Causes of back pain
Back pain does not only mean serious pathologies. For example, pain when coughing or walking can be caused by simple overexertion. However, it is often a symptom of various diseases, the manifestations of which depend on many factors.
Why does my back hurt after sleep?
Possible reasons why you feel back pain in the morning after sleep:
- hypothermia;
- sudden lifting of weights during the day (or 3-4 days), causing night pain;
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- incorrect body position when lying down;
- incorrectly selected mattress;
- in women, among the reasons is pregnancy;
- curvature of the spine, leading to asymmetric muscle contraction;
- excess weight and muscle weakness;
- stress.
Diseases associated with joints and the spinal column
Back pain means in this case that the following may be present:
- osteochondrosis;
- spondylolisthesis;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- osteomyelitis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- displacement of intervertebral discs;
- Reiter's syndrome;
- intervertebral disc herniation.
Muscle-related diseases
Why do my back muscles hurt?
Very often, muscle pain is associated with heavy workload, fatigue, and hypothermia. Cramping and induration may occur, as well as decreased mobility and soreness (fibromyalgia). In addition, the back may hurt due to the following muscle pathologies:
- Charcot's disease, or ALS;
- dermatomyositis (additionally manifested by a rash);
- rhabdomyolysis;
- polymyositis;
- infection of muscle tissue, abscess;
- polymyalgia rheumatica.
Spinal cord pathologies
The spinal cord is an organ that provides communication between the body and the brain. Through the openings between the vertebrae, pairs of spinal nerves depart from the spinal cord - there are 31 of them. Each nerve innervates a specific area of the body. If you find numbness of the skin (locally), weakness of muscles, limbs, the spinal cord or some nerve may be damaged.
More diseases:
- compression of the spinal cord (for example, with a fracture or cervical spondylosis, abscess, hematoma);
- spinal injury;
- cavities filled with liquid;
- an inflammatory process caused, for example, by acute transverse myelitis;
- impaired blood supply to the organ;
- HIV;
- abscess;
- deficiency of copper, vitamin B;
- syphilis;
- benign or malignant neoplasms;
- hemorrhages;
- multiple sclerosis.
Back pain due to psychosomatics
Psychological reasons are officially recognized by medicine. Psychogenic factors can influence processes that cause dysfunction in a particular location. Thus, chronic stress and long-term depression, dissatisfaction with intimate life can lead to constant aching pain in the lumbar region.
Types of back pain
Different diseases cause different types of back pain. Let's consider the main pathologies and the nature of pain associated with them.
| Nature of pain | Diseases that cause it |
| Aching back pain (acute and chronic) | Lumbago (shooting in the lower back). The reason is hard physical labor. It usually goes away on its own within a few days. |
| Myositis, muscle strain, sudden heavy lifting, hypothermia, maintaining an uncomfortable position for a long time, for example during work. | |
| Displacement of intervertebral discs. The most common cause is osteochondrosis, but displacement can also occur with sudden heavy lifting and constant high physical activity. | |
| Sharp, radiating to the extremities | Osteochondrosis. Causes nagging pain in the back that radiates to the leg and becomes stronger when sneezing, coughing, or straining. |
| Radiculitis. Constant sharp (stabbing) or dull pain. It is usually localized on one side, can radiate to the thigh, buttock, leg, lower leg, and sometimes causes numbness and itching. The pain can also be burning and intensifies with movement. | |
| Intervertebral hernia. With this pathology, pain occurs when bending over, lifting heavy objects, intensifies when sneezing, coughing, moving, and is accompanied by weakness in the leg. | |
| Throbbing pain, severe, may not go away after taking an analgesic | Osteochondrosis, cracks in the vertebrae, lumbago, intervertebral hernia, spondylosis. |
| Bursting | In the upper back and in the middle of the sternum - may indicate angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism. In the lower back - intestinal obstruction, spondyloarthrosis. |
| Pressing | Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, problems with the gallbladder (pain occurs after eating), atherosclerosis, hypertensive crisis. |
Features of pain in women
In female patients, aching pain in the right side of the lower back may be associated with gynecological diseases. If the pain is regular, then it is necessary to at least undergo an ultrasound and check the condition of the internal organs.
For women's diseases
Uterine formations - benign and malignant, in many cases have a symptom in the form of pain in the dorso-lumbar region.
Endometriosis is an inflammatory process that starts inside the uterus, which provokes severe pain that intensifies during menstruation.
Menstrual pain caused by uterine contractions is transmitted to the back.
