An abdominal muscle strain is an injury that affects the internal structure of the abdominal muscles. With this diagnosis, the patient experiences tears or stretching of muscle tissue. In the vast majority of cases, such injuries can cause discomfort.
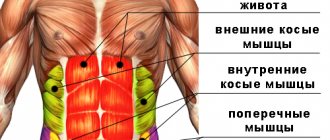
In such a situation, a stretch of the abdominal muscles is an injury to the muscle fibers of the lateral, anterior or posterior muscles of the peritoneum, which occupy the area between the upper part of the pelvis and the lower contour of the part of the body limited by the ribs.
Degrees of abdominal muscle stretch
Diagram of the abdominal muscles
Experts distinguish 3 degrees of stretching of the abdominal muscles:
- Moderate, when mild pain subsides within a few days.
- Average degree. Symptoms go away within a couple of weeks. In this case, patients require qualified medical care. Recovery of such patients can be observed after 3-6 weeks.
- Abdominal muscle rupture. In this situation, the patient experiences excessive pain on the left or right side of the abdomen. In this case, the stretched muscle can no longer contract. This type of lesion occurs due to very strong pressure on the rectus abdominal wall muscles. Typically, the rupture occurs in the connecting bridge of the muscles that make up the wall of the abdominal cavity. In some circumstances, when there is a rupture of the abdominal wall with displacement of internal organs, urgent surgical intervention is required. Treatment of such patients can take an average of 3 months.
Ligament rupture, muscle rupture and tendon rupture
Rupture of ligaments, muscles, tendons are injuries with partial or complete disruption of the anatomical integrity of these formations. They are quite common among people with an active lifestyle - athletes, at work, or when performing heavy physical labor. Such injuries can affect the ability to work and lead to complications. You need to be able to distinguish ruptures from bruises and sprains, because their treatment is different.
Ligament rupture.
Articular ligaments prevent excessive range of motion in the joint and protect against instability. Their rupture occurs when excessive force is applied to the joint, while movement in it occurs in a larger volume, the ligament does not cope with its task and breaks. More often, the ligament is damaged near the place where it attaches to the bone. Most often, ligament rupture occurs in the ankle joint when the foot is twisted while walking or running.
There are three degrees of ligament rupture.
- Several fibers break. Pain during active movements in the joint and slight swelling are typical.
- Less than a third of the fibers are broken. The pain is already stronger, the swelling is pronounced, a subcutaneous hematoma or hemorrhage into the joint cavity (hemarthrosis) may be observed.
- Rupture of more than a third of the fibers up to complete discontinuity of the ligament. The victim feels severe pain, the joint is swollen, unstable, i.e. dislocation occurs.
Rupture of the pelvic ligaments (rupture of the sacroiliac joint, rupture of the pubic symphysis).
These injuries occur in a complex of multiple injuries during road traffic accidents, falls from a height, i.e. only when applying great force. When the pubic or sacroiliac joint is completely ruptured, the pelvis becomes unstable.
Signs - sharp pain, inability to support the legs, the leg is turned outward (with a complete rupture of the pubic symphysis), bruises, shock. Patients with such injuries usually end up in the intensive care unit.
Hip ligament rupture.
Rupture of the hip ligaments occurs when the leg is put under improper load, often in athletes.
Signs are acute pain in the groin, it intensifies when trying to move the joint, hemorrhage, swelling.
Knee ligament rupture.
The most common cause of this injury is a twisted shin, less commonly a fall from a height, a blow to the shin or knee. In the knee joint, the internal and external collateral ligaments, the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments, and the proper patella ligament can be damaged.
Signs: swelling, hemorrhage into the joint cavity (hemarthrosis) may occur. In the case of hemarthrosis, the knee joint is enlarged, the kneecap “floats”, “balloons”. There is a noticeable limp when walking. And with a complete rupture of one or both collateral ligaments, the victim cannot lean on his leg, the lower leg is twisted, and the joint is deformed. If the patellar tendon is torn, the lower leg may sag when the thigh is raised when lying down.
The most common knee ruptures are:
- rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament
Ankle ligament rupture.
Ankle ligament rupture occurs when the foot rolls inward or outward. Such an injury is possible in icy conditions, when wearing shoes with unstable heels, jumping, or when the peroneal nerve is damaged, which causes weakness of the lower leg muscles.
Signs are pain that intensifies when feeling the place where the damaged ligament is attached to the bone, swelling, bruising, pain when moving the joint.
Shoulder ligament rupture.
