Kettlebells are an excellent exercise tool, but this type of training is not for everyone. Let's start with the fact that to practice with them you need to have some skill and get used to them. But the main thing here is that they have weight restrictions. It’s unlikely that any of you have seen a weight weighing more than 32 kg.
However, kettlebell CrossFit is common enough that many professional athletes have contributed to this type of training. Although kettlebells cannot be classified as a separate type of exercise, they can introduce many innovations into the training process.
What muscles are involved?
Kettlebells in CrossFit are used both simply as additional weight and as separate equipment. On one hand, you can pick up a kettlebell and squat it to increase your overall weight. On the other hand, you can do kettlebell swings, and then you will work exclusively with their weight.
There are a huge number of exercises for which a kettlebell is suitable. We can say that with the help of this projectile you can effectively work out almost every part of the body. Let's look at some of them.
Crossfit complexes
| Name of the complex | W.G. |
| Task: | Complete as many rounds and reps as possible in 10 minutes. |
| Tasks: |
|
Strength functional training (CrossFit) contains a huge number of exercises that can be effectively combined with the kettlebell squat press. You can come up with your own complex, and do the exercise for about 5 sets per workout. The number of repetitions may vary depending on your training experience.
Athletes who practice CrossFit often work using a superset system. You must perform all exercises without resting between them. This can include fast, intense cardio movements, as well as dumbbell presses and rows. With regular training, the kettlebell squat press will help strengthen a large number of muscle areas in the body.
Author Yaroslav Khvatov
Training experience - more than 8 years. Winner and medalist of All-Russian powerlifting and deadlift tournaments. Candidate for Master of Sports in deadlift.
Alternating kettlebell swings
For this exercise, you will need relatively light weights so that you can easily perform each arm separately. Thus, the shoulder girdle is well worked out, especially the front and central beam.
In addition, the exercise develops grip and forearm strength well, and also engages the core stabilizer muscles.
- Stand up straight, take a weight in each hand with an overhand grip;
- In the initial position, the arms with weights hang freely along the body;
- Raise your outstretched arm forward so that it reaches shoulder height—no need to raise it any higher;
- Hold your hand at the highest point for a second, then slowly lower it, and repeat for the other hand.
During the exercise, you must keep your back straight and not slouch. There is also a variation of the single kettlebell swing. The exercise has a slightly different execution technique, so it will be considered separately.
How to replace the French bench press?
Today there are quite a lot of exercises for triceps. However, none of them provide as much progress as the French press. This is achieved through the biomechanics of movement and concentration of the load exclusively on the triceps muscle.
However, despite the accessible technique, some may find it difficult. Because:
- You need to constantly monitor the position of your elbows and at the same time concentrate on the target muscle.
- Some cannot perform the exercise due to damage to ligaments, joints, certain injuries, etc.
- Doing the same exercise for a long time is not recommended. The muscles adapt and the response to the load becomes weaker.
Let's try to look at other triceps exercises that can become a complete alternative to the French press.
No. 1 Close-grip barbell press
A wonderful analogue of the narrow barbell press, it is a basic exercise that loads:
- lateral head of triceps;
- inner chest;
- front delts.
The main advantage is that, unlike the French press, the elbows are not so heavily loaded. Thanks to this, even if you have certain problems, you can work with light weights as part of exercise therapy complexes.
No. 2 Extension of arms in a block simulator
A worthy alternative, however, is more suitable for “polishing” the triceps, as it allows you to achieve relief and endurance. However, if you use the maximum working weight, you can achieve an increase in strength and mass.
But, still, you should not rely on this exercise, since this will not be enough for the triceps alone. Use different handles, perform with two hands or one at a time. In the second case, you can achieve better stretching of the muscle.
No. 3 Lifting dumbbells from behind the head
The biomechanics of the movement are similar to the French press, but there is still a difference due to the fact that the movement does not go straight down, but to the side. Those. the dumbbell moves in the direction of the opposite shoulder, which, on the one hand, relieves the load on the elbow joint, and on the other, puts the most load on the long triceps bundle. At the same time, the remaining beams do not receive sufficient load.
No. 4 Push-ups with emphasis on the bench at the back
An excellent exercise in which you can work either with your own weight or use weights. But, as a rule, in most cases, your own weight is enough. The technique is simple:
- We rest our palms on the bench behind us.
- We stretch our legs forward and leave them on the floor or, to complicate the exercise, we throw them on another bench.
- By bending the arms at the elbows, we lower them as low as possible.
Most of the load goes to the medial fascicle, and the deltoids and abdominal muscles also take an active part.
#5 Push-ups with narrow arms
The biomechanics of the movement are somewhat reminiscent of a close-grip bench press, but we work with our own weight. This engages not only the triceps, but also the inner chest, as well as various stabilizer muscles, ligaments and tendons.
One alternative to push-ups with a narrow arm position is diamond push-ups, which are definitely worth trying. By working with your own body weight, you can increase the strength and volume of your triceps. Also, the use of weights is allowed.
#6 Dips
A great bodyweight exercise that focuses on the lateral and medial heads of the triceps.
It is very important to perform push-ups technically and not spread your elbows to the sides so that the load does not shift to the joints
Swing kettlebells with two hands
This is one of the basic kettlebell exercises in CrossFit, allowing you to work several large muscle groups at once: arms, core muscles, hips, buttocks and back.
- Take the weight with both hands and hold it between your legs;
- Squat down slightly so that the weight is below knee level;
- Carry out the simultaneous movement - straighten your knees and throw your arms up, lifting the weight to the level of your head.
There are many variations of this exercise, where you can throw the weight up to overhead level. The greater the amplitude of movement of the kettlebell, the more the muscles of the shoulders and arms are involved in the movement.
Execution technique
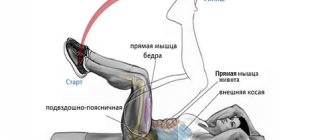
So how do you perform goblet squats correctly? Despite its apparent simplicity, this original exercise has the most complex technique. Otherwise, its effectiveness decreases and it becomes very traumatic.
So, the correct technique for performing goblet squats is as follows:
- To begin with, the correct projectile is selected. Ideally, for beginner athletes, this is a kettlebell weighing 8-12 kg with a short handle.
- Next, take the starting position. While maintaining a bend in the lower back, you need to lift the weight with both hands with a medium grip to chest level and hold the projectile in this position.
- After the position of the weight is fixed, you need to do a squat. The technique of the squat itself is extremely simple - it looks like a deep squat with a large protrusion of the body back.
- Having descended to the lowest point, you need to make several springy movements with your toes while maintaining balance.
- After this, we raise the body while maintaining the deflection in the lower back.
Kettlebell push
This exercise is designed to work the areas of the legs, back extensor muscles, shoulders, pectoralis major, arm and forearm muscles.
- Hands with weights are folded on the chest - wrists facing each other;
- The legs are set slightly wider than shoulder level;
- The exercise begins with the legs - first do a small squat, slightly tilting the body back;
- Make a powerful push with your legs and back, while at the same time throwing your arms up and pushing out the weights;
- Next, you need to sit under the weights with your knees slightly bent;
- Then, finish the movement by fully straightening your legs.
- At the top point, your arms should be fully straightened and positioned above your head.
This exercise has many different variations, but the classic one, with a small range of motion, was considered here.
Kettlebell Squats
In principle, the exercise can be classified as classic squats, with the only difference being that you will hold the additional weight in your hands.
- Take the weight by the handle and press it to your body at approximately chest level;
- Place your feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart;
- Squat down, trying to move your pelvis back and not bring your knees beyond the line of your toes;
- Pause at the bottom for a second and return to the starting position.
Squats using weights can be very different - some prefer to use two weights. You can hold the kettlebell at chest level, above your head, behind your head, or on the sides of your body. Various variations shift the main emphasis of the load to one or another area of the legs.
Rowing
If you want to build or maintain more muscle while burning buckets of fat, it's time to tap into rowing power.
You can burn a ton of calories in a short time, making this exercise ideal for achieving an athletic physique for an athlete who doesn't like cardio or doesn't have the time to do it.
Performance:
To start, simply set the footpegs to match your foot size and the damper to the distance you intend to walk. For example, if you plan to do interval training that will require less overall training time, set the damper above the 7-9 mark. If you are going to work over a longer distance and time, use range 4-7.
From the beginning until the end of the movement, maintain correct posture and aggressively push your feet off the footrests in the same manner as you would perform a leg press. The only difference is in the leg press, no sudden movements.
When your legs become almost straight during the movement, lift your chest up and lean back while pulling the cable handle towards your chest. Pause for a second, straighten your arms, bend your hips and waist forward, and then bend your knees, returning to the starting grip position.
Overhead Kettlebell Lunges
A fairly complex technical exercise that is recommended for athletes with at least an average level of training. In addition to the muscles of the lower body, it develops the core muscles and flexibility of the athlete, and additionally helps improve coordination.
- Raise the weights with your arms straight above your head. For convenience, the grip should be such that the weight is behind the level of the body, and not in front of it;
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart, keep your back straight, gaze directed forward;
- Lunge with one leg forward. At the same time, do not violate the position of your arms and back - they should always remain straight;
- The back leg should lower to the level at which the knee touches the floor;
- Return to the starting position and repeat on the other leg.
It is recommended to first practice the technique with minimal weights, then use heavier projectiles.
Jump on the stand
The jumping jack is not exactly an advanced exercise. It has been used by athletes and crossfitters for years, but it definitely has a place in the training program of right-thinking athletes. Explosive movements have been shown to excite the central nervous system, thereby improving athletes' energy output during a strength training program.
A more advanced form of this exercise is jumping on a block with additional weight (for example, a medicine ball) - the ideal potion for gaining muscle mass. Try doing three sets of five reps and practice your technique before you consider using additional weight.
Performance:
The exercise can be done on any safe surface 30-60 centimeters high, but plyometric boxes will work best. The athletic ability and strength of your lower body will determine your boxing height. Start at 30 cm and progress from there. Take the starting position in front of the cabinet, standing straight, feet shoulder-width apart. Squat down slightly to jump, moving your arms back.
Using the strength of your thigh muscles, push off the ground, swing your arms forward and jump as high as possible onto the box. Land softly on both feet in a squat with your thighs just above parallel. Get off the stand and repeat the movement.
Kettlebell row to the chin from a squat position
It is also called the high pull deadlift. One of the most popular kettlebell exercises in CrossFit. Allows you to develop the strength of the leg muscles, and also works well on the deltoids and forearm strength.
- You need to start the exercise from a squatting position. Hands on the handle of the weight, the weight stands on the floor;
- Perform a powerful jerk upward using the strength of your legs and back;
- At the same time, begin to lift the weight up so that when your legs are fully straightened, it is at chin level;
- At the top point, your elbows and palms should be higher than shoulder level.
Exercise also helps improve muscle tone in the lumbar region.
Romanian kettlebell deadlift
The exercise helps to stretch the lower back and buttocks, and is excellent for their comprehensive training.
- Take the weight by the handle, your hands should hang down freely with it at approximately the level of your feet;
- The back is straight, the legs are slightly wider than shoulder level;
- Tilt your pelvis back, slightly bending your knees;
- The body should lean forward during a squat, but the back should remain straight;
- Hold this position for a second, then return to the starting position.
The exercise can also be performed with a light kettlebell as a warm-up before performing complex exercises such as deadlifts.
Recommendations for performing the exercise
What are the important points when performing this exercise? Pay attention to the following nuances:
- Firstly, when reaching the lower phase of the amplitude movement in the exercise, it is necessary to protrude the tailbone back as much as possible. Otherwise, the lower back under the shifted center of gravity is subjected to excessive stress.
- Secondly, watch the movement of your knees. Again, due to the changed load and overall center of gravity of the body, you need to ensure that your knees are aligned with your toes. Any deviation from this trajectory greatly harms the joints.
- Breath. Due to the static load, proper breathing must be constantly monitored. In particular, exhale only when rising.
To preserve the knee joints, the exercise is done at a relatively fast pace, but the legs at the knee joint are not fully extended, and a slight tilt of up to 5 degrees is maintained.
It is best to use triple insurance when performing the exercise (especially at first):
- weightlifting belt - to preserve the muscles of the lower back;
- straps for holding weights with the muscles of the forearms - since for many, the static load may be excessive at first;
- knee pads and elastic bandages that secure the joint.
Push-ups + kettlebell rows
Includes classic push-ups, as well as kettlebell rows for the latissimus dorsi and rear deltoids.
- Place two weights on the floor and take a lying position so that your hands rest against the arms of the weights;
- Do push-ups;
- After the push-up, raise one hand with the weight to about the level of your stomach;
- When you pull the kettlebell, you should tense your lats, trying to bring your shoulder blades as close together as possible.
You should pay great attention to how you pull the kettlebell back. The main effort should come from contracting the latissimus muscles, not the biceps.
Execution technique
Technically correct execution of the exercise is only possible with adequate weight. Kettlebell fitness experts recommend that women start with a weight of 8 kg, and men - 16 kg. It makes no sense to use smaller projectiles, since the core cannot be used with them.
Classic version
The most difficult thing here is taking the projectile in the stance. The tilt is performed by flexing the hip joint, and the athlete grasps the kettlebell or dumbbell with both hands on both sides. Then, due to extension in the pelvis with slightly bent knees, the weight is placed on the chest
It is important to “substitute” your chest under the weight so that it loads the center of the body, and is not just held by your hands. During the lift, the back is tense, the shoulder blades are brought towards the spine, the abs are tightened
After capture comes stabilization. You should not immediately bend your knees and sit down. The athlete must stabilize the center of the body so that the weight rests firmly on his chest and does not slide. The point is to redistribute the weight between the body and arms so that the athlete does not overexert himself and does not squeeze the weight with his hands. This is an important skill, it is practiced separately. If you don’t work it out, you won’t be physically able to lift a normal weight of weight onto your chest.
After stabilizing the weight, you need to place your feet so that the heels are slightly wider than the pelvic bones, approximately at the level of the middle delta. The toes of the feet are spread to the sides, as convenient as possible. The athlete bends the knee and hip joints, and at the same time drives the knees towards the toes.
The bottom of a squat is the point at which the pelvis drops below the knee. Ideally, the thigh is in full contact with the shin. Achieving such depth should only be achieved by those athletes who can avoid the “pelvic dive,” that is, turning the pelvis at the bottom of the squat in the opposite direction.
This option allows you to fully stretch your gluteal muscles and use them to start from the bottom. The buttocks contract, the impulse is transmitted to the thigh muscles, the knee and hip joints extend. The goblet should be one, unified movement, in which there is no room for tilting the body, or moving the pelvis upward due to active contraction of the back muscles and upward thrust of the hips.
The point of the exercise is to keep the projectile in front of your chest at all times. Other implementation options are not allowed.
Goblet Squat / Goblet Squats. Crossfit
Watch this video on YouTube
Sumo option
The goblet squat in sumo refers to the same movement with very wide feet. So much has not been written about its benefits. Some people believe that this way the quadriceps are turned off from work, but in fact, this option does not turn off the quadriceps, but simply leads to the fact that the adductor muscles of the thigh are included in the work
Therefore, those who are afraid to pump themselves up at least something should pay attention to this valuable information
The sumo variation requires significant flexibility and mobility in the hip joint. The athlete takes a wide stance, knees pointing almost to the sides, feet turned out strongly. The movement of the knee joint is in the same direction as the toes, that is, not in a plie, but in a slightly smaller angle. It is advisable to lower the buttocks below the knee joint.
The movement is considered beneficial for the development of the gluteus medius muscle, since pushing out the weight occurs due to the contraction of this particular muscle.
Pros and cons of using kettlebells in training
The kettlebell is a universal apparatus with which you can diversify any program. In addition, it can also be used as a simple weight when you need to use additional weight.
The undoubted advantage of using kettlebells is that they can be used to work every muscle group of the body, depending on the exercise. In addition, with the help of such a projectile you can create an effective program for home workouts.