The pain itself can be of a different nature, depending on the disease.
Typically, pain syndromes from pathologies of the pelvic region organs are transmitted precisely to the area below the lumbar region.
The symptoms are as follows:
- white purulent mucous discharge;
- non-menstrual bleeding;
- burning pain in the perineum;
- sexual intercourse becomes painful;
- urination becomes painful.
During pregnancy
Most women, after they become pregnant, experience problems associated with certain unpleasant sensations in the lower back, below the lumbar region. This phenomenon is completely natural and is associated with natural physiological changes in the structure of the pelvic girdle.
Therefore, aching pain in the lumbar region is a consequence of a very rapid increase in body weight and the retention of the fetus in the lumbar region. In the final months of pregnancy, in addition to your back, your stomach may also hurt, which is also normal and is not a reason to see a doctor.
After childbirth
When labor is over, postpartum patients are advised to undergo spinal correction to avoid chronic back problems.
Common Causes of Low Back Pain
If you have lower back pain, this does not mean that the cause lies in the spine. Lower back pain can be a consequence of diseases of the internal organs, especially the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes pain can be felt due to diseases of the kidneys and genital organs; many women experience lower back pain during menstruation.
However, the most common cause of lower back pain is various diseases and injuries of the spine and back muscles.
It is especially often caused by osteochondrosis, in which the intervertebral discs lose their elasticity and strength.
Sharp, sudden pain in the lower back may be a symptom of a herniated disc or radiculitis. In these cases, the pain becomes stronger with deep inspiration and active movement.
Quite often, pain in the lumbar region occurs in people suffering from slipped intervertebral discs, scoliosis, which is a curvature of the spine, as well as some other growth diseases;
Various inflammations, such as rheumatoid arthritis and Reiter's syndrome, as well as infectious diseases affecting the spine and intervertebral discs (tuberculosis, brucellosis, epidural abscess) lead to severe pain in the lumbar region.
They can also be caused by a tumor located near the spine or in the spinal cord.
To identify the underlying disease causing pain and discomfort, it is necessary to undergo a complete medical examination.
On this topic:
What to do for lower back pain, what treatment methods exist
When prescribing conservative therapy, three main goals are pursued: getting rid of pain, drawing up a program of treatment and preventive measures to treat the underlying disease causing pain, and returning the patient to normal life as soon as possible.
Whatever the cause of lower back pain, medications are most often used to treat the underlying disease. In addition, the doctor may prescribe painkillers - in the form of tablets or ointments, and in case of severe pain - in the form of injections.
As a complement to them - or as an alternative, if treatment with medications is contraindicated - a course of therapeutic massage or manual therapy is prescribed. Of course, massage should be performed by a highly qualified specialist, since if performed incorrectly, it can do more harm than good.
In recent years, patients with lower back pain are often recommended to undergo a course of acupuncture. This method is very effective in relieving pain and muscle tension.
For many diseases of the spine, physical therapy and yoga have a good effect, but such exercises should in no case be carried out on one’s own initiative - the program must be drawn up by a specialist.
It is also important to follow the regime and not overload your back. If you have lower back pain, you should not lift weights vigorously, but moderate exercise is necessary
Try to walk as often as possible and take short breaks during the workday to do a couple of simple exercises and warm up.
Pain in the lower back is always a sign of a disease that will not go away on its own. Painkillers only hide the problem, but do not solve it.
With adequate treatment, as the patient's condition improves, the pain goes away on its own, but complete recovery takes time. To relieve pain, a whole course of measures is required, which can only be carried out in a specialized medical institution.
But no matter what causes lower back pain, it is necessary to find out the cause. If the doctor cannot install it for a long time and prescribes painkillers, there is a risk of the situation getting worse. Then the pain can develop into chronic pain, and painkillers can become addictive.
Relief from lower back pain
One of the modern effective methods of treating chronic pain in modern clinics is the Pain Management technique. The essence of the method is a series of practically painless injections in the lumbar region, which block pain by destroying nerve endings in the area of inflammation. Pain Management is an opportunity to get rid of pain for a long period (one and a half to two years, until the nerve endings are restored) during which, following the doctor’s recommendations, you can take the necessary measures, find and eliminate the root cause of the pain.
To relieve pain, other programs are also used, including drug treatment and physical therapy methods - therapeutic exercises, massage, acupuncture, electrical stimulation, as well as ozone treatment, Botox therapy and much more.
