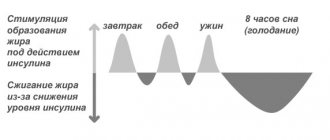
The breakdown of fat as a result of metabolism is necessary to maintain vital body functions. The processed fat is stored as a reserve source of energy that can be used when needed. Fat provides insulation to keep the body warm. Subcutaneous fat is a source of heat when skin temperature decreases. Adipose tissue cushions and protects internal organs and, in addition to the liver, provides a medium for fat-soluble vitamins. The myelin sheath in the brain is also 70% fat. Strength training, as well as gender, can affect the rate of fat metabolism.
Fat metabolism process
Fat metabolism is a collective concept that includes a huge number of different biochemical processes. When diagnosing the state of metabolism, emphasis is placed on 7 main stages.
- Receipt, oxidation.
- Lipolysis is the breakdown of fats.
- Absorption of fatty acids and glycerol (lipid components) in the intestine.
- Metabolism of fat components.
- Metabolism of fatty acids for energy.
- Construction of complex substances of lipid nature.
- Lipogenesis is the formation of fats from glucose that the body does not need.
This is the order in which fat metabolism occurs in humans. Each stage has its own characteristics, and a violation of at least one component leads to negative health consequences.
Features of metabolic processes
Each of the 7 main processes contributes to the functioning of the human body, so you need to know what the essence of them all is. But before that, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic concepts that appear in this topic.
- Lipids (fats) - substances consisting of glycerol and fatty acids, are used to obtain energy or build more complex compounds.
- Lipoproteins are a complex substance consisting of protein and a fat base (it is in this form that fats are absorbed from the intestines).
- Phosphorolipids are a combination of fat and phosphorus group that are involved in cellular metabolism and also serve as a protective layer in membranes.
- Steroids are lipid-based sex hormones that play an important role in fat metabolism and hormonal function.
The meaning will be revealed at different stages of fat metabolism in the body.
Formation of fats in the human body
Fats are esters of glycerol. During the digestive process, they are emulsified by bile salts and come into contact with enzymes, with the help of which they are hydrolyzed. Thus, the released fatty acids are absorbed into the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, which is the end of the process of fat synthesis. After this, the fat passes through the entire portal system of the body as microparticles that bind to proteins in the blood. Metabolism occurs in the liver.
Fat synthesis is possible thanks to excess carbohydrates that do not participate in the formation of glycogen. In addition, lipids are obtained from certain amino acids.
Compared to glycogen, fats are a compact energy store. However, it is not limited in any way, since it has the form of neutral lipids in fat cells. Lipogenesis occurs due to the synthesis of fatty acids, since they are contained in almost all lipid groups.
Intake and oxidation
Fats come into the body from various foods, but unlike carbohydrates, their absorption is much more difficult. After lipids enter the stomach, their primary oxidation occurs under the action of enzymes and gastric acid.
The bonds in these substances are too complex, so only partial release of energy occurs, and fats enter the intestines in a slightly modified form. More aggressive substances act inside the intestines - enzymes, bile and pancreatic juice. They provoke partial breakdown into fatty acids and glycerol.
How fat is formed in the body. How is the fat layer formed in the human body?
Where does lard come from? Fat is an important component of the body, without which its normal functioning is impossible. It is fats, along with carbohydrates, that give a person energy for life and work. If there are malfunctions in the internal systems, for example, due to hormonal imbalance, unwanted fat can be deposited. This is due to the following circumstance: when consuming fat, the human body is prone to producing lipase - enzymes that break down dietary fiber entering the digestive system.
Until the absorbed fats are broken down by lipase, that is, until they are completely broken down, their deposition in the tissues of the body is impossible. After the process of splitting and breakdown in the intestines, lipids enter the blood. In case of their excess, deposition occurs in the form of internal (visceral) fat. This fat forms around the internal organs. The remaining lipids are “converted” into energy to maintain the body’s performance.
How is human adipose tissue structured?
The breakdown of accumulated fat occurs during lipolysis, which increases with a decrease in calorie intake, as well as when a fat person does strength and cardio exercises. In addition, adrenaline and thyroxine are responsible for the breakdown of triglycerides. Insulin, in turn, interferes with the process of fat breakdown.
Important! Before admitting your own powerlessness over obesity and signing up for liposuction surgery, you need to contact an endocrinologist and check your hormonal levels. The cause of obesity may lie not only in overeating and lack of physical activity.
It's no secret that the most common cause of excess weight is gluttony. The daily requirement of a person weighing 65-70 kg for consumed fats is from 1 to 1.5 g per kilogram of weight. The Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation has established the norm of fat consumption per day at a level of 70 to 154 g for men and 60-102 g for women. For comparison, one tablespoon of vegetable oil contains the daily requirement.
How much fat you can gain in a day is a purely individual question. The answer will depend on the individual's metabolic rate, body fat balance, physical fitness, current physical activity, and the amount of calories consumed. According to some scientists, in one day you can gain up to 100 mg of fat. You can gain 1-2 kg in a week.
