Abdominal muscles ache after intense training or work in the garden. This is a pleasant ailment that goes away over time after a good rest. Sometimes this symptom indicates a more serious problem.
How long have you had this pain syndrome?
- Several days (26%, 976)
- First day (21%, 799 Votes)
- Several months (12%, 452)
- Week (10%, 376)
- Several weeks (10%, 358)
- About a month (8%, 312)
- Chronic form (6%, 236)
- About a year (6%, 210)
Total voters: 3 720
Loading …
Use search Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
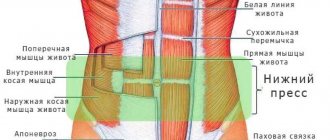
Causes of pain in the muscle structures of the abdomen
It is not always possible to accurately determine the location of the pain. It all depends on their reason for their appearance. In medicine, there are three main factors that lead to pain in the abdominal area.
Muscle pain in the lower abdomen often occurs when exposed to psychogenic factors. Many people are familiar with the situation when they experienced physical overexertion, sports overload on muscles, depression.
Most often, the muscles in the lower abdomen hurt due to spastic tension and hypertonicity. This condition is often considered a protective feature. Pain always occurs in the place where the injury was caused or inflammation occurred.
The degree of manifestation of an unpleasant feeling depends on the speed of spread of the inflammatory process, as well as on the functionality of the nervous system.
When abdominal pain is characterized by an acute course, the cause may be hidden in the following:
- acute appendicitis;
- perforation of an ulcer in the intestinal canal or stomach;
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- vascular abnormalities in the form of impaired arterial or venous outflow of blood, ischemia, infarction of the intestinal tract;
- acute inflammation in the gallbladder or pancreas;
- rupture of the tube due to the development of an ectopic pregnancy;
- aortic aneurysm in the abdominal cavity;
- acute inflammation in the pelvis in the female half of the population.
If acute type anomalies are excluded, then why do the abdominal muscles hurt? Then the reasons may be hidden in the following:
- pinching of a hernia or prolapse of internal organs through a hole formed in the abdominal wall;
- stretching of the abdominal muscles. Very often, pain occurs due to small microtraumas in the internal structure of muscle fibers. The reasons are physical overexertion, strain, sports training, carrying heavy loads;
- injury to the abdominal area with a blunt or sharp object. This process leads to the formation of intra-abdominal bleeding. In the absence of timely assistance, peritonitis develops. Blunt trauma often results in the formation of an intra-abdominal hematoma and the appearance of abdominal pain;
- rupture of abdominal ligaments and muscles. This phenomenon is characterized by a violation of the integrity of the muscle tissue structure. The rupture can be either partial or complete. Spontaneous breakdown of muscle fibers occurs during intense physical activity.
Stomach pain can also occur for other reasons in men and women, for other reasons:
- osteochondrosis of the lumbar region;
- spondylosis;
- tuberculosis of the skeletal system;
- spinal column injury.
Much more dangerous is the condition when pain occurs when the walls of a hollow organ are perforated. This can cause hemorrhage and death of some tissues.
Diastasis
Diastasis occurs when the linea alba (the junction of the broad muscles) separates. The reasons are pregnancy and childbirth, heredity or obesity. Diastasis recti can occur in men and children.
During pregnancy, the connective tissue between the vastus muscles becomes loose so that the belly can expand. After childbirth, the tissue itself strengthens and the shape of the abdomen is restored within a year. But if a woman works hard on her abs or lifts weights, the tissue does not contract.
Pathology appears with obesity or sudden weight loss, when the connective tissue does not have time to contract, which leads to its “excess”. Muscle divergence also causes an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, for example, a hacking cough, heavy lifting, constipation, or playing sports.
With dysplasia, the structure of ligaments and tendons is disrupted, which leads to excessive extensibility of the connective tissue and provokes the occurrence of diastasis or the formation of hernias. Pain in the abdominal muscle fibers when impaired can vary in nature, strength and duration. The pain often intensifies with prolonged walking, physical activity, and heavy lifting.
