Organic antidepressants help maintain health and cope with bad mood. One of them is tyrosine. The substance is widely used in medical practice as a neurotransmitter and mild psychostimulant. From this article you will learn what tyrosine is and what it is needed for, get information about its signs of deficiency, excess and interactions with other medications.
Now Foods, L-Tyrosine, 500 mg, 120 Capsules
★★★★☆
from 758 ₽
More details
General information
Tyrosine (2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoic acid) is a conditionally essential amino acid from the aromatic category. The Latin name of the substance is L-Tyrosine.
The nutrient was first discovered in 1846, when the German scientist Justus von Liebig isolated it from casein, found in cheese and meat liquids. The substance received the name tyrosine in 1857 - it comes from the Greek word tyros (cheese). At the same time, scientists discovered that the enzyme is contained in all fermented milk and some plant products.
Interesting! Later it became known that the amino acid is part of the proteins of all living organisms, can act as an anti-stress compound and prevent memory problems caused by depression.
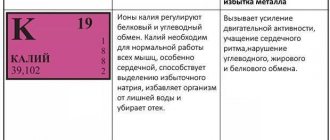
Tyrosine enters the body with food or is synthesized from phenylalanine. The substance forms such active compounds as melanin, norepinephrine, thyroid hormones - triiodothyronine and thyroxine, DOPA, adrenaline, dopamine.
Disorders of amino acid metabolism cause some hereditary diseases. Thus, with phenylketonuria, the process of converting phenylalanine into tyrosine suffers, which is why an excess amount of the first and its derivatives is created in the body. With hereditary pathology - alkaptonuria - the activity of the homogentisate decreases. The result of the abnormal reaction is the accumulation of homogentisic acid and deterioration in the quality of connective tissue. Another rare disease is hepatorenal tyrosinemia, which also occurs against the background of impaired tyrosine catabolism.
Beneficial properties of tyrosine and its effect on the body
Repeated clinical experiments have proven that the best natural antidepressant is tyrosine.
Scientists have noted a certain pattern according to which the higher the level of tyrosine in the blood, the higher its ability to withstand stress. It is important to note that the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine components is related to the amount of tyrosine in the body.
This amino acid, without the need for additional use of chemicals, controls the amount of tyrosine in the human body and, therefore, reduces the likelihood of depressive disorders, stress, anxiety and irritability.
It is generally accepted that it has a significant effect on the functioning of the peripheral and central nervous systems. Tyrosine components have a significant impact on improving the quality and intensity of training in athletes, reduce the time factor of periods of rest and work, reduce fatigue, and are responsible for the prevention of overtraining.
It was noted that tyrosine molecules are included in the process of production of the thyroid hormonal component, which provides an opportunity to increase the hormonal action of the thyroid gland.
The effects of tyrosine components have been observed to reduce the painful effects of the premenstrual period.
When the required level of tyrosine is found in human cells, an improvement in the functioning of the blood-brain barrier is observed.
It is a barrier between blood flow areas and brain cells. They form membranes, allowing only molecules of certain types of substances to pass through and creating a barrier for other types (bacteria, viruses, proteins, low-molecular toxins). The ability of unwanted elements to penetrate the brain is determined by the strength of the protective barrier of the EBC. Protection of the amino group by chemical elements allows the beneficial amino acid to pass through the barrier protection and protects it from unnecessary substances.
The enormous beneficial effects of tyrosine have been identified in the fight against addiction to caffeine and narcotic drugs, and in the fight against uncontrolled drug use.
Tyrosine is the starting material for the production of certain hormones, such as dopamine, thyroxine, epinephrine and some others.
In addition, as a result of the transformation of tyrosine, the production of melanin pigment is noted.
Signs of tyrosine deficiency in the body
- obesity;
- fast fatiguability;
- state of depression;
- poor resistance to stress;
- sudden mood swings;
- premenstrual pain;
- decreased appetite;
- decreased brain activity;
- manifestations of Parkinson's disease;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- hyperactivity;
- disruptions in the functioning of the adrenal glands.
Signs of excess tyrosine in the body
- loss of muscle mass;
- manifestation of hypertension;
- decreased body temperature;
- increased heart rate.
