Greetings, dear readers! Today I want to discuss such a common phenomenon as clogged muscles. Many gym goers experience this. Some people think that this is how it should be and that this is a sign of well-conducted training. Others are afraid and try in every possible way to avoid being overwhelmed.
Quite recently, one of my friends, who recently started training with iron, complained that the next day after training he felt sore muscles. This prompted me to write an article, because he is probably not the only one who has questions about this phenomenon.
Why do our muscles get tired?
Let's understand the mechanisms that occur in our muscles during and after training.
When we lift weights, our muscle fibers begin to contract. This process requires energy. The main energy source for muscles is ATP (adenosine triphosphoric acid), which in turn can be synthesized in several ways. But during strength training, we tend to use up muscle glycogen. From which ATP is formed during the reaction of anaerobic glycolysis.
But every coin has a flip side, so as a result of the above chemical reaction, a by-product is formed - lactic acid (lactate). It is the culprit of muscle fatigue during training. Fortunately, the body quickly copes with its concentration in muscle tissue. And as soon as we rest after an approach for 1-2 minutes, we are ready for the next approach.
But this process is not endless. The fact is that the blood circulating in the muscle removes lactic acid, but this takes more than 30 minutes. And we only rest for 2 hours, so lactate slowly accumulates and our performance decreases.
Usually, gym enthusiasts get so carried away that by the end of the workout they can barely drag their feet. And the next day they can’t get out of bed or even brush their teeth because they can’t lift their arms. Is it all because of lactic acid?
Causes of muscle soreness
No, the reason here is no longer lactic acid. She safely left the muscles 30-60 minutes after training. Post-workout pain is caused by microtrauma to muscle fibers caused by overuse. Because someone doesn't know the limits. But most often, sore throat, also known as muscle pain, is observed in beginners. Since their muscles are not yet adapted to the load and receive many microtraumas, which lead to severe soreness.
Minor muscle soreness is not dangerous and usually ends after a recovery period. As your training progresses, pain after exercise may stop appearing altogether.
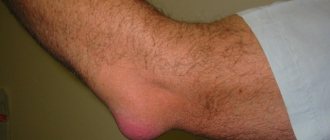
How can you clearly understand that your muscles are clogged? First of all, this is expressed in some swelling of the muscle, it looks swollen. After all, protein-rich tissue fluid and lymph rush to the site of damage. Movements become more constrained due to the fact that tension in the muscle group is accompanied by pain.
It happens that the soreness is pronounced and does not go away for a long time. What could this mean?
- Training too hard
Perhaps you overdid it in your workout. Scientists have found that pain mainly occurs during eccentric muscle contraction. That is, when the muscle lengthens, but at the same time is under tension (an example from life is going down the stairs). Therefore, negative repetitions contribute the most to muscle damage. For those who don’t know, a negative movement is the phase in which a muscle is stretched, such as lowering a barbell during biceps curls.
- Not recovering
Small muscle groups such as arms or shoulders require 2-3 days to recover. And large ones - legs, back, chest - from 3 to 7 days. If you train them more often, there is a high probability of overtraining. In simple words, the muscles will simply become clogged and will not be able to work at full strength. Working weights will fall or stand still.
- Neglecting stretching
You're neglecting stretching. The fact is that after removing the load from the working muscle, residual deformations may be observed in it. That is, the muscle tissue does not relax completely. If you leave this fact unattended, over time it can lead to muscle spasms, cramps and a constant feeling of congestion.
- Asymmetrical muscle development
Despite the fact that we seem to be symmetrical relative to the sagittal plane (the vertical plane of human symmetry), our muscles on one side and the other may not develop equally. There are many reasons: for left-handers, the left hand will be more developed, for those who are used to leaning on their right leg, it will be stronger than the left.
Sometimes this can cause the muscles to become clogged on one side. This type of congestion occurs during training. For example, when you do dumbbell curls, one hand can still lift the dumbbell, but the other is no longer able to do it. Or another striking example - the barbell press - when a person squeezes one side faster than the other.
- Daily Activities
Muscle congestion is not always associated with training. The back, neck and calves can get tired whether we exercise or not. This is caused by their functions in our daily life. The neck, back and, in particular, the lower back stabilize the position of the head and spine and are especially heavily loaded when we sit for a long time, especially in incorrect positions.
The calves maintain balance when walking and are responsible for pushing off the foot when moving. Their constant tension, especially static, leads to negative consequences. Blood flow in the muscles deteriorates and this leads to a lack of nutrients and spasms.