Lipolysis
This stage can take up to 10 hours. It is influenced by the hormone cholicystokinin (in obesity, it can be produced one and a half to two times more), which commands the gallbladder and pancreas to produce bile and enzymes. They break down molecules to release water, fatty acids, glycerol and energy.
How much the latter will be released can be found out by understanding the formula of the substance, but the average value is 38 calories per 1 gram.
After the decay, the next phase begins. A disturbance in the period can cause a slowdown in the general (energy) metabolism in the body, which is characterized by lethargy, fatigue, lack of appetite, indigestion, and it also affects a person’s weight - it tends to go down, because the required amount of calories is not supplied.
It is worth remembering that lipolysis occurs not only during the digestion of foods. For example, when a person’s body feels a calorie deficit, the body uses internal reserves in exchange.
There is a mobilization of fatty tissue, from where the body can get a lot of energy. Such oxidation is also accompanied by the release of energy, water and other substances. But this happens only when the reserves of glycogen, the body’s stored carbohydrate, run out, because the mobilization of fats is a labor-intensive process.
Basic provisions
Note 1
Fats and lipoids constitute a group of substances that have similar physicochemical properties. Lipoids include fat-like substances: sterols, phosphatides, cerebrosides, etc.
The main functions of fats and lipoids:
- Plastic function. Lipids are an integral part of cell membranes and largely determine their properties (membrane phospholipids).
- Energy function. The heat-forming capacity of fats is more than twice as high as that of proteins and carbohydrates. The breakdown of 1 g of fat releases 38.9 kJ of energy.
- A significant amount of hormones are of lipid nature.
- Subcutaneous fats support the body's thermal homeostasis.
- Fats contribute to the supply of certain vitamins to the body: D, A, K, E.
Body fats are triglycerides of palmitic, oleic, stearic and other higher fatty acids.
The main part of lipids is found in adipose tissue (subcutaneous tissue, in some organs - muscles, liver, around organs - perirenal tissue).
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Lipid metabolism and its regulation. Fat depot 480 rub.
- Abstract Lipid metabolism and its regulation. Fat depot 260 rub.
- Test work Lipid metabolism and its regulation. Fat depot 210 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Fat depots are places where adipose tissue accumulates in the body.
The total amount of lipids in the body is normally 10-20% of body weight, but can vary widely. In morbid obesity, the proportion of fat can be up to 50%.
The amount of reserve fat directly depends on the amount of food, the nature of nutrition, the characteristics of the body’s constitution, age, gender, and characteristics of energy consumption during physical activity.
The amount of protoplasmic fat is a constant and stable value.
Suction
Once oxidation and breakdown has occurred, the body needs to "take" fuel from the intestines and meet the body's energy needs. Cell membranes are made of proteins, so penetration of fats would take a long time. Nature decided to facilitate this process by “clinging” proteins to them, forming lipoproteins, which are quite quickly absorbed by the intestinal villi into the blood.
With obesity at this stage, hyperfunction of the villi occurs, that is, they take up to 98% of the broken down fat, and the norm of this value fluctuates within 70% (exactly how much lipids can be absorbed depends on age, activity, and genetics). Next, lipids enter various organs, where they can change, provide energy for work, or become the basis for other substances.
General information
Fat metabolism in the body, contrary to popular belief, is a fairly important component of the full metabolism of all nutrients. The thing is that many people misinterpret the transformation of fatty acids into nutrients. So, when a fat cell enters the body, it begins to disintegrate under the influence of lipase enzymes.
Then some factors come into play.
- Is fat tissue consumed with anything else?
- Is there enough lipase enzymes in the body?
- Type of adipose tissue.
- Presence of transport protein.
If adipose tissue is consumed along with carbohydrates, then the body, under the influence of an insulin injection, opens all cells, and circulating polyunsaturated fatty acids are simply sent directly to the fat depot to complete triglyceride molecules along with carbohydrates.
If adipose tissue is consumed separately, then with a sufficient amount of transport protein, the molecule in a split form enters the organs. Due to the fact that different types of adipose tissue have different numbers of cholesterol molecules, there is a major myth associated with it. If you eat fatty foods, then during transportation “bad cholesterol” settles on the walls of blood vessels. This is due to its sticky structure.
At the same time, the completed form of cholesterol, which is involved in the synthesis of sex hormones, is not sticky and, therefore, will not stick to the walls of blood vessels, which will lead to complete delivery of the polyunsaturated fatty acid to the target organ.
Building complex substances
Lipoproteins, phosphorolipids, glycolipids, steroids, esters... The list of complex substances that the human body can create from fat can be continued for a very long time, but the essence is the same - you need to use fat. It enters the blood into the adrenal glands, the site of steroid synthesis, and penetrates the Golgi cell complex, where the main synthesis of complex substances occurs. Many factors influence this: hormones, enzymes, signaling substances. The liver, genitals, and other hormonal organs can also “complicate” fats.
