When pain is normal
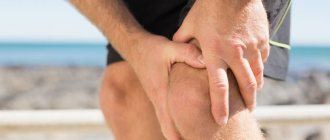
Knee pain after exercise is familiar to many. This pathological symptom can be provoked by dysfunction of the musculotendinous and osteoarticular complexes of the knee joint. The norm is considered to be minor pain in a group or individual muscle fibers of the lower leg and thigh. They appear under stress, as a result of the production and accumulation of lactic acid in the tissues.
The nature of the pain depends on the fitness of the muscles; usually the discomfort disappears after a few days. The pain is aching in nature and can manifest itself in the form of slight compression in the area of the knee joints. But they do not have a clear localization.
Normal pain after exercise is short-term and mild. Their decrease, and eventually disappearance, occurs after rest. If the situation develops in the opposite way, you need to reconsider the activity of your activities in the gym and your lifestyle. This way you can find out what leads to the appearance of a pathological symptom.
Anatomy of the knee joint ↑
Since the main “culprit” of pain in the knee is the knee joint, let’s briefly consider its anatomy. So the terms used below to describe pathology will be much clearer.
This joint is the most complex of all.
It is in this joint that the longest lever bones of the lower extremity “meet”; only in this joint, in addition to the bones themselves, there are many more formations: condyles, a huge number of ligaments, articular capsules.
The joint is formed by the following bones: femur, tibia and patella.
The surfaces of the articulating bones themselves do not correspond to each other in shape, so special cartilaginous plates - menisci - are inserted between them.
The meniscus on the inside (medial) looks like a crescent, while the outside (lateral) practically forms a circle.
Both of these cartilages are crossed obliquely from above by a special ligament, which is called the transverse patellar ligament.
The articular capsule in this joint is special.
It is attached just a few millimeters above the edges of the articulating femur and tibia bones, encircling the patella so that it is covered by it, and muscles and ligaments are attached to the edges of the long tubular bones.
The inner layer of the joint capsule, called the synovium (it is what forms the fluid that “lubricates” the joint), forms a bursa above the patella, between the skin and the femur.
It is in it that inflammatory fluid can accumulate in case of joint diseases.
This suprapatellar bursa in some cases can also be isolated from the joint and closed.
There are other bursae:
- under the skin in the area of the patella (it’s called the subcutaneous bursa);
- under the fascia, slightly more superficial than the anterior surface of the patella;
- under the branching of the tendons of the quadriceps muscle (quadriceps) of the thigh;
- Between the ligament supporting the patella and the tibia there is a bursa called the “deep infrapatellar ligament”.
The first three bags are not necessarily all present, there can be only one or two of them, they can either be separate from the joint or communicate with it.
Everyone has the last bag.
Between it and the tibia there is a small fatty body, which, like the bursa, is called “infrapatellar,” that is, it lies under the patella.
The ligamentous apparatus of the knee is represented by a huge number of ligaments that run both outside and inside the joint:
- on both sides of the hip, two collateral extra-articular ligaments are directed to the underlying tibia and fibula;
- behind the capsule lie two ligaments: the arcuate and oblique, which are so named because of the location of their fibers;
- the quadriceps tendon also plays the role of an extra-articular ligament, passing in front of the joint, completely entwining the patella and attaching to the tibia;
- Inside the joint there are 2 cruciate ligaments that connect each of the menisci to the opposite tibia. These ligaments conditionally divide the joint into 2 parts - anterior and posterior. They prevent the penetration of exudate from one part to another.
The synovium, lining the cruciate ligaments, forms two folds containing fat on the anterior surface of the joint.
They fill the gaps between the bones moving in the joint, making movements in the knee smoother and more comfortable.
How to get rid of spurs on your heels? Find out about different methods of treating heel spurs on our website.
Why does it hurt under the ribs on the left? Read here.
Causes of pain
Data from studies indicate that there is a widespread misconception that training with effort, through severe pain, is a variant of the norm. It is very harmful when unpleasant sensations bother a person regularly.
