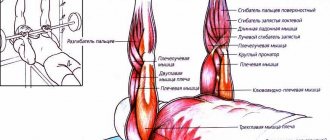
Raising the knees while hanging on the horizontal bar is an exercise for the lower part of the abdominal muscles and a little touches the upper, it works this area very well thanks to the rotation of the pelvis. The exercise has different ways of doing it for different levels of training. It is much easier to perform than straight leg raises; it is considered one of the best exercises for working the lower abs. You can perform bent leg raises wherever there is a horizontal bar; the main difficulty lies in physical preparation. It is necessary to have strong arms, shoulders, grip and abs, because the whole body is tense at the same time, which may seem too difficult for an untrained person.
Description of the exercise
The hanging knee raise on the horizontal bar is a basic exercise designed to train the abs. This exercise is a variant of the more complex exercise Hanging Leg Raise on a Horizontal Bar and can be used to train technique and gradually increase the load at the initial stage. In addition, this exercise works well on the muscles that flex the legs at the hip joints.
Initial position
Hang from the horizontal bar, grasping the bar with an overhand grip. The distance between the palms is approximately shoulder width apart, the arms are fully straightened. The legs can be either straight or slightly bent at the knees. Also, your feet should not touch the floor, so use a horizontal bar of a suitable height. In the starting position, just before starting the exercise, tighten your abs.
Trajectory of movement
We take a deep breath and raise our legs, bending them at the hip and knee joints. Keeping the abs tense, we try to raise our knees as high as possible. Your legs should be raised until your thighs are parallel to the floor. This is considered the primary position at the top. However, the legs can be raised higher, up to the level where they are pressed to the chest. Having reached the top point of the movement, stay in this position for a couple of seconds and, as you exhale, slowly straightening your legs at the knees, return them to their original position.
Abdominal training on the horizontal bar (level No. 1)
Abdominal exercises on the horizontal bar are more suitable for advanced exercisers. If you have difficulty performing crunches on the floor, then it is better to postpone abdominal exercises on the bar for now. Due to a weak core, you will not be able to perform them technically and risk injuring your back. Continue to train your abs on the floor; you can also gradually add simple exercises on the horizontal bar: for example, a regular hang or alternately pulling your knee to your chest. Be sure to check out our selection: 30 core exercises.
Please note that if you regularly perform exercises on the bar, it is still better not to exclude standard crunches and leg raises on the floor from your training program. If you want to comprehensively pump up your abs and core muscles, then include a variety of core exercises in your program to achieve maximum results.
Ready-made strength training plans for men:
- Strength split training for men ready-made plan for 3 days
- Full body strength program for men with dumbbells for 3 days
- Weight loss workouts for men without equipment
Abdominal training on the horizontal bar (light level):
- Knee to chest raises: 10-15 reps (2 sets).
- Static corner: from 20 to 60 seconds (2 sets).
- Lateral raises: 8-10 reps per leg (2 sets).
- Pulling the knees to the chest alternately: 10-12 repetitions on each leg (2 sets).
- Leg raises in the corner position (optional): 10-12 repetitions (2 sets).
Rest between sets 30-60 seconds, between exercises 2-3 minutes. Beginners perform one set of each exercise, not two. You can cut the number of repetitions in half.
Knee to chest raises
How to do it: Grab the bar so that your hands are wider than shoulder-width apart. Straighten your legs, hang calmly, your body does not twitch. From the starting position, lift your knees bent towards your stomach. Pause for a second and slowly lower your legs, returning to the starting position. Do not swing your body, your chin is fixed, only your abdominal muscles work on the bar. Even 5 lifts with correct technique will be better than 15 incorrect ones.
Features: The exercise is aimed at pumping the entire core with an emphasis on the lower abdomen. Thanks to the participation of the pelvis, the muscles contract better than in any other exercise. Raising your legs to your chest will help lay the foundation for the progress of other abdominal exercises on the horizontal bar.
