Anatomy of the neck muscles
Neck muscles, anatomy (the table well illustrates the complexity of the structure of this part of the body) which, despite the small volume of the organ, is very complex and includes 9 groups:
Neck muscles. Anatomy
| Name | Where is it located? | Functions performed |
| Subcutaneous or platysma | Superficial muscle group |
|
| Sternocleidomastoid | Group of superficial muscles |
|
| Digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid, stylohyoid muscles. | Suprahyoid subgroup of muscles, middle group of neck muscles. | Lowers the lower jaw and moves the hyoid bone. |
| Scapular-hyoid | Median group, subgroup of sublingual muscles. |
|
| Sternohyoid | Median group, subgroup of sublingual muscles. | Pulls the hyoid bone down. |
| Sternothyroid | Median group, subgroup of sublingual muscles. | Downward movement of the larynx |
| Thyroid-hyoid | Median group, subgroup of sublingual muscles. | Participates in the movement of the larynx and hyoid bone, bringing them together. |
| Front, middle and rear stairs | Lateral group of deep cervical muscles. |
|
| Longus capitis, rectus lateralis, longus colli, rectus capitis anterior. | Medial group of deep muscles. |
|
Isometric exercises for the neck
Isometric exercises are exercises in which the muscles do serious work, but there is no movement of the body or part of it. Isometric muscle work is maintaining a certain body position with fairly strong tension.
These neck exercises are just isometric. We use our own arm strength to apply pressure on the head in different directions. And the neck muscles should resist and prevent your hands from moving your head. Please note that all isometric exercises should be performed with a light to moderate load. Don't apply too much pressure! This may cause injury to the neck area. Increase the load and duration of exercises gradually, from session to session. Never hold your breath when performing isometric exercises. Breathe calmly and rhythmically. Exercises can be performed not only in a standing position, but also in a sitting position.
Front hand pressure
The exercise develops the muscles lying in front of the neck, including the sternocleidomastoid muscle (sternocleidomastoid muscle in the top picture). Stand up straight. Place your hands on your forehead. Apply pressure on your forehead in a backward direction. It is optimal to apply pressure in the eyebrow area. Use your neck muscles to resist this pressure. The exercise is performed for 10 counts. They pressed gently and counted to ten. We rested. Then they repeated it again. Perform no more than 3 approaches with a pause of 30 seconds.
Neck exercise – front hand pressure
Hand pressure on the back of the head
This exercise develops the muscles in the back of the neck, which pull the head back. They are the strongest. The long back muscles also work actively here. While performing the exercise, you may even feel tension in the thoracic spine and even in the lower back. No surprise!
While standing, place your hands with your palms on the back of your head. Apply pressure with your hands forward, trying to tense your neck muscles to prevent your head from moving. It is optimal if you apply pressure to the back of the head at approximately the level of the eyes or bridge of the nose. Pressure duration is 10 seconds (10 counts). Perform 3 sets with a pause of 30 seconds.
Hand pressure on the back of the head
Side hand pressure
This exercise develops the lateral muscles of the neck, making it visually wider. Press your palm into the area above your ear. Apply pressure with your hand and resist with the force of your neck muscles. Do the exercise for 10 counts. Then apply pressure with your other hand for 10 seconds. Repeat 2-3 times.
Apply pressure with your left hand
Apply pressure with your right hand
Classification of neck muscle diseases
There are many different pathologies. More often these are inflammatory lesions or degenerative changes in the components of the spinal column. Injuries are less common.
- Purulent inflammation caused by pyogenic flora.
- Viral myositis is an inflammatory process of muscle tissue provoked by viruses.
- Dermatomyositis, which is a parallel involvement in the pathological process of not only muscles, but also skin. It is a systemic pathology treated by a rheumatologist.
- Neuromyositis, combining pathology of nerve fibers and the muscles themselves.
- Chondrosis of the discs between the vertebrae with reflex pain.
- Arthrosis of the uncovertebral joints, which secondarily affects the muscle masses of the neck area.
- Stretching the muscles of the cervical region.
The danger of tense muscles
Muscle fiber can be in 2 functional states: either contracted during work, or relaxed at rest. The first state is called muscle tone.
In order to make movements or maintain a state of balance, certain muscle structures are relaxed, while others contract. When a muscle is in working mode for a long time and cannot relax, it is said to be in a state of spasm. This is a pathological condition. Especially when it manifests itself clinically.
Neck muscles, anatomy (the table provides clear information about functionality) of which provides that a tense state in them is not harmless. On the contrary, it can provoke a deterioration in blood flow to the brain, face and other organs.
Such changes are especially dangerous for people in the older age group. If you have a history of strokes and chronic cerebral vascular ischemia, you need to be especially careful about spasms.
What is a muscle spasm, the nature of the pain, where does it go?
We are talking about long-term contraction of muscle fibers. In this mode, they are overstrained and can compress both nerve fibers and blood vessels, as well as other structures located anatomically in the neighborhood.
The first concern with muscle spasms in the neck is pain. It is localized in the neck, back and sides. Less commonly, the pain syndrome is located in the front. Irradiation depends on which muscle is tense and in a state of hypertonicity. Usually the pain radiates to the shoulder and shoulder girdle.
It happens that this symptom is the only manifestation of cervical muscle spasm. It is masked by limited movement in the shoulder joint and therefore this condition is often regarded as a manifestation of shoulder osteoarthritis.
Often, patients with neck muscle disease present with discomfort and severe heaviness in the occipital region. Symptoms worsen at night.
The next possible symptom is a headache. It occurs due to the fact that the inflow of blood to the contents of the skull, organs of the head and neck, and the outflow from them is hampered. The pain is not throbbing, but rather constant and dull. The equivalent may be dizziness, indicating a lack of oxygen supply to the brain.
People of all ages experience instability in blood pressure. It manifests itself as darkening of the eyes, flickering “spots”, up to episodes of loss of consciousness. Sometimes there is only a headache in the back of the head or some stiffness.
When spasm in the neck muscles becomes constant and chronic, long-term manifestations are possible. So, the color of the skin on the hands changes, it becomes colder to the touch. Sensitivity changes. This is a crawling feeling or a complete loss of sensitivity.
In more severe cases, weakness appears in the muscles of the hands and forearms. Some atrophy of the arm muscles may occur. It becomes more difficult to feel the pulse due to altered vascular tone. The hand may swell on one or both sides.
Causes and localization of spasm
The main causes of spasms are:
- Neoplasms of bone structures, muscle masses and other tissues (primary and metastatic).
- Myositis of various nature.
- Chondrosis of the cervical vertebrae.
- Radicular syndrome.
- Myelopathy at the level of the cervical vertebrae.
- Pathology of posture (torticollis).
- Spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis.
- Uncovertebral arthrosis.
- Neck injury.
- Muscle strains.
- Psychotic and neurotic disorders.
- Deficiency of magnesium, calcium in the body, as well as hormonal imbalance.
Elimination of spasms in the neck muscles
The table of functionality of all 9 muscle groups of the cervical spine and their anatomical features indicates a fragile local balance. Spasmodic pain and stiffness significantly complicate daily life, causing temporary disability. And if chronic without treatment, this condition can lead to disability.
To get rid of spasm, a whole range of measures are taken. These are not only medications, but also physical treatment, and during the period of pain subsiding, therapeutic exercises and physical education, which is aimed at strengthening the neck muscles.
Medicines
Muscle relaxants are used first. We are talking about drugs that relax muscles. This is a symptomatic and pathogenetic direction of treatment. Both centrally and peripherally acting drugs are used.
Doctors recommend injections into the muscle in the first days. This measure allows you to quickly achieve the desired effect. The only danger is a decrease in blood pressure levels.
This should be kept in mind in persons taking antihypertensive drugs, as well as in persons prone to hypotension. Incorrect dose selection can cause vascular collapse, which is very dangerous, especially for elderly patients.
Among the famous names are Sirdalud, Mydocalm, Tizanidine. After 5 days of parenteral administration, switch to tablets. Here it is also very important to adequately titrate and select doses of drugs to avoid unwanted side effects.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help with myositis and chondrosis, as causes of muscle spasm. The approach is the same stepwise: therapy begins with injections and ends with pills.
Hormonal drugs are prescribed for severe pain. They are used with caution at high blood pressure levels. Droppers with Dexon or Prednisolone are prescribed. They rarely switch to tablet forms.
Drugs aimed at restoring the conduction of nerve impulses along fibers are another area of therapy. With prolonged muscle tension, the nutrition of all structures is disrupted. Including nerves.
Therefore, prolonged spasm leads to various disturbances of sensitivity, and sometimes to disorders of motor activity, including paresis (mild disturbances in the muscle tone of the forearms and shoulders). Before prescribing this group of drugs, consultation with a neurologist is necessary. Usually drugs based on thioctic acid are used, as well as vinpocentine.
Vascular drugs are used as adjuvant therapy. It allows you to slightly improve blood flow. But caution should be exercised when prescribing medications from this group in relation to elderly people and those who have a history of heart rhythm disturbances. Actovegin, Pentoxifylline and other analogues are used.
Physiotherapy
In the acute period, with severe pain, the use of physiotherapy is not indicated. On the contrary, their use can aggravate the situation and increase muscle spasm.
As clinical manifestations subside, electrophoresis and galvanization can be prescribed. This includes the effect of currents and faster, targeted administration of drugs to the site of the pathological focus.
In the future, it is possible to use darsonvalization, as well as electrical stimulation. If there is a neurotic component, electrosleep is prescribed, as well as a contrast shower and hydromassage.
Among the therapeutic mechanisms of physiotherapeutic procedures, the elimination of muscle spasm comes first. Therefore, they can even eliminate convulsive syndrome. Stimulating techniques improve blood flow, strengthening the vascular wall. As a result, the analgesic effect of medications is reinforced.
Relaxation techniques
At the stage of severe pain, aggressive massage techniques are unacceptable. They will only intensify the spasm of muscle fibers and aggravate the pain. Light self-massage and smooth stroking massage movements are allowed.
Massage and self-massage of muscles
Movements are allowed not only in the neck region. They can descend to the forearms and torso muscles. Aggressive movements, as well as any movements that cause pain, are extremely undesirable.
The neck muscles (anatomy, table of the main functions it provides, makes it possible to assess the degree of risk in these groups) are quite capricious. It is important to touch them very carefully so as not to cause collapse by touching the neurovascular bundle. You can perform the massage with one or two hands.
Touch the skin with both your palms and gently with your fingers. Light “pinching”, “kneading”, “stroking” are acceptable. As tolerated, pressure is allowed, but not through pain.
Among the acceptable areas where massage and self-massage can be done are regions such as the back, chest, and abdomen. If there is a neurotic component, a relaxing facial massage will not be amiss.
Gymnastics
Exercises are recommended as soon as the pain subsides. In addition, gymnastics can be done later and as part of prevention.
To do this, it is recommended to resort to sets of simple exercises twice, thrice a week, or even more often. It is better to develop them individually with a physical therapy doctor.
Treatment at home
The neck muscles (anatomy, data table provides analytics for the need for immobilization) need rest. It is recommended to use the Scheinz collar until you see a doctor. This measure is necessary to limit neck mobility.
At home you can also use the Kuznetsov applicator. But first you should consult with your doctor about how long and how best to do this.
Exercises with weights to develop the neck muscles
Athletes often train in combination with deltoids and trapezius. However, if at the end of the workout you perform several isolating elements (purely on the neck), the effect produced will double.
- Raising the head from the “lying on your back” position. This type of exercise is best performed on a flat horizontal surface. The head, upper spine and shoulders should remain suspended. A weight plate from a barbell is placed on the center of the forehead, previously covered with a towel, and held in place with both hands. Exhale - the chin slowly reaches towards the chest, inhale - return to the starting position. 6-8 repetitions. This element will help those who are interested in how to pump up their neck at home (instead of iron, you can take any weight), because all tissues are being worked on. This exercise can be performed with dumbbells.
- Raising the head from the “lying on your stomach” position. Work on the same principle as in the previous exercise, only you need to lie on your stomach and hold the pancake with your hands on the back of your head. Exhale - the head stretches back, and so on for 6-8 repetitions.
- Traction with a strap. A special strap will help you quickly pump up your neck, the first side of which is thrown over the head, and the other is used to attach the load. The initial pose is the body bending forward to a right angle. Exhale - the head slowly lowers lower until the weight touches the floor, and after that the athlete returns to the starting position. Repeat 6-8 times.
Important! Inflating your neck with a strap is quite dangerous. This type of exercise can only be performed by professional, experienced athletes with previously trained muscles.
Causes and symptoms of neck muscle strain
Sprains today are considered the second most common among all injuries to the cervical region. The leading position is occupied by bruise. Sprains are painful injuries. Therefore, it must be treated adequately and promptly.
The essence of the injury comes down to the fact that with an excessively large load on the muscle masses of the neck, their fibers become overstrained and can become overstretched. It's traumatic for them overall.
Therefore, some of them may even become damaged and tear or tear. Blood and lymph may accumulate, which subsequently, without treatment, can cause severe inflammation and even suppuration when a pyogenic infection is attached.
What is the mechanism of injury:
- excessive physical activity;
- long-term antiphysiological position of the head and neck;
- road accident;
- a fall;
- hit;
- dislocations and subluxations in the cervical spine;
- performing sports exercises without warm-up exercises.
Neck muscles can be damaged not only during an injury. There are also provoking factors. Traumatologists and neurosurgeons include existing problems with the neck. These are fibroimalgia, spondyloarthrosis, chondrosis and the presence of hernias in the intervertebral discs of various sizes.
Among the symptoms, neck pain comes to the fore. It is usually one-sided. In this case, the severity depends on the area of the lesion, the force of the impact and the integrity of the muscle fibers. It is difficult for the patient to make various movements. Tilts and turns are especially difficult. Therefore, in order to turn your head, you have to move your whole body.
Externally, the sprained area may be swollen. Sometimes hematomas are visible. They are painful on palpation. The skin may be red and hot at first. This is an inflammatory reaction.
The muscles in the area in question go into spasm, so when palpated they can be sharply painful. The most severe pain can be found at the attachment sites.
Treatment
In case of sprains, you should immediately contact a traumatologist. After all, it is unknown without a picture and an in-person examination by a doctor what actually happened.
During the first aid phase, you can apply cold or ice to the affected area. If there is a Scheinz collar, then with its help the neck is immobilized, increasing the distance between the vertebrae and minimizing further trauma.
Drug therapy
Among medications, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the most effective for sprains. The described injury is accompanied by severe pain. Therefore, preference is given to drugs with the most pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. These are Ketorol and Nimesil.
A stepwise approach is suitable for treating sprains: first, injections of drugs, and then a smooth transition to tablets or suspensions, powders. Ketorol is injected into the muscle when the pain intensifies, and Diclofenac can be used twice a day. As the pain subsides, the injections are replaced with Ibuprofen or Meloxicam tablets.
It is important to remember to protect the stomach, because all of the above drugs weaken the barrier of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, significantly increasing the likelihood of developing defects: erosions and even ulcers. For this, Razo, Omez or Emanera are used. All NSAIDs are used only after meals and not on an empty stomach.
In parallel, NSAIDs can be used topically. These are ointments, gels and creams based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory components. They should be rubbed into the neck area carefully, without aggressive massage movements. Light rubbing only.
Complex drugs help quite well. Thus, Indovazin gel combines not only NSAIDs (indomethacin), but also the venotonic Troxerutin. The product effectively eliminates inflammation at the site of sprain and eliminates formed and developing hematomas.
For this purpose, heparin ointment and Lyoton gel can be prescribed. With caution for persons receiving Warfarin and other anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents.
Once the acute pain has subsided, a warming effect can be used. It will improve trophism, speed up metabolic processes and stimulate blood flow. Among the effective remedies are Viprosal and Nayatox.
If there is muscle hypertonicity, muscle relaxants are prescribed. Both central and peripheral action.
Use of traditional medicine
Non-traditional methods of treatment should not be an alternative to officially recognized ones. They can be used as an addition to them and only after the permission of the treating doctor. After all, it’s easier to do harm on your own than to help.
Of the known methods, raw potatoes are considered the least safe. It must be wiped. Sometimes cabbage leaves are added. The pulp is applied as a compress to the affected area. Exposure time is up to half an hour.
There is also a folk recipe for rubbing infusion. Lingonberry leaves are poured with boiling water, allowed to cool and brew, and then the resulting solution is applied with rubbing movements to the area of injury.
Restoring neck muscle function
Once neck pain and stiffness have passed, it is important to restore lost function. After all, the muscles atrophy somewhat, while other fibers remain completely torn.
For these purposes, a full-fledged medical massage and sets of exercises are prescribed as part of physical therapy. The doctor will select the necessary loads. The exercises are quite doable at home. In addition, the muscle corset of the neck is well strengthened by swimming in the pool under the supervision of a trainer.
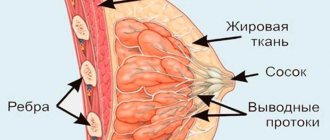
Organs
There are a considerable number of anatomical structures located in the neck. The internal organs and tissues that form it perform different functions and have a rather complex structure. They are important for human life.
Main organs of the neck:
- pharynx;
- larynx;
- trachea;
- thyroid;
- esophagus;
- spinal cord;
- connective tissue;
- subcutaneous fatty tissue.
The special structure of the listed cervical organs allows you to repeat movements when rotating or tilting the head. At the same time, they remain safe and sound.
Pharynx
It has a complex structure. It consists of three parts - the nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx. Its first two components do not relate to the neck. They are associated with the oral cavity. The last one, the laryngopharynx, is directly related to the larynx.
It begins at the level of 4–5 vertebrae and passes into the esophagus around 6–7. The pharynx performs many vital functions:
- Food crushed in the mouth is pushed through the swallowing movements of this organ into the esophagus.
- The inhaled air passes through the pharynx and enters the body.
- Speech features are directly related to the pharynx. By changing its shape and volume, it is able to change the timbre of a person’s voice. And pathological changes in the pharynx contribute to speech impairment and distortion.
- The mucous membrane on the back wall of the pharynx has many cilia that play a protective role, preventing bacteria and harmful substances from entering the body.
The pharynx is involved in important processes such as digestion and respiration. And its protective function helps prevent a number of diseases.
Larynx
Participating in the respiratory process, this organ plays an equally important role in the formation of sounds. The color of a person’s voice and its individual sound depend on the features of its structure.
Its structure is characterized by the presence of nine cartilages, of which three are paired and three are single:
- supraglottic (2);
- thyroid (2);
- cricoid (2);
- wedge-shaped (sometimes vestigial);
- arytenoid;
- horn-shaped.
They are movably connected to each other by ligaments, membranes and joints. The larger cartilage (thyroid) is formed by two plates. In men they connect at an acute angle, in women at an obtuse angle. In the stronger sex, the junction is clearly visible. This is the so-called Adam's apple or Adam's apple.
The upper part of the larynx is attached to the hyoid bone, the lower part is connected to the trachea. On the sides and in front of it is the thyroid gland, behind it is the laryngopharynx. The inside of the organ is covered with a mucous membrane. The vocal cords are attached to the thyroid and arytenoid cartilages, and the glottis is located between them.
When the muscles contract, the shape of the larynx changes, the gap between the ligaments becomes either wider or narrower, they become tense and the exhaled air creates a certain sound. The functions of this organ are similar to the laryngopharynx, with the exception of the digestive component.
Trachea
The length of its tube connecting the larynx to the bronchi ranges from 8.5 to 15 centimeters. This value depends on the physiological characteristics of the human body. It originates from the cricoid cartilage. Only a third of its part is located in the cervical region.
In front of the trachea is the thyroid gland, behind it is a bundle of nerves and blood vessels, consisting of the jugular vein, carotid artery and vagus nerve.
With the help of the trachea a person breathes; in addition, it performs a protective function. Through the tracheal tube, air enters the lungs, and foreign particles that come with it settle on the ciliated mucosa and are pushed back to the larynx. In this way, a protective mechanism is triggered, and all this is removed by coughing.
The structure of the trachea is simple, but it is impossible to do without the functions it performs. Sometimes damage and pathology of this important organ lead to serious consequences.
Thyroid
This small organ plays a huge role in the human body. Despite its size and weight of 25 grams, this gland is considered one of the most important. It produces hormones that are necessary in almost all life processes. These are intracellular metabolism and metabolism. These hormones are involved in mental, physical development, metabolic and reproductive processes.
The thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly. It consists of two identical lobes connected to each other by a special isthmus. It is located in the front of the neck and is easily palpable during a medical examination.
The main purpose of the thyroid gland is to supply produced hormones into the blood, which, in turn, control the functioning of the human body and influence its most important mechanisms.
Esophagus
This organ is more related to the thoracic and abdominal region of the human body, since it is located only one third in the neck. But it is precisely on the way from the larynx to the stomach that food inevitably moves through the cervical region.
The esophagus is a hollow tube attached to the lower edge of the larynx. Its length reaches 25 cm. On top it is equipped with a sphincter, which helps push food into the abdominal cavity.
Functions of the esophagus:
- Motor skills and food evacuation.
- Facilitating the movement of food due to the secretory mucus secreted by its walls.
- Preventing food and bile from entering the oropharynx.
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the neck muscles
Myositis occurs in different age groups of patients. But more often this is the lot of young people. This is a local inflammation of the neck muscles. As a rule, the condition is caused by hypothermia or exposure to infection. An autoimmune nature cannot be ruled out in some cases.
Manifestations include primarily pain. In acute situations it is very pronounced, but not shooting. Develops within a few hours after hypothermia. Chronic pain occurs in the morning, dull in nature, but very debilitating.
When trying to move the neck, the muscles resist and spasm. By palpation, lumps are felt in the affected area. They are painful.
In treatment, the first step is to ensure the patient’s rest. A sick leave note is issued and bed or semi-bed rest is recommended. The main drugs are NSAIDs. The first days they are used by injection. Then they switch to tablets and add a warming component. As the pain goes away, exercise therapy and massage are allowed.
The neck muscles are susceptible to spasm, injury and inflammation, especially when they are not sufficiently strengthened. Their anatomy, according to the table, is characterized by less pronounced fiber development. The muscles themselves are thinner. They need to be strengthened through exercise in the pool and exercises. These preventive measures are the most effective.