Today, carbohydrates are the most controversial organic substance found in foods. For years, nutritionists and doctors have taught us that fat is bad and leads to obesity and high cholesterol. People who wanted to lead a healthy lifestyle deliberately removed animal fats and red meat from their diet, which also led to obesity.
Why do carbohydrates lead to obesity? Nowadays, nutritionists say that it is carbohydrates that are to blame for health problems and recommend avoiding them. In turn, WHO guidelines and other health organizations have consistently taken the position that carbohydrates should form the basis of our diet. So where is the truth?
What types of carbohydrates are there?
A young man who has an excellent metabolism, eats fairly healthily and exercises a lot will not gain weight even when his diet is unbalanced (up to a certain point, of course). If every day we eat a lot of carbohydrates and little protein and fat, then every mistake in nutrition will pose a risk of additional pounds for us.
It is also important to separate carbohydrates into different categories:
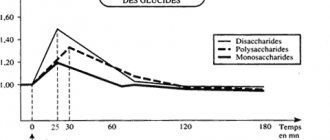
Sugars are simple sugars with a sweet taste that are found in candy, regular sugar, fruit, honey or fruit syrup.
Carbohydrates found in potatoes, flour or vegetables. Under the influence of temperature, the digestibility of carbohydrates increases, this can be easily observed by eating raw and boiled carrots.
Fiber, that is, fibers that the human body is not able to digest. This is important due to intestinal motility and the health of gut bacteria.
Obesity from carbohydrate consumption? The main feature of carbohydrates is that they are a source of easily digestible energy. The body breaks down sugar molecules, which then increase blood glucose levels. This leads to the secretion of insulin, which converts carbohydrates into fat cells, leading to obesity.
Fiber does not directly provide energy, but it does have a positive effect on our intestinal flora.
Human taste buds respond to sugar alcohols (sorbitol, mannitol), which have a sweet taste but do not provide calories. For some people, they cause digestive problems.
Kinds
Having understood what slow carbohydrates are and how they affect the body, it is necessary to study what belongs to this group of nutrients. The main types are:
- Cellulose. These are coarse plant fibers. They improve intestinal function, remove ballast deposits, and give a feeling of fullness. Products containing fiber include whole grain cereals, fruits, greens, legumes, and beets. Fiber is practically not digested, so it is not converted into fat; 90% is excreted from the body naturally.
- Starch. This is a substance characterized by a low calorie content. It helps control blood sugar levels, stimulates metabolic processes and improves immunity. Bread, buckwheat, oatmeal, potatoes, pasta are foods rich in starch.
- Glycogen. This complex carbohydrate is essential for building and repairing muscle mass. There is extremely little of it in food; the highest concentration is found in fish, beef, and liver.
- Pectins. These substances act as absorbents. They attract and remove toxins, poisons, and heavy metals from the body. Pectins are found in root vegetables, algae, and fruits.
Complex carbohydrates have different caloric content, nutritional value and glycemic index (GI). The latter is an indicator of the speed at which the product is broken down and glucose enters the blood. Products with a low glycemic index (up to 40-50 units) are the most beneficial.
Foods with average readings of up to 60-70 units should be taken with caution, in moderation. If a product belongs to the GI category above 70 units, like wheat bread, it is better to exclude it from your diet completely. What foods are not recommended to eat can be found in the table below.
Are all carbohydrates empty calories?
There is a very big difference in quality between different varieties of carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates are now viewed so negatively because they only supply calories and contain no other ingredients. Sugary drinks provide a very high dose of calories and do not give us a feeling of fullness, and also do not supply our body with vitamins and minerals.
The situation with plant carbohydrates is completely different. Regular potatoes, in addition to starch, contain potassium, phosphorus, beta-carotene, B vitamins and a lot of fiber.
A worse product is, for example, refined flour or white rice, which are deprived of the main elements - the grain shell. By eating white buns, you only supply empty calories to your body.
Eating simple carbohydrates can have negative effects, such as blood glucose levels rising and then falling, leading to fatigue and hunger. This condition is less common in people who eat complex carbohydrates. Vegetables (also legumes), fruits and whole grains do not cause blood glucose levels to fluctuate as much and additionally contain fiber, vitamins and minerals.
Is a low carb diet safe?
Every obese person dreams of a diet that will:
- safe;
- not requiring fasting;
- very tasty;
- effective;
- no side effects.
For many people, the solution to obesity is a low-carbohydrate diet. The Atkins, Jan Kwasniewski or Dukan diets allow you to lose a few extra pounds in a short time and can be a salvation for people who need to lose weight because obesity threatens their health.
They can be followed, keeping in mind that increasing the amount of protein and fat you take and limiting carbohydrates may have adverse effects on the body in the long term. Research on this topic is constantly being conducted, and some scientists are inclined to believe that, for example, the Kwasniewski diet has, paradoxically, a beneficial effect on the heart. The diets listed above do not work the same for everyone because each of us has a different metabolism.
Carbohydrate reserves in the body and the process of fat accumulation
A certain amount of carbohydrates (about 500 g) is stored in the body in the form of glycogen, 2/3 of which is in the muscles and 1/3 in the liver. Glycogen reserves in the liver are consumed in 12-18 hours .
