combine this supplement with?
We can definitely say that if you take only Creatine, you will not notice any special results. This supplement should be taken in combination with other sports nutrition that complements its effect.
We recommend reading a useful article with the nuances of taking sports nutrition: How to take sports nutrition correctly?
Basic additives should be:
- BCAA;
- Protein;
- fatty acids;
- Multivitamins.
We also recommend adding a pre-workout supplement to this complex. This will give you more emotional stamina and focus during your workout and will complement the physical stamina and strength that Creatine will provide.
If you want to improve the effectiveness of your pre-workout supplement, we recommend reading the article: How to take a pre-workout supplement?
Men can expand the complex with a testosterone supplement, a supplement that increases natural testosterone levels. What's in it for you? Everything that your testosterone gives, but in multiplied quantities: strength, endurance, increased libido, better health, activity, etc.
We suggest you look at the list of the best supplements in their category below:
BCAA
Core Labs X Amino Power
Price: 3290.00 rub.
Card Product
Bio Tech Nutra Muscleade
Price: 2900.00 rub.
Card Product
Go to BCAA category »
Protein
Blackstone Labs Isolation
Price: 3390.00 rub.
Card Product
Revange Nutrition Iso Pro
Price: 2990.00 rub.
Card Product
Blackstone Labs Formula 19
Price: 4410.00 rub. 4210.00 rub.
Card Product
Go to the Protein category »
Multivitamins
Infinite Labs Men's Multivitamin
Price: 1990.00 rub.
Card Product
Infinite Labs Women's Multivitamin
Price: 1990.00 rub.
Card Product
NOW Vitamin D-3 5000 ME (120 capsules)
Price: 1150.00 rub.
Card Product
Go to the category Vitamin and mineral complexes »
Fatty acid
NOW Super Omega 3-6-9 1200 mg (180 capsules)
Price: 1870.00 rub.
Card Product
NOW Ultra Omega-3 500 EPA/250 DHA (90 capsules)
Price: 1780.00 rub.
Card Product
Infinite Labs Omega 3,6,9
Price: 1580.00 rub.
Card Product
Go to Fatty Acids category »
Pre-workout supplements
APS Mesomorph
Price: 2990.00 rub. 2530.00 rub.
Card Product
Blackstone Labs Dust X
Price: 2590.00 rub.
Card Product
Blackstone Labs Hype
Price: 2290.00 rub.
Card Product
Go to the Pre-workout complexes category »
Biochemistry and physiology
Creatine is an essential natural substance (methyl guanidoacetic acid) that is found in the muscles of humans and animals and is required for energy metabolism, muscle movement and overall functioning. The human body contains about 100-140 g of this substance, which acts as a source of energy for muscles. The daily consumption of creatine under normal conditions is approximately 2 g.
Creatine is as important to life as protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals. Without creatine, people and animals could not live. Creatine deficiency is associated with several physical and muscle disorders.
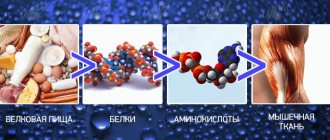
The human body synthesizes creatine from three amino acids: glycine, arginine and methionine. In humans, the enzymes involved in creatine synthesis are localized in the liver, pancreas and kidneys. Creatine can be produced in any of these organs, and then transported by the blood to the muscles. Approximately 95% of the total creatine reserve is stored in skeletal muscle tissue. The remaining 5% is found in the heart, brain and testes. The total pool (reserve) of creatine in humans consists of creatine in free form and in the form of phosphocreatine. In skeletal muscle tissue, phosphocreatine makes up two-thirds of the total creatine pool, with the rest being free forms of creatine.
In the absence of exogenous (obtained from the diet) creatine, the rate of excretion as creatinine in humans is about 1.6% per day. Thus, with a body weight of 70 kg and a total creatine reserve of 140 g, a person will lose approximately 2 g of creatine per day during normal household activities. As physical activity increases, creatine turnover also increases, and its supply must be replenished through diet or through the body's own natural production. Dietary creatine is found primarily in meat, fish and other animal products.
Plants contain only trace amounts. The average daily diet of meat and vegetables contains approximately 1 g of creatine. Since the daily need for creatine can only be partially covered by diet, the rest is forced to be synthesized by the body itself. The resulting creatine enters the muscles through the bloodstream, where, under the influence of the enzyme creatine kinase, it is converted into creatine phosphate. Creatine phosphate accumulates in the cell as a source of chemical energy for adenosine triphosphate (ATP). After the release of phosphate, creatine is converted into creatinine, which is excreted through the kidneys as waste.