Disruption of processes at this stage negatively affects hormonal levels, slows down cell regeneration, and impairs the absorption of substances. This can even be noticed by the condition of the skin, for example. If it peels off, but at the same time it is very dry and reddish, then there has been a failure in the synthesis of complex fat-based substances.
Fatty acid metabolism
When the human body has satisfied all the needs for building substances, the metabolism of fatty acids starts, which go directly to the needs of the body. How much of them needs to be split depends on the person’s activity during this period of time.
Mobilization of amino acids from the cytoplasm of cells occurs in mitochondria, where energy is extracted from them. If the metabolism at this stage is slowed down, then weakness is felt, and fatty acid residues accumulate. Such a violation leads to excess weight gain.
How fat is formed in the human body. Types of fat in the body. Subcutaneous and visceral fat
There are 2 types of fat in the human body:
1) subcutaneous
2) visceral
, as you already understood from the name, is located under the skin in our body, throughout the body. If excess calories begin to enter the body for a long time, then subcutaneous fat is deposited first. Moreover, the structure of subcutaneous fat depends on what foods you eat. For example, excessive consumption of lard (lamb, pork) leads to the fact that the fat layer becomes dense and elastic, this is especially noticeable on the stomach. But excessive consumption of high amounts leads to the fact that the fat layer becomes flabby and viscous, and has a jelly-like structure.
Also, where this fat will be deposited first depends on what gender you are, woman or man. In men, subcutaneous fat is primarily formed on the abdomen. But on women’s legs and buttocks.
is fat that accumulates around the organs of our body. When excess calories enter the human body for a long time, subcutaneous fat is deposited first, and then visceral fat. Well, when the moment comes when a lack of calories enters the human body, the opposite is true. Visceral fat “burns” first, and only then subcutaneous fat.
Both men and women are prone to the deposition of visceral fat. You have all seen people with oversized, huge bellies; in men it is also called a beer belly. So a huge beer belly is nothing more than excess visceral fat.
Spring fat metabolism
There is such an unscientific term as “spring metabolism” of fats. Every person experiences it, and it is associated with seasonal nutrition. How many vegetables and fruits low in fat and carbohydrates, but high in fiber, do we eat in winter? Almost zero, because potatoes and canned food, which are energy concentrates, are stored for a long time.
Because of them, fat metabolism is disrupted and slowed down, and excess calories are stored in fat. In spring, the body begins to receive lighter foods containing more fiber (greens, fruits, vegetables), which speed up metabolism.
In spring, it becomes possible to move more, which has a positive effect on metabolism. Lighter clothes, in which the body itself must keep warm, that is, burn extra calories.
Even with obesity, weight loss is observed in the spring due to a general acceleration of lipid metabolism.
Metabolism in obesity
This disease is called the plague of the 21st century, because millions of people around the world suffer from it. But where did this problem come from when just a century ago many were dying of hunger?
With obesity, a disruption of one (or several) phases of the lipid metabolic cycle occurs in the body, due to which more fat is consumed, absorbed, and produced than necessary. Special diagnostics will help determine where the failure occurred, which must be done if you are overweight (when your body mass index is more than 26).
It often happens that with obesity, the 5th and 6th phases fall out, and after the 4th the 7th immediately follows, that is, the broken down components form fatty tissue without releasing energy. That's why overweight people are constantly hungry.
Diagnosis can be carried out not only for obesity, but also for its prevention. It is done in special centers and includes a set of exercises, during which instruments will monitor the body’s reaction, and tests will also be taken.
Maintaining normal metabolism
You can maintain fat metabolism at a normal level even at home by following a few simple tips.
- Eat the right amount of fat (in grams it is equal to a person’s weight multiplied by 1.2).
- Eliminate saturated (lard, butter, margarine) and trans (sweets, fried foods, fast food) fats from your diet.
- Do not give up unsaturated fats (oils), because they are the ones who “take care” of the health of the human body.
- Consume lipids before 16.00 – at this time the metabolism slows down.
- Don't forget to exercise at least a couple of times a week.
- Can't go to sports classes? Take 10 thousand steps a day, then your figure will not be afraid of any wrinkles.
- Do yoga. During it, a person breathes deeper, which means more oxygen appears for lipid oxidation.
- Healthy sleep is the key to fast and high-quality fat metabolism.
It is worth mentioning a good mood, as well as giving up alcohol, cigarettes and drugs, which disrupt all cycles in the body.
Lipid metabolism is important for the body, so maintain it by following simple recommendations, and also take care of your overall health - undergo metabolic diagnostics at least once every 2 years.
Bottom line
Understanding the processes of lipid metabolism allows you to customize your nutrition plan much more accurately. But most importantly, by understanding how to properly consume fatty foods, what to combine them with and in what proportions, you will definitely get rid of the classic misconceptions regarding diet myths. But the most important thing to remember is that a small amount of properly selected omega fatty acids is not taken into account in calorie content, since they are not spent on transformation into glycogen or other processes occurring in the liver, but directly, in the presence of transport proteins, go to their intended purpose