With diastasis, muscle fibers are weakened and do not perform their function, so pain can appear even with little physical activity. Due to improper distribution of the load, internal organs may become mixed up, an umbilical hernia may form, digestion problems may occur, and pain in the spine may occur.
If your abdominal muscles hurt due to exercise, no special treatment is required, since the symptom will go away on its own in 1-2 days. You can reduce pain by doing a massage or taking a contrast shower. Tension of the abdominal muscles is one of the symptoms of an “acute abdomen”, which requires surgical intervention.
Therefore, if your abdominal muscles hurt severely for no reason (you have not previously engaged in physical labor or exercise), and there are other symptoms, for example, nausea, general weakness, fever, abnormal bowel movements, then you need to seek medical help. Only after finding out the causes of long-term or periodic muscle pain can you understand what needs to be done to eliminate them.
Pain syndrome is an indicator of a disorder present in the body. The field of gynecology is no exception. Women experience unpleasant sensations due to inflammation, an infectious or tumor process, or damage. Only a doctor can find out the cause of deterioration in health. Only after the prescribed examination and the results obtained, it becomes clear what to do if a woman’s lower abdomen hurts, how to help her and what methods to stop the underlying pathology.
Associated symptoms with abdominal muscle injury
Only a doctor after a thorough diagnosis can tell why your stomach hurts and what caused the muscle tear. The first step is to evaluate for additional symptoms. They are divided into several types.
Pathogenetic signs include:
- colic, spasms in the smooth muscles. These symptoms always occur spontaneously. Sometimes they have a paroxysmal character. The intensity decreases after taking antispasmodics and warming procedures. Spasms radiate to the lumbar or dorsal region;
- referred abdominal pain. At the same time, it is aching or pulling in nature. In most cases, it is difficult to determine the location;
- paroxysmal pain. Occurs due to a sudden disruption of blood flow. It can grow very strong.
During diagnosis, the patient and doctor also need to determine the presence of other symptoms:
- If the painful feeling increases instantly and is acute and painful in nature, then this indicates perforation of an ulcer in the stomach or intestines, rupture of an aneurysm, myocardial infarction, biliary colic.
- When the pain syndrome appears unexpectedly, is intense and lasts more than 12 hours, then such symptoms indicate pancreatitis, intestinal obstruction.
- Painful sensations in the abdomen and muscles can increase gradually, but their duration can last up to several days. Then cholecystitis or diverticulitis is diagnosed.
- With appendicitis, cyst rupture and ectopic pregnancy, symptoms will occur in the form of tachycardia, blueness of the skin, a sharp drop in pressure, increased temperature, nausea and vomiting. In this case, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance.
If there is a stretching of the abdominal muscles in men or women, the pain syndrome will have a pulling and aching character. The pain intensifies during movement, but goes away on its own after two to three days.
Pathologies that provoke myalgia
Myalgia is pain in muscle tissue, which is accompanied by spasms. Among the most common diseases that cause myalgia in the rectus and oblique abdominal muscles are:
- pathologies associated with metabolism - diabetes, gout, metabolic syndrome;
- viral infections – for many people, one of the first symptoms during the flu is muscle pain;
- vascular disorders, including aortic aneurysm.
However, myalgia can also be triggered by such trivial factors as prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position.
Myalgia can be distinguished from simple tension by such a sign as long-term persistence of pain. The symptoms in this case do not go away after rest, as they are associated with more serious processes. With myalgia, a burning sensation, nausea, and chills often occur.
Myositis as a form of myalgia
Myositis is an inflammation that occurs in skeletal muscles. One of the most serious forms of myalgia, which can be associated with serious diseases of the musculoskeletal system. But in some cases, myositis develops as a result of ARVI, tonsillitis, or with excessive physical exertion.