License of the Ministry of Health of the Moscow Region No. LO-50-01-009095 dated October 12, 2020.
Recommendations for self-study
Of course, if it is not possible to contact a specialist, you can try performing one or another set of exercises, but you need to remember that all exercises must be performed smoothly, without jerking, and they should not cause pain. If pain occurs while performing an exercise, then you need to stop doing it and not endure the pain.
The need for an examination (including x-rays of the spine) before therapeutic exercises will be determined by your attending physician. If you do not have illness or pain, and you want to do gymnastics as a preventive measure, then a special examination is not required, but it is better if, for example, an instructor at a fitness club shows you and monitors the correct execution of the exercise.
And the main rule is that at the beginning of independent training, try to avoid excess load, sudden movements, exercises with weights and jumping.
There are basic exercises that help strengthen the main muscle groups, but we must remember that you should start doing them gradually, gradually increasing the load, and also that for each age the exercises will differ in the direction of easing the load.
It is important to monitor your heart rate so that during exercise it does not exceed 60-70% of the MHR (maximum heart rate = 220 - age).
Aerobic exercise is especially useful (ellipse, Swedish walking, walking on a treadmill, jogging, exercise bike, swimming), it should be performed 2-3 times a week, in a pulse zone of 60-70% of MHR, 5 minutes - warm-up, 25- 40 minutes - work in the pulse zone, 5 minutes - cool down.
Aerobic exercise improves the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, increases tissue capillarization, and has a positive effect on the functioning of the endocrine system.
Depending on age and existing diseases, I would classify as basic exercises those that strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, gluteal muscles, and paravertebral muscles in people over 50 years of age. For younger people, it may be more energy-intensive: burpees, pull-ups, push-ups, planks in all its varieties.
An increase in muscle tissue increases overall metabolism and has a positive effect on well-being and overall activity.
Do you trust doctors and their prescriptions?
Yes
20.6%
No
12.06%
I trust, but I check all medications for reviews on the Internet from people who have already tried them and only then do I start taking them.
50.75%
Yes, but only to appointments and doctors from paid clinics.
16.58%
Votes: 199
Why does it give to the right and left sides?
Spinal diseases
Degenerative processes, injuries and other pathologies of the vertebrae, intervertebral discs or nearby structures (nerves, muscles) are common causes of discomfort in the sides.
Most often in this case, the lumbar or sacral spine is affected; less often, the pain can radiate lower due to damage to the thoracic spine.
Spinal disc displacement
Spondylolisthesis is a displacement of a vertebral body relative to another with deviation of the spinal axis. Popularly, this condition is often called “displaced intervertebral discs,” but such a formulation is erroneous, since only the vertebrae can be displaced.
Pathology develops for various reasons (injuries, age-related changes, improper loads, etc.) and leads to irritation of nerve fibers or their complete pinching, which causes swelling, inflammation and aching or acute pain in the back.
Osteochondrosis
Degenerative changes in the spine, or osteochondrosis, are most often observed in older people.
Due to the influence of negative factors, the nutritional processes of the cartilage tissues of the spine are disrupted, causing them to lose elasticity and the ability to regenerate.
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis are limited mobility of the spine and burning, aching or throbbing pain in the back, including the lower back and sides.
If symptoms appear, be sure to visit your doctor.
Vertebral fractures
A vertebral fracture is a serious injury to the musculoskeletal system, which requires long-term and complex treatment. Violation of the integrity of bone tissue occurs due to external influences (strong blow, fall from a height, etc.) and is manifested primarily by pain.
Its features depend on the degree and location of the damage, but most often the pain syndrome is intense, girdling in nature, accompanied by neurological disorders - sensory disturbances in the limbs, headaches, etc.
Attention: pain in the sides that occurs closer to the lower back due to diseases of the spine can be distinguished by two criteria: most often they are associated with movements or changes in body position, and are accompanied by neurological symptoms - sensory disturbances, numbness, “pins and needles” in the limbs, etc. .
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a curvature of the spinal column, which causes asymmetry of the figure and disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
In the first stages, the disease manifests itself as discomfort and pain in different parts of the back (with lesions of the lumbar region, they are localized in the sides and lower back), increased fatigue and impaired mobility of the spine; if the pathological process is advanced, problems with urination and defecation are possible.
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylosis (Bechterew's disease) is a fairly rare pathology of the musculoskeletal system that affects the intervertebral, shoulder and hip joints.