What is a shoulder ligament rupture? The cavity of the scapula, in which the head of the humerus is located, is shallow. The joint is protected from instability by ligaments that are woven into the joint capsule. The cause of ligament rupture is indirect trauma, often the rupture is combined with a shoulder dislocation.
Signs - unlike injuries to the ligaments of other joints - the absence of pronounced swelling. With untreated injuries to the ligaments of the shoulder joint, a complication is possible - a degenerative process in the periarticular soft tissues (humeral periarthrosis).
Rupture of the ligaments of the elbow joint.
Occurs in athletes, rarely in everyday life. Partial rupture of elbow ligaments without dislocation is not a serious injury; with timely treatment, consequences are rare. The signs are typical - swelling, bleeding into the joint cavity, pain, especially when trying to make a movement involving the injured ligament. If microtraumas are repeated many times, as happens in tennis players, golfers, and baseball players, the ligaments become inflamed, and constant pain in the elbow and forearm is typical. To prevent these conditions, full elbow extension should be avoided during training.
Rupture of the ligaments of the wrist joint.
Happens when falling on the hand or sudden movements. Characterized by acute pain, painful movements, swelling, and in severe cases, instability of the wrist joint. Similar signs can be observed with wrist fractures, so an x-ray should be taken.
Rupture of ligaments of fingers and toes.
When one of the lateral ligaments of the interphalangeal joint is ruptured, a deviation of the phalanx in the opposite direction is noticeable. If both ligaments are torn, the finger is straightened at the joints.
Spinal ligament rupture.
Causes: throwing the head back when the car suddenly stops, playing sports, lifting heavy objects, falling. The ligaments of the lumbar and cervical regions are most often damaged. The victim experiences pain of varying severity, spasm of the back muscles, and painful movements of the spine are observed. The ligaments of the spine are poorly supplied with blood, so their healing process is long, up to a year.
Treatment of ligament rupture.
It is necessary to immobilize the limb using a splint from improvised means, apply a pressure bandage (this can be an elastic bandage or a regular one), apply cold, and give an anesthetic tablet (pentalgin, ketorol). Next, the doctor will determine the degree of the rupture, and further measures will depend on it.
For grade 1-2 tears, an elastic bandage or plaster splint is applied for 10-14 days, rest, anti-inflammatory drugs, often locally (Nise, Febrofide, Ketonal), and physiotherapy are prescribed. If there is blood in the joint cavity, a puncture is performed. Grade 1-2 ligament tears are usually treated on an outpatient basis. It should be remembered that these injuries may accompany other serious injuries. For example, a rupture of the medial collateral ligament of the knee is combined with damage to the medial meniscus. Often this injury requires surgical intervention.
Grade 3 tears require comparison of the articular surfaces (reduction of the dislocation), longer immobilization of the joint (plaster splint for 1-2 months), and, often, surgical treatment. The tactics depend on which ligament and in which joint is torn.
Tendon rupture.
Tendons are a continuation of muscles and, when attached to bones, provide active movements in the joints. They can be damaged by direct application of force (wound, blow with a blunt object) or indirect force (sharp muscle contraction).
Might be interesting
Back pain
Hip ligament rupture
Shoulder ligament rupture. Operation.
Such injuries are more common in athletes, manual workers, and less often in older people; their tendon tissue is not so elastic due to destructive processes in the joint. The most common sites for tendon rupture are the Achilles tendon and the rotator cuff tendon. There are partial and complete tendon ruptures. A rupture with intact skin is called subcutaneous.
Degenerative tendon ruptures also occur due to their overstrain, which leads to microtrauma. This happens with repeated repeated loads (for those involved in sports, heavy physical work).
In some cases, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging are required to confirm the diagnosis.
Quadriceps femoris tendon rupture.
The quadriceps muscle (quadriceps) extends the knee. Damage to the tendon is typical for runners and jumpers, although it also occurs in everyday life, especially when blood flow in the tendon is impaired.
Signs: a click and acute pain at the time of injury, a defect above the knee is palpable, hemorrhage, inability to straighten the leg at the knee, lameness.
Achilles tendon rupture.
The Achilles tendon is the largest in the human body. It breaks in jumpers (when trying to jump from a place), when slipping from a step, or when a blunt object hits the lower part of the shin from behind, injuring this area.
Signs: acute pain, a click at the moment of rupture, inability to pull out the toe, lameness, hemorrhage.
Biceps tendon rupture.