Some forms of myositis are thought to develop due to exposure to bacteria and toxins. This condition can be caused by abuse of alcohol, cocaine, and certain medications (statins, interferons, colchicine).
With myositis, a purulent process begins in the muscles, associated with chronic infections in the abdominal cavity. Symptoms rarely affect only the abdomen: not only the external oblique muscle hurts, but also the fibers of the neck, lower back, lower leg and chest. Myositis is accompanied by swelling, fever, fever and headaches.
Causes of muscle pain not associated with myositis
Acute muscle tension can occur in the following conditions when the abdominal wall becomes hard:
- inflammation of the appendix - pain is usually located on the right in the iliac region;
- intestinal obstruction – combined with symptoms of acute intoxication, accompanied by prolonged constipation and a strong increase in the size of the abdomen;
- perforation of the ulcer - acute dagger pain is associated with gastric bleeding, blood is present in the vomit and stool;
- vascular accidents - infarction of the intestines and other organs, thrombosis;
- acute cholecystitis - pain is located on the right hypochondrium, requires immediate surgical assistance;
- acute pancreatitis - symptoms are similar to cholecystitis, but the pain can be localized on the left;
- rupture of the fallopian tube during an ectopic pregnancy - the woman’s well-being rapidly deteriorates;
- rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm - a person feels acute diffuse pain;
- inflammation of the ovaries or uterus - endometritis, adnexitis, as well as hemorrhage in the ovary.
All these pathologies require immediate surgical care - when the first signs appear, you should consult a doctor. These symptoms are usually distinguished by unbearable pain, pallor, vomiting and nausea, fainting and bloody discharge in women.
Other conditions in which pain in the rectus abdominis muscles are severe include: strangulation of an umbilical or inguinal hernia, acute strain of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall as a result of lifting heavy objects or injuries. Similar symptoms can be observed in people with diseases of the spine: tuberculosis, spondylolisthesis, osteochondrosis, trauma.
Features of pain during pregnancy
In pregnant women, constant pain in the oblique or rectus abdominal muscles may be associated with some serious abnormalities:
- Placental abruption. The pain is severe, localized at the bottom, often combined with bleeding and watery discharge. There is a high risk of fetal death as a result of hypoxia.
- Risk of miscarriage. The pain is combined with small amounts of blood, and a pulling sensation appears in the lower back.
- Ectopic pregnancy. The pain is very strong, radiating to the groin and back, the symptoms are localized on the left or right side - depending on where the egg is implanted.
- Digestive system disorders. Due to compression of the intestines and stomach by the growing fetus, constipation, flatulence, and bloating often occur.
- Stretching the abdominal muscles. This is a normal process that intensifies in the 3rd trimester.
Also, in women during pregnancy, chronic diseases worsen, pathologies of the pancreas, bile, and intestines arise, and appendicitis appears.
Unpleasant sensations during pregnancy
Women can also have a tummy tuck during pregnancy. The thing is that the oblique and rectus abdominis muscles gradually stretch due to the enlargement of the uterine cavity. This condition is physiological in nature.
But the causes of unpleasant sensations are also hidden in a pathological condition. This group includes:
- threat of termination of pregnancy, miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- fibroids;
- rupture of the uterine cavity;
- preeclampsia;
- placental abruption;
- acute pyelonephritis;
- aneurysm rupture. Rarely encountered;
- formation of hematoma in the muscles.