Factors influencing the content of the substance in the body
With a healthy, nutritious diet that includes components containing tyrosine, it is possible to maintain the required level of this substance in cells with the help of nutritious food. The recommended dose for a healthy person is 16 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
The second way the body obtains tyrosine is through the conversion of phenylalanine, which occurs in the liver.
Tyrosine for beauty and health
Interest in tyrosine has increased in the beauty industry. This amino acid helps to achieve a deep, dark tan by regulating melanin production. The list of components of lotions and creams for tanning always contains tyrosine components. Although, scientists' opinions on this matter differ.
Recent studies have revealed the positive effects of tyrosine on reducing human fat reserves and healthy weight loss.
Tatyana Eliseeva chief editor of the Food+ project
Ask a Question
Rating:
1
/10
Votes: 1
Material usefulness 0
Reliability of information 1
Article design 0
Physicochemical characteristics
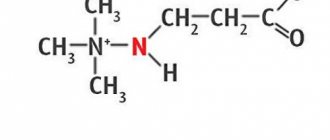
The structure of tyrosine is not much different from other α-amino acids that make up proteins. The substance has L- and D-isomers, and also exists in the form of the DL configuration (racemate). But only L-tyrosine has biological activity and is part of proteins.
Chemical formula of the enzyme: C₉H₁₁NO₃
Photo - Structural formula of tyrosine
According to the formula, it is clear that the amino acid contains a phenolic hydroxyl group OH−, which is the site of attack of protein kinases that regulate cell growth and apoptosis (death process).
In its pure form, tyrosine is a crystalline powder with a melting point of 343 ° C and a molar mass of 181.19 g/mol. The enzyme is highly soluble in water, quickly comes into contact with ethanol, but does not interact with diethyl ether. It also readily forms salts with both acids and alkalis.
Amino acids
Amino acids are the structural chemical units that make up proteins. In turn, it is proteins that make up any living organism without exception (you can learn more about proteins from the article “Protein and its components in food”).
Important!
Proteins are synthesized in the human body from amino acids formed during the breakdown of proteins found in foods. Conclusion: amino acids are the most valuable nutritional elements.
There are about 28 amino acids that can be nonessential or essential. Replaceable ones are synthesized in the human liver, while essential ones must necessarily enter the body from the outside, namely with food.
Benefits of amino acids
- Regulating the functioning of the brain.
- Improved absorption of vitamins and minerals.
- Supplying energy to muscle tissue.
- Accelerating protein synthesis by stimulating the secretion of the hormone insulin.
- Promoting fat burning.
- Decreased appetite.
- Stimulating immunity in the fight against viruses and infections.
- Improving metabolic processes.
- Activation of the production of enzymes that help maintain normal mental tone.
- Promoting hemoglobin production.
- Increased physical endurance.
Amino acid deficiency
Important!
Protein synthesis occurs in the body constantly. In the absence of at least one essential amino acid, the process of protein formation is suspended, which can provoke indigestion, depression, the development of fatty liver degeneration, and growth retardation.
The main causes of essential amino acid deficiency:
- poor nutrition;
- infection;
- use of certain medications;
- disruption of the absorption process in the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent consumption of fast food;
- stress;
- nutritional imbalance;
- injuries.
Important!
The lack of amino acids is especially dangerous in childhood, when the body requires a full range of biologically active substances that ensure normal physical and mental development.
Symptoms of a lack of amino acids in the body:
- weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- anemia;
- exhaustion of the body;
- deterioration of skin condition.
Damage to amino acids
Not only a deficiency, but also an excess of amino acids can harm the body.
Thus, the most harmless manifestation of an excess of amino acids is food poisoning with all the ensuing consequences (we are talking about nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, weakness). In addition, excessive consumption of amino acids can provoke disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular and nervous systems.
What foods contain amino acids?
Important!
Amino acids obtained from natural foods do not have side effects, which cannot be said about synthetic dietary supplements, an overdose of which can lead to the above-mentioned disorders.
Amino acids are found in the following foods:
- mushrooms;
- meat;
- cereals;
- dairy products;
- nuts;
- soy;
- fish;
- legumes;
- cereals;
- eggs;
- bananas;
- sesame;
- dates.
