It is very unpleasant when, after an intense workout, a sharp and painful sensation suddenly arises, which is accompanied by an involuntary convulsive contraction of the muscle. This lasts from a few seconds to 15 minutes, and may repeat periodically. The range of pain varies from simple unnoticeable tingling to unbearable pain. Therefore, it is necessary to be able to immediately determine the cause of seizures and provide first aid. This will alleviate the athlete’s condition and prevent subsequent risks.
What are cramps
A cramp is an involuntary muscle contraction that causes sharp pain and lasts from a few seconds to 10-15 minutes. Cramps can occur in any muscle, but most often in athletes, cramps in the legs: the muscles of the thigh and lower leg suffer. Less often, it can cramp your arms (skiers and swimmers), and your abs (skiers). Muscle cramps can occur during a hard workout, during a competition, and even the next day during recovery. Cramps often occur during sleep, when blood flow to the muscles slows down.
Measures for muscle cramps
The following simple exercise will help relieve spasms in the back of the thigh: leaning with one hand on the back of a chair, bend your cramped leg at the knee, grab your foot and pull it up towards your buttocks.
After muscle performance has been restored, it is necessary to apply a warm compress or heating pad to the source of recent pain , but it is better to take a hot bath or warm up in a sauna . Try to limit the mobility of the affected limb to prevent recurrence of seizures.
Causes of seizures
The exact cause of muscle spasms is not yet known. They last a short period of time and depend on many factors that influence each other. The cause must be determined individually in each case by observing the body.
Overload and muscle fatigue
When overloaded, microtraumas appear in the muscles, and the transmission of nerve impulses that regulate muscle contraction and relaxation is disrupted. Instead of the usual contraction and relaxation, uncontrolled tone occurs - convulsions.
Cramps can appear from systematic overwork when muscles do not have time to recover between workouts. To avoid this, dose the load correctly and take rest days. To recover after hard workouts, get a massage, relaxing baths, and get enough sleep. Rolling out the muscles on a massage roller .
To avoid cramping during competitions, include fatigue training in your plan. For example, running on tired muscles after strength training. The stronger the muscles, the less likely it is to cramp, so strength training in the gym and repeated accelerations uphill are important in preparation.
Violation of water-salt balance
Why is the water-salt balance disrupted?
- Increased sweating and high concentration of salts in sweat
- Insufficient consumption of water and mineral drinks during exercise
- Lack of minerals and fluids in the daily diet
During exercise, the body loses moisture and minerals - this can be seen by white stains on the body and clothes after training. Sodium is lost mainly through sweat, with a much smaller portion coming from other minerals. With the loss of these substances, the water-salt balance of the body is disrupted. A lack of electrolytes leads to rapid muscle fatigue and impaired nerve conduction. If you continue to load the body in this state, the muscles will begin to cramp. Therefore, with large sweat losses, it is better to drink not just water, but isotonic drinks or non-carbonated mineral water.
Read: Nutrition for long distance competitions .
During exercise, only part of the losses can be replenished, so regular balanced nutrition is important. The body must receive enough substances from food. In cases where it is not possible to eat well regularly, you can use special nutrition. In hot climates, athletes use sports drinks or salt capsules with water.
Musculoskeletal problems
The cause of cramps can be muscle imbalance and other abnormalities. The most common is flat feet. Due to the lowering of the arch, the foot cannot absorb shock and falls inward. The load is distributed unevenly, which leads to cramps in overloaded muscles.
To prevent flat feet from interfering with your life and training, purchase orthopedic insoles, run in properly selected sneakers and strengthen your foot muscles .
Read: What is pronation and hyperpronation of the foot .
Various diseases
If cramps are in no way related to exercise and occur randomly, be sure to consult a doctor. Cramps can occur in different muscles throughout the body, including internal muscles. The cause may be various diseases, ranging from acute respiratory viral infections to varicose veins, renal failure and cirrhosis of the liver.
Symptoms
- The manifestation of cramps is mainly noted in the muscles of the calves of the legs. They are so strong that they force the entire limb to move;
- When the leg is brought together, severe pain is felt that intensifies with movement. It seems that a hard lump is forming in place of the shin, which is about to burst;
- muscle pain gradually disappears and slow relaxation of the calf occurs. There remains a feeling that the repetition of the spasm will not be long in coming at the slightest movement.
Sometimes, a cramp during training is not a consequence of overexertion, but a symptom of a serious illness. They can be distinguished by accompanying characteristics:
- hallucinations and clouding of consciousness - a change in the perception of the surrounding reality: voices, smells, images - an impending epileptic seizure;
- during a convulsion, involuntary urination or bowel movements occur - clonic or tonic convulsions;
- fainting with convulsions – head injury, sharp increase in intracranial pressure, alcohol poisoning, hysterical attack;
- rapid breathing, agitation, motor activity, convulsions with breathing problems are signs of hyperthermic syndrome. Occurs due to disturbances in thermoregulation, heat exchange, or while taking medications.