The biceps flexes the arm at the elbow. There are ruptures of the lower and upper parts of the biceps tendon. Causes: lifting weights with a jerk, degenerative processes in tendon tissue in older people.
Signs: acute pain, clicking when injured, bruising. When the lower part is torn, there is a displacement of the muscle upward and its abdomen is visible under the skin like a ball; the person bends his arm at the elbow with difficulty. If the upper part of the tendon ruptures, the muscle, on the contrary, falls lower, the function of the elbow joint is not particularly affected, since the tendon in the upper part has two heads, and both of them tear very rarely.
Rotator cuff tendon rupture.
The rotator cuff is made up of three muscles, each of which is responsible for a specific movement in the shoulder joint. Damage to the tendons of these muscles is typical for athletes, people who lift weights, and the elderly due to degenerative processes.
Signs are pain, especially at night and when trying to make one or another movement in the joint. More often the supraspinatus tendon is affected, in which case the person cannot raise his arm above his head. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is often necessary to undergo magnetic resonance therapy.
Rupture of the tendons of the fingers.
There are ruptures of the flexor and extensor tendons of the fingers. The extensors are damaged by open wounds of the hand, less often by blows.
Signs: a wound on the dorsum of the finger, the finger is in a half-bent position, active extension is impossible. When the extensor muscle is torn at the level of the superior interphalangeal joint, the finger is deformed: the nail phalanx is straightened and the middle phalanx is bent.
The flexor tendons are damaged by incised wounds of the hand. The victim cannot actively bend the finger.
Treatment of tendon rupture.
First aid is the same as for a ligament rupture.
Treatment is often surgical, although there are exceptions (preserved traction function of the tendon). For a fresh injury, the surgeon performs a suture of the tendon, and for an old injury, plastic surgery.
Muscle rupture.
Excessive muscle tension from heavy lifting, falls, sports, or direct trauma leads to muscle tissue damage. Less commonly, fascia (the film covering the muscle) ruptures, resulting in a protrusion - a muscle hernia.
A distinction is made between complete and incomplete muscle rupture. In case of incomplete damage, weakness of the damaged muscle and pain during its contraction are characteristic. With a complete rupture, the pain is quite severe and the muscle loses its function completely.
Sometimes muscle tissue, like tendon tissue, is damaged as a result of systematically repeated microtraumas, which lead to poor circulation and degenerative processes. An example is muscle strain in athletes, assembly line workers, and musicians. People in these professions often experience muscle pain during or after physical activity.
More often, a rupture occurs in a muscle that is not prepared for the load, so when playing sports, a warm-up (stretching exercises) is necessary before training.
More often, ruptures occur in the quadriceps femoris, biceps brachii (biceps), and calf muscles. The symptoms of rupture of these muscles are similar to the symptoms of damage to their tendons, only the defect can be felt throughout the muscle itself.
Signs of muscle tear.
- Acute pain, sometimes a click is heard at the time of injury.
- Divergence of the ends of the muscle and palpation of the defect.
- Hemorrhage, hematoma.
Treatment of muscle rupture.
If there is a suspicion of muscle rupture, it is necessary to immobilize the limb and apply cold. For incomplete ruptures, after a period of rest, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, and massage are performed. Complete ruptures are treated surgically with U-shaped sutures.
Polimedel
Treatment of ruptures is significantly accelerated when using POLYMEDEL film. The film was invented by Leningrad scientists in the 80s of the 20th century, and underwent clinical trials in dozens of medical and research institutions, as well as in the field conditions of military hospitals. This is a therapeutic electret film that:
- improves blood supply to the affected area,
- restores the capillary system in the application area,
- enhances metabolic processes and the process of tissue regeneration,
- activates immunity (local and general),
- structures biological fluids, mainly blood and lymph,
- imparts an electrical charge to the cell membrane, which it loses due to toxins,
- has anti-edematous and antimicrobial effects,
- relieves pain
- enhances the effect of drugs.
You can learn more about Polimedel and also purchase the film HERE
(consultations by phone)
Abdominal muscle strain: possible causes
Performing physical exercises without prior warming up the muscles
As experts note, there are a number of provoking factors that increase the likelihood of receiving this type of injury (abdominal muscle strain). These include overstrain or not very good stretching of muscle fibers, weak muscles, fatigue, as well as performing sports exercises in the cold. If we talk about the main reasons for this problem, they include:
- excessively heavy physical activity;
- strong twisting movements of the body;
- performing physical exercises without prior warming up the muscles;
- lifting excessively heavy things;
- incorrect exercise technique;
- insufficiently well developed muscle corset;
- pregnancy.