Its symptoms include pain in the back and sides, which intensifies with muscle tension and changes in weather, curvature of the spine, paresis and paralysis. The disease is incurable, progresses slowly but steadily, and usually leads to disability.
Pilonidal hernia
A coccygeal hernia is observed less frequently than hernias in other parts of the spine, since the vertebrae of the sacral region are stronger and more durable.
It develops as a result of a combination of factors, which include degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system, infections and inflammation of internal organs, and trauma.
With a coccygeal hernia, the patient feels severe pain in the coccyx and lower back, which radiates to the sides and perineum, intensifies in a sitting position and is not relieved by painkillers.
Women most often suffer from coccygeal hernia, since the most common provoking factor of the disease is difficult childbirth.
What to do if you have lower back pain
What to do if you feel nagging lumbar pain. To begin with, you can independently determine whether this is a symptom of a disease that requires treatment, or a consequence of an incorrect lifestyle.
If the patient does not have chronic pathologies that can cause this pain syndrome, the steps are as follows.
- take painkillers to relieve or eliminate pain;
- remember whether the lumbar area was exposed to cold and draft the day before. If yes, you can apply light heat to your back (wool, fur, a special belt);
- If the pain was preceded by a strained back from heavy lifting, take a position that relaxes the muscles after taking pain relief medication. Lie with your back on something flat and hard, bend your knees and place a pillow under your knees;
- for pain that occurs during menstruation or pregnancy, you should also take a comfortable position in which the pain syndrome is alleviated.
The pain should not intensify; on the contrary, it will decrease until it goes away completely. Important! If you have a lumbago or a torn back, it may take from several hours to three days to reduce the pain. But if the pain intensifies, takes on a different character, or is aggravated by additional symptoms, you should not hesitate, you need to go to the doctor
What to do?
If the reasons are not due to illness
In a situation where your back hurts and you can’t straighten up, but the condition is one-time, not indicating the presence of a serious pathological process, then several ways will help relieve the unpleasant symptom:
- Take a special therapeutic position. Lie on the floor on your back, raise your knees bent, place your shins on a chair. Move towards the chair so that your hips are at right angles to your body. In this position, the lower back will arch back, the back will touch the floor, the spine will be completely straight from the thoracic region to the sacrum. The pain will disappear immediately; if you spend some time in this position, the compression will go away;
- Kneel in front of a chair, rest your forearms on it. Bend forward and backward, 5-6 times in each direction. Do this slowly, fixating motionlessly at the top/bottom point for a few seconds;
- The starting position is the same as in the previous exercise. Do the same deflections, but now - swaying from side to side. Perform 5-6 bends left and right. At the left/right point as far as possible from the chair, fix yourself motionless for 2-3 seconds;
- Take a pose with emphasis on your knees and palms. Slowly arch your back upward, and hold motionless at the maximum point for 2-3 seconds. Now return to the starting position, lock in it for 2-3 seconds. Then bend your lower back down, fixate for 2-3 seconds at the lowest point, and return to the starting position. Repeat the exercise 5-6 times down/up.
It is forbidden to do therapeutic exercises if you are not sure that there is no pathological process. Gymnastics and massage are contraindicated in case of exacerbation of diseases, as they can cause increased compression, swelling, deterioration of the patient’s condition and well-being. However, the therapeutic position will have a positive effect in acute pathological conditions.
Local heat will help relieve acute pain - a hot compress, warming ointment (Voltaren). General warmth (hot shower) will remove the aching pain. The methods are especially effective for spasms and muscle hypertonicity. It is recommended to maintain physical rest of the affected area for half an hour to an hour after their use.
If the cause is illness
Back pain when bending, which is a sign of a pathological process, must be treated symptomatically and comprehensively - treat both the pain and the cause of its occurrence. Typical approaches to therapy are:
- Osteochondrosis: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures (magnet, UHF) for up to 14 days to relieve inflammation and pain. Chondroprotectors to stop the pathological process. At the rehabilitation stage - massage, therapeutic exercises;
- Spondyloarthrosis, ankylosing spondylitis: a course of NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, physiotherapy. Gymnastics, massage at the rehabilitation stage. Special diet, consumption of vitamins, normalization of metabolism to nourish tissues on an ongoing basis;
- Osteoporosis: similar, excluding chondroprotectors;
- Myositis: short course of NSAIDs, physical rest, physiotherapy (UHF). After the exacerbation is relieved, a course of therapeutic exercises and therapeutic massage;
- Injuries: are treated individually depending on the nature;
- Displacements, scoliosis, weakening of the muscular frame: massage, therapeutic exercises, wearing a corset;
- Urolithiasis: dissolution of stones with drugs, ultrasonic crushing, surgical removal.