Diagnostic measures
The examination plan for a patient with severe sprain includes the following physical and instrumental methods:
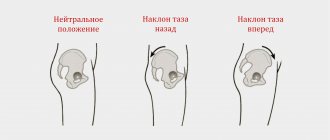
- Palpation of the abdomen
. A test can determine the presence of diastasis: the patient is asked to lie on his back, bend his knees, and tense his abdominals. In this case, the doctor can palpate the protruding ridges along the edges of the rectus muscles and assess the width of the discrepancy. The method is not effective enough in patients with excess body weight due to difficulties during palpation. - Ultrasound of the abdominal wall
. Sonography is an accessible non-invasive study that visualizes stretching and thinning of the linea alba, which is accompanied by an increase in the distance between the rectus muscles. When using the ultrasound method, it is possible to determine the presence of complications such as hernia of the anterior abdominal wall, prolapse of the abdominal organs. - Radiography
. Survey radiography of the abdominal cavity makes it possible to assess the size and relative position of the internal organs. 84% of patients have gastroptosis of varying severity. The method also helps to differentiate diastasis from other pathological conditions accompanied by a similar clinical picture.
Diagnosis for muscle pain
What to do if the patient has an unpleasant feeling in the upper or lower abdomen? The first thing you need to do is visit a doctor. First, he will ask about the presence of accompanying symptoms and take a medical history of the patient.
When making a diagnosis, special attention is paid to women during pregnancy, elderly people over 60 years of age and children, as well as patients who have a history of certain diseases:
- kidney and liver pathologies;
- diabetes;
- endocrine system disruption;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- insufficient blood flow and vascular type disorders;
- spinal column injury.
Diagnosing painful sensations includes several stages.
- It is necessary to avoid physical strain and stretching during training.
- Avoid injury to the abdominal muscles from impacts, falls or accidents.
- Women undergo a biochemical test and ultrasound to detect pregnancy.
- Urine is taken for analysis to detect infection in the urinary system.
- An X-ray of the spinal column, electrocardiography, and fibrogastroduodenoscopy are performed.
The doctor also looks for some symptoms:
- pain in the abdominal area and dizziness;
- decreased blood pressure and pulse, development of tachycardia;
- feverish condition;
- bleeding in women;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal enlargement and absence of stool for more than three days.
Based on this, an accurate diagnosis is made.
Principles of treatment of abdominal pain syndrome
Treatment of pain syndrome should first of all be aimed at the cause that caused it, i.e. for the treatment of the underlying disease.
If the onset of pain is caused by excessive physical exertion, then treating it will not be difficult. First you need to give rest to the muscles of the abdominal wall.
For this purpose, an immobilizing bandage or bandage can be used, however, warming agents should not be used. If you follow these recommendations, the pain will go away in 2-3 days without a trace.
When treating acute or chronic pain, approaches vary. If the pain is acute, then, first of all, it is necessary to establish the correct diagnosis and adequately anesthetize the patient.
In the presence of chronic pain syndrome, its cause, as a rule, has already been established, but for some reason it is not possible to eliminate the manifestations.
Therefore, in this case it is necessary to influence the pathological parts of the disease in order to relieve pain.
Since abdominal myalgia is usually a consequence of muscle spasm, antispasmodics must be used for treatment.
According to the mechanism of action, this group of drugs is divided into myotropic drugs, which affect smooth muscle cells, and neurotropic drugs, which interrupt the transmission of pain impulses along the processes of nerve cells from muscle tissue.
Emergency conditions require immediate medical attention. While waiting for help, patients often try to alleviate their condition in ways that are unacceptable in such a situation.
Remember, if you have acute abdominal pain, you should not:
- Take painkillers. This contributes to the “blurring” of the clinical picture, which leads to difficulty in making a diagnosis;
- Apply measures to warm the abdominal area. This can provoke the development of intra-abdominal bleeding from dilated blood vessels;
- Take laxatives or use enemas;
- Eat food and drink plenty of fluids.
Therapeutic therapy for pain in the abdominal muscles
Treatment for pain in muscle structures depends on the type of disease. If the pathology is physiological in nature, then it is enough to remain in bed for several days and completely eliminate physical activity. The pain will go away on its own after a few days.
Therapeutic treatment for abdominal pain is:
- in the normalization of structural disorders in the abdominal organs;
- in normalizing the functionality of organs that create pain;
- in normalizing the functioning of the nervous system.