Main reasons
The areas where the muscle meets the tendon are the most vulnerable. Tears most often appear in the back, thighs, forearms, calves and shoulders. The abdominal muscles, neck and chest are much less likely to be injured.
Damage to muscle fibers is caused by:
- sharp swings and turns;
- uncomfortable workout clothes that limit joint mobility;
- warm-up before training is too short or absent;
- too intense loads;
- training in a state of physical or emotional exhaustion.
Blows, falls and cuts lead to muscle tears. The risk of serious injury increases if the patient is retired or has recently had an infectious disease. In old age, the structure of muscle fibers is disrupted, and they become more susceptible to mechanical damage and sprains. Similar changes occur in soft tissues during serious illness.
Signs of damage
Often, the symptoms that appear with this type of injury may indicate some other health problems. Only the attending physician can make a final diagnosis. The following symptoms of abdominal muscle strain are distinguished:
- pain in the abdominal wall;
- a feeling of discomfort in abdominal tissues that can contract;
- pain when touching muscle tissues, when they are tense or when the body is bent;
- muscle spasms;
- formation of hematomas;
- swelling on the right or left side of the abdominal wall, depending on which abdominal muscles are injured.
Abdominal pain with abdominal muscle strain
First aid for muscle rupture
Serious muscle tears require emergency medical attention. If a hematoma, severe swelling and impaired motor function appear in the area of damage, you should consult a doctor. First aid at the scene of injury in such situations does not require special knowledge and skills:
- it is necessary to limit movement in the area of damage;
- apply cold (cold water bottle, bubble or ice pack);
- give the victim a pain reliever;
- take him to a medical facility.
Treatment of injury
If one of the peritoneal muscles is stretched, then treatment will directly depend on how pronounced the symptoms of the disease are and the degree of injury suffered. Thus, the degree of stretching of the abdominal wall muscles will determine the duration of therapy.
The key point for such patients is complete rest for the abdominal muscles and the absence of even the slightest stress. At home, the patient should avoid heavy lifting and sudden movements, which increase muscle tone. This is especially important during the first two days after the injury.
If the patient has suffered moderate to severe sprains, then in this case experts recommend applying cold to the injury, which must be done in sessions lasting 15-20 minutes. After they expire, you should take a break.
In order to apply cold to the injury, you can use ice cubes wrapped in cellophane and a towel. It is not recommended to apply them directly to a bare area of the body.
Abdominal muscle strain: tips
In order to relieve unbearable pain, the attending physician may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics in the form of tablets, injections or ointments. This will significantly alleviate the patient’s condition and improve his well-being.
In order to get back into shape after an injury, the patient will have to make some efforts. Do not forget that if sharp painful sensations occur as a result of lifting heavy objects or performing sports exercises, you must immediately stop the load on the body. Physical activity should be limited or completely suspended. This will depend on the severity of the injury.
At the same time, during the period of treatment and restoration of health, it is recommended to rest regularly, apply cold compresses for 1-2 days after the injury, do not refuse to take painkillers, and gradually stretch the abdominal muscles when the pain begins to recede.
Causes of damage to muscle structures
In general, ruptures and sprains of muscle structures belong to the same class of injuries and differ only in severity. Thus, classic sprains correspond to mild forms of the pathological process, in which only individual fibers of soft structures are susceptible to damage. At the same time, muscle ruptures can be partial or complete.
Among women
As practice shows, quite often in pregnant women in the last stages of gestation, also during childbirth, the muscles can be damaged accordingly, forming partial tears. Such spontaneous pathologies primarily manifest themselves in women in the muscles of the lower section (lower abdomen) pyramidal and rectus.
In addition to the above reasons, direct injuries to soft fibers as a result of strong physical impact, overexertion, usually against the background of insufficient muscle development, are also considered classic predisposing circumstances.
In men
In representatives of the stronger sex, it is often quite difficult to visually identify a specific type of injury to the abdominal muscle.
Obvious causes of systemic damage to fibrous structures are extremely strong physical stress on the abs and abdominal area.
These loads are formed in men as a result of sports, hard work, or in everyday activities associated with lifting weights against the background of insufficient muscle training.
During pregnancy and after childbirth
Most often, sprains or ruptures of the abdominal muscles in women after childbirth and during their process are formed when the expelled fetus ceases to exert pressure from the inside and the corresponding structures contract extremely quickly. Surgical intervention, for example, caesarean section, with the formation of a number of complications, also has a pathological effect.