If you feel any symptoms of sore throat, then carefully look to see if you fall under one of the above points.
A familiar feeling - sore throat
If you woke up one day and couldn’t get up calmly due to muscle pain because yesterday there was an active workout, it doesn’t matter whether you’re a beginner or a regular at the gym, then you felt all the delights of clogged muscles. The cause of soreness is micro tears, which, when healing, increase the growth of muscle tissue.
In order for your muscles to recover, you must take a rest day between workouts. Also causes of muscle congestion are diseases of the nervous system, shock and stroke. From a biochemical point of view, the causes of blockage are:
1. Lack of lactic acid in bloated muscles.
2. Lack of blood access to the muscles due to their contraction.
On the one hand, muscle congestion is an indicator of a good workout, after which you feel aching and bloated muscle tissue throughout the day, on the other hand, it creates a feeling of “cottoniness”.
How do you know if your muscles are clogged? If the following symptoms are observed, then this is about your condition:
- a feeling of “stoniness” in the legs/arms/back after direct exposure to heavy training or running;
- the muscles are swollen (for example, trousers become tight not because of poor nutrition, but because of short-term swelling of the muscles);
- cramps, knee pain.
How to deal with sore throat?
How to deal with muscle congestion? You are unlikely to find a universal recipe, and once a sore throat occurs, you will not be able to get rid of it. But you can ease your suffering and speed up the process of muscle recovery. Here are some tips for you.
- A thorough warm-up before training is paramount. If you do not prepare the body for the load, the likelihood of developing sore throat increases. For example, before squatting, don’t forget to thoroughly stretch the muscles involved in the exercise—your hips and buttocks.
- Stretching is one of the most effective ways. But you don’t need to stretch your muscles the day after training, when they are already sore. Although this is also welcome. It is much more important to do stretching immediately after training. Or even between sets. It is not necessary to stretch all the muscles, just do a couple of exercises for the working group
- Temperature effect. These can be either baths with water of variable temperature, or a sauna or bathhouse. Increased temperature will help both relax tired muscles and improve blood flow
- Massage. Mechanical impact on tired areas of muscles leads to improved blood and lymph flow, normalizes muscle tone and promotes the elimination of metabolites (metabolic products). During massage, you can use various ointments that help warm up the skin, improve microcirculation, relieve swelling and prevent skin irritation
- Repeated loading. What to do if your muscles hurt from exertion? That's right, load them again. It sounds crazy, but it might work. Of course, we are not talking about the load that led to pain. For repeated exposure, you can use cardio equipment when it comes to your legs. For the upper body, you can use the same exercises, but with 2-3 times less weight. And the goal will no longer be to clog the muscles, but simply to stimulate blood circulation
It is better to use all of the above methods in combination, so you will achieve greater results. But from now on, I advise you, instead of thinking about how to correct the soreness that has arisen, to prevent its occurrence. It is not at all necessary to hammer muscles during training. After all, it has already been scientifically and experimentally proven that pain is not a sign of muscle growth!
Well, hardware fans, I hope the article was useful to you. Leave your comments and questions. I will be only too happy to answer them!
Subscribe to updates and share useful information with friends on social networks. See you soon!
Muscle recovery time after training. What happens to muscles during exercise?
Question: why do you go to the rocking chair? Answer: swing. The question and answer are familiar to all of us, but it does not reflect the real state of affairs, i.e. what actually happens to muscles. In the gym, during the process of strength work, the athlete only creates the prerequisites for changing his physique and muscle growth, the latter occurring exclusively at the stage of recovery after the gym. Therefore, to say that you go to the gym to exercise (from the point of view of the processes occurring inside the muscles) is incorrect; you go to the gym to create stress for the body/muscles.
When you practice intense exercise, muscle fibers are damaged, and microtrauma activates the body's self-healing mechanisms. As a result, specific cells called satellite cells fuse together with the damaged muscle fibers to repair them. Some of these cells mature and form new myofibrils, which are components of muscle fibers, so once they attach to existing fibers, they trigger hypertrophy—the growth of muscle diameter.
Whenever muscle fibers are damaged during exercise, satellite cells must initiate a cascade of events that promote muscle repair and growth.
Several hormones, mainly growth factors, are needed to support the strengthening of new muscle fibers as well as to facilitate the recovery process.
Insulin also plays a role in muscle recovery as it enhances protein synthesis and facilitates the entry of glucose into muscle cells. Glucose is then stored as glycogen, which is used as fuel for all cells, including satellite cells. Growth hormone and testosterone also promote muscle hypertrophy, and the availability of amino acids that come from dietary protein greatly influences muscle recovery.