How much to perform: 10-15 repetitions (2 sets).
Static corner
How to do it: To assume the static corner position, grab the bar, arms slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, body forming a straight line. Raise your straight legs up to a right angle with your body. Fix the pose. Maintain this position without lowering or spreading your legs. Concentrate, try to keep your body toned and collected. If you find it difficult to maintain a straight leg position, bend your knees slightly.
Features: The static corner helps strengthen the abdominal muscles, including the deep stabilizing muscles. In addition, the thigh muscles are also well worked out - you will definitely feel a burning sensation in your legs when doing it. Also, this exercise for the press on the horizontal bar helps to draw relief on the stomach.
How long to perform: from 20 to 60 seconds (2 sets).
Lateral lifts
How to perform: Starting position – hanging freely on the horizontal bar, body taut, stomach tense. Begin to alternately raise your bent knees diagonally, first to the right, and the next repetition to the left. Feel the oblique muscles working. Do not make sudden movements, control the smoothness of lifting and lowering. The exercise is not difficult, but do not lose concentration.
Features: Lateral raises on the bar are aimed at working the oblique muscles of the abdomen and the lateral area. In addition to them, the iliopsoas muscles are also included in the work. A great moderate exercise that will add value to your pull-up bar routine.
How much to do: 8-10 repetitions on each leg (2 sets).
Pulling your knees to your chest alternately
How to perform: Starting position – hanging freely on the horizontal bar, body straight and tense. From the starting position, alternately lift your left and then your right leg so that your knee reaches approximately chest level. Raise your legs smoothly, without jerking. As soon as the upper leg begins to go down, we begin to lift the lower one. Tighten your core: you should feel that it is the abdominal muscles that are contracting, and not just the thigh muscles.
Features: While performing the movement on the crossbar, the rectus abdominis and oblique abdominal muscles are perfectly worked out, the gluteal muscles are slightly involved in the work, blood flow in the pelvis is normalized, and the thigh muscles are used. This movement can easily be made into a fat-burning cardio exercise by increasing the speed and bringing your knees toward your chest at a fast pace.
How much to do: 10-12 repetitions on each leg (2 sets).
Leg extensions in a corner position (optional)
You can stop the workout at four exercises, but if you feel strong, finish the program with this challenging complex exercise for the abs on the bar.
How to perform: Fix the starting position - hanging on the horizontal bar, arms wider than shoulders, body concentrated and tense, legs raised to an angle of 90°. Begin to spread your straight legs to the sides, trying not to sway and maintaining a stable position. The distance between your legs should be such that you feel comfortable enough (this is not a stretching exercise, so you don’t need to spread your legs too far). Watch every repetition, only the correct technique will give the desired result. If you find it difficult to do leg raises with your legs straight, bend your knees slightly.
Features: This exercise on the bar is aimed at working the rectus abdominis (especially the lower part), oblique muscles, and core muscles. In addition, the muscles of the inner thigh work. At first, you don’t have to raise your legs to a right angle with your body, but gradually try to reach this position.
How much to perform: 10-12 repetitions (2 sets).
Exercise “Pulling the knee to the chest”
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles .
Starting position: lying down, legs bent, feet hip-width apart. As you exhale, pull your right knee toward your chest. As you inhale, return your knee to its place. As you exhale, pull your left knee toward your chest. As you inhale, return your knee to its place. Continue moving with the rhythm of your breathing.
Our readers successfully use Sustalaif to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Try to stretch your spine. Lengthen your tailbone down toward the floor, with the top of your head up. The shoulders are straightened, the shoulder blades are on the floor, the stomach is tucked. Breathing is calm, even and rhythmic.
As you pull your knee toward your chest, make sure your buttocks don't leave the floor. Repeat the exercise 6-10 times. With another exhalation, pull your legs to your chest, foot forward towards you, raise your head, stretch your forehead to your knee, stay in this position for 3-5 breaths. You feel the tone in the abdomen and the tone in the lower back. Switch sides. Left thigh towards the stomach, extend the right thigh, shorten the foot. As you exhale, lift your head from your knee, maintaining the position and continuing to breathe. As you exhale, relax and lower your head.