Inflammatory processes in organs are treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics and immunomodulators.
5 more types of this movement
In addition to the classic version, there are several different variations.
Classic on outstretched arms
This is a more difficult type of exercise. We perform it in the same way as the previous version, but we focus on outstretched arms.
With emphasis on one leg
We use the same muscles as in the previous version. All back muscles are worked well.
- We perform the starting position, as in the classic plank.
- Raise your right leg parallel to the floor and hold it straight for several seconds.
- We raise our legs one by one until slightly tired. We increase the total execution time gradually.
With swinging legs
The same muscles are involved as in the previous version of the exercise.
- Starting position as in the classic plank;
- We make alternate swings with straight legs. The body remains elongated, like a string.
On one hand
We use the same muscles as in the previous versions of the exercise. But in this case, there is a lot of stress on the hands.
- We take the starting position. We connect our hands in the middle.
- Focus on your right hand, stretch your left hand forward parallel to the floor.
- We repeat the movement, focusing on the left hand, raising the right hand.
Lateral
In this case, we work the following main muscles: peroneus, vastus, rectus femoris, pectoralis minor, gluteus medius, internal oblique and rectus abdominis.
- We squat on our left thigh, lean on our arm bent at the elbow joint and straighten our legs.
- Raise your pelvis to one line.
- Bend your right arm slightly at the elbow and place it on your side. Hold the position for several seconds. We increase the number of repetitions gradually, from lesson to lesson.
- Lower your pelvis and return to the starting position.
- We change the position of the body, squat on the right thigh and repeat the exercise.
When performing any of the plank variations, we first of all strengthen the back muscles and form a muscle corset. This not only helps to achieve the desired slim figure, but is also an excellent prevention of spinal diseases. You can choose any type of plank and perform it several times a day.
Helpful advice! In parallel with the bar, you can connect swimming, fitness, and walking. These types of physical dynamic loads go well with static planks and will allow you to achieve the desired results in a shorter time.
Fitness instructors advise not to forget about balanced nutrition - this will help improve health and control weight.
Causes
Painful sensations in the back occur even due to harmless reasons. If a person has been in an uncomfortable position for a long time or slept on a hard surface, then soon such discomfort will go away on its own. If you experience frequent and prolonged pain attacks, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Natural
Nagging pain in the back does not always indicate the development of a pathological process. Often the cause of such consequences is excess body weight, as well as excessive stress on the back. Staying in an uncomfortable position can provoke discomfort - washing clothes by hand, weeding beds, long-term cleaning of the house. It is easy to recognize such pain - it occurs only when moving and is not accompanied by additional discomfort.
Another reason why the lower back is sore and painful is pregnancy. During pregnancy, significant changes occur in a woman's body. The growing fetus puts pressure on the spinal column, which causes pain. After the baby is born, the discomfort will disappear.
Pathological
The causes of nagging pain in the lower back are not always due to natural processes. Most often, discomfort occurs due to pathological changes in the body. Among the main reasons for this ailment are:
- Osteocondritis of the spine. A disease of the spinal column in which degenerative changes occur in tissues. Discomfort worsens after excessive physical exertion or working with heavy objects. The pain usually radiates to the extremities, and increases significantly when raising the legs. If you tilt your head forward, the discomfort becomes more pronounced.
- Intervertebral hernia. Common pathology of the spinal column. The intensity of pain depends on the size of the tumor. It puts pressure on nearby tissues, causing the nerve endings to contract. This leads to powerful painful sensations. If you do not receive treatment, the person becomes disabled.
- Lower lobe pneumonia and pleurisy. During inflammatory processes in the pleura of the lung, the infiltrate begins to compress the nerve endings on the spinal column. Because of this, a person experiences painful sensations, which are significantly aggravated by coughing. The pathology is aggravated by general malaise, decreased appetite, and increased body temperature.
- Myositis of the lumbar muscles. In this case, nagging pain in the lumbar region occurs several days after hypothermia or prolonged exposure to a draft. The pathology is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, the muscles become inflamed and cause discomfort.
- Cardiovascular diseases. Pathologies in the functioning of the heart valve provoke the appearance of nagging pain in the left side of the lower back. Most often, this symptom is characterized by chronic heart pathology.