Therapy for acute and chronic cases differs significantly from each other. In acute cases, it is necessary to determine the cause as soon as possible. If the pathology threatens the patient’s life, then surgical intervention is performed.
If an acute condition develops, an ambulance is urgently called. At the same time, it is forbidden to eliminate the unpleasant feeling with the help of antispasmodics and painkillers, warm the stomach, take laxatives and give enemas, eat and drink. All this can lead to a deterioration in the patient’s condition and blur the clinical picture of the disease.
In chronic cases, treatment is permanent. During an exacerbation, medications may be prescribed to relieve symptoms. During remission, therapy consists of strengthening immune function.
If your abdominal muscles hurt, before going to the doctor you need to remember what caused the pathology.
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Pain in the abdominal muscles is often called the general term abdominal pain syndrome, which in turn can be the leading symptom complex that guides the diagnostic and therapeutic strategy. However, contrary to generally accepted opinion, abdominal pain is not always related to gastroenterological problems; they can be provoked by various organic, functional, and inorganic, dynamic factors.
If we divide pain symptoms according to the mechanism of occurrence, it turns out that only a few types are directly related to myalgia (muscle pain):
- Visceral abdominal pain is a pathological stretching of the walls of hollow internal organs and vascular disorders. Only pain in the smooth muscles of organs is related to muscle tissue.
- Somatic abdominal pain is a combined pathology of internal organs and the peritoneum itself, hypertonicity of the abdominal muscles.
- Referred abdominal pain - anatomical infringement, organ damage, pain irradiation, partially to the abdominal muscles.
- Psychogenic abdominal pain is a pain symptom that does not have an organic or vascular cause, often manifesting as myalgia.
Pain in the abdominal muscles associated with traumatic damage to muscle fibers. This symptom is an independent sign of dysfunction of the abdominal muscular system.
Preventive measures
To prevent another abdominal muscle strain, you should take note of the following useful tips:
- Before you begin training related to physical activity, you need to thoroughly warm up, thereby warming up all the tissues and ligaments of the body.
- During training sessions, you should not overexert yourself. To do this, it is important to be able to calculate your strengths and capabilities.
- Exercises aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles will be useful.
- If you want to lift very complex objects, you should first familiarize yourself with this technique, and the first lesson is best done under the supervision of a trainer or a more experienced friend.
- If you feel tired, you must immediately stop the training process.
Causes of pain in the abdominal muscles
It is sometimes very difficult to determine why and where the stomach hurts; accordingly, the causes of pain in the abdominal muscles are not easy to differentiate from abdominal pain of another nature. As a rule, factors that provoke pain in the abdominal area are divided into three broad categories, including various nosological groups:
Also, the causes of pain symptoms can be psychogenic factors (depressive state) and situations are familiar to everyone - physical overexertion, sports stress on the muscles and injuries.
Since pain in muscle tissue most often develops due to spastic tension and hypertonicity, it is advisable to consider the symptom as a protective mechanism; in clinical practice it is called protective tension of the abdominal wall muscles. Such a reflex tonic response of the muscles of the anterior zone of the peritoneum always corresponds to the site of innervation of inflammation or injury. The degree of intensity of tension depends on the speed of development of the inflammatory process and on the condition, type of nervous system. Most often, obvious protective hypertonicity and pain in the abdominal muscles occur with the clinical picture of an acute abdomen, provoked by the following diseases:
- Acute appendicitis.
- Perforation of an ulcer of the duodenum or stomach.
- Acute intestinal obstruction.
- Acute vascular conditions - disturbance of arterial or venous blood flow, ischemia, intestinal infarction.
- Acute inflammation of the gallbladder, pancreas.
- Tubal rupture during ectopic pregnancy.
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- Acute inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs in women (tumor, cyst).
If an acute condition is excluded, the most likely causes of pain in the abdominal muscles may be:
- Strangulation of hernia abdominalis - abdominal hernia or prolapse of internal organs through openings in the peritoneal wall (artificial, traumatic or natural).