Abdominal training on the horizontal bar (level No. 2)
This collection includes more complex abdominal exercises on the bar. Therefore, it is better to move on to it only when you confidently and technically perform the previous program.
Remember that even regular workouts will not get you in shape if you do not adjust your diet. The percentage of body fat directly depends on the quality and quantity of food consumed, so along with training, start monitoring your diet.
- Proper nutrition: 10 steps where to start
- Calorie deficit: how to lose weight correctly
Ab workout on the horizontal bar (difficult level):
- Corner leg raises on the horizontal bar: 10-15 repetitions (2 sets).
- Knee rotation: 8-10 clockwise rotations, 8-10 counterclockwise rotations (2 sets).
- Scissors in the corner: 15-20 dilutions (2 sets).
- Pulling the knees to the chest with straightening: 10-15 repetitions (2 sets).
- Windshield wipers (optional): 8-10 reps on each side (2 sets).
Rest between sets 30-60 seconds, between exercises 2-3 minutes. Beginners perform one set of each exercise, not two. You can cut the number of repetitions in half.
Corner leg raises on the horizontal bar
How to do it: Starting position – hanging freely on the horizontal bar, body taut, stomach tense, legs together, feet not touching the floor. Begin to slowly raise your straight legs to a height just above parallel with the floor, being careful not to separate them. The knees are pulled up, the legs do not bend. Pause for a second in the top position. Then lower your legs as slowly as you can, being careful not to throw them. If you find it difficult to perform this abdominal exercise with straight legs, bend your knees slightly while keeping your legs together.
Features: This is a classic exercise on the bar for the press, which involves working the muscles of almost the entire body. In this exercise, it is very important to avoid inertial swings of the legs without engaging the abdominal muscles. To do this, tense your abs and lift your legs slowly, concentrating on working your core. Otherwise, predominantly the thigh muscles will be used with minimal involvement of the abs.
How much to perform: 10-15 repetitions (2 sets).
Knee rotation
How to do it: This exercise is a more advanced version of lateral knee raises. Starting position – hanging freely on the horizontal bar, body taut, stomach tense. Begin to raise your knees diagonally toward your chest. In the upper position, make a circular motion with your knees bent, moving them to the other side. Then slowly lower yourself to the starting position. Make deliberate, clear movements. Follow your technique, even if it’s hard for you. A small number of high-quality repetitions will bring the greatest benefit. Remember to rotate first clockwise, then counterclockwise.
Features: This exercise on the horizontal bar puts emphasis on the oblique abdominal muscles, and additionally pumps up the entire muscle corset. The thigh muscles are also involved in the work. Doing this exercise will evenly work out problem areas of the abdomen, especially the sides and lower abs.
How much to perform: 8-10 clockwise rotations, 8-10 counterclockwise rotations (2 sets each).
Scissors in the corner
How to do it: Take the starting position - a standard hang on the horizontal bar, arms slightly wider than shoulders, core tense, legs raised to a right angle with the body. Start making vertical swings with your legs, quickly spreading them apart in a small amplitude. During execution, you are allowed to slightly bend your knees, but it is not recommended, as this reduces efficiency. Move your legs continuously, smoothly, without jerking. The pace of execution is average.
Features: This static-dynamic exercise for the press on the horizontal bar helps to evenly use the entire muscle corset, with special emphasis on the rectus abdominis muscle. Due to the static hold, the stabilizing muscles are activated and the grip is strengthened. The muscles of the thighs and buttocks also work.
How much to perform: 15-25 dilutions (2 approaches).
Pulling the knees to the chest with straightening
How to do it: Starting position – hanging freely on the horizontal bar, hands at a comfortable distance from each other, but not too wide. Start bending your knees and pulling them towards your body. After raising your knees until your thighs are parallel to the floor, immediately straighten them, forming a right angle between your legs and body. Hold for a second, then bend your knees again and slowly lower back to the starting position. Do not throw your legs, perform the exercise with concentration and without swaying.