- Kidney diseases. Diseases such as nephropathy and renal colic cause pain. Nephritis, traumatic damage to an organ, and pathological processes in the urinary tract can also provoke its appearance.
- Pathologies of the digestive system. Biliary dyskinesia, pancreatitis, and gastroduodenitis can cause pulling sensations in the lower back.
- Gynecological abnormalities. It has been proven that pathologies of the ovaries, cervix, and fallopian tubes can provoke discomfort in the back. The uterus increases in size and puts pressure on nearby tissues. This leads to extremely unpleasant sensations.
- Worm infestation. As the helminths develop, they spread to the entire body and gradually form tubers. Due to their large volume, they compress the nerve endings, after which they begin to cause discomfort in the lower back.
- Oncological diseases. Cancerous tumors in the lungs, intestines, and kidneys can provoke sharp nagging pain in any side of the lower back.
Is pain after or during exercise normal?
The plank requires serious effort, so it is difficult for an unprepared person to stand for a full minute the first time. After only 10-15 seconds, the body will begin to tremble treacherously, and for some, when doing the plank, the lower back or back begins to hurt, which also makes it difficult to maintain the allotted time. If there really is discomfort in the back, you need to stop and understand its causes.
It is normal for your back to hurt after doing the plank, but only if it is muscle pain. Remember your first trip to the gym - the next morning your legs hurt so much that it was impossible to get out of bed? This is a muscle overload that happens when you are too actively immersed in physical education. And the back muscles stop hurting after doing the plank after about 2 weeks, when the body gets used to regular exercise.
If it is joint pain, the problem is more serious. These may be consequences of scoliosis, kyphosis or other spinal pathologies. Such painful sensations will not go away after a while, but will only intensify.
This area hurts most often because it takes the load from the upper body. Constantly carrying heavy weights, sedentary work, incorrect technique for lifting something heavy from the floor - all this leads to chronic osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region. This disease may not make itself felt until there is a strong load on the lower back.
When doing a plank, the lower back often hurts due to insufficient tension in the abdominal muscles. If the abs are relaxed, then a double load comes to the lumbar region. So she can't stand it. The pain can be piercing and sharp, which indicates serious protrusions and the need to urgently consult a doctor. But more often the pain is growing, aching, and does not go away for a long time - the exercise must be interrupted and not resumed until the pain goes away. And consulting a specialist will also not be superfluous.
By the way! If after the plank exercise your lower back or entire back hurts, but there are no pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, then you are doing something wrong (the technique is not followed).
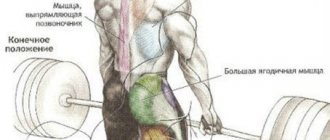
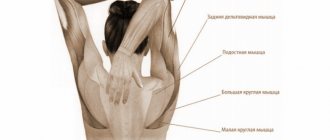
The benefits of this movement and what muscles does it use?
The plank is an excellent option for a static load; it is recommended to perform it in combination with other static exercises, such as the “Chair” against the wall. By performing this movement, we use many important muscle groups:
- pectoralis major;
- Deltoid shoulder;
- The muscle that straightens the trunk;
- Latissimus dorsi;
- Straight hips;
- Intermediate wide hips.
- Gluteus major.
Those who perform this exercise regularly claim that it has a multifaceted positive effect on all back muscles and promotes:
- Strengthening the muscle frame;
- Formation of correct posture;
- Improving blood supply to the spine;
- Improving nutrition of intervertebral discs.
However, if your goal is to get rid of lower back pain and other spinal problems, the 12-step “Crocodile” system from Dr. Antipko, or the legendary Japanese method for the back with a roller, will be much more effective in this regard.
It is also very important to familiarize yourself with the 6 rules of health from Katsuzo Nishi
The benefits of exercise and working muscles
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles ...
Read more "
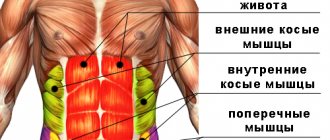
A person feels cheerful if the muscle corset is maintained in good shape. And when performing the plank correctly, the necessary muscles that form its basis are tensed:
- belt (neck);
- deltoid and large (chest);
- rhomboid, deltoid and latissimus (back);
- quadrate and iliacus (lower back);
- straight and outer (stomach);
- intermediate, wide, medial, straight, sartorius (hips);
- anterior tibial (tibia).
