Taking Glycine in bodybuilding is considered necessary by both doctors and trainers, because the amino acid accelerates the recovery and strengthening of muscles against the background of excessive physical exertion. This element takes part in the production of creatine and collagen, which are necessary for muscle growth and rapid recovery after injury.
Glycine is often included in sports nutrition supplements, but it can also be taken as standard pharmacological drugs. The daily dosage of any supplement containing glycine is 1 capsule 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is 1 month, after which you need to take a break from therapy for 30 days.
Amino acid glycine - role in the body
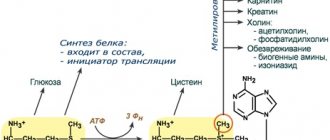
Glycine is a proteinogenic amino acid that is used by the body in building protein molecules. It also participates in the formation of creatine, porphyrin, serotonin, and purine nucleotides.
Glycine can be found not only from sports nutrition manufacturers, but also from pharmaceutical companies. Glycine is available for free sale in pharmacies, and its cost in a pharmacy is relatively low when compared with foreign companies producing dietary supplements.
In pharmacology, glycine is used as a sedative with antidepressant, sedative and tranquilizing effects. Glycine also helps improve memory and mental performance. Most often, glycine is produced containing vitamins B and D3 in the preparation.
You can take glycine for the following indications:
- Decreased mental performance.
- Stress and psycho-emotional overstrain.
- Increased irritability and excitability.
- Emotional instability.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Stroke.
- Alcoholism.
Analogues of the drug
The pharmacological industry produces several analogues of Glycine, the composition of which is enriched with B vitamins:
- Glycine-Canon;
- Glycine-Vis;
- Glycine-Bio.
Glycine-Canon Glycine BIO from Pharmaplant Glycine-Vis
These drugs also belong to dietary supplements and have an identical effect on the body. Replacement of sports nutrition based on amino acids or standard Glycine preparations should be carried out by specialists - a doctor or sports trainer/instructor.
We recommend reading the article about the features of the drug Glycine Bio. From it you will learn about the differences between the drugs Glycine and Glycine Bio, instructions for use, indications for use, side effects. And here is more information about the benefits and harms of taking Glycine.
Glycine in bodybuilding is a necessity that helps normalize the functioning of the heart, blood vessels and central nervous system even during excessive physical exertion. Amino acids increase the physical endurance of athletes, which allows them to achieve great achievements and at the same time maintain health.
Why is glycine used in sports?
In sports nutrition supplements it is a taste and aroma enhancer and is listed as food additive E640 .
It is known that athletes need additional amino acid intake for training and preparation for competitions. However, the additional use of glycine as a separate component is necessary not only for high physical stress, but also for psycho-emotional stress. Overtraining, physical fatigue and the athlete’s anxiety cause some central nervous system disorders that glycine fights: it improves concentration, increases calmness and endurance, and also increases motivation. It is these qualities that an athlete needs in the pre-competition period, 2-4 weeks before the competition, and athletes adhere to this course of treatment.
Content in food
The amino acid is found in foods rich in protein. Their presence is important in a sports diet. To compensate for the deficiency of the required component, the body needs to receive:
- meat products and liver;
- quail and chicken eggs;
- cottage cheese;
- buckwheat and oatmeal;
- nuts, pumpkin seeds, soybeans.
The most popular use of glycine is in bodybuilding as it helps build muscle mass. Glycine in bodybuilding changes the appearance, the entire appearance of a person, as relief forms appear, and fat deposits are replaced by muscle mass. Its deficiency leads to the breakdown of muscle fibers consisting of proteins, which also include amino acids.
Important: How to take Glycine in sports and how long this can be done has not been studied enough. It has been found that taking 3-6 g per day actually improves performance and endurance. But its regular use has also been found to cause headaches.
The benefits and harms of glycine
Benefits of glycine for the body:
- Increases mental performance.
- Reduces stress, tension and psycho-emotional fatigue.
- Has a sedative effect.
- Improves sleep and makes it easier to fall asleep.
- Improves brain function and restores its cells, including when drinking alcohol.
- Improves memory.
Disadvantages of glycine:
Of course, you need to take glycine only as directed ; you shouldn’t take it additionally on your own without a reason. In some cases, glycine can cause side effects, although the amino acid is considered harmless and its overdose has not been identified.