Features: During knee pull-ups, the core and lower abs muscles work perfectly. This exercise on the bar is similar to the standard corner, and therefore, when extending the legs, the thigh muscles are additionally involved.
How much to perform: 10-15 repetitions (2 sets).
Benefits of chair exercises
You can perform these exercises wherever it is convenient for you - at home in front of the TV or at work. To carry out the training, you only need a hard chair or stool and a stable surface for it. Save our collections of exercises and train even in the office - just sitting at your computer desk!
By regularly doing this short seated workout, you can tighten your stomach and make it flatter, work your sides, and even tone your thighs and buttocks. And this in just 10-15 minutes a day! In addition, such a set of exercises will give you strength and energize you.
Important! During exercises, always keep your back straight and never round it. Otherwise, you will overload the work of the lower back, which may cause pain in this area. Leaning on the back of a chair is also prohibited.
Interesting: Exercises with a towel roller for the back
Adviсe
- To better work out the lower abs during the exercise, I advise you to wear straps or hooks, especially for girls and women, then it will become easier to hold on and you will be able to concentrate more on working the muscles of the lower abs. Guys and men are not recommended to use sports equipment; train your grip strength.
- Beginners who want to learn how to perform the exercise of lifting legs on a horizontal bar (because doing it is a direct road to six packs) need to start by lifting the knees.
- Beginners are advised to raise their legs to a horizontal position until all abdominal muscles (including the lower abs) are strengthened. This method of performing the exercise is less effective and is therefore considered transitional. Your main task is to raise your knees to your chest.
- Beginners can lift their limbs with their knees fully bent. For greater load, you need to gradually straighten your knees, thereby making the exercise more difficult.
- To increase the load during the exercise, attach additional weights to your ankles or place an elastic band on your knees.
- The most correct option for performing the exercise is to raise the knees from a horizontal position to the chest, so the iliacus muscle is least involved, taking a lot of the load on itself, reducing the pumping of the abs.
Lower back pain: what causes it and what to do?
The most common cause of lower back pain is a sedentary lifestyle and poor development of the corset muscles, which are unable to support the spine. In addition, the cause may be various pathologies, excessive stress, or simply a sudden awkward movement that provoked pain. Most of these problems can be neutralized with lower back exercises.
What can cause lower back pain:
- staying in one position for a long time;
- weak back and core muscles;
- excessive loads or non-compliance with exercise technique;
- hypothermia of the body;
- rachiocampsis;
- osteochondrosis;
- large excess weight;
- improper diet and vitamin deficiency.
Gymnastics for osteoporosis: sets of exercises, rules for their implementation
Have you been struggling with JOINT PAIN for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles...
Read more "
Osteoporosis is a chronic disease that leads to disruption of the structure of bone tissue. As a result of various reasons, calcium is washed out of bones, their mass and strength decreases. Externally, the process is asymptomatic and the diagnosis is made after the fact after fractures of the femoral neck, spine, or radius have occurred. Osteoporosis is most common in older people and women in late menopause.
Contents of the article: General rules What not to do Complexes Bubnovsky exercises
Gymnastics for osteoporosis is one of the important components of the prevention and treatment of the disease. Regular performance of an individually selected set of exercises will help delay the onset of pathology and significantly slow down its progression.
General rules for performing exercises
Preventive and therapeutic exercises are selected individually by a rehabilitation physician. It is necessary to take into account the following factors: the patient’s age, his weight, level of physical fitness, stage of the disease. The initial implementation of the exercise therapy complex should take place in the presence of a medical professional. This will allow you to control the optimal load, the correct execution of movements and reduce the risk of injury.
Basic rules for performing exercises for osteoporosis:
- Physical activity must be constant. As a result of clinical studies, it has been shown that feasible physical activity provides an increase in bone tissue mass by 4–6%.