It is logical that after the plank the lower back hurts: after all, it is involved in the exercise. Pumping each muscle group separately will take a lot of time, but the bar allows you to achieve similar results in 2-4 minutes a day. It does not provide only cardio load, so you can do a warm-up run before performing the exercise.
Why does my lower back hurt after squats?
As a rule, there can be a whole variety of reasons. Alas, beginners are not always able to determine on their own why their back hurts after squats. Therefore, it is recommended to contact a competent specialist. He will be able to help determine the origin of the pain syndrome and develop measures to counter it.
As practice shows, the main reasons for problems with the back and lower back are non-compliance with the technique of performing the exercise. This is what causes various injuries. No one is immune from this, neither experienced nor newbie.
Main types of painful sensations:
- Muscle microtraumas. They arise as a result of overwork and stretching of muscle fibers. As a rule, they occur as a result of a good load. This is a natural and normal process for muscle growth. Characterized by nagging pain.
- Osteochondrosis. As a rule, it occurs in the lumbar region due to deformation of the spinal column.
- Pinched nerve. Due to the high mobility of the vertebrae, they can pinch nerve endings and cause very unpleasant and sharp pain.
- Intervertebral hernia. If the hernia is large enough, it can irritate the nerve or cause inflammation of the surrounding tissue. This will be accompanied by back pain.
Let's look in more detail at what each of the above problems means.
Muscle pain
We can say that it is the safest and even natural after doing squats. When we feel it, we say, “they pulled the lower back.” But in fact this is not entirely correct:
- When performing squats, the back muscles at the lumbar level are actively involved in the work. Therefore, the muscles in this area may naturally ache later from fatigue.
- Discomfort may remain for 2-7 days, depending on the degree of fatigue and the body’s recovery abilities. Even with the correct technique.
When working with heavy weights, a certain part of it is compensated by the lumbar muscles. That is, your muscles are not yet ready for such weight, so the body evenly distributes the load. For muscle pain, a good remedy would be:
- warm baths,
- regular warm-up
- warming ointments.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
As a rule, such a disease develops over years, and squats only worsen the situation. To prevent this from happening, it is better to work with light weights, and you can use a special orthopedic belt that will give the spine additional support:
If you have such a disease, you can squat, but be careful. This means that strict adherence to execution technique is a prerequisite.
It’s better to squat an extra few times with an empty bar, but do it as technically as possible.
In addition, the best solution would be sumo squats
Due to the wide stance of the legs at the lower back, the range of motion is reduced.
The type of pain in lumbar osteochondrosis is acute. As a rule, it can appear both during the exercise and the next day, within 12 hours after training.
The pain is quite unpleasant and causes discomfort when sitting for a long time and bending the lower back:
- In such a situation, it is better to reduce the load or eliminate it altogether.
- In case of severe pain, painkillers can be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Pinched nerve
Occurs almost instantly, as a result of compression of the nerve by muscles, cartilage or tendons. Just a second ago everything was fine and then there was a sharp pain.
The degree of pain will depend on the strength of the pressure. It can be so strong that you can hardly walk, and in the worst case, you can barely move at all. Then you need to urgently call an ambulance.
If you find yourself in this situation during a squat, throw the barbell back or go as low as possible until you place it on the safety frames. In such a situation, you should abandon the workout and go home.
In most cases, the pain is not severe at first, but the next day it can become so severe that it becomes difficult to walk. It is recommended to consult a doctor.
There can be several reasons why a pinched nerve occurs:
- Presence of intervertebral hernia;
- Rounding of the back due to incorrect technique;
- There is too much weight on the bar that the muscles cannot handle.
Intervertebral hernia
A fairly common occurrence not only among athletes, but also among ordinary people. As a rule, it occurs due to lifting heavy weights with a rounded back, or failure to comply with squatting technique. The vertebrae cannot withstand such a load.
How to get rid of pain?
The first thing to remember is that the exercise should be stopped as soon as the body begins to give distress signals. Take a relaxed position, relax and evaluate your own sensations. It may have just been a muscle spasm or mild strain, but there is the potential for real damage to your health.
Also, pay special attention to maintaining proper technique. After a competent plank exercise, the lower back does not hurt, does not cause a feeling of discomfort or severe tension. These symptoms are sure signs that you are making mistakes. Study our guides on different types of planks and how to perform them correctly to reduce the risk of damage to the body to zero.