However, a vegetarian’s daily need for creatine can only be met through endogenous (passing inside the body) synthesis, and this amount is sometimes simply catastrophically insufficient.
Here are the approximate levels of creatine in foods (in grams of creatine per 1000 g food source): shrimp - traces, cod - 3 g, herring - 6.5-10 g, salmon - 4.5 g, tuna - 4 g, beef - 4 .5 g, pork – 5 g, milk – 0.1 g, cranberry – 0.02 g. Now you can conclude for yourself that animal food sources are important for the synthesis of creatine and its extraction from food.
How does creatine work? Useful practical properties of creatine monohydrate
The decisive factor for achieving high results in sports is the body's ability to release large amounts of energy in a short period of time.
Basically, our body constantly receives energy by breaking down carbohydrates and fat. The immediate source of energy for skeletal muscle contraction is a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The amount of ATP immediately available is limited and is decisive for athletic performance.
All fuel sources - carbohydrates, fats and protein - are first transformed through various chemical reactions into ATP, which then becomes available as the only molecule the body uses for energy. Everything must first be converted to ATP before it can be used as fuel. ATP is a simple substance consisting of one molecule of adenosine and three molecules of phosphate.
When ATP releases energy to fuel muscle contractions, the phosphate group is broken off and a new molecule called ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is formed. This reaction is reversible due to phosphocreatine, an energy-rich substance.
Creatine combines with phosphate in the body to form phosphocreatine, which is a determinant of energy production in muscle tissue. Phosphocreatine supplies the phosphate group of ADP, resynthesizing this substance back into the ATP molecule, thus making it again ready to release energy, allowing it to fuel continuous muscle contractions. ATP is an energy-carrying substrate present in muscle, while phosphocreatine is a precursor to ATP. Free form creatine accumulates in working muscles and is then rephosphorylated to form phosphocreatine.
During high-intensity exercise, ATP demand in working muscles increases significantly, hundreds of times higher than at rest. During the first 10 seconds of exercise with a maximum load of 1 to 6 repetitions, muscle work occurs in the phosphagen range; that is, they use stored ATP and phosphocreatine for energy.
High-intensity exercise can completely deplete phosphocreatine stores within 10 seconds. Depleted stores of ATP and phosphocreatine must be constantly replenished in order for muscle contractions to continue at peak levels of frequency and intensity. By increasing your phosphocreatine levels by taking creatine monohydrate, you can increase your ATP and thus the number of repetitions in any exercise.
Additionally, people who supplement with creatine typically experience impressive results within just seven days. An increase in dry body mass of 2 to 5 kg is not uncommon. Studies have shown that creatine monohydrate can increase your bench press rep max by 10kg, improve sprinting ability and help you gain 2 to 5kg of lean muscle in less than 30 days.
Not only does creatine increase strength, speed, and muscle size, but it also improves the appearance of muscles. As it is absorbed into muscle cells, creatine monohydrate binds to water. Since creatine accumulates in the muscles, water is drawn into the muscle cell along with creatine. This explains the hydrating effect of creatine on muscle cells, which are approximately 75% water. Bodybuilders notice that a well-hydrated muscle appears fuller, more rounded, and more toned in appearance.
Types of Creatine in Sports Supplements
Creatine monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate occupies a leading position among all types. Its cost is low, and many studies have been conducted on its use. Its popularity is due to its high effectiveness, which no other non-hormonal sports supplement has. Creatine monohydrate consists of 88% pure creatine, the remaining 12% is water.
The first creative supplements to appear on the sports nutrition market consisted of large particles that were difficult to digest and absorb into the body. Digestive problems often occurred. Nowadays, creatine supplements are micronized, and the powder particles have become 20 times smaller. Modern supplements do not cause digestive problems.
Creatine ethyl ester
Creatine ethyl ester is a relatively new type of sports supplement that has already become incredibly popular. It ranks second in popularity after creatine monohydrate. Scientists combined the ether with creatine, which allowed the elements of the resulting substance to pass through cell membranes much more efficiently. As a result, creatine ethyl ester penetrates cells much faster.
Other types of creatine
- Creatine anhydrous. This is the same creatine monohydrate, only without water molecules. It contains 6% more pure creatine than monohydrate.
- Creatine citrate. This type of substance appeared shortly after creatine monohydrate. It is a combination of creatine molecules with citric acid molecules. Citric acid significantly affects the mechanisms of aerobic energy production in muscle tissue, so creatine citrate is believed to provide the athlete with a large amount of energy. This fact has not yet been proven scientifically.