Convulsions also occur after:
- stroke;
- vaccinations;
- operations;
- binge drinking;
- cough;
- at high temperature;
- poisoning;
- and other various conditions.
Why do my muscles cramp at night?
Cramps at night are not limited to people who play sports. There may be several reasons: poor circulation, muscle hypertonicity, overwork or lack of necessary substances. Night cramps can occur both from excessive exertion and from low mobility. For example, professional drivers and people who have to work on their feet for a long time. To avoid night cramps, self-massage the problem muscles, apply a little warming ointment, or relax the muscles with warm water. This is necessary to relieve hypertension and improve blood circulation.
If cramps continue to occur regularly, see your doctor to look for the cause.
Are seizures dangerous?
Short-term cramps after physical activity are safe for health. If cramps from sports appear regularly throughout the body or are not associated with physical activity at all, be sure to consult a neurologist. Muscle spasms throughout the body can be life-threatening because the chest muscles responsible for breathing or other important internal muscles may spasm. It is also worth seeing a specialist if seizures are accompanied by swelling, fever, redness of the skin and other symptoms.
If cramps appear without exercise, they can be symptoms of various diseases, such as varicose veins, flat feet, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, renal failure, Parkinson's disease, liver cirrhosis, spasmophilia, multiple sclerosis.
Source: joeallam.co.uk
What to do if your muscles cramp
If your muscles cramp during training or competition, stop and try to slowly stretch the sore muscle. Most often, cramps appear in the calves, in this case, pull your toes towards you. The same method helps when the foot cramps. Stretch the muscle until the cramp goes away. When the pain goes away, you can continue moving.
Another effective emergency treatment is to prick the muscle with a needle or pin. Don’t forget, the needle must be clean, pre-treated with alcohol.
When the acute phase has passed and there is no acute pain, do a massage, relaxing baths and stretching, you can apply a little warming ointment.
Stretching exercises
- We stand on our toes and walk on a flat surface for several minutes;
- If you can't stretch your calf muscle well, simply clench your toes for a few seconds. This can be done alternately on each limb. This stretch is perfect for office work;
- Stand facing the wall at a distance of half a meter. Try to lean each foot completely against the wall, swaying, but so that the heel barely touches the floor. In this stretching exercise, you can feel the work not only of the calves, but also of the hamstrings as a whole;
- A classic exercise to stretch the hamstrings. Sit on the floor, straighten your legs. Slide your palms along the surface of the floor towards your ankles. Once you reach the peak, hold this position for 30 seconds;
- Standing position. This stretching method requires a support assistant, such as a chair. Take a stable position next to him. With your right hand, grab the tendon of the long extensor of the big toe, try to pull it with your heel towards your lower back (you can lean forward slightly). This exercise is a great stretch for the quadriceps femoris muscle;
- A good option would be to imitate any shape of twine. Transverse and longitudinal capture various muscle groups;
- The most enthusiastic can master yoga techniques that use more complex stretching exercises. Yoga has many directions, the main thing is to decide on the desired result and the level of your training.
We suggest you read: Why do my arms and legs go numb at night while sleeping?
Don't forget to do these exercises regularly, at work, at home or in the fitness club. Try to devote time to prevention, because this is what your success in training depends on.
Prevention of seizures in athletes
Follow these simple tips to avoid seizures:
- Do a warm-up and cool-down. This improves blood circulation, prepares the body for stress and recovery.
- Increase your training volume gradually, starting strength training with the lightest weights
- Take a vacation. During recovery, the muscles “digest” the load and adapt to it. Relax your muscles with a massage, bath, sauna
- Don't forget about restoring your nervous system. Get enough sleep, take complete rest days from training
- Stay hydrated - drink water or isotonic water. In hot weather over long distances, try to drink mineral water (still), isotonic water or take salt capsules
- Make a competent training plan that will lead you to your goal. Gradually adapt your muscles to the loads, be sure to do strength training. For example, if you are going to run a marathon in the heat, it is not enough to train for 5 km in cool weather.
Always monitor your body and pay attention to the conditions under which cramps occur. It could be hot weather, increased sweating, or some specific load. Then you will know the weak points of your body and work on them.
Abdominal muscle spasm - causes, symptoms, treatment
In that article we collected the most complete information about abdominal muscle spasms, their causes, symptoms, and treatment.
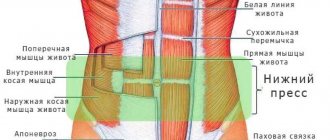
Abdominal muscles
The human abdominal wall consists of several types of muscles. The abdominal muscles perform important functions. The main line of our body is supported precisely by the abdominal muscles.
The peritoneum is responsible for intestinal motility, controls internal abdominal pressure, and helps maintain the placement of internal organs in appropriate positions.
Any weakening or damage to the peritoneum leads to muscle strain. This especially affects women after 50 years of age, who stop taking care of their physical shape long before that.
The most unpleasant thing that can await a woman is prolapse of the internal genital organs. Simply put, prolapse of the internal pelvic organs.
Modern medicine offers patients to use a bandage for prolapse; you can even buy it on the Internet. But this is not a reason to give up daily exercise and training, but a reason to think about your health and take all measures to preserve it.