The knee joint can be compared to a hinge, the planes of which rub against each other when moving. As a result, bone tissue and cartilage wear out over time. To function normally, the joint produces special substances - glycosaminoglycans, which “lubricate” the bone surfaces.
When carrying out loads, tissues wear out more intensively, which cannot be said about the process of producing useful substances. Gradually, the condition of the joint worsens, causing pain and discomfort. There are several reasons why knees hurt after training.
Overtraining
With overload and poor nutrition, degenerative-dystrophic processes develop in the joints of the knees. If the pain does not disappear after two days, it is recommended to consult an orthopedist.
Normally, knee joints recover over time after stress.
If overload in the gym is aggravated by factors such as old age, genetic predisposition, infectious and inflammatory diseases, then the ability to self-heal is significantly reduced. All this leads to the development of a chronic form of the disease and constant pain.
Age-related changes
Statistics indicate that knee pain after exercise is more common in men and women over 30 years of age. The reason for this is inhibition of collagen production. There is no need to panic in such a situation - it is better to correct the loads being performed.
Injuries
Knee pain can occur due to injury. To properly combat the problem, you need to consult a doctor. The nature of the pain, its intensity and location depend on the type of injury. Thus, a sprained ligament is indicated by the lack of stability of the joint and its excessive mobility. Warming up before exercise helps reduce the risk of injury and prevent pain.
Inflammatory processes in the joint
The development of inflammation can be triggered by:
- impacts and damage to joints that are regularly repeated;
- infectious processes;
- metabolic disorders;
- overload;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- decreased immune defense of the body;
- genetic predisposition;
- overweight;
- bad habits, especially smoking.
If we talk about athletes, then inflammation appears after knee injuries. Common pathologies are:
- bursitis - inflammation of the knee;
- synovitis – accumulation of fluid, leading to the development of arthrosis;
- tendonitis is an inflammatory process of the tendons.
Overweight
If you are overweight, every kilogram increases the load on your knees by 6 times. This is what causes knee pain. That is why you should monitor your diet (the body must receive enough vitamins and minerals) and exercise.
Failure to comply with exercise technique
It is necessary to analyze the situation and determine when pain appears, with what exercises, and then correct it. It is better if the set of exercises is selected by an experienced trainer.
Wearing inappropriate shoes
Poor quality shoes or the wrong size can lead to improper load distribution and pain. When attending sports activities, you need to take this factor into account.
Hereditary predisposition
In first place in terms of prevalence is a disease such as flat feet. It causes the kneecaps to shift inward and cause the sensation that they ache. Infectious diseases and previous injuries can also provoke a pathological symptom. Knees hurt due to arthrosis and arthritis, and at the same time joint movement worsens. Swelling, skin hyperemia and pain are observed.
Pain in the joints of the lower extremities
The most common factors contributing to the occurrence of painful sensations are presented in the table.
Table 3. Painful syndrome in the joints of the legs.
| Where does it hurt | Why does it hurt |
| Pain in the hip joint after exercise is caused by sprained ligaments. This is usually typical for women, who are more flexible than men. |
| Injury to tendons or ligaments. In rare cases, pain occurs due to an ankle fracture. |
| Those at risk include gymnasts, wrestlers, tennis players, skiers and football players. They experience pain due to damage to the ligamentous apparatus. In bodybuilders, powerlifters and weightlifters, pain is provoked by abrasion of the cartilaginous membranes. |
The most severe injury is damage to the knee ligaments. In the most severe cases, an athlete's career can end.
Swollen knee after exercise
The appearance of swelling and pain may indicate:
- knee injury;
- arthritis or arthrosis in the acute phase;
- meniscal injury.
With a meniscus injury, body temperature, hyperemia and pain upon palpation of the knee increase. Soreness may occur after exercise, at night or in the morning, regardless of movement.