Adequate protein intake provides sufficient amounts of readily available amino acids within the body, and these nutrients are necessary for satellite cells to initiate reactions that allow them to repair damaged tissue. A lack of amino acids (as a result of a protein-depleted diet) will slow down the muscle recovery process because satellite cells cannot multiply effectively and therefore cannot begin to repair damaged tissue immediately after exercise.
Now let's look inside the damaged tissue and take a closer look at the process of its restoration.
During strength exercises in the gym, muscle fibers are torn, resulting in microtraumas in the muscles. After some time, the microtraumas heal and the muscles increase in size. The so-called supercompensation effect is observed, that is, when the muscles after training have recovered to their previous level of fitness and exceeded it.
There are several scientific theories, and each of which has the right to live, one claims that muscles grow due to hyperplasia, that is, an increase in the number of muscle cells, and the other is hypertrophy, which means an increase, proliferation of muscle tissue, due to an increase in muscle cells in volume
Achieving the effect of supercompensation, that is, making muscles grow, cannot be done in just one way; all three factors must come together:
- Training program
- Recovery
Nutrition
How to make muscles grow
Each of these parameters is extremely important for muscle growth. For example, the basis, the basic framework for gaining weight, is:
- high-calorie nutrition (the athlete must create a surplus of calories in the body)
- adequate training program (alternating or periodizing light, medium and heavy training)
- proper rest (minimum energy consumption and stress, as well as 8-9 hours of sleep)
By increasing your level of training, you increase your body's ability to absorb glycogen, creatine phosphate in the muscles, as well as a number of other nutrients. Thus, by supplying the body with “fuel”, getting plenty of rest and exercising regularly, you are guaranteed to make your muscles grow.
Calorie nutrition for gaining muscle mass
Rest time between workouts
The optimal rest between approaches in your programs for gaining weight should be 1.5-2 minutes, rest between workouts from 1 to 3 days, but no more than 4 days, this time will be enough for you to rest, recuperate and not fall into detraining.
The choice of ± 1-2 days of rest between workouts should be based on what kind of training was or will be (hard, light or moderate), that is, if you have done a high-power workout and feel that your strength has not yet recovered (signs of increased irritability , fatigue, muscle and joint pain), take an extra break, thereby protecting yourself from the common overtraining that often interferes with the increase in muscle mass and strength results in any sport, not just bodybuilding.
Rest time during training between sets
After how many workouts will I see results?
Before talking about the results that can be obtained from strength training, you need to decide what you expect from the gym:
- Muscle growth
- Increase in strength indicators
- Drying, muscle relief
Weight loss is not included in this list, due to the fact that energy supply in strength training comes from the consumption of muscle glycogen and creatine phosphate, which is why training in the gym is pointless for burning fat.
If you have never exercised, or have been doing it for a very long time, and want to increase your muscle mass, but you will need 1 to 2 years of regular exercise (3 workouts per week) for your body to transform and increase the size of your muscle tissue. Much in this matter will be decided by your body type, how good your metabolism is, how well you absorb nutrients, how strong your tendons and ligaments are to increase working weights in exercises, and of course how much lean muscle mass you initially have and fat. All these parameters directly affect the speed of obtaining results from training in the gym.
Speaking specifically in numbers, the average beginner can, in one year, increase strength by 40-50 kg in the deadlift, by 20-30 kg in the bench press, 30-40 kg in squats with a barbell, while the mass will increase on average by 5-10 kg. These are real numbers that are achievable for everyone if you approach the training process competently.
Drying muscles, working on relief, is advisable for those athletes who already have significant muscle mass (not fat!), through cardio exercises, in combination with a low-carbohydrate diet and strength exercises in pump mode, you can achieve excellent results in 6-12 months.
How long will it take for the muscles to respond to the force load?
Some sports fans believe that clogged muscles are the result of fruitful sports activities, and, most likely, the disease will go away on its own. But it is not so. During exercise, muscles are pumped. And if you play sports for a long time, then the muscle fibers do not have time to become saturated with oxygen. As a result, lactic acid is formed.
Restless athletes often do not pay attention to clogged muscles and continue to train as usual. Perseverance in sports is, of course, good, but in this case, muscle tissue rupture is inevitable. Signs of sore throat are as follows:
- Blood accumulates in the legs and arms in large volumes.
- Microcracks and microfractures.
- Muscle swelling due to the formation of lactic acid.