- Creatine phosphate. Another of the first types of substance in which creatine molecules are connected to phosphate molecules. This same combination of elements is obtained naturally in muscle cells. It was believed that combining creatine and phosphate molecules before entering the body's tissues would improve athletic performance. But it turned out that creatine phosphate is not as effective as expected.
- Creatine malate. A relatively new type of creatine, which is a chemical compound with malic acid. Malic acid has the same effect on the body as citric acid. It promotes the production of aerobic energy in the muscles. To date, too few studies have been conducted that could confirm the effectiveness of this type of substance.
- Creatine tartrate. Creatine tartrate is a combination of creatine and tartaric acid. This type of supplement is often used in tablets, capsules, and also chewable tablets.
- Magnesium creatine. This is a chemical combination of creatine and magnesium. It promotes the absorption of creatine in the body, helping it pass through the gastrointestinal tract. Magnesium is also involved in the process of converting creatine phosphate into ATP. Magnesium creatine is very effective, but only in a ready-made compound. Taking creatine and magnesium as separate supplements will not have a positive effect.
- Creatine glutamine taurine. It is a complex of compounds consisting of creatine, taurine and glutamine. Under the influence of both glutamine and taurine, cells increase in volume. It is believed that combining them with creatine will increase the benefits to the body. Taurine also has the property of increasing the strength of an athlete.
- Creatine HMB. It is a chemical compound of creatine with HMB (beta-hydroxy-beta-methylburate). HMB promotes muscle growth and regeneration. In general, this compound is more easily absorbed by the body. Once in the circulatory system, creatine and HMB are separated. This type of supplement has relatively recently appeared on the sports nutrition market; very few studies have been conducted to confirm its effectiveness.
- Creatine is effective. This type of supplement has been on sale for several years. It usually contains creatine monohydrate or creatine citrate, citric acid and bicarbonate salt. Available in the form of effervescent tablets, when lowered into water, creatine is formed, which carries a neutral charge. It is better absorbed by the body. Also, in a diluted state, it retains its properties longer. Very convenient for those who make a creatine drink at home to take with them to the gym.
- Creatine titrate. This type of supplement has the same principle of action as creatine efevesent. It also retains its properties in diluted form for a long time and is better absorbed in the human body.
- Liquid creatine. The liquid form of release allows for easier absorption by the body. Unfortunately, dissolved creatine loses its properties very quickly. This is especially true for earlier forms of release. Modern liquid forms of creatine have been significantly improved; now they can be stored for up to a year without losing their properties.
- Creatine chewable tablets. Slower but more uniform intake of creatine into the body.
- Long-acting creatine. This is a new type of creatine that ensures slower and more uniform absorption by the body. There is heated debate about its effectiveness. Due to its slow absorption, such creatine does not provide the required concentration of the substance in the body. And many believe that this is the key to a good result.
Safety factor
Creatine is a natural metabolite excreted daily through renal filtration. Numerous scientific experiments have shown its safety even in large dosages. A British study conducted by the University of Nottingham Medical School found that subjects consuming as much as 20g of creatine monohydrate daily for five days followed by 5g of creatine daily for six continuous weeks showed no adverse effects. The researchers concluded that "acute dietary fortification with creatine monohydrate does not pose any apparent health risk in young adults."
However, it is best to start a creatine supplementation program with lower dosages and monitor performance improvements. Remember that more is not necessarily better. If there is too much creatine, it will simply be excreted in the urine, further straining the kidneys.
Its creatine can be regarded as a safe product as long as the supplement is pure and free of impurities. Its various varieties are currently available in the market, but some are of very poor quality. Low quality creatine will not provide the same benefits as pure creatine monohydrate. In fact, if it is replaced with cheap fillers or contaminated with impurities, the likelihood of poor health increases. Creatine is a white crystalline powder that has no taste. If your creatine has a bad smell or a yellowish color, beware!
When purchasing creatine, choose a product from companies that guarantee quality. If the creatine is high quality and your kidneys are functioning normally, then it is extremely unlikely that the supplement will cause toxic effects on the body, even when taken at 15 to 30 grams per day, which is a common loading dosage. If you notice anything outside the normal range, simply reduce the dosage.
Despite the absence of any contraindications, many researchers do not recommend taking it to adolescents.
What is endogenous creatinine clearance?