If the vessels are damaged, hemarthrosis forms (blood accumulates in the joint). Ligament rupture is accompanied by blockade of the joint, when it does not bend or straighten.
How to treat? ↑
As you can see, a huge variety of diseases can lead to joint pain. Each of them has its own treatment.
Which doctor should I contact?
The joints of an adult are treated by a traumatologist and a rheumatologist. The child needs to be taken to an orthopedist.
Folk remedies
Their purpose also depends on what pathology was found in you.
For example, for gonarthrosis, which is the most common cause of non-traumatic pain in the knee, the following recipes are used:
- Celery root – 250 g (you can replace it with nettle) mixed with 120 grams of garlic and three lemons. All this is twisted through a meat grinder, mixed, placed in a three-liter bottle and filled to the top with boiling water. The jar is wrapped in a blanket and allowed to brew. When the infusion temperature reaches room temperature, you can drink it, starting with 100 ml once a day, gradually moving to three times a warm infusion. Store the jar in the refrigerator.
- Jellied meat is made from beef hooves and knees. They need to be cooked until the meat completely falls off the bones. The resulting jelly is drunk 100 ml half an hour before meals.
What to apply?
You can only apply anti-inflammatory ointments: “Diklak”, “Voltaren”, “Ibuprofen”, “Finalgon”.
Is it possible to heat it?
You need to ask the doctor who is treating you about this.
You can warm your knee when:
- gonarthrosis or chondromalacia: this can improve blood supply to the joint and slightly slow down the process of cartilage degeneration
- sprains, ruptures of ligaments or tendons - from the third day after the injury, and only if you do not have a temperature, the skin above the knee itself is not hot, there is no change in well-being.
Under no circumstances should you use heat if your knee is swollen, the general or local temperature is rising, or the condition is worsening.
Exercises
Only a doctor should tell you when to start them and which ones to use, depending on the nature of the detected pathology.
The general principle is this:
- muscles must be trained - when inflammation subsides;
- you cannot perform squats, flexion-extensions, walk for a long time and perform movements that increase pain in the joint;
- start training lying down;
- the first exercises will be to develop the thigh muscles, for which the leg must be straightened and raised as far as it does not hurt, and held as long as possible;
- then they move on to strengthening the muscles of the foot, making rotational movements with it, actively moving their toes;
- The knee muscles are the last to be developed.
Video: exercises
Massage
Its necessity, technique and timing at which to begin massaging the knee are determined by the doctor individually in each situation.
Surgery
Used according to indications:
- removal of fluid from the joint or periarticular bursae;
- suturing torn tendons or ligaments;
- removal of a “joint mouse” - a piece of tissue that has entered the joint;
- removal of a damaged meniscus;
- surgical fixation of the patella;
- dissection of adhesions after chronic inflammation of the joint;
- removal of dead areas of bone or cartilage in certain diseases;
- removal of Becker's cyst;
- If there is significant degenerative damage to the joint, endoprosthetics can be used.
Does your elbow hurt? Find out the causes of elbow pain from our article.
Is it possible to treat foot arthrosis with folk remedies? Read here.
What is fibrous dysplasia of bone? See this material.
Algorithm of actions for knee pain
If pain appears after training, you need to reduce the load on your legs for at least 7 days or until the pathological sensations completely disappear. It is also recommended to avoid sudden movements.
To reduce the intensity of pain, you need to fix the sore knee, you can use an elastic bandage or wear a special knee brace. The joint will move less, which will reduce the risk of injury.
If the pain does not disappear, this may indicate arthrosis or arthritis. It is best to seek help from a medical facility to eliminate these risks and establish the exact cause of the pain.
Reason for pain
Not every knee problem is a sign of a disease. My knee often hurts when the weather changes. If the knee is cold or injured, the pain periodically reminds itself.
The appearance of constant discomfort in the knee is a reason to visit a medical facility, make a diagnosis, and prescribe treatment. Often the disease is not the only cause of knee pain. Injuries and deformations of the component elements cause discomfort when walking and bending/extending the knee.