- Abdominal muscle strain. Most often, pain is provoked by microtraumas of the internal structure of muscle tissue. Causes: physical overexertion, strain, sports training, moving loads, heavy loads, and less commonly, pregnancy.
- Abdominal injuries can be blunt or penetrating. Penetrating trauma leads to intra-abdominal bleeding and even peritonitis; blunt trauma often results in intra-abdominal hematoma and pain in the abdominal muscles.
- Rupture of ligaments and abdominal muscles. Violation of the integrity of muscle tissue can be complete or partial. Spontaneous, partial muscle rupture is provoked by intense physical exertion on atrophied, atonic abdominal muscles.
In addition, abdominalgia (pain in the muscles of the abdominal area) can be provoked by vertebrogenic causes:
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral zone.
- Spondylosis.
- Tuberculosis of the skeletal system.
- Spinal injury.
Quite often, myalgia affecting the abdomen is caused by myofascial pain syndrome (MFPS). With MFPS, the rectus and oblique muscles hurt, the cause of the pain is vertebrogenic pathology or physical overstrain, a characteristic sign is the presence of diagnostically significant trigger pain points.
It should be noted that according to statistics, most often defense musculaire - protective hypertonicity and pain in the abdominal muscles occurs with inflammation of the appendix, gallbladder and pancreas. Also, pain and muscle tension are expressed when an ulcer of a hollow organ is perforated, and to a lesser extent - during inflammatory processes and hemorrhage into the peritoneum.
[4], [5], [6], [7]
Muscle pain is a normal condition after physical activity. But it happens that the rectus or internal oblique abdominal muscle hurts for no apparent reason. And if you look closely, you can find additional symptoms of an unpleasant condition, indicating the development of certain diseases.
Myositis
One of the forms of myalgia is myositis. Fiber disruption is caused by an inflammatory process occurring in skeletal muscles. It is characterized by increased pain when moving, swelling and, rarely, redness of the skin.
Myositis is often a complication of influenza, acute respiratory viral infection or chronic tonsillitis, but can be caused by excessive physical exertion, mechanical trauma, deterioration of blood supply to tissues, exposure to toxic substances, autoimmune disease, and parasites.
It is assumed that myositis develops due to the action of bacteria on the muscles or due to the action of toxins released by them. Alcohol and cocaine can also provoke inflammation in the fibers; short-term damage can also occur when taking medications (colchicine, alpha-interferon, statins).
A purulent process may begin in the muscle fibers due to infection in an open wound, the presence of a chronic infection in the abdominal cavity, or non-compliance with injection rules.
There are 6 types of myositis:
- infectious non-purulent (develops with viral lesions, syphilis, bruzcellosis, tuberculosis) is characterized by severe pain in the muscle fibers and general weakness;
- acute purulent (diagnosed with purulent as well as necrotic processes) leads to swelling and pain at the site of the lesion;
- parasitic nature (against the background of an allergic reaction, more often develops with toxoplasmosis, echinococciasis, trichinosis, cysticercosis) provokes pain, local swelling, abdominal tension, weakness, low-grade fever;
- ossifying (appears after injury) causes degenerative processes and aching pain;
- polymyositis (formed in autoimmune diseases) provokes pain and growing muscle weakness;
- dermatomyositis. A disease that affects the skin, organs, abdominal muscles, pelvis, neck and shoulder girdle.
As a rule, inflammation affects the muscles of the neck, lower back, lower leg, chest, and much less often other muscle fibers, including the lateral and oblique abdominal muscles. Clinical symptoms include aching pain that increases with movement and touching the abdomen, and muscle weakness also appears.
Hyperemia and swelling in the area of the inflamed tissue, fever or low-grade fever, and headache may occur. The acute form of myositis mainly appears after trauma to the abdomen, excessive stress, or hypothermia.