A more accurate assessment of kidney function can be made by calculating the rate of creatinine excretion from the body. This indicator is called endogenous creatinine clearance and characterizes the glomerular filtration rate. Endogenous creatinine clearance can be calculated in two ways:
- Creatinine clearance (CrCl, ml/min) is calculated using a formula using the measured serum creatinine level (CrCl, mg/dL). The patient's age in years is subtracted from 140, and the resulting value is multiplied by his weight in kilograms. The result of the calculation is divided by the serum creatinine level multiplied by 72. For women, the resulting value is multiplied by a factor of 0.85. Briefly the formula looks like this:
- Men: KlKr = ((140 – age)×weight)/(72×KrPl);
- Women: KrKr = ((140 – age)×weight)/(72×KrPl)×0.85.
- Creatinine clearance can also be calculated by measuring the level of creatinine in a 24-hour urine sample and its level in the blood (Rehberg-Tareev test). The obtained values are compared. 6 hours before urine collection and blood sampling, the patient should not eat meat, poultry, fish, coffee and tea. During the day while urine collection is being carried out, the patient should not be subjected to heavy physical activity. Urine is collected in a container with a volume of about three liters. The container with collected urine is stored in a cool place; no preservatives are added to it. If necessary, the patient's weight and height are noted. At the end of the day, the volume of collected urine is assessed, about 20 ml of urine is poured into a special container, which is sent to the laboratory to determine the level of creatinine. The remaining volume of urine is destroyed. At any time of the day, while urine is being collected, a blood sample is taken from a vein, followed by determination of creatinine.
Normal values of endogenous creatinine clearance
| Age | Clearance of endogenous creatinine | |
| Men | Women | |
| Children under 1 year | 65 — 100 | 65 – 100 |
| Ages 1 to 30 | 88 — 146 | 81 – 134 |
| Adults aged 30 to 40 years | 82 — 140 | 75 – 128 |
| Adults aged 40 to 50 years | 75 — 133 | 69 – 122 |
| Adults aged 50 to 60 years | 68 — 126 | 64 — 116 |
| Adults aged 60 to 70 years | 61 — 120 | 58 – 110 |
| Adults over 70 years of age | 55 — 113 | 52 — 105 |
If creatinine clearance is below normal
The measured values of creatinine clearance can be reduced by taking thiazides, diazoxide, triamterene, nephrotoxic drugs, opioid drugs and cannabis.
Low creatinine clearance may indicate the presence of the following diseases:
- Kidney diseases: glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, congenital kidney diseases, interstitial nephritis, acute tubular dysfunction, papillary necrosis,
- Common diseases: amyloidosis, malaria, myeloma, cystinosis, Wilson-Konovalov disease, vitamin D-resistant rickets.
- Conditions accompanied by decreased blood supply to the kidneys: shock, blood loss, dehydration, heart failure.
- In obstetrics: preeclampsia, eclampsia.
By degree of reduction:
| up to 30 ml/min/1.7 m2 | moderate decrease in kidney function; |
| 30-15 ml/min/1.7 m2 | renal failure, compensated, subcompensated; |
| < 15 ml/min/1.7 m2 | decompensated renal failure. |
If creatinine clearance is higher than normal
The clearance of endogenous creatinine can be increased by: a protein diet, excessive physical activity, amino acid-based drugs, furosemide, carbenoxone, levodopa, methylprednisolone.
High clearance rates can occur with hypertension, diabetes, burns, and pregnancy.
Forms of creatine[edit | edit code]
The popularity of various forms of creatine
Modern pharmacology identifies the following forms of creatine:
- Creatine monohydrate
- Kre-Alkalyn
- Creatine Ethyl Ester Creatine Ethyl Ester Malate
- Creatine ethyl acetate
- Tri-Creatine Malate
Creatine comes in tablet, powder, or pill form and can be liquid, effervescent, or chewable.
Introduction to Creatine Supplements
What are creatine supplements?
Of all protein sports supplements, creatine is the most effective in the world for building muscle mass and achieving athletic performance. They provide an increase in the strength qualities of athletes by 10-15%, an additional gain of pure muscle mass up to 5 kg. They really are the best in terms of price-quality ratio.
Creatine supplements come in powder, tablet, and solution forms. Since powdered creatine is the most popular among athletes, there are a huge number of dry mixtures for preparing drinks with different flavors. The most common flavors are grapes and assorted fruits.
Brief historical background
In 1912, Harvard University discovered that human intake of the substance leads to an increase in its content in muscle tissue. In the next decade, creatine was proven to stimulate an increase in muscle metabolism.
The world first learned about creatine supplements at the Barcelona Olympics in 1992. That same year, the British newspaper The Times published an article about the details of creatine use by a group of athletes. Among them was Linford Christie, an Olympic champion in the 100m, as well as several members of the British rowing team.