In addition to unpleasant sensations, patients complain of stiffness in the movement of the knee: it does not bend, does not move to the side. Redness of the skin around the knee, swelling appears, and the temperature of the body area near the affected joint rises. These signs indicate the development of arthritis.
There are more than 200 causes of knee pain. Here are some of them:
- rheumatoid joint disease;
- rickets;
- bruises, injuries from falling, hitting the knee;
- dystrophic deformation of cartilage tissue, arthrosis;
- overweight;
- popliteal fossa cyst;
- deformation, damage to bursitis, meniscus;
- pathological congenital changes in joints;
- the formation of inflammation in the joint - arthritis.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis and determine why the knee hurts after exercise, the doctor examines the patient. The specialist collects anamnestic data and, if necessary, prescribes:
- biochemical blood test;
- X-ray examination of the joint;
- knee arthroscopy;
- MRI.
Based on the results, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. Comprehensive measures are selected to help get rid of pain.
Safety precautions in the hall
Following simple rules significantly increases the likelihood of keeping your joints safe and sound. Even with regular intense strength training.
- During any squats, the knees should not go beyond the line of the toes;
- In the upper phase, after lifting, never straighten the knee joint completely. Let it remain half-bent;
- During squats, always keep your back straight, but you can bend your lower back a little;
- During the press, do not move your knees to the sides. Always move along the same axis.
Remember, if your knee hurts, even after light exercise on an exercise bike, never ignore the symptom. Cartilage tissue is not restored, so the destroyed joint will have to be replaced with an artificial one. And this is a very expensive operation. Fitness and strength sports should be practiced competently and without fanaticism. Avoid doing exercises that place unnatural stress on the joint. Work with adequate weights and use knee wraps. Be healthy!
Treatment tactics
A doctor should treat joint pain; only he can determine its exact cause and select an adequate treatment regimen. Trying to get rid of the problem yourself can only worsen the general condition and cause complications.
First aid for knee pain
If, after training, pain suddenly appears in the knee joints, swelling, hyperemia, and the mobility of the joint has become limited, it is necessary to provide assistance to the victim:
- Cold compress. Ice or any other cold is applied to the affected area; it is allowed to hold it for no more than 15 minutes (otherwise the sensitivity of the nerve fibers may be impaired). The ice must be wrapped in a towel or some other fabric. The cold will prevent the bruise from spreading and eliminate swelling of the joint.
- The injured leg must be raised above the level of the head.
- Take a pain reliever.
The next day, the affected area can be lubricated with warming ointment. If this does not give a positive result, you need to consult a doctor.
Carrying out the above actions is justified only when there is a suspicion of damage. If the pain is caused by arthritis or arthrosis, the treatment is specific.
Drug treatment and physiotherapy
Drug therapy effectively combats pain. The doctor selects the medications and duration of treatment. It takes into account the patient’s age, type of pathology and severity. In most cases, preference is given to:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac, Naklofen, Voltaren Emulgel is applied topically;
- decongestants;
- chondroprotectors – Chondroxide;
- drugs to strengthen the vascular wall (Actovegin);
- vitamins and minerals.
It is not recommended to self-medicate, as this can worsen the situation and cause complications. Positive changes will only occur with proper complex therapy.
In order for treatment to be effective, drug therapy is combined with physiotherapeutic procedures. They stimulate blood circulation and metabolic processes in the affected area. The following procedures are considered the most effective:
- electrophoresis;
- paraffin applications;
- magnetic therapy;
- wave treatment.
Exercise therapy and surgery
In order for the therapy to be complete, it is recommended to undergo a course of physical therapy. For each specific case, the doctor selects his own set of exercises aimed at combating the inflammatory process and strengthening the ligaments.