The downside of kettlebells is that they have too large weight gaps. That is, there are weights of 4, 8, 12, 16 kg and so on. When using dumbbells, the weight can be adjusted up to 0.5 kg, which is much more convenient for both beginners and experienced athletes.
In addition, the weight of the weights is limited. That is, you will not be able to properly train for muscle mass - since you will have to use either weights that are too light or too heavy for you. You won't be able to gradually increase the load as you would with dumbbells or weight plates.
Using kettlebells in CrossFit requires one more factor. You can achieve the correct execution of the exercise only if you have a strong grip. This is especially true with heavy weights - you can easily pull it with the target muscle, but whether it will slip out of your wrists or not is another matter.
Therefore, we can say that working with this sports instrument is more suitable in CrossFit programs with kettlebells for men.
For girls, it is better to pay attention to dumbbells and other types of weights. Video Kettlebell Press
How to replace the bench press?
A few years ago, I ran into a problem that forced me to look for something to replace the bench press with. During one of my chest workouts, while performing a bench press, I felt a sharp pain in my left shoulder joint. It is clear that I could no longer perform the bench press on a horizontal bench. I had to look for some kind of replacement for this exercise. I found that when performing the bench press on a positive incline bench, there was virtually no pain. Therefore, to work the pectoral muscles, I used two basic exercises - the incline barbell press and the incline dumbbell press. Of course, I started with light weights. After a few months, the pain completely disappeared and I could already perform a bench press on a horizontal bench. But what to do if it is not possible to perform a bench press? What then can you replace this exercise with?
In bodybuilding, all exercises are usually divided into basic (multi-joint) and isolating (single-joint). The bench press is a basic exercise for the pectoral muscles. Therefore, you also need to replace it with a basic exercise for the chest muscles. Replacing a multi-joint exercise with a single-joint one, for example, a bench press with a dumbbell fly or vice versa, is not correct, or rather, not an acceptable option. Only as a last resort, if you do not have the opportunity to replace the bench press with another basic exercise, you can replace it with an accessible isolation exercise for the pectoral muscles.
Let's look at what multi-joint basic exercises for the pectoral muscles are:
- bench press at various angles;
- dumbbell bench press at various angles;
- push-ups on parallel bars with a forward bend;
- Hummer bench press;
- wide grip push-ups.
A better alternative to the barbell bench press is the dumbbell bench press. Unlike the barbell bench press, the dumbbell bench press is a more natural movement and has a greater range of motion, which allows you to use small stabilizer muscles and better work the pectoral muscles.
Bent dips are also a good substitute for the bench press. Tilt of the body forward allows you to shift the emphasis of the load from the triceps to the lower part of the pectoral muscles. Push-ups with additional weight significantly increase the load on the muscles, stimulating them to grow.
To train your chest at home, you can do wide-grip push-ups, but only with additional weights on your back. Push-ups are like bench presses, but in reverse. To evenly distribute the load over the entire surface of the pectoral muscles, place your legs on a small hill. The wider the position of the arms, the greater the load on the chest muscles.
The best exercise for the pectoral muscles
You can often hear that the bench press is the best and most effective exercise for the pectoral muscles. In fact, this is far from the case. The classic bench press is the most popular and common chest exercise, but not the most effective. The fact is that everyone wants to bench press a lot, because the more you bench press, the tougher you look in the eyes of others. If you want to pump up huge and harmoniously developed chest muscles, then I recommend that you perform a bench press with a barbell or dumbbells on a bench with a positive incline, after which you can add dumbbell flyes while lying on an incline bench or crossover curls.
The incline bench press helps distribute the load more evenly across the entire surface of the pectoral muscles. In the case of a classic bench press, most of the load falls on the lower pectoral muscles. In most athletes, it is the upper part of the pectoral muscles that lags behind. Therefore, I always recommend performing incline presses with your head up. The optimal angle of inclination of the back of the bench is approximately 30 degrees relative to the horizontal. Remember that the greater the angle of inclination, the more the load is shifted to the anterior deltoid muscles.