- The occurrence of pain in muscles, bones and joints is a signal to stop training; it is necessary to adjust the gymnastics complex.
- A good mood is an important component of success. A positive attitude will improve the quality of exercise therapy.
Exercises to prevent osteoporosis
It is important to start preventing osteoporosis early. While all physical activity is good for the body, there are some exercises that are less effective in preventing osteoporosis:
- swimming;
- aerobics in water;
- a ride on the bicycle.
For osteoporosis under the age of 50, the best results are shown by complexes that use weight-bearing and load-bearing exercises. This is a type of loading in which the body overcomes natural gravity and forces muscles and tendons to act on bone tissue, stimulating its formation and increasing bone density. The main types of exercises to prevent osteoporosis:
- Running is a great way to prevent loss of bone density and keep your body strong and healthy.
- Walking is an excellent alternative to running if it is difficult for a person. Regular and long walks, walking on stairs give excellent results.
- Exercising with additional weights increases bone density. Additional muscle tension activates osteoblasts, the cells that build bone.
- Team sports - football, handball, volleyball.
- Aerobics and gymnastics not only strengthen bones and develop flexibility, but also improve coordination of movements. This is very important to prevent falls.
Principles of compiling exercise sets
When selecting the type and intensity of physical activity, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s age and stage of osteoporosis. When diagnosing a pathological process in a specific area of the skeleton (spine, hip and wrist joints, bones of the leg), special attention is paid to the load on this part of the body. Basic rules for compiling therapeutic exercise complexes for osteoporosis:
- The minimum load level is selected depending on the age and conditions of the body. The optimal training duration is from 20–30 minutes (for untrained people) to 40–45 minutes every day. If possible, it is recommended to distribute the load throughout the day.
- Exercises for exercise therapy should be selected in such a way as to minimize the risk of traumatic injuries. In old age, it is advisable to stop using dumbbells and active aerobic exercises, replacing them with calmer ones.
- At the beginning of training, the simplest exercises are performed. The complexity of the gymnastic complex increases only when the person’s condition improves.
What exercises should you not do?
It is important to exercise some caution when exercising, especially in old age. Remember that excessive stress will increase the risk of fractures. Some types of exercise are not recommended if you have diagnosed osteoporosis:
- jumping and running can lead to spinal fractures;
- strength exercises with heavy loads;
- exercises that include twists and bends in the lumbar region, exercises on a rowing machine, bending towards the toes, because they can cause damage to the vertebrae.
Important! If you have osteoporosis of the hip joints, jumping is strictly prohibited.
Exercises for the spine
Before starting the main complex, you need to do a warm-up to prepare the body for the load and warm up the muscles. After finishing the exercises, do not forget to do a cool-down to return the body to a calm state. The main complex of gymnastics for the treatment of spinal osteoporosis:
- Lie on your back on a hard surface (floor). You can use a special mat. Place your arms above your head parallel to each other, bend your foot as much as possible at the ankle joint. Do 5–12 repetitions.
- Lie on your stomach, place your hands in front of your head. Pressing your chest toward the floor, try to lift both legs. Do 6–9 repetitions.
- Standing on the floor, rest your hands on a chair. Perform shallow lunges with your legs. Make sure your knee is level with your ankle. Perform 6–9 times.
- While on your side, lean on your arm bent at the elbow. Swing your legs up one at a time, 6-9 times.
- Lie on your back and bend your legs simultaneously or one at a time. At the same time, the feet slide over the floor surface. Repeat 6–9 times.
Exercises for the hip joint
The main complex is carried out in a horizontal position on the floor. Movements are performed smoothly, without jerking. If pain occurs, stop gymnastics.
- Lying on your back on a hard surface, raise your straightened legs about 300 from the floor and cross your legs for 40–60 seconds.
- In the same position, spread your legs shoulder-width apart. Pull your toes towards you. Do 12–16 times.