We recommend watching a useful video on how to get rid of back and lower back pain:
Associated symptoms and nature of pain
The nature of lower back pain, as well as some accompanying symptoms, can help identify the cause of the discomfort.
| Cause of pain | Symptoms |
| Spinal injuries | The patient tries to take an unnatural position for him; there is a muscle spasm in the inflamed area |
| Osteochondrosis | The patient complains of constant aching pain that radiates to the lower extremities. The back is limited in movement and stiffness is felt. Stiffness can increase with load on the spinal column, with awkward movements, or with bending. If the patient takes a comfortable position, the stiffness subsides somewhat. |
| Consequences of coccyx injury | It is difficult for the patient to change position and bend. Painful sensations can be of a different nature: they can be dull, aching, or sharp, shooting-like. |
| Intervertebral hernia | Discomfort can spread to the lower limbs, groin area, and also to the tailbone. The pain is worse in the morning, but becomes weaker by the afternoon. Sometimes severe pain may subside after the patient "disperses." |
| Pathologies of the sacroiliac joints | The pain is most often one-sided. The patient's gait changes, cramps appear in the lower extremities, and the patient begins to limp. |
| Spondylolisthesis | The pain is aching, dull. Usually appears after a direct bruise or a strong jump. |
| Pathologies of the development of the spinal column | They appear unexpectedly. The cause is usually a heavy load, falling on your feet, or poor body movement. |
| Dilatation of the sigmoid colon | The pain is stabbing, bursting in nature. Usually the pain radiates to the lower abdomen. The patient has stool problems (diarrhea or constipation). |
| Prostatitis | Pain sensations are localized on one side or in the center |
| Malignant neoplasms | Most often, pain occurs in the later stages of the development of the disease and is aching, dull in nature. The pain intensifies closer to night, and weakens after rest. |
| Infectious diseases | The pain is not intense, is constant and does not disappear after rest. During physical activity, the pain intensifies. |
| Metabolic disorders | Painful sensations are long-lasting, aching, not intense |
| Menstrual pain | The pain is paroxysmal in nature, not intense, and can radiate to the lower limbs and groin area |
| During pregnancy | The pain is aching in nature and weakens if the patient lies on her side or in another position comfortable for her. |
Pay attention to these articles:
- Read more about lumbar pain and its nature here
- Why does the lower back hurt on the left and back in men and women?
- Find out what diseases cause low back pain due to bending of the torso, follow this link https://spinatitana.com/diagnostika/bol-v-poyasnitse-pri-naklone.html
- Why walking causes lumbar pain, you will find out on the page https://spinatitana.com/diagnostika/pochemu-voznikayut-boli-v-poyasnitse-pri-khodbe.html
How to do a plank correctly?
Only correct execution will give results. Also, following the technique will help you avoid lower back pain after doing the plank. There are many modifications to the exercise. Let's look at its most popular type, the one most often used to start with - the classic straight bar on the elbows (forearms). You need to lie on your stomach and straighten up completely. Then rest your toes on the floor and place your hands on your forearms. Next, we track the position of each part of the body.
- Head. Slightly raised and eyes looking forward. Or on the floor.
- Shoulders. Perpendicular to the floor.
- Forearms. They lie completely on the floor.
- Breast. Doesn't touch the floor.
- Back. Smooth, without bending or bending.
- Small of the back. Smooth, does not fall through.
- Buttocks. Tense, not protruding.
- Stomach. Tense, does not sag.
- Legs. Straight, toes pointing to the floor.
© undrey — stock.adobe.com
You need to stand in the plank motionless, without relaxing any part of the body. The optimal time is 1 minute. You should do 3 approaches a day.
Features and specificity of the disease
Osteochondrosis is often called the disease of the century. It affects more than 60% of the world's population. The factors causing the disease are numerous: from physical inactivity coupled with extra pounds to excessive sports stress and injuries.
Doctors note that the disease is rapidly becoming “younger” and is increasingly being diagnosed in people aged 23-25 years.
The first and main sign of osteochondrosis is pain in various parts of the back. But this is just a symptom. The mobility and flexibility of the spine is provided by intervertebral discs - cartilaginous plates made of connective tissue. It is they who are affected by osteochondrosis: they become deformed, become smaller in height and thinner. Stiffness, curvature and even immobility of the spine are added to the pain.
In the last stage, the fibrous ring surrounding the intervertebral disc protrudes into the spinal canal, forming an intervertebral hernia. This is the most severe consequence of osteochondrosis, often requiring surgical intervention. In other cases, doctors relieve pain and prescribe physical therapy and exercise therapy.
Depending on the area where the pathological changes began, osteochondrosis is distinguished: