How to practice
If you're working your entire body in one workout, choose an exercise for each muscle group. If you prefer splits, take two exercises from each point and add them to your back day or deadlift day.
Some of the exercises described in the article pump up several muscle groups at once. Take this into account when creating your program. For example, you can choose one that will work both your upper and lower back well, or work these areas separately.
Select the weight of the equipment in such a way that the last repetitions in the approach are difficult, but without compromising the technique. The number of sets and repetitions will be indicated for each exercise.
If the movement is performed with body weight, do it as much as you can.
How to avoid injury?
The lower back is considered the most vulnerable part of the body. It is most exposed to stress. Only twenty percent of adults can boast of a complete absence of pain in this area. This means that performing hyperextension requires maximum caution, since the main load, and, most importantly, the stretching, falls on the muscles in this part of the spine.
To avoid injury, you need to follow a few simple rules that apply not only to sports, but also to everyday life:
- It is necessary to lift heavy objects not with the efforts of the back, but with the legs. If you strain your back, you can easily injure it.
- Do hyperextension not occasionally, but regularly. The best thing, of course, is daily. This will strengthen the most vulnerable part of the body.
- Control your weight. Obesity negatively affects overall muscle tone, health and, of course, the back.
- Stretch your back muscles every day. This will avoid unnecessary tension in this area.
Nutrition is of great importance for the prevention of injuries in the lumbar region. Food should be rich in minerals and vitamins and not empty calories. In order not to have to struggle with excess weight, if there is such a predisposition, it makes sense to periodically arrange fasting days.
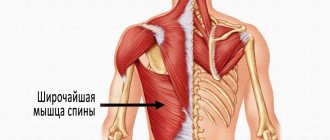
How to do exercises for the latissimus dorsi muscles
These exercises will also help target the trapezius, rhomboids, infraspinatus, teres major, and teres minor muscles.
Upper pulley to chest
Sit on a bench with your feet flat on the floor and grab the handle straight The Effect of Grip Width and Hand Orientation on Muscle Activity During Pull-ups and the Lat Pull-down Effects of grip width on muscle strength and activation in the lat pull -down shoulders - this position of the arms will allow you to put more stress on the latissimus muscles.
You can tilt the body back a little and lock it in this position. Fixation is of great importance: if you want to fully load your back, swinging must be eliminated.
Lower your shoulders and squeeze your shoulder blades together, pull the handle until it touches your chest, and then smoothly and under control return it to the starting position. There is no need to A Comparative Analysis and Technique of the Lat Pull-down raise your shoulders to your ears at the extreme point - keep them down and your shoulder blades retracted.
Perform 3-5 sets of 10-12 reps.
Pull of the lower block to the stomach
In addition to the lats, abdominal rows work well Variations in muscle activation levels during traditional latissimus dorsi weight training exercises: An experimental study of the middle trapezius and rhomboids. Therefore, if you want to pump up both the upper and lower back with one exercise, include this option in your workout.
Sit on the machine, place your feet on the platform, and grab the handle. Lower and straighten your shoulders, straighten your back. As you exhale, pull the handle toward your stomach, then return it to the starting position and repeat.
Do not jerk your back or lean back: only your arms move throughout the entire exercise.
Do 3-5 sets of 10-12 reps.
Incline Pull-Ups
Another universal exercise that works well on almost all back muscles. Unlike regular pull-ups, it is suitable for any level of training: just change the position of the body and legs, and even a beginner can do a pull-up.
Find a low crossbar. If you work out at the gym, you can use a barbell on racks. Grasp it with a straight grip slightly wider than your shoulders: this position of the hands will more engage the latissimus dorsi and trapezius muscles. If possible, do inclined pull-ups on loops or rings - this will increase the load on your back Effects of hand-grip during the inverted row with and without a suspension device: An electromyographical investigation.
Hang on the selected apparatus, tighten your abs and buttocks, and stretch your body in one line. Lower your shoulders and squeeze your shoulder blades together, pull yourself up until your chest touches and lower back down.
You can simplify the exercise in two ways: find a higher bar so that your body is in a more vertical position, or bend your knees at a right angle and place your feet on the floor.
Incline pull-ups can be made more difficult by using elevation. Place your feet on the stand so that your body is in a horizontal plane.
Perform 3–5 sets of 15–20 reps.
Straight grip pull-ups
For maximum loading of the lats, use an overhand grip The Effect of Grip Width and Hand Orientation on Muscle Activity During Pull-ups and the Lat Pull-down slightly wider than shoulder width. If possible, try rotating pads on the horizontal bar: they not only pump up your hands and forearms, but also put more strain on your back.
Grasp the horizontal bar, lower your shoulders and squeeze your shoulder blades together. Pull yourself up so that your chin goes beyond the level of the horizontal bar, lower yourself back down and repeat. When doing pull-ups, do not jerk or swing. At the top point, do not pull your chin up to reach the horizontal bar; at the bottom point, keep your shoulder blades retracted.
You can make the exercise more difficult by wearing a weight belt. Instead of simplifying, it is better to replace it with lat pull-downs or Australian pull-ups.
Perform 3-5 approaches at close range.
Bent-over barbell row
This exercise works well ACE-SPONSORED RESEARCH: What Is the Best Back Exercise?; Comparative electromyographical investigation of the biceps brachii, latissimus dorsi, and trapezius muscles during five pull exercises; Effect of grip width on electromyographic activity during the upright row of almost all back muscles: latissimus, trapezius, rhomboids and even extensor muscles. And if you only have to choose one exercise for your back, this is a good option.
Grab the barbell with an overhand grip slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Bend your body slightly above parallel with the floor, bend your knees slightly, hold the barbell in your lowered hands, squeeze your shoulder blades together, straighten your back. As you exhale, pull the barbell toward your stomach, lower it, and repeat. Do not change your body position until the end of the exercise.
Do 3-5 sets of 8-10 reps.
Exercises for lower back pain: stretching
We offer you stretching exercises for the lower back muscles, which are suitable for eliminating painful spasms and as a preventive measure. Stay in each pose
for 20-40 seconds
, you can use a timer. Remember to do exercises on both sides, right and left. If any exercise gives you discomfort or pain, then interrupt it; the workout should not bring discomfort.
Downward facing dog
From a position on all fours, move your buttocks back and up, stretch your arms, neck and back in one line. Imagine that your body has formed a slide: try to make the top higher and the slopes steeper. You can simplify the position a little by bending your knees and lifting your heels off the floor.
Here and below, photos from the youtube channel are used: Allie The Journey Junkie
How to do exercises for the trapezius muscles of the back
These exercises load the trapezius muscles Comparative electromyographical investigation of the biceps brachii, latissimus dorsi, and trapezius muscles during five pull exercises; Effect of grip width on electromyographic activity during the upright row; Surface electromyographic analysis of exercises for the trapezius and serratus anterior muscles; ACE-SPONSORED RESEARCH: What Is the Best Back Exercise? the best thing.
Barbell row to the chin
Grab the barbell with Effect of grip width on electromyographic activity during the upright row. 1.5–2 times wider than shoulders. As you exhale, pull it up to the level of your collarbones, pointing your elbows up. Lower back down and repeat.
Do 3-5 sets of 8-10 reps.
Reverse dumbbell swings lying on your stomach
Lie on your stomach on an incline bench, take dumbbells, turn your hands back to front. As you exhale, spread the dumbbells to the sides, while simultaneously turning your hands with your thumbs up. Lower back down and repeat.
Do 3-5 sets of 10-12 reps.
IYT climbs
Lie on your stomach on an incline bench, hold dumbbells in your hands. As you exhale, raise your arms above your head with the backs facing up and then lower them to the starting position.
Now raise your arms up diagonally so that your posture resembles the letter Y, with your palms facing upward with your thumbs. Lower to the starting position.
Then spread your arms out to the sides with your thumbs up so that your body resembles the letter T. Lower to the starting position. This was one approach.
Do the same 3-5 times for 4-5 repetitions.
Lower lat region
Use reverse-grip exercises—reverse-grip pull-ups/latt rows, reverse-grip barbell rows—to place more emphasis on the lower latissimus dorsi. One of the few isolation exercises for the lower part of the lats is a pull-down from the upper block with straight arms (standing pullover).
The best exercises: reverse-grip lat pull-downs, straight-arm lat pull-downs.
Reverse grip lat pulldown to chest
- Grab the handle with an underhand grip, shoulder-width apart. This will allow you to move your elbows back as much as possible, stimulating the lower part of the latissimus dorsi muscles well.
- Keep your torso straight and bend slightly at the waist, extending your arms fully up. Keep your chest forward and arched throughout the movement; this will help concentrate more load on the back muscles.
Tip: To focus on working the lower lats, keep your chest high and your back arched. When you pull the handle down, pull it towards your upper chest or even a little lower for better muscle contraction.
Straight arm lat pulldown
- Grasp the handle of the overhead pulley with both hands and stand far enough away from the machine to keep your arms almost straight (with a slight bend in your elbows) throughout the movement.
- Pull the handle down in an arc with straight arms until it touches your hips. Concentrate on feeling the movement of your lats; your hands should act as levers.
- Movement should occur only in the shoulder joints.
Tip: To further contract this area of the lats, perform the exercise with one hand, this will increase the range of motion beyond the hip, which will contract the muscle more strongly.
How to do back extensor exercises
These two best exercises are Trunk muscle activity during stability ball and free weight exercises; Muscle activation during various hamstring exercises for the back extensors work well on the entire posterior chain, including the glutes and hamstrings.
Deadlift
Stand over the barbell with the bar over the laces of your shoes. Push your hips back, bend over with a straight back, and grab the barbell with an overhand grip slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
As you exhale, straighten your hip and knee joints, keeping your back straight. Bring the barbell close to your shins, almost touching them. Lower it to the floor and repeat.
Perform 3-5 sets of 6-8 reps.
Hyperextension on GHD
This exercise is often used at the beginning of a workout to warm up and strengthen the back, buttocks, and hamstrings.
Place your feet under the rollers of the GHD machine and place your hands behind your head. Lower your body and then return to the starting position. At the top, rise above the parallel of your back with the floor and look forward. Perform smoothly and under control, without rocking or jerking.
Do 3-5 sets of 15-20 reps.
You can also alternate hyperextension with EMG hold EMG study of erector spinae and multifidus in two isometric back extension exercises of the core and legs on the GHD machine.
Hold it to failure for as long as you can. Perform 3 sets.
What muscles work
To evaluate the benefits of back extension on a bench, you need to take a closer look at which muscle groups are involved in this exercise:
- Straightening the spine. It is the target muscle that is the main focus during hyperextension. It is used both when extending the back at a right angle (90 degrees) until it is parallel to the floor surface, and when straightening the body at an acute angle (45 degrees). The muscle responsible for straightening the spine is a group of bundles that articulate with the pelvis, ribs, and spine. They are located along the entire length of the spine. Their strengthening has a beneficial effect on posture and the correct curves of the spinal region.
- Hip Extenders. Includes the buttocks and muscles located on the back of the thighs. They, like the straightening muscle, are involved when performing any version of hyperextension. The hip extensors, like the core muscles, begin to weaken if not given proper attention. This is true not only for those people who do not lead an active lifestyle. Often, even during training, they are little involved. Thanks to hyperextension, they regain their tone.
- Neck extensions. These extensors are small and located at the back of the neck. They are responsible for the mobility of the cervical spine. These muscles definitely need to be strengthened. This is especially true for people who spend a lot of time at the computer. They awaken and are activated when hands are placed on the head or neck, performing hyperextension. This option is considered more complicated.
The effectiveness of back extension on a bench is beyond doubt. The main thing is to know how to do this exercise correctly.
Hyperextensions - Technique. 7 variations.
Back workout
- Include one exercise in your program that targets each area of your back.
- To work on hypertrophy, after warm-up sets, do 3-4 working sets of 8-12 repetitions.
- To increase strength, do heavy sets with low reps (4-7 reps).
- To increase muscle endurance, use less weight and perform sets with higher reps (15-25 reps).
Mass training that focuses on growing the lats also targets other areas of the back. This workout will look something like the one below (not including the warm-up).
Rest 1-2 minutes between sets.
- Pull-ups (wide grip) / upper and outer lats - 3 sets of 12, 10, 8 reps.
- Bent-over barbell row (wide grip) / outer lats – 3 sets of 8, 10, 12 reps.
- Seated horizontal row on a block (narrow grip) / middle back - 3 sets of 8, 10, 12 repetitions.
- Lat rows (reverse grip) / lower lats – 3 sets of 12, 10, 8 reps.
- Back extension/lumbar region – 3 sets of 12, 12, 12 reps.
Lumbar region
Use exercises that involve you bending at the waist (rather than at the hips to target the glutes and hamstrings) to target the lower back muscle, a critical area to strengthen to prevent lower back pain.
Best Exercises: Back Extension, Stiff Leg Deadlift
Back extension
- Once you're on the bench, cross your arms over your chest or behind your head (this is more difficult); Alternatively, you can press a barbell plate to your chest to increase the intensity.
- Slowly bend down, bending at the waist as deeply as possible, rounding your back as you go.
- Tighten your lower back muscles to lift your torso to the starting position. Do not use jerking movements or lift your body too high; Contrary to what some people call this movement hyperextension, excessive back extension is not a good idea.
Tip: Set up your back extension bench so that your hips are completely supported by the pads. This will prevent hip movement and concentrate the load on the lower back muscles.
Deadlift on straight legs
- In the straight-legged deadlift version, the barbell is brought closer to the floor than in the Romanian deadlift, the range is increased, which works the lower back more.
- As you bend at the waist, leaning down, push your hips back and allow the barbell to hang down freely. Legs should be straight.
- Keep your lower back muscles tense as you resist lowering the weight.
- Push your hips forward as you lift the weight. Stand straight and don't lean back. The bar should rest on your upper thighs.
- When extending your torso, focus on working the muscles of your back and hips, not your arms.
Tip: Unlike the Romanian deadlift, allow your lower back to slightly round in the bottom position with this exercise.