Research
Glycine was first isolated and described by the French chemist and pharmacist Henri Braconneau. The scientist obtained sweet crystals during experiments with gelatin in the 20s of the 19th century. It was only in 1987 that the cytoprotective properties of this amino acid were described. It has been found that it promotes the restoration of living cells after hypoxia. Experiments on animals have shown that this compound is used by the body to neutralize the effects of ischemia - a violation of the blood supply.
However, under conditions of severe stress, for example, during an ischemic stroke, glycine temporarily becomes a conditionally essential amino acid, that is, it cannot be synthesized by the body.
When administered externally, it perfectly protects cells from oxygen starvation. Presumably, glycine reduces the permeability of the cell membrane, thereby maintaining electrolyte balance and preventing the destruction of cellular structure.
Mostly Russian scientists are engaged in research into the properties of the amino acid; in the West it is recognized as ineffective and is practically not studied. The only use of the compound in the United States is as an irrigation solution for interventions performed by the transurethral route.
Russian scientists are more busy researching the nootropic, tranquilizer, antitoxic, and antidepressant properties of glycine. Some of them showed the effect of this compound in eliminating sleep disorders.
Glycine has also shown a neuroprotective effect: when taken in the first 3-6 hours after an ischemic stroke, the drug reduces the extent of its consequences. Russian scientists also came to the conclusion that the use of amino acids has a sedative effect as a nootropic.
Western colleagues do not share the point of view of Russian researchers, believing that all observed actions are due to the placebo effect. Indeed, it has still not been possible to substantiate the effectiveness of the drug using evidence-based medicine.
What sports nutrition can it be combined with?
Glycine is compatible with taking full cycle amino acids and BCAAs, protein supplements and gainers.
How to combine glycine with creatine
Since glycine is involved in the synthesis of creatine molecules, taking both supplements is not prohibited. Creatine, depending on the dosage regimen, is taken in the morning or before training; during the loading phase, the dose is distributed throughout the day. Glycine is taken during or after meals, but simultaneous use with creatine before training is not advisable. It is better to take supplements at different times.
What is Glycine
Glycine is one of the simplest amino acids that have multifunctional properties:
- muscle recovery after overexertion;
- stabilization of brain activity;
- acceleration of muscle mass gain.
One of the advantages of Glycine is the almost complete absence of contraindications. In addition to this, Glycine goes well with other drugs. Ideal for athletes.
Top 4 Glycine Supplements
- Now Foods Glycine - another American manufacturer produces glycine 1000 mg in one tablet. One jar contains 100 capsules. The packaging indicates that the supplement is vegetarian . It is recommended to take 1-3 capsules per day on an empty stomach.
- DOPPELHERZ ACTIVE GLYCINE + B-VITAMINS - a German pharmaceutical company produces a glycine supplement of 500 mg in 1 capsule, vitamins are also added to it: B1 - 1.7 mg, B6 - 2 mg, B12 - 3 mcg. Take 1 capsule per day with meals for a month.
- Evalar Glycine forte , a well-known manufacturer of dietary supplements in our region, produces glycine 500 mg in one tablet, and also adds vitamins B1, B6, B12. It is recommended to take one capsule twice a day for a month. The supplement is available in packages of 20 and 60 tablets.
- Solgar - glycine from an American manufacturer, 500 mg per tablet. One jar contains 100 capsules.
Is it possible to get glycine for athletes from foods?
Glycine is found in many foods, so it is important for athletes to include them in their menu. The most effective foods in terms of replenishing amino acids in the body are:
- chicken meat (glycine contains 1.5 mg per 100 g);
- fish (0.5 mg per 100 g);
- pasta (0.2 mg);
- chicken eggs (0.35 mg);
- cottage cheese and all fermented milk products (0.05-00.18 mg);
- buckwheat (0.8 mg);
- beef (1.4 mg);
- oatmeal (0.45 mg).
If an athlete consumes these foods in small quantities, this will provoke an amino acid deficiency. The result will be problems in the digestive system, which provokes classic disorders - nausea, heartburn, loss of appetite, diarrhea or constipation, intestinal colic.
Experts, including representatives of official medicine, believe that amino acids from food will not be enough for a bodybuilder’s body - it is imperative to take glycine in the form of dietary supplements.
Consequences of shortage
With Glycine deficiency, the following may occur:
- physical weakness;
- deterioration in the appearance of hair, nails, skin;
- slow protein synthesis;
- risk of injury;
- increased excitability;
- mental retardation;
- disturbed sleep;
- reduced immunity.