If you create a carbohydrate deficiency for a long time, this will lead to the deposition of fat in the liver cells. Therefore, completely no-carbohydrate nutrition and no-carbohydrate diets are very harmful.
Very often, during the period of losing weight, many people cut the amount of carbohydrates to a minimum, hoping that the body will switch to burning fat. But in reality, the process happens differently. More on this later. Carbohydrates suddenly begin to turn into fat only when they are consumed in large quantities or if they are quickly absorbed.
Do carbohydrates cause obesity?
Before answering this question, let's look at what carbohydrates humans have had access to over the centuries. Early humans only had access to fruits in season, and the sugar content of these fruits was much lower than today's varieties. Today in the store you can buy sweets with such a concentrated composition that the human body is not adapted to.
Regular sugars for sweetening or honey were a delicacy, today we replace healthy foods with them every day, increasing our glucose levels to incredible levels. Same with other foods, a hamburger is a pure carbohydrate that will not make you feel full due to the lack of fiber.
Carbohydrates and obesity, where is the connection? The reason for obesity is simple - today a person has unlimited access to food with such a nutrient content that he is not ready for. The main culprit in obesity is carbohydrates, due to the fact that they are much more enjoyable to consume than fats or proteins. A good example is, for example, eating chips or cookies in front of the TV - the brain does not receive information that it is full.
Are carbohydrates necessary for health?
On the other hand, nutritionists sound the alarm that a diet must provide all the ingredients, while biologically a person can do without sugar. When we don't eat carbohydrates, the body enters ketosis, a state in which the brain begins to feed on ketones. Ketosis is also one of the reasons why we lose weight on a low-carb diet without feeling hungry. In this state, blood glucose levels do not fluctuate and we do not feel hungry.
Eliminating carbohydrates completely from your diet won't kill you, but it may have some negative effects.
Foods containing carbohydrates tend to be high in fiber, and a lack of fiber can cause:
- constipation;
- problems associated with intestinal microflora;
- increased risk of cancer (fiber reduces the absorption of chemicals).
- Vegetables and fruits rich in carbohydrates are also a source of vitamins and minerals. They should be divided into good and bad carbohydrates.
Good carbohydrates include all vegetables, most fruits, legumes, nuts, seeds, brown rice and dark, unprocessed flour, potatoes and sweet potatoes.
You will find bad carbohydrates in sugary drinks and fruit juices (even those without sugar), light bread, ice cream, candy, potatoes and chips.
Description and functions of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
is a broad class of organic compounds that perform a huge number of functions. These are integral structural components in all tissues of the human body and consist of two chemical elements: carbon and water.
This is the main source of energy - and therefore the life of our cells. Their content varies significantly depending on the functions performed by the organ - for example, the concentration of glucose in the nervous tissue of the brain reaches 0.5 grams/kg.
- Energy
― this is the main source of energy necessary for the normal maintenance of all physiological processes and functions in the body. This is a substrate that, undergoing a series of biochemical processes, will ultimately be sent as firewood to the furnace of mitochondria. In this, of course, the most important role goes to glucose - it is the main actress of the metabolic performance unfolding on stage.
- Structural
- carbohydrates are part of various components of cells, in particular: nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), which ensure the storage and transmission of hereditary information; glycolipids and glycoproteins located in all tissues and organs of the human body - including the brain and spinal cord.
- Protective
― mucus and joint fluid, of which they are components, protect cell surfaces from various types of damage.
In combination with proteins, they form antibodies, interferons, complement components - in other words, they actively participate in immune defense reactions.
Plasma albumins and globulins, blood clotting factors - all these substances also contain carbohydrate molecules.
- Signal function
- are part of various cellular receptors and ligands.
Remember your high school biology lessons: long carbohydrate chains, called glycocalyx, are anchored into cell membranes. This is somewhat reminiscent of the branched tentacles of an octopus, which extend in all directions, providing intercellular interaction and selectivity in relation to chemical substances entering the body.
- Regulate osmotic pressure
- one of the main parameters of homeostasis.
- Storage
- the liver pantry is prudently filled with glycogen jam.
- Detoxification
- glucuronic acid neutralizes toxic indirect bilirubin by binding to it; as well as various rotting products.
- Included in coenzymes
and other biologically active substances (for example, ATP).
- Carbohydrates can form lipids
,
amino acids
and other compounds.
Should you eliminate carbohydrates from your diet?
If a person has significant obesity, it is very likely that he acquired it through uncontrolled consumption of carbohydrates. Particularly dangerous are simple sugars with a high glycemic index (chips, beer, rolls), which slow down metabolism and contribute to weight gain. If you notice your weight has increased slightly, eliminate simple carbohydrates and limit complex carbohydrates in your diet.
People who don't have weight problems should also avoid typical sweets, but limiting complex carbohydrates will do more harm than good.
Remember that our diet depends on daily dietary choices that will add up over time. If you avoid sugar every day, but you eat chips or pie every now and then, it won't affect your health. However, if you eat them every day, your risk of getting sick will be much higher.