Below we will consider in more detail the properties of individual amino acids and their content in products.
Role and metabolism in the human body
The body needs tyrosine for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and pituitary gland, the formation of red and white blood cells, and the production of melanin. In addition to these functions, the substance is a precursor to most neurotransmitters.
Attention! Research has shown that a non-essential amino acid can be beneficial in situations such as physical exhaustion, fatigue, lack of sleep, and nervous shock. It improves the cognitive properties of the brain, increases performance, reduces stress hormone levels and prevents weight loss caused by depression.
Under normal conditions, tyrosine increases the concentration of dopamine, thyroxine and norepinephrine in the plasma, improves mood, and promotes proper metabolism. Research conducted in 2014 by Lawrence Colzato confirmed the effect of the amino acid on mental activity, speed of perception, analysis, return and memorization of various information.
The experiment compared the success of people who took a dietary supplement with tyrosine and those who drank a placebo. The first group of subjects was distinguished by unusual creative thinking, quickly came up with extraordinary solutions and collected disparate parts of the overall picture of events, i.e. they showed divergent thinking.
Other functions of tyrosine:
- localization of attacks of restlessness and anxiety;
- decreased appetite;
- increased performance, social activity, mental energy;
- skin rejuvenation;
- improved mood;
- prevention of psychological disorders.
A lack of tyrosine can cause significant harm to the body:
- worsen the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- lower blood pressure;
- cause signs of muscle weakness;
- rapidly increase body weight;
- provoke the appearance of nervousness;
- promote hair loss.
In children with amino acid deficiency, cases of hyperactivity, problems with adaptation, and disruption of mental and physiological processes are observed.
Now Foods, L-Tyrosine, Extra Strength, 750 mg, 90 Veggie Caps
★★★★★
from 947 ₽
More details
What are the benefits of tyrosine for the body?
The main function of tyrosine is to participate in the production of neurotransmitters responsible for good sleep and general well-being of a person, as well as a number of other biological processes. The body absorbs tyrosine in the form of dopamine, norepinephrine and adrenaline - catecholamines (physiologically active substances that act as chemical intermediaries. The listed substances affect neurophysiological processes:
- mood,
- memory,
- energy,
- attention,
- vigilance.
We recommend studying:
“GABA is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter important for all humans.”
Tyrosine is responsible for the synthesis of several other substances in the body. For example, melanin is the pigment that determines the color of hair and skin. Tyrosine is also important for the functioning of organs that produce hormones. These are the thyroid gland, pituitary gland and adrenal glands.
Taking this into account, the beneficial actions of tyrosine include:
- protection from anxiety and nervous shock;
- improved mood;
- creating a sense of subjective well-being;
- giving vigor;
- increased vigilance, especially in those who do not get enough sleep;
- stimulation of the production of dopamine (“pleasure hormone”);
- improved cognitive function, especially during times of stress.
The most important ability of tyrosine is considered to be the weakening of stressful conditions, which is due to the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine. The amino acid helps relieve fatigue, especially after heavy exercise.
We recommend studying:
“How to lower cortisol, get rid of stress and finally lose weight.”
The amino acid is necessary for the production of dopamine, without which a person cannot experience a feeling of pleasure, and norepinephrine, which is responsible for memory. Tyrosine is also used for weight loss, as it helps reduce fat accumulation and suppress excessive appetite. Such actions are due to the fact that the amino acid increases the levels of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine, which act as neurotransmitters in the body.
For those losing weight it will be useful:
“What is chitosan, or how crayfish will help you lose weight.”
Why is tyrosine needed in sports?
Tyrosine is used in bodybuilding to avoid fatigue, eliminate drowsiness and increase endurance. As a precursor to dopamine (a substance involved in synthesis), the amino acid helps improve well-being, improve exercise technique and improve mood.
Sports nutrition uses L-tyrosine, a form of tyrosine that protects muscles from catabolic (destructive) processes. Thus, the supplement is used to preserve muscle mass, and additionally to burn fat deposits.
Daily requirement
The dosage of the amino acid depends on the therapeutic goals . The scientific literature usually indicates a prophylactic dose for healthy people. It averages 100 mg of the substance per kilogram of weight for an adult.
