No one will argue that running is the most popular sport of all. Running is practiced by both professionals and just people who want to keep their body in good shape. If you do everything correctly, running will be very beneficial for the body.
Positive effects of running:
- Running promotes weight loss;
- The lungs develop;
- Improves muscle tissue;
- Increases endurance;
- Development of endurance of the cardiovascular system;
- Toxins are removed from the body;
There are three types of running: short distances, middle distances and long distances. This article will discuss in detail long-distance bottom running, its features and technique.
What is long distance running?
Long-distance running is a cross-country race whose length exceeds 3000 meters. This is an ideal sport for keeping the body in good shape. Helps to lose excess weight, strengthens the body, and helps eliminate depression.
Running is accessible to everyone - no need to spend money on a gym membership or buy expensive equipment. At the same time, this is a natural movement that a person learns in early childhood. For example, you first need to learn how to swim or skate, and only then can you begin long distances.
It’s unlikely that you don’t know how to run, which means that the only limitation for a future runner is your health. If you don’t have any problems or complaints, feel free to buy your own sneakers and choose the nearest park. Don't forget to read the article, there is a lot of useful information here!
The technique and tactics of long-distance running need to be honed - without this, you are unlikely to enjoy the activity. This means that the new habit will not stay in your schedule for long. Do you want to know how to quickly learn to run long distances, how to properly use energy and minimize the risk of injuries and sprains? We'll tell you about it right now.
Jumping on a support
We will need a static support 20-40 cm high. Push off the floor with both feet and land on the support and back. The exercise can be performed with both legs at the same time, or in turn. It is performed for a while; to begin with, you can do three rounds of 40-60 seconds and a minute of rest. By doing this activity, you develop your calf and calf muscles well. The ankle is strengthened and the correct movements for running are honed.
Exercises using elastic bands or bands are very useful for runners. Such exercises help strengthen muscles and tendons, thereby preventing injuries and improving the technical part of performing movements.
Race phases
First, let's list the standard phases into which long-distance running is divided. We call them standard because they are present in almost all athletics disciplines:
- Start;
- Starting acceleration;
- Main mileage;
- Finishing.
The entry and exit of each phase requires careful consideration.
- This discipline uses a high start, in which the athlete’s main task is to make a powerful jerk.
- Next, the acceleration phase begins, which lasts 60-100 m. In this phase, the athlete moves at maximum speed in order to gain an advantage. However, during the rest of the distance, the leaders will still give way to each other in order to allow themselves to rest. Therefore, it would be more correct to say that the starting acceleration is needed in order not to fall too far behind the other runners.
- During the main race, the athlete saves energy that will be spent on the finishing spurt.
If you are wondering how many meters long distance running is, we emphasize that the minimum distance is 5 km (a 3 km route is sometimes also classified in this category, however, it is more correct to consider it the upper limit of average races). Next comes 10 km (Olympic discipline), 15 km, 20 km, 25 km, etc. up to the marathon race.
As you can see, the main running phase takes up the lion's share of the entire route, and it is this phase that requires a colossal amount of endurance. The athlete must be able to maintain an even pace and rhythmic cadence.
- Finishing is the phase that determines the winner. It begins 400 m before the final line and requires the mobilization of all the athlete’s strength. There is a powerful acceleration, and in the last 50 meters the athlete demonstrates his maximum.
Running tactics
As an example, I will give three well-known tactics in stayer running. Each of the options was tested in competitions. The optimal tactics can be determined based on personal preferences and indicators that depend on individual characteristics.
Behind the opponent's back . After the start, try to spot an athlete who is capable of showing a good result and follow him the entire distance. There is a chance that the choice will be made incorrectly and then you can cling to a runner who is head and shoulders above your skill and not maintain the pace, or, on the contrary, find that the athlete is clearly behind the group.
Personal experience has shown that tactics work with an error. Once, having caught on to one of the participants, after 3000 meters I noticed that I was stepping on my heels. Having accelerated in the last 5 laps, I won about 300 meters from him, but lost the same amount to the leader.
Leadership. If you have self-confidence, then you can try to pull a group of participants along with you. In this case, two things can happen:
- Your opponents will be forced to run after you as long as they have enough strength, and then noticeably lag behind.
- Among the pursuers there will be a participant who will be much more resilient and will confidently bypass at the end of the distance.
Again from personal experience. I had seen some of the participants before, knew approximately their results and was well prepared for the race. At first, I held the lead of 50-60 meters in the distance. In the last 200 meters, the opponent began to sharply reduce the gap and almost leveled out, which forced him to increase the pace to the limit. After finishing, I was once again convinced that interval running is very useful even over long distances.