Less than a year has passed since creatine supplements became available to ordinary customers. In 1993, EAS launched a product called phosphagen (creatine phosphate). In 2004, creatine ethyl ether became the sales leader.
What forms of creatine supplements are there?
- Powder. Creatine powder is the most popular and widespread form of release. Sold both in pure form and for diluting drinks.
- Capsules. Creatine capsules or tablets have gained widespread popularity in recent years. They are sold both in pure form (100% creatine) and in combination with other additives, namely vitamins, minerals, amino acids.
- Liquid form. The liquid form of the supplement was created as the most convenient for use. Despite this, it did not gain widespread popularity.
- Mixtures. Mixtures of creatine with other additives - mineral elements, carbohydrates, vitamins, herbal extracts - are designed to enhance their overall effectiveness, accelerate absorption by the body and improve athletic performance.
Benefits of Creatine Supplements
You have gained an idea of the benefits of creatine for human health and its anabolic effects on the body. Now it’s worth getting acquainted with the main advantages of the supplement.
- Extra energy. Creatine supplements provide athletes with a burst of energy, allowing them to train much longer and harder. When the body needs more strength, adenositol triphosphate (ATP) provides it. The problem is that ATP energy only lasts for 10-15 seconds. Creatine helps restore it faster, allowing you to train with greater impact.
- Protein synthesis. Recent research has found that creatine supplements stimulate protein synthesis in muscle tissue.
- Volume of muscles. Creatine supplements help build muscle mass and strengthen muscle cells.
- Lactic acid. Creatine prevents the formation of lactic acid, thereby reducing the time it takes for muscle fatigue to accumulate. As a result, you have longer training sessions or greater performance during athletic performances.
Who uses creatine supplements?
Supplements have become most popular among bodybuilders or representatives of strength sports. The substance increases endurance, strength and muscle mass. It allows the body to draw additional strength when the athlete is already tired before the end of any sports game, or if we are talking about achieving some kind of record.
Creatine benefits human health. It strengthens muscle cells, helps fight diseases, and improves mental and mental well-being. Also, vegetarians who do not get the substance from meat cannot do without creatine supplements.
Body-building. Bodybuilders use creatine to increase lean muscle mass and produce additional energy.
Powerlifting. Athletes use creatine to help them withstand long, intense workouts and also to increase their strength.
Sports where the main criterion is endurance. Runners, cyclists and other endurance athletes use creatine to extend their workouts. The supplement also allows them to find strength in their body for the final pushes before the finish line.
Team sports. Players of team sports resort to the help of creatine to acquire additional strength qualities and energy reserves to maintain strength during the game.
Improving the body. Creatine is used not only by athletes, but also by people who want to change their appearance for the better and have a good figure. Supplements improve their strength qualities. Also, gaining muscle mass leads to a decrease in the percentage of body fat.
Vegetarianism. Vegetarians need creatine supplements to maintain good health. As mentioned earlier, a lack of creatine in the body can lead to certain problems.
Creatine supplements and natural sources of creatine
In general, a healthy person gets about 1 g of the substance from food every day. Foods rich in creatine:
- herring - 1.4-2 g per 1 kg;
- pork - 1 g per 1 kg;
- beef - 0.9 g per 1 kg;
- salmon - 0.9 g per 1 kg;
- tuna - 0.8 g per 1 kg;
- cod - 0.6 g per 1 kg;
- milk - 0.02 g per 1 liter;
- cranberries - 0.0005 g per 1 kg.
It is worth noting that creatine is almost not found in chicken.
The minimum amount of creatine required in the body is 5 g per day. As you can see from the list above, you will have to eat an incredibly huge amount of meat to reach the goal. Also, thermal processing of food destroys a significant amount of creatine. Conclusion: creatine supplements are needed to get the missing amount of the beneficial substance, since natural products simply do not contain as much of it as the body needs.
Which creatine is better to choose?
The sports supplement is a white powder with small particles resembling powdered sugar. The additive has no taste or smell, sometimes tastes bitter, and comes in two forms. Encapsulated and in powder form.
Despite the abundance of companies promising certain effects from use, creatine remains just creatine, so you should not chase any specific company or price. Even the cheapest product will work no worse than a newfangled one in beautiful and expensive packaging.
Capsules are much more convenient than powder, but the crumbly form may be more convenient in cases where, in addition to creatine, an athlete must consume several types of sports nutrition at one time, the total amount of water is one and a half liters. If you take it in powder, you can pour half a liter of water into a shaker, then throw in a portion of creatine, BCAA (also in powder) and maybe even a gainer in one go.