To improve local blood circulation in the affected area and eliminate tension in muscle fibers, massage is prescribed. If all of the above methods of struggle are unsuccessful, the knees also hurt, the doctor decides on the issue of surgical intervention. Surgery is used to:
- stitching damaged ligaments and tendons;
- removal of part of the meniscus;
- eliminating adhesions caused by the inflammatory process;
- fixation of the patella;
- elimination of necrotic tissue.
Injuries
If your knees hurt after training, and this is not the first time, it may be a bruise, sprain, rupture or other injury. Any problem of this nature requires examination by a specialist, since the correct diagnosis must initially be made.
Depending on the injury, the nature and location of pain may differ. So, when the cruciate anterior ligament is sprained or torn, the knee may lose stability and become too mobile. And if after training there is pain in the back of the knee, the cause may be an injury to the femur, as well as a pinched nerve in the lumbar region due to osteochondrosis, radiating to the knee joint.
To prevent injury, consider the following points:
- Before training, be sure to do a warm-up, which will consist of gentle warming up and stretching exercises. This will make it possible to maintain joint flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
- To immobilize the knee joints, you can use a two-meter elastic bandage . It is better to check with your trainer regarding the method of wrapping your leg.
Prevention
Unpleasant consequences of training can be avoided. There will be no knee pain if you follow a few simple rules.
Nutrition
If your knees hurt after training, you need to make adjustments to your diet. Doctors recommend that athletes:
- take the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates per kilogram of weight required by the body;
- monitor the caloric intake of the diet (calculated individually);
- drink plenty of liquids - water, juices, fruit drinks;
- consume dairy products;
- eat a lot of fruits and vegetables;
- eat steamed and boiled food.
Following these simple rules will reduce the risk of premature joint wear. This will allow you to never know what knee pain is.
Pre-warm-up
To prevent knee pain, you need to remember to warm up, it should last at least 20 minutes. The purpose of the warm-up is to warm up the muscle fibers and prepare them for the upcoming loads. Exercises should be easy, but such that they affect not just any specific part, but the whole body. You need to load yourself gradually, in no case making jerks. This rule applies not only to beginners, but also to those who already have sports training.
Don’t forget about medical examinations; they should be regular, even if there is no discomfort.
Experts recommend drinking a lot of fluid, 2 liters or even more (but only if there are no contraindications). For normal functioning of joints you need to consume fish oil and flaxseed oil. These products contain omega-3 fatty acid, which acts as a lubricant.
Squats with weight
When performing squats with a weight parallel to the floor, the knee joint is under heavy load. It is better to perform a full squat to the floor, this will remove excess stress on the joints and reduce the risk of knee injury. If for certain reasons it is impossible to perform the exercise this way (or there is no desire), you can squat until your thighs are parallel to the floor. This can be done without weights or with a barbell up to 15 kilograms.
Stretching at the end of your workout
Stretching will ensure muscle elasticity and joint health. Without it, after exercise, the muscle fibers do not immediately return to their normal state; they are shortened and, as a result, overload the joint and provoke pain. This situation is very serious and can cause the muscle to be torn from the bone.
Balance between antagonistic muscles
The front surface of the human thigh is much stronger than the back. During exercise, the more developed muscle is exposed to the main load. This imbalance causes rapid wear and tear on the joints, resulting in knee pain.
Using moderate weight
Many people try to get into perfect shape by lifting heavy weights. Few people will be able to achieve perfection, but after a month of such exercises you can forget about healthy knees. Therefore, you need to remember the correct technique for doing the exercises. It is important to stick to it and not chase quick results. You need to train muscle fibers and knee joints gradually so that they have time to get used to the load.
The appearance of pain after the first run is normal; in this case, muscles that are not accustomed to running ache. Most trainers and doctors indicate that muscle soreness after exercise is beneficial. It indicates sufficient load.
If pain occurs in a person who runs constantly, it is worth looking for the provoking causes.