Ragged run. In the mid-20th century, the Frenchman Gordon Pirie shone, who was the first to use ragged running as a tactic. He accelerated from the beginning of the distance to a pace close to a sprint and maintained it for 200 meters, then lowered the pace to a level below average. Then the acceleration was repeated. Throughout the distance, the rivals repeated Piri’s actions as long as they had enough strength, and then fell behind.
The good thing about this tactic is that the ability to withstand significant changes in tempo almost guarantees victory. However, the functional state of the body suffers and wears out faster. It is believed that it was precisely the running tactics that did not allow Gordon Pirie to raise a generation of athletes during his coaching activities. He lived to be 60 years old.
The tactics of running in segments are also used, when the athlete sets himself the task of running each part of the distance in a set time. Typically, similar tactics are used during competitive training. That is, the athlete participates in competitions, but his task is not to win, but to complete the task set by the coach.
Features of the technology
Proper long-distance running technique for beginners involves careful development of 4 aspects.
- Body position.
According to the rules of long-distance running, the slower the athlete moves, the more vertical the torso is held. During acceleration, there is a slight lean forward. The head is held straight, the gaze is directed forward. You should not look around, look around, or be distracted by others. Relax your upper body, bend your elbows. You can bend slightly in the lower back, bringing your shoulder blades together.
- Hand position.
The arms move synchronously with the legs, in opposite orders. They are held close to the body, bent at a right angle. Many people are interested in how to increase their speed in long-distance running, and they will be surprised to learn that arm movements have a significant influence on this process. To put it simply, the faster an athlete moves, the more energetically he works with his arms, thereby helping himself to increase his pace.
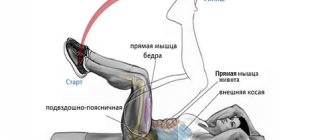
- Leg movement technique.
Let's continue to figure out how to learn how to run long distances correctly. Let's move on to the most important part of the technique - moving the legs. When running, it is important to place your foot on your toes, gently rolling it onto your heel. At the moment the leg lifts off the ground, the shin moves up to the highest point. At this moment, the second leg fully straightens and pushes. Alternation occurs and a new cycle begins. No matter how strange it may sound, it is also important to be able to relax your legs, otherwise you will not be able to overcome the long route.
- Breath.
The technique of long-distance running requires the development of correct breathing. The latter plays a fundamental role in increasing the runner's endurance limit. If you learn to breathe correctly during long distances, consider half the job done! Just hone your technique and feel free to sign up for the marathon! Breathing should be rhythmic and even. The frequency of inhalation/exhalation depends on the speed of the athlete; the formula “4 to 1” is most often used. This means one inhalation/exhalation is performed for every 4 steps. Inhale through the nose, exhale through the mouth.
Running on uneven surfaces
Running uphill helps improve performance by increasing your lactate threshold and reducing your running time. You can run on uneven terrain or use a special mode on the treadmill. But, unfortunately, on a treadmill you will not be able to simulate running down a mountain, and this is a very important part of training.
- Before running on uneven terrain, jog for 10-15 minutes at an easy pace. Try to find a hill with a gradual slope that extends approximately 100-200 meters.
- Start your uphill run at 5K pace. You'll want to push yourself up the hill, but don't force the form, go gradually. At the top of the mountain, stop, take a short rest and jog down.
- The number of repetitions depends on your experience and level of training. Beginners should start with 1-2 repetitions, adding one additional repetition every week for 3-4 weeks. Experienced runners can start with 6 reps and add one each week, ending at 10 reps.
- After completing all the repetitions, you need to jog for 15 minutes at a slow pace.
How to learn technique and how to increase speed?
Let's look at how to learn to run long distances faster, and also give recommendations for mastering the technique as quickly as possible.
- Preliminary training should be aimed at developing strength, endurance and speed. Choose the optimal program that will improve your performance in these areas.
- Make sure you are healthy enough to actually run long distances;
- During training, it is important to develop all muscle groups, because running uses the muscles of the whole body. Do not forget to add a strength complex to the program, as well as stretching exercises and therapeutic massage;
- Study safety precautions when running long distances, pay special attention to the selection of high-quality shoes and sports equipment.
- If you plan to train professionally, together with your coach, analyze the most successful tactics for overcoming distances;
- The biomechanics of long-distance running involves a significant consumption of glycogen, therefore, the athlete must follow a special diet. The diet should be rich in protein, healthy fats and complex carbohydrates (percentage ratio 20:20:60).
If you are interested in how to improve your long-distance running speed, develop joint mobility, foot flexibility, breathing and willpower. An excellent exercise to improve running endurance is interval running.
To understand how to improve your long-distance running technique, in addition to practice, study theory. Watch thematic videos, communicate with like-minded people, hire a coach. The latter will help identify weaknesses in your training, tell you how to prepare for the race, and explain how to start and where to start.
How to train?
Preparing a runner for distances over 3000 meters includes 4 training methods, carried out as the athlete completes a program plan in which the load is distributed for the week, month and even a year in advance.
- Distance training. Occupies 60-70% of the total load performed by the athlete during training. It consists of jogging for a limited time of 30-50 minutes at a pace of 70-80% of the maximum heart rate.
- Threshold training. It consists of repeating segments of 500-1500 meters several times with a rest break of no more than 2 minutes. The running intensity is about 80-90% of the maximum possible heart rate. With the help of threshold loads, the level of anaerobic metabolism is trained - performing efforts with a high oxygen debt. The later the anaerobic threshold occurs, the longer the body is able to work in optimal condition.
- Interval training. The athlete runs a certain distance (5 or 10 km) and performs accelerations limited by time or distance (1 minute 20 seconds or 400 meters). After which he reduces the pace that was before the acceleration and continues to run for 1-2 minutes or 300-500 meters.
- Speed training. Running is used in segments of 400 meters (circle of the stadium) with the goal of running 5-10 seconds faster than during the entire distance. Thus, the athlete trains speed-strength endurance and develops the ability to overcome each individual segment of the distance faster than before.
Running long distances requires minimal energy expenditure during the effort. This is done by regularly improving technique and increasing the runner's physical fitness.
Benefits and harms
In conclusion, let's look at the benefits and harms of long-distance running, and what this sport gives to ordinary people (not professional athletes).
- Running helps to form a beautiful figure and improves overall well-being;
- Long distance is an excellent endurance trainer, which is important in many sports;
- Blood circulation improves, the body is saturated with oxygen;
- The cardiovascular system is strengthened;
- Veins and blood vessels become more elastic;
- Prevention of varicose veins;
- The mood rises, stress goes away, depression recedes.
At the same time, let us remind you that we are not discussing a standard morning jog of 1-3 km, but a serious and long distance with a completely different technique.
The latter is especially important, because if you master it with an A+, there will be no problems. So, let's find out what the consequences of non-compliance with the recommended movement technique are:
- Failure to comply with the technique can lead to injuries to the musculoskeletal system;
- The cardiovascular system will experience severe stress. If you have heart complaints, we recommend that you consult your doctor and get approval;
- A thoughtless approach to training can cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Make sure you have no contraindications.
So, we discussed what trains long-distance running, what its technique is, phases, features. In conclusion, we would like to emphasize that proper technique is a solid foundation for your future relationship with the sport. Don't be lazy to spend time studying it. This is the only way any marathon race will be as easy for you as breathing!
Top
1.1 Pushups*
- Main muscles involved: pectoral
- video
- 2-3 sets of 8-10 times. If it’s really hard, you can do push-ups from your knees.
1.2 Pullups / chin-ups
- Main muscles involved: latissimus dorsi, trapezius, forearm flexors and extensors, biceps, core muscles
- video: forward grip, reverse grip
An excellent complex exercise and also my pain. With regular approaches to the horizontal bar and at the best of times with a reverse grip, I can do 2 pull-ups. Without regularity - zero times. Direct grip – zero times. I do reverse pull-ups: I climb up using aids, and I try to go down as slowly as possible.
By the way, in the gym I do lat pull-downs with a weight greater than myself, but how to activate the necessary muscles when doing pull-ups remains a mystery.
Reverse grip pull-up – 1 pc.
1.3 Bench dips*
- main muscles involved: triceps
- video https://www.bodybuilding.com/exercises/bench-dips
- 3 sets of 10-12 reps
Any bench, stable chair, or other structure of suitable height will do. The further the legs are extended forward, the more difficult it is. Elbows should be bent to 90 degrees.
A lighter version of the exercise. To make it more difficult, you need to stretch your legs forward with emphasis on your heels, and lift your toes up.
1.4 Dumbbell shoulder press
- Main muscles involved: shoulders
- video
- 3 sets of 8-10 times
1.5 Dumbbell lateral raise
- Main muscles involved: shoulders
- video
- 3 sets of 8-10 times
1.6 Front dumbbell raise
- Main muscles involved: shoulders
- video
- 3 sets of 8-10 times
1.7 One-arm dumbbell row
- main muscles involved: back (middle part)
- video
- 3 sets of 10-12 times