- Lying on your back, alternately bend your legs, pressing them to your stomach, 4-12 times.
- Position yourself on your back. Bend your knees and roll your pelvis and hips to the right and left. Do 5-7 repetitions for each side.
- Standing on the floor, lean on the back of a chair and spread your feet outward as much as possible. Do 10–15 shallow squats.
Exercise therapy for hands
The arm gymnastics complex is quite simple and can be performed in your free time.
- Spread your fingers in a fan shape, tense the muscles of your hand. Hold this position for 12–18 seconds. Repeat 25 times.
- Clench your fingers tightly into a fist. The thumb is located inside the fist. Then change its position - the thumb is on the outside. Repeat 15 times alternately with your right and left hands.
- Collect all fingers of your hand into a handful. Squeeze them tightly and repeat 12–18 times.
- Use your thumb to touch all other fingers in turn. Perform 16–18 times.
- Squeeze and unclench a small exercise ball. 25 times with the right and left hands.
Physical education for older people
A diagnosis of osteoporosis is not a reason to stop exercising completely. On the contrary, dosed physical activity, subject to certain precautions (excluding jumping, running, sudden bends), will increase the tone of the body, prevent loss of coordination and slow down the loss of bone tissue.
For elderly patients, the following are recommended as regular exercise: walking, moderate-intensity aerobics, and exercises with light weights. A good option is quiet work in the garden, on a personal plot, excluding sharp bends and heavy lifting.
What exercises can be done for older people with osteoporosis?
At the beginning of classes, the number of repetitions may be minimal. As your training progresses, it is recommended to increase the number of repetitions to the maximum. Gymnastics for osteoporosis in the elderly:
- Sit on a hard surface, extend your arms along your body. Pull your hands and feet towards you. Record the position of maximum voltage. You need to hold on like this for a few seconds and relax. Repeat 5-8 times.
- Lying on your back, arms extended along the body. Tighten your thigh muscles and hold in the position of maximum tension for 5–10 seconds. Then relax. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Lie on your back, on a hard surface, with your arms extended along your body. Stretch your chin, bending your cervical spine towards your chest. Hold the position for 5 seconds, then return to the starting position. Repeat 5-8 times.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees. As you inhale, lift your pelvis, pressing your lower back to the floor, and as you exhale, lower it. Repeat 4-8 times.
- Lying on your stomach, clasp your hands under your chin. Raise your straight legs one at a time. Repeat 4-8 times with each leg.
Bubnovsky's exercise system for osteoporosis
Basic exercises from the complex of therapeutic gymnastics in the treatment of osteoporosis.
Standing on the floor on your knees resting on your palms. As you exhale, carefully and smoothly arch your back upward, and as you inhale, slowly bend down. Repeat 10 times.
Get on all fours. Smoothly extend one leg back and sit on the other. Do 15–20 repetitions. After a short rest, change position and repeat with the other leg.
Get on all fours. Stretch your torso forward without bending at the waist. Maintain balance for 10–15 seconds. Repeat 9 times.
Lie on your back on a hard surface, clasp your hands under your head, bend your legs at the knee joints. Raise your upper body, trying to touch your elbows to your knees, 5-10 times.
Lie on your back, try to lift your pelvis up as high as possible without lifting your shoulder blades from the floor, 15–20 times.
Doctor's advice
Before starting classes, consult with a physical therapy doctor or rehabilitation specialist. A specialist will assess your body’s fitness level and select the optimal training complex.
If exercises cause pain, stop doing them. If discomfort occurs repeatedly, consult a doctor for additional examination.
Don't forget the most important principle of training - regularity. It is better to give yourself a small load every day than to exercise intensely 1-2 times a week.
If you are elderly and have been diagnosed with osteoporosis, avoid jumping, running, and sharp bends in the lower back. Perform all movements smoothly, without jerking.
The people were taken aback! Joints will recover in 3 days! Attach...
Few people know, but this is exactly what heals joints in 7 days!