Sports activities should be carried out with gradual complication. For running, you need to choose tracks with a special shock-absorbing coating. For those who want to build muscle, it is better to train in the gym and under the supervision of an instructor. He will select a set of exercises individually. Otherwise, the desire to be strong and fit can lead to serious health problems.
The information provided in the article is useful for beginners in sports and experienced athletes. If you carefully listen to your body's signals, follow a healthy lifestyle and the recommendations listed above, you can achieve the desired results without harm to your health.
Basic methods for pain relief
Pain that occurs due to natural causes is easy to eliminate. This is usually done by stroking the knee and then vigorously rubbing it. There is an intense rush of blood to the structural elements of the joint, muscle spasm is eliminated, and the elimination of lactic acid is accelerated. Professional athletes know well what to do if their knees hurt after training:
- straighten up, place your hands on your sides, rise up, focusing on the toes of first one, then the other leg. Shake your feet vigorously and roll onto your heels. Perform exercises 20 times in 2-3 approaches;
- legs spread wide and slightly bent, arms position is arbitrary. Sway gently from side to side to warm up. Then do shallow lunges, using both knees;
- stand up straight, straighten your back, move your legs back one at a time and use your hands to pull your feet towards your buttocks. Perform the exercise 10-15 times in 3 approaches.
Knee massage for joint pain.
Sometimes painful sensations persist even after knee massage and physical therapy. Sports doctors have various types of gels and ointments with a cooling effect. Typically, their main ingredients are menthol and camphor. They act on the receptors of subcutaneous tissue, exhibiting analgesic, distracting, and locally irritating activity. After applying the ointment or gel, a pleasant feeling of coolness occurs, and the discomfort completely disappears. What else can you do if your knee joints hurt after training:
- use cold compresses. Cooling helps reduce the intensity of discomfort. A bag of ice cubes wrapped in thick cloth is applied to the knees for 10-15 minutes;
Cold compress on the knee.
- rest for 30-60 minutes. You can simply lie down or sit down and put your feet on a pillow or put them on a low stool;
- secure the knee with an elastic bandage. To do this, use a narrow bandage of medium or high stretch, which is wrapped around the knee several times. Pharmacies and medical equipment stores sell sports bandages that are comfortable to wear and do not restrict movement. Sports doctors recommend using them during training to reduce the likelihood of injury.
A special Ben-Gay cream (in green packaging) with menthol is positioned by the manufacturer as a product that improves the tolerance of prolonged physical activity. The drug is recommended for use both before and after training. But it contains methyl salicylate, which is included in the group of non-steroidal drugs. Therefore, frequent use of Ben-Gay can lead to an excessive pharmacological load on the body with the likelihood of developing an allergic reaction.
What to do when joints hurt after training is decided only by a doctor after carrying out diagnostic measures. If the results of instrumental studies do not reveal degenerative tissue degeneration, then wearing soft bandages and a good warm-up before training will help eliminate discomfort in the knees. And if developing articular pathology is detected, long-term therapy with chondroprotectors, analgesics, and NSAIDs is required.
Why might your knees hurt?
Knees hurt for both pathological and natural reasons. The latter include pregnancy, serious physical activity, and natural aging of the body. But much more often, discomfort is provoked by inflammatory or degenerative diseases.
Frequently or periodically occurring pain syndrome indicates a malfunction of one of the structures that ensure the functioning of the joint. It is formed by two bones, the surface of which is lined with hyaline cartilage.
The ligamentous-tendon apparatus, muscle fibers, nerves, and blood vessels are responsible for its functioning. When they are damaged, pinched by inflammatory edema or a bone growth formed, pain is felt directly in the joint itself.
In orthopedics and rheumatology, the main pathologies are distinguished. They are the ones most often diagnosed in patients.
Deforming osteoarthritis
Deforming osteoarthritis of this localization is called gonarthrosis. Due to the progressive degenerative changes in bones against the background of destruction of the cartilage lining, arthralgia occurs.
Age-related changes act as a provoking factor. Collagen production decreases and regeneration processes slow down. The cartilage slowly but persistently deteriorates and ceases to soften the impacts of the bones, which leads to their deformation.
Osteoarthritis cannot yet be completely cured. At the initial stage, it is possible to slow it down by taking chondroprotectors and dosed physical activity.
If it is detected too late, then conservative treatment is ineffective - bone grafting, arthrodesis, and endoprosthetics are required.
Arthritis
When the connective tissue elements that form a joint are inflamed, discomfort is felt constantly or during its flexion and extension, including while walking.
Before treatment, it is necessary to establish the cause of the lesion. This may be a previous injury, the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms, and even the use of certain pharmacological drugs.
Arthritis develops due to hereditary predisposition, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, deficiency of fat- and water-soluble vitamins, micro- and macroelements.
The prognosis is mostly favorable. Especially if you seek medical help in a timely manner.
Bursitis
Due to acute, subacute or chronic inflammation of the synovial bursa, exudate constantly forms and accumulates in it. Bursitis develops, the characteristic symptoms of which are a rise in body temperature, malaise, pain, swelling and redness in the affected area, and moderate limitation of movements in the joint.
The main method of therapy is fluid extraction using puncture in a hospital setting, followed by a course of antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Chronic bursitis is much more difficult to treat than acute bursitis due to the peculiarities of its course and rapid progression.
Synovitis
The disease is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the synovial membrane, which does not spread beyond its boundaries.
Abundant exudate accumulates in the joint cavity, pressing on sensitive nerve endings. Since the synovial membrane is responsible for the proper production of lubricating fluid for bone surfaces, there is a high probability of damage to them.
Synovitis can be triggered by the penetration of infectious and allergic agents, hematopoietic disorders, endocrine and metabolic disorders.
It is indicated by an increase in the volume of the joint, weakness, pain, which increases with movement. When drawing up a therapeutic regimen, the doctor focuses on the type of synovitis.
Tendinitis
The pathology occurs as a result of inflammation of one of the tendons that ensures the correct displacement of the articular elements. It is important to diagnose it as quickly as possible. And also start treatment in a timely manner. The greatest danger is chronic tendinitis.
The discomfort is mild or moderate and is usually felt with a sudden change in weather, hypothermia, or heavy lifting. Therefore, the patient is in no hurry to see a doctor. ,
And at this time, irreversible destruction of the cartilage lining occurs. Tendonitis can be treated quickly and successfully. It does not have a long rehabilitation period either.
Osteochondritis dissecans
This is a rarely diagnosed disease of the knee joint, leading to the death of a small osteochondral area.
It is located on the articular head and subsequently falls directly into the cavity. There, the fragment of cartilage moves freely, without showing itself in any way. But as soon as it gets between the bone surfaces while moving, the functioning of the entire joint is disrupted.
Doctors often adhere to a wait-and-see approach, but only in children, adolescents, and young patients.
Osteochondritis dissecans often disappears after a course of medications that improve blood circulation. In older patients, it is diagnosed extremely rarely and requires surgical intervention.
Baker's cyst
A small hernia occurs in young adults, children and adolescents. Baker's cyst is so small that it is not always detected by palpation.
Hernial protrusion does not pose a threat to the health of adults and children; at the initial stage it causes minor discomfort.
If the cyst enlarges, then their severity increases due to compression of the nerve roots, especially when bending and straightening the leg.
Theta healing for pain
Little is known to humanity about the theta-healing technique, which will help in the fight against muscle pain. This method is available to a person for independent development, but there are a lot of articles on this topic, courses and trainings.
Thetahealing is a meditation that helps you learn to listen to your own body and reduce the discomfort that appears due to chronic diseases.
The brain, working at the theta frequency, is able to relieve the person suffering from pain, the body subsequently trains, and the healing energy helps to heal injured parts of the human body.
The main condition for recovery using the theta-healing technique is liberation from all negative thoughts that prevent energy from penetrating into the human soul.