Dietary supplement manufacturers recommend consuming 500 to 1,500 mg of tyrosine per day, divided into 2-3 doses.
For various diseases, the daily amount of tyrosine may be greater. The required dosage and frequency of use in this case is determined by the doctor.
Table 1 - Daily amount of nutrient for various conditions
| Indications for use | Tyrosine norm |
| Insomnia | 1500 mg in the afternoon and before bed |
| Depression, stress, nervous disorder | From 0.5 to 1 g three times a day |
| Phenylketonuria | The dose is calculated according to the formula - 6 g of substance per 100 g of absorbed protein |
There is an opinion that to achieve the best effect in the treatment of severe forms of depression, a drug based on the nutrient should be taken with herbal infusions of chamomile, mint or St. John's wort.
To accurately determine the level of tyrosine in the body, a urine test for amino acids is performed. An average portion of morning urine is collected in a clean container and sent for examination using liquid chromatography. One day before the test, you should not drink alcohol, and you should avoid taking diuretics 48 hours before the test.
Normal levels of tyrosine (TYR) in adults are in the range of 18-180 mg (10-100 µmol), in children - 0-20 mg or 0-11 µmol.
Application and dosage[edit | edit code]
The single and daily dose of tyrosine is largely determined by the purposes of use. It is necessary to follow the recommendations indicated on the packaging, and it is also advisable to consult with your doctor or pharmacist regarding the dosage regimen.
People who suffer from insomnia and take tyrosine in the morning after a sleepless night may need 1500 mg of tyrosine per day. This is the maximum dose that is usually prescribed to adults. The duration of the course is approximately 3 months.
For phenylketonuria, the recommended dose of tyrosine can vary over a wide range and reach 6 grams for every 100 grams of protein consumed. It is important to consult with your doctor to select the appropriate dose for the treatment of phenylketonuria and at the same time avoid the development of unwanted side effects.
Some manufacturers of tyrosine preparations recommend taking 5 grams of this amino acid twice a day, but the feasibility is extremely questionable.
Natural springs
Tyrosine, which is released in the body from phenylalanine, is found in animal products. There is a lot of it in fermented milk products and some plants.
Table 2 – Amino acid content in natural sources
| Products | Amount of tyrosine, mg/100 g |
| Hard cheese (Dutch) | 1407 |
| Soy flour | 1306 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 1000 |
| Processed cheese | 937 |
| Chicken | 896 |
| Fat cottage cheese | 875 |
| Beef | 795 |
| Sesame | 710 |
| Eggs | 652 |
| Beans | 484 |
| Tofu | 405 |
| Rye bread | 375 |
| Milk | 175 |
| Full fat kefir | 155 |
When composing a menu rich in amino acids, it should be taken into account that unprocessed meat contains one third and 50% less tyrosine than fried and stewed meat. When smoking animal products, the amount of tyrosine in them is reduced by 15%.
A diet high in carbohydrates is also unable to provide the body with sufficient amounts of nutrients. To compensate for the deficiency, it is necessary to supplement the diet with an accessible form in the form of nutritional supplements.
You will learn about what other foods contain amino acids from the video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q_4G3qYo2rk&feature=emb_logo
Tyrosine in foods
Tyrosine is found in foods such as meat and eggs, as well as some plant foods, but in smaller quantities. Tyrosine is found to a greater extent in foods such as:
- Organic dairy products such as raw milk, yogurt or kefir
- Meat and poultry
- Fish
- Eggs
- Nuts and seeds
- Beans and legumes
- Whole grains such as oats, etc.
- Protein powders
In order for tyrosine to be converted into neurotransmitters, you need to consume additional nutrients such as vitamin B6, folate and copper. This means regularly including foods high in these nutrients in your diet. These include eggs, beef, greens, asparagus, oranges, legumes, nuts, sunflower and chia seeds. As well as whole grains such as quinoa and wheat germ, avocado and broccoli.
Unlike the amino acid tryptophan, which can have the same stimulating effect as tyrosine, tyrosine levels increase. This happens if you eat high protein foods or take supplements. Tryptophan and tyrosine actually compete with each other in the body. This means that when the level of one increases, the content of the other usually decreases.