Cure arthrosis without drugs? It's possible!
Get the free book “Step-by-step plan for restoring mobility of the knee and hip joints with arthrosis” and start recovering without expensive treatment and surgery!
Get the book
X-ray of the foot is considered the most informative and simple way to diagnose diseases associated with bone damage. X-rays are done in cases of foot pain and deformity. This is a non-invasive research method that allows a specialist to obtain information about the integrity of bone tissue.
Indications for use
A healthy foot provides support and cushions sudden mechanical stress, and also plays an important role in balancing the body. Pain in the foot indicates the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The most common of them can be identified:
- Dislocations. Often accompanied by joint damage, as well as ligament rupture. Mainly observed in the lower leg area.
- Osteoarthritis. Metabolic disorders, as well as intense stress, cause premature destruction of cartilage tissue. With this disease, blood circulation deteriorates and salts are deposited. This leads to the development of an inflammatory process.
- Fractures. Violation of the integrity of the foot negatively affects the functioning of the entire limb. All elements of the foot are susceptible to fractures.
- Flat feet. Weakness of the muscular system leads to flattening of the foot, which begins to bend.
- Plantar fasciitis. A bone growth forms that resembles a thorn. A heel spur occurs on the sole of the foot near the Achilles tendon.
- Consequences of concomitant pathologies, such as gout or diabetes.
- Osteomyelitis. The disease is characterized by the formation of a fistula. An x-ray will determine the area of the bone in which the destructive process occurs and the location of purulent formations.
- Malignant neoplasms. Radiography will detect a tumor at the first stage of development.
It is advisable to take an X-ray after any injury. Feet are subject to excessive stress, so injuries are common. An x-ray will allow you to immediately detect a dislocation or fracture. Without this study, it is difficult to determine the type of injury and its location.
Basic prerequisites for radiography:
- frequent manifestation of pain in the foot area without previous intense exercise;
- presence in the anamnesis of various injuries;
- obvious changes in the appearance of the foot: violation of the size, shape and color of the skin;
- the patient is at risk of developing diseases of the musculoskeletal system (high body weight, professional sports, genetic predisposition);
- infectious disease of the joints;
- inflammatory process in the bones;
- if you suspect flat feet.
In addition, x-rays are prescribed during therapy to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment regimen.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
X-rays are taken in a simple way or with a load. The feasibility of the method is determined by a specialist, indicating in the direction of the method of conducting the study.
Standard method
This is the main diagnostic method for identifying foot injuries. During an x-ray, several pictures are taken not in two projections, but in four:
- anterior-posterior - performed simultaneously on the left and right feet;
- dorsal-plantar - the patient tilts his leg back, and the radiation is adjusted vertically;
- oblique - the rays are directed at an angle of 45°;
- lateral - X-rays are directed perpendicular to the lateral area of the foot.
No special preparation is required before the radiation dose is received. But they must cover the genital area, and for women they also cover the mammary glands with aprons containing lead plates.
To take a direct projection photo, you will have to lie on your back with your knees bent. Oblique projection - lying on your side, placing a pillow between your knees.
If a metatarsal fracture is obtained, then a lateral view is needed. The victim lies down on the side where the injury is located, and stretches the uninjured leg forward. To make the most accurate diagnosis, a combination of techniques is often used.
With load
To detect flat feet or hallux valgus, the doctor needs to simulate the position of the foot under load.
The specificity of this diagnostic method is characterized by the fact that photographs are taken in various projections and at a time when the patient stands on the injured leg and presses the other to the stomach. This is necessary to obtain more accurate results, since the doctor sees the condition of the foot under load. The patient stands on the film and a front view photograph is taken. The cassette is then placed on the side of the ankle and a lateral view is taken.
If the foot photograph has to be repeated, the patient should take the same position as before.
What does the procedure determine?
The image is reviewed by a radiologist who does not make a diagnosis, but simply records the destruction in the structure of the foot. The resulting radiograph is transferred to the attending physician, who makes a final diagnosis and selects the correct treatment regimen after decoding the image.
X-rays can detect many ankle pathologies:
- gout and arthritis;
- congenital diseases of joints and bones;
- damage to bone tissue (cracks, dislocations and fractures);
- development of cancer (osteoma);
- degenerative process in joints;
- heel spur;
- flat feet;
- metabolic disorder;
- age-related changes.
Analyzing the image, the doctor evaluates:
- Condition of the bone surface. With cancer, it is clear that the top layer of bone tissue is destroyed. But the opposite happens: ossification of the periosteum occurs and its further peeling off.
- Shape, size and position of bones. If the bone size is increased, then hyperostosis is diagnosed - an increase in the mass of bone substance. A decrease in size indicates bone atrophy due to lack of physical activity.
- Condition of the joint space. In the presence of arthritis, it narrows unevenly. In a neglected state, connective tissue fuses together the elements of the joint and transforms into bone, thereby blocking the mobility of the joint.
- The structure of bone tissue. Darkened areas on bone structures may indicate osteoporosis. In this case, an expanded medullary canal is visible with a thin outer layer of bone. Sometimes osteosclerosis is diagnosed, which is characterized by increased bone density. The photographs clearly show dead tissue.
- Foot angle. Obvious deviations from normal values indicate longitudinal flatfoot. In order to identify transverse flatfoot, look at the inward deviation of the big toe.
If flat feet are suspected, you should carefully study the picture. It is necessary to measure the angle of the arch of the foot, it should not exceed 130°, and the height of the arch should be more than 3.5 cm.
Fractures on an x-ray appear as small stretched shadows with broken contours. You can immediately determine the location of a crack or fracture, the presence of fragments and their possible displacement.
An image of a healthy foot shows bones with unbroken integrity and a homogeneous structure, with clear and uniform contours, without any shadows.
Conclusion
X-rays are performed using modern equipment and are safe. The latest devices do not require powerful radiation to obtain informative images. Radiation exposure is minor and kept to a minimum. The benefits of this research far outweigh the potential negative impacts.
Igor Petrovich Vlasov
- Site Map
- Diagnostics
- Bones and joints
- Neuralgia
- Spine
- Drugs
- Ligaments and muscles
- Injuries
Frog leg raises[edit | edit code]
Frog Leg Raises
Execution
When performing the Third Level exercise, bent leg raises, instead of pausing in the upper position (Fig. 66), straighten your legs - they should be perpendicular to the floor (Fig. 67). This two-step movement is performed while exhaling. Most abdominal exercises would have you doing the reverse action now, but not this one. Your muscles are stronger when they lower under resistance (due to gravity), and the frog takes advantage of this. Resisting gravity, lower your straight legs (Fig. 68) (do not bend your knees to return them to the starting position) - this is the most difficult part of the exercise. In the lower position, the legs should be at a height of several centimeters from the floor (Fig. 69). Most exercises take 2 seconds to move up and down, but this exercise takes 4 seconds to lower your legs to allow your body to work its strongest position. As you lower your legs, take a full breath. Repeat the exercise.
Cross-sectional exercise
Both when performing on the floor and when performing while hanging, the difference between lifting bent and straight legs is huge, and lifting straight legs requires an order of magnitude more strength. Changing the position of the legs - straight to bent - helps gradually build strength and train the muscles to lift straight legs: an intermediate exercise, so to speak, that trains the hips and back and increases mobility of the hip joint. Unfortunately, the exercise is not so well known in sports circles—they forgot about it back in the seventies, when crunches reached the peak of popularity.
Training norm
| First level | 1 series of 8 repetitions |
| Average level | 2 series of 15 repetitions |
| Advanced level | 3 series of 25 repetitions |
Improvement of technology
If the exercise is difficult to perform, focus at the top of the exercise on the straightening technique with your legs in the air. Over time, the muscles will strengthen and you will be able to lower your legs low enough.