For athletes, normal consumption of Glycine is especially important. It is this amino acid that allows you to stimulate growth hormone and also optimize muscle development and growth. With a lack of glycine, the protein in the muscles disintegrates, the body's relief gradually disappears and the result of many hours of work follows it.
Beneficial features
Essential for the production of a powerful antioxidant
Glycine is one of three amino acids that the body uses to synthesize glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals.1
Without enough glycine, the body will produce less glutathione, which can negatively impact the body's resistance to oxidative stress.2
Contains creatine
Glycine is also one of three amino acids that our body uses to synthesize creatine.
Research has shown that when combined with resistance training, creatine supplementation helps increase muscle and strength.3
May protect against muscle loss
Glycine may reduce muscle wasting, a condition that occurs with aging, malnutrition, or when the body is under stress, such as severe illness or severe burns.
Glycine has been shown to help protect muscles from muscle wasting caused by a variety of causes.4
Improves sleep quality
Many people have trouble falling or staying asleep. Glycine has a calming effect on the brain, it lowers body temperature and may help with sleep.5
Studies of people with sleep problems have shown that taking three grams of glycine before bed reduces the time it takes to fall asleep, improves sleep quality, and reduces daytime sleepiness.6
Essential amino acids for the brain
This type of amino acid is synthesized by the body independently and also comes from food.
Alanin
The brain requires a lot of energy to function, and this amino acid is its source. Alanine also supports immune function and regulates glucose levels. This amino acid is very often used in psychiatry, as it helps reduce irritability and apathy, and also relieves migraines. Alanine's ability to regulate glucose levels allows you to not feel hungry for a long time.
Foods rich in alanine will help compensate for the deficiency: meat, eggs, gelatin, dairy products.
Asparagine
The amino acid removes ammonia from the body and protects the central nervous system from its toxic effects. Asparagine regulates all processes of the central nervous system, preventing its excessive excitation or inhibition. There is also an opinion that this element plays an important role in the body’s resistance to fatigue, that is, it increases endurance. The largest amount of asparagine is found in meat.
Amino acid deficiency leads to muscle pain, a noticeable decrease in performance, and memory impairment. However, excess is also dangerous. It can provoke aggression, sleep problems, and headaches.
Arginine
This element is involved in the synthesis of insulin and growth hormone, and also stimulates the body's protective functions. It is very important for muscle growth, as well as maintaining mental health. Due to its active effect on the production of growth hormone, it is not recommended for children to take arginine, so as not to provoke gigantism. Also, excess arginine causes skin problems and allergic reactions, provokes nausea and diarrhea.
To compensate for arginine deficiency, you need to eat dark chocolate, dairy products, wheat, nuts, gelatin, and oatmeal.
Glycine
Glycine is a nootropic and is known to many as a remedy for depression. It is able to normalize the psycho-emotional state, improve memory and learning ability. Glycine deficiency primarily leads to lack of energy and chronic fatigue. People with a deficiency of this amino acid often experience problems with intestinal function and sleep poorly.
Glycine is used in synthetic form. In nature, it is found in beef, liver, and oatmeal. It is very difficult to deal with an excess of glycine, since it does not accumulate in the body, but is freely excreted.
Cysteine
This amino acid protects brain cells from the toxic effects of ethyl alcohol and nicotine, as well as other harmful chemicals. Cysteine also slows down the aging process in the body and facilitates the clinical manifestation of diseases. A deficiency can cause decreased immunity, skin diseases, hair loss, and brittle nails.
Cysteine is present in chicken eggs, garlic, onions, nuts and oatmeal.
GABA
The content of this amino acid in brain tissue is very high. It has an anticonvulsant and sedative effect. Often prescribed for brain pathologies, decreased mental activity, chronic and severe depression. A deficiency in BUN results from excess physical activity combined with poor nutrition and low amounts of nutrients in food. To compensate for the deficiency of this amino acid, it is recommended to drink tea.
Histidine
This amino acid is useful for tissue repair and body growth. It helps fight stress, normalizes the gastrointestinal tract, protects against infections, and removes heavy metals from the body.
Excess histidine leads to psychosis and other mental illnesses. This amino acid also affects sexual arousal. With histidine deficiency, sexual desire decreases, in addition, hearing problems may occur and blood clots may increase. Histidine is found in fish, red meat, and cereals.
Glutamic acid
This is an important neurotransmitter that has a nootropic effect and is necessary for normal brain function. Glutamic acid serves as a source of energy for brain cells. In synthetic form, it is prescribed for epileptic seizures and problems with mental development in children. Glutamic acid deficiency can lead to early gray hair, bad mood, and decreased immunity. Glutamic acid is found in meat products, iconic, and natural milk.