Indications for use
Tyrosine is recommended to be taken as an organic antidepressant in difficult life situations, with childhood hyperactivity, insomnia, fatigue, panic attacks and anxiety.
Other indications for use:
- PMS and menopause;
- Parkinson's disease (amino acid increases dopamine levels in the blood and brain);
- adrenal dysfunction;
- hypothyroidism;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- impaired memory and concentration due to stress;
- excess weight;
- alcohol or drug addiction;
- metabolic disorder;
- polio;
- instability of the nervous system;
- vitiligo.
The nutrient is indicated for athletes during intense training to relieve muscle tension and quickly recover after exercise, as well as to increase motivation.
The amino acid protects brain cells and the central nervous system from the damaging effects of toxins, reduces the effects of hypoxia and circulatory disorders. For older people, the nutrient helps restore the sleep-wake pattern, increase the body's resistance, reduce fatigue, improve brain activity, and improve the quality of life.
Interesting! In pregnant women suffering from phenylketonuria, the amino acid can prevent congenital defects of the fetus, the formation of intrauterine damage to heart structures, and low baby weight.
However, studies conducted in 2009 and published in the journal Molecular Genetics and Metabolism showed that exceeding the daily intake of the substance can adversely affect the health of the mother and child. Therefore, pregnant women must take dietary supplements in consultation with their doctor.
Other beneficial functions of tyrosine include anti-aging and regenerating properties. Enzyme-based preparations restore skin tone, slow down the appearance of the first age-related changes, improve complexion and promote an even tan.
Benefits for the thyroid gland
The amino acid, like iodine, is a necessary component for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. However, if used incorrectly, tyrosine can suppress organ activity.
Under normal conditions, the nutrient stimulates the production of thyroid hormones, helps to lose weight and prevents the development of hypothyroidism or alleviates its course. The amino acid is slowly eliminated from the body, so the amount needed to maintain the concentration of active substances is retained for a long time.
Attention! The tyrosine replacement therapy regimen is selected individually and depends on the severity of the condition. All prescriptions and recommendations are made only by a doctor. People with thyroid diseases should not self-medicate.
What is tyrosine needed for - 5 important functions
Protects against stress and may help manage symptoms of depression
The first and most important thing that tyrosine is needed for is participation in the process of producing neurotransmitters that affect good mood and energy production for life. Neurotransmitter production is affected by your diet, especially the amount and types of amino acids you consume. Tyrosine affects levels of dopamine, which regulates your reward and pleasure centers, and adrenaline, which is responsible for your fight-or-flight response when you're under stress. Stressful situations increase the release of catecholamines, which can deplete their levels. According to research examining the effects of L-tyrosine on stress, the amino acid may help restore energy levels while providing protection against cognitive decline and mood changes caused by stress (mostly physical) ().
Consuming more of this amino acid may be beneficial for people who are under a lot of stress or suffering from depression because when dopamine and norepinephrine levels fall, symptoms such as irritability, fatigue and moodiness increase. A 2020 paper published in the Annals of Neuroscience states that depression is associated with abnormal brain levels of certain neurotransmitters. L-tyrosine is a precursor to more than one of the neurotransmitters affected by depression. Many studies suggest the use of L-tyrosine as an antidepressant ().
There is some evidence that higher levels of tyrosine may help improve your mood and improve alertness, ability to cope with stress, and overall cognitive functioning. Some scientific evidence suggests that tyrosine may also be beneficial during physical activity, including those that are of interest to the military, such as when soldiers are exposed to cold at high altitude or stress due to prolonged wakefulness ().
However, some experts believe that tyrosine's effects are not strong enough to have a real stress-reducing effect in most people eating a balanced diet. And not every study has shown that this amino acid has a significant antidepressant effect ().
May help increase energy and mental performance
The second thing that tyrosine is needed for is to produce energy and give the body strength to stay awake and toned for a long time.
Research shows that during stressful situations, tyrosine may help reduce mental fatigue and improve cognitive function, including memory. L-tyrosine has stimulant effects, so it can be used to improve learning and alertness and reduce brain fog.