Chronic forms against the background of infectious and toxic lesions and occurs with less severe symptoms. It reminds you of itself during static loads, overexertion, hypothermia, and weather changes.
If there is a fever, antipyretic drugs are prescribed. Analgesics can reduce pain, and anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Diclofenac) fight inflammation. After it has been established why the abdominal muscles hurt so much, antibacterial drugs, anthelmintics or others, that affect the source of infection are prescribed.
For local lesions, warming ointments are effective; due to their irritating effect, they help to relax, which reduces spasm. For purulent myositis, the lesion is opened and antibiotics are prescribed.
Common causes of abdominal muscle pain
The most common situation is pain in the abdominal muscles associated with natural physiological causes: overexertion, sports, sudden stretching. However, there are also pathological factors that lead to discomfort:
- Stretching of organ walls. Pain in this area may result from an increase in the size of the stomach, intestines and arteries. These processes occur not due to overeating, but due to dangerous pathological processes, as well as during pregnancy in women. Symptoms of organ stretching affect only smooth muscles, and the pain is called visceral.
- Mechanical damage to muscle tissue. If there is a strong blow to something, or a person is pierced with a sharp object, the muscle tissue tears, swells, and pain appears.
- Psychological disorders. Some people experience muscle pain as a result of stress and overexertion.
- Dysbacteriosis. One of the reasons for the increase in intestinal size. With dysbacteriosis, the organ becomes greatly stretched, symptoms such as constipation or diarrhea appear, the temperature rises, and nausea occurs.
If you have chronic diseases, you can suspect their exacerbation when pain appears in the rectus or oblique abdominal muscles.
Stretching
A sprain appears due to muscle overstrain, which happens when the load is greater than permissible, since the muscle corset is not sufficiently developed. With a strong increase in intra-abdominal pressure, a rupture of the abdominal wall is likely, which leads to displacement of organs (hernia), this often happens when lifting weights.
Microtraumas and muscle strains provoke spasms, which leads to pain. There are 3 degrees of severity:
- moderate (pain is not intense, goes away after 3–5 days);
- average;
- rupture (appears due to excessive pressure on the rectus abdominis muscles).
When the muscles are stretched, they need rest; it is recommended to avoid stress and sudden turns for at least two days. A cold compress will reduce pain. For severe pain, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. People often ask if muscles can ache for a week after an intense workout. When muscle tissue ruptures, pain lasts for more than 1.5 months.
Methods of diagnosis and treatment for muscle pain
Diagnosis of pain in the abdominal muscles occurs in several stages. The first is palpation. The doctor determines the condition of the abdominal wall. Next, they take blood and urine tests, and also do an ultrasound. In some cases, x-rays and an ECG are required.
Treatment methods depend on the type of disease. Gynecological disorders are treated by a gynecologist; for gastrointestinal diseases, therapy is prescribed by a gastroenterologist. In acute conditions, surgical intervention is often required, followed by antibacterial therapy: removal of a ruptured ovary and fallopian tube, elimination of an inflamed appendix.
Symptomatic therapy includes taking antispasmodics, NSAIDs, probiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs when necessary. Be sure to prescribe a gentle diet to avoid unnecessary stress on the internal organs.
To prevent pain, it is important to monitor your health and treat chronic diseases in a timely manner. You should not overexert yourself when playing sports; you should always warm up before training. To prevent pain from appearing, you need to train different muscle groups on different days.
What to do if your muscles hurt a lot after training?
In order to at least slightly reduce the pain after playing sports, you need to do another workout, but with less strength loads. During training, you should not do more than you can realistically do. First of all, evaluate your capabilities, and then you can begin to gradually increase the load. And don't forget to stretch before and after your workout. Stretching will help you in the fight against sore throat, and can also prevent its occurrence. Another option is to use a warm shower or bath. And for a relaxing effect, you can add a couple of drops of essential oil and get maximum pleasure from it.