Glutamine
This amino acid removes ammonia from the body and reduces its toxic effects on the body. It improves brain function, therefore it is recommended for people with epilepsy, impotence, and schizophrenia.
Glutamine is produced in synthetic form, but such preparations must be stored as far as possible from moisture, otherwise ammonia will be released. For serious liver diseases, such drugs are not prescribed.
The amino acid is found in many foods, but is destroyed during heat treatment. To compensate for glutamine deficiency, it is recommended to eat raw parsley and spinach.
Approximate regimens for the use of drugs during the transition phase
Light volume training period
Duration 2-3 weeks. Characterized by a decrease in training intensity with a frequency of 3 times a week. After the competitive stage, it is aimed at restoring the athlete’s performance and preserving muscle mass.
Scheme 21
- Karsil (Legalon)
- Vitamin B1, B6, B12
- Safinor
- Trental
Scheme 22
- Karsil (Legalon)
- Vitamin C
- Folic acid
- Calcium glycerophosphate
- Camplamin
Scheme 23
- Safinor
- Cobamamide
- Folic acid
- Ginseng
- Karsil
Active rest period
Duration 2-3 weeks. It is characterized by a sharp decrease in all types of power load, up to their complete elimination. It is useful during this period to switch to other sports and aerobic outdoor games (swimming, cycling, skiing, running, etc., as well as volleyball, football, basketball, etc.). During this period, it is necessary to completely eliminate drugs in order to give the body the opportunity to recover and take a break from the pharmacological load.
Free form amino acids - dosage regimens Currently, free form amino acids occupy a special place among restorative pharmacological agents: Arginine, Histidine, Lysine, Cysteine, Tryptophen, Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine, Glycine, Ornithine, etc. This is due to the fact that a number of amino acids free forms tend to stimulate the release of hormones, in particular growth hormone (somatotropic hormone) and other hormones. Stimulation of one's own hormones leads to a powerful increase in anabolic processes and, as a result, to an increase in muscle mass and muscle strength. They can be taken together with the above drugs or independently at various periods of the athlete’s training.
Schemes for the use (combination) of free form amino acids:
SCHEME 1. 1.2 g lysine, 1.2 g arginine, 0.9 g ornithine. Take on an empty stomach immediately after training or before bed. SCHEME 2. 1-4 g of leucine, 1-4 g of isoleucine, 1-4 g of valine, 100 mg of vitamin B6. Use 30 minutes before training, and 30-60 minutes after it. SCHEME 3. 1 g arginine, 1 g ornithine, 4 g glycine. Take at night, before bedtime. SCHEME 4. 1.5 g of ornithine, 3 g of glycine, 0.5 g of tryptophan, 100 mg of vitamin B6, 250 mg of vitamin PP. Take before bed, on an empty stomach. SCHEME 5. 2.2 g arginine, 1 g ornithine, 1 g tryptophan, 1 g. glycine, 250 mg vitamin B6, 250 mg vitamin PP. Take before bed, on an empty stomach. SCHEME 6.1.5 g ornithine, 2 g tyrosine, 1 g arginine, 1 g vitamin C, 200 mg vitamin B6. Take in the morning, on an empty stomach.
The recommendations are intended mainly for fairly well-trained athletes (fitness, bodybuilding) with at least 1-2 years of training experience.
Where is he kept?
Aminoethanoic acid enters the body from food products. A significant amount of it is found in protein foods, namely:
- beef, chicken, liver;
- chicken and quail eggs;
- cottage cheese;
- buckwheat and oatmeal porridge;
- walnuts, pine nuts, peanuts.
A large dosage of glycine is found in soybeans and pumpkin seeds.
If the required amount of this element is present in a person’s blood, the need to consume sweets will decrease. After all, glucagon is produced by amino acids, and it is an activator of the action of glycogen.
How to use
The procedure for taking Glycine has not been fully studied. Experts accurately name the recommended doses of the drug:
- for athletes during physical activity, the daily dose is from 2 to 6 g per day;
- for people leading a sedentary lifestyle - no more than 3 grams per day.
In this case, it is best for athletes to take Glycine 30-40 minutes before meals. It is allowed to take Glycine during meals or before bed (to normalize sleep). The tablet can be taken neat or swallowed with any non-alcoholic drink.