Causes of abdominal muscle strain
The main cause of abdominal muscle strain is excessive tension. This can happen due to excessive overvoltage when too much load is applied. Excessive tension can also be caused by injury or sudden abnormal movement of the body along its axis. This typically occurs due to lifting, pushing, or pulling heavy objects.
Sports activities can cause tension in the abdominal muscles. Peritoneal spasm can occur during breaststroke, ice skating, or playing hockey. Abdominal spasms can occur when an obese person tries to perform movements that are unusual for him.
Excessive tension in the fibers leads to micro tears and can cause injury. In the case of severe deformation, the muscle burdened by spasm may be partially or completely torn from the ligament. Which will lead to internal bleeding or a hernia.
Find out more Kidney cancer: features of the disease and causes.
Symptoms of a sprain
As a result of a sprain, a person begins to experience sharp pain in the area where the muscles were damaged. The pain may be so severe that the person cannot contract the abdomen. When you try to do this, the pain intensifies many times over.
Types of pain
Tension or spasm can be broadly divided into three types of pain. It all depends on the severity of the sprain and muscle damage.
- The first type of muscle tension is a condition when the abdominal muscles contract relatively weakly. This does not entail any serious restrictions in movement. It is enough for a person to straighten up and take his usual body position for the spasm to subside.
- The second type of muscle tension is a condition where the pain is moderate. Tension of the abdominal wall muscles during a spasm does not allow a person to turn the torso by twisting the body.
- The third type of tension is accompanied by severe pain in the abdominal wall. Muscle spasms cause such severe pain that even basic movements become difficult to perform.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the cause of abdominal tension can generally only be done through a physical examination. Indirect signs of tenderness, such as swelling, functional loss of muscle strength in a specific area, indicate injury to the abdominal muscles.
A muscle rupture, a hernia and the presence of a gap felt upon touch, upon palpation, clearly indicate the presence of an injury. Hardware diagnostics will help make a more accurate diagnosis. This includes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound or CT.
Treatment
Treatment for cramps depends on the underlying cause. Possible options include:
Home Remedies
To treat abdominal cramps, it is recommended to drink water or sports drinks in moderation.
Many people get relief from home remedies. Pregnant women should talk to their doctor before using home remedies as they may be inappropriate or dangerous for use during pregnancy.
Home remedies that are effective:
- Rest. People experiencing cramping due to pulled muscles will find relief by resting their abdominal muscles while avoiding abdominal exercises.
- Warm. Applying a heating pad to the stomach relaxes the muscles and relieves pain.
- Massage. Gentle massage of the abdominal muscles improves blood flow and relieves pain.
- Hydration. Drinking plenty of water helps avoid dehydration, which can cause or worsen cramps. Sports drinks that replenish electrolytes are also beneficial, but should be used in moderation as they are often high in sugar.
- Epsom salt baths. Warm baths using Epsom salts are a popular home remedy for cramps and spasms. Warm water relaxes muscles, and Epsom salts contain a lot of magnesium, which helps with muscle spasms.
- Peppermint oil is considered an antispasmodic. It has an effect by reducing the influx of calcium into smooth muscle cells. It reduces abdominal pain. Peppermint oil is well tolerated. The most common side effect is heartburn.
Drug treatment
Both over-the-counter and prescription medications help with abdominal cramps. Use depends on the underlying cause of the spasms.
Types of medications that are recommended:
- Aminosalicylates, corticosteroids. Used to treat forms of IBD (inflammatory bowel disease.
- Antacids, inhibitors (PPIs). These medications reduce levels of stomach acid, which contributes to the cramping associated with gastritis.
- Antibiotics. They are prescribed for bacterial infections that cause gastritis and gastroenteritis.
- Antispasmodic drugs. Bentyl (dicyclomine), Hyoscyamine. People with IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) experience a reduction in cramps when using these medications.
- Painkillers. Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and acetaminophen (Tylenol) relieve pain.
Learn more How to keep your eyes healthy?
General treatment features
The main treatment is to reduce swelling, pain and bleeding. Treatment of the abdominal muscle is complicated, first of all, by the fact that complete relaxation in this area is impossible.
Therefore, a person should take a lying position in which the abdomen does not stretch. This will relieve the pain to some extent. The duration of treatment directly depends on the severity of the injury.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain within the first two days.
If the pain is significant, the doctor may prescribe pain-relieving injections. Sometimes an elastic bandage is loosely wrapped around the abdomen to limit movement and provide relief.
Muscle rupture is considered a serious injury and cannot be avoided without surgical intervention.
Abdominal muscle strain can be avoided by strengthening your abdominal muscles with proper exercises.
Watch the video: strengthening abdominal muscles for beginners
It is equally important to perform these exercises correctly. If possible, do this under the guidance of a good trainer. And then tension, spasms, sprains will not be scary for you.
(7 3,57 of 5) Loading...
Source: https://vippsy.ru/sovet-zdorovye/spazm-brushnyh-myshc.html