One noteworthy effect of taking this amino acid is increased alertness during sleep deprivation. One study found that tyrosine helped increase alertness by about three hours among people who were sleep-deprived due to night shift work. Study participants were awake throughout the day when the experiment began and were awake for more than 24 hours by the end of testing. Six hours after the start of the experiment, half of the subjects received 150 mg per kilogram of body weight of tyrosine (in a divided dose), and the other half received a placebo. Those given tyrosine experienced a significant increase in mental performance on psychomotor tasks, lasting about three hours, compared to the control group ().
Does Tyrosine Make You Drowsy?
As a rule, no. In fact, it produces the opposite effect. While tryptophan is known to increase sleepiness, tyrosine is thought to improve concentration and productivity.
Related articles:
- Vitamins for energy for women: 11 best remedies...
- Diet for hypothyroidism
May support weight loss
Does L-tyrosine help with weight loss?
According to scientists, there are no studies specifically showing that L-tyrosine promotes weight loss. However, when used in combination with other natural fat-burning substances such as cayenne pepper, green tea and caffeine, there is some evidence that it may help with fat loss in overweight adults, although not significantly. A 2007 study showed a very modest weight reduction of approximately 0.9 kg when tyrosine was taken in overweight adults along with capsaicin, catechins and caffeine ().
Can tyrosine cause weight gain?
No, even though it won't necessarily lead to weight loss or affect your appetite. However, there is evidence that among people needing to gain weight, such as those recovering from anorexia, tyrosine may help improve appetite and exercise tolerance ().
Supports Thyroid Health and Your Metabolism
Why does the thyroid gland need tyrosine?
Tyrosine is used to produce thyroxine, a thyroid hormone. Thyroxine is the main hormone released into the blood by the thyroid gland and helps regulate metabolism and control levels of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4. It is important to produce enough thyroxine because it helps reduce symptoms of an underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism. This disease is characterized by sluggish metabolism, fatigue, sensitivity to cold, weight gain, constipation, moodiness and weakness.
On the other hand, people with thyroid conditions characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, including hyperthyroidism and Graves' disease, should not take tyrosine as it may increase thyroxine levels too much, which can interfere with other medications they are taking and make symptoms worse.
May help reduce withdrawal symptoms
Research has shown that the rise and fall of dopamine can make people more vulnerable to addiction. Dopamine, adrenaline and norepinephrine (catecholamines) are known to be responsible for motivation, energy, interest, sexual function, pleasure and reward, drive, attention and concentration. They are associated with positive stress conditions such as love, playing sports, listening to music and sex. Their deficient levels contribute to difficulty initiating or completing tasks, depression, poor concentration, low energy and lack of motivation. Habits such as drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking, gambling and overeating may also occur ().
Current research suggests that tyrosine may be useful for treating heroin and alcohol withdrawal symptoms, as well as reducing alcohol consumption when used along with the drug naltrexone. Taking a combination of tyrosine, 5-hydroxytryptophan (HTP), phosphatidylcholine, and L-glutamine has the greatest effect on improving mood and sleep in adults addicted to heroin and alcohol, likely because it helps balance catecholamine levels.
Contraindications and precautions
The amino acid has a serious impact on the course of life processes, so it is not suitable for everyone. There are a number of contraindications for which the supplement should not be taken:
- pregnancy and lactation (unless there are special indications);
- hypertension;
- individual intolerance to the substance;
- schizophrenia;
- treatment with antidepressants.
Children and adolescents are not prohibited from drinking tyrosine, but the intake must be agreed with a pediatrician.
Release forms
As food supplements, the amino acid is produced as an independent dietary supplement or in combination with other nutrients. The most available forms of release are capsules, tablets and powder. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Table 3 - Tyrosine release options
| Dosage form | pros | Minuses |
| Capsules | Convenient to receive. The daily dosage is calculated quickly and easily | Takes a long time to digest. Not all patients can swallow large capsules |
| Pills | The most common form of the drug. There is no need to dose anything - everything has already been done by the manufacturer | They have a low concentration of the active substance and additional components that can cause allergies. Long absorbed |
| Powder | Quickly absorbed, does not contain excipients, therefore safer than other forms | Before use, measure the required amount and dissolve in water or juice. |
When choosing the optimal release form, you should focus on preferences and ease of use . If you have problems swallowing tablets and capsules, it is better to take the powder. The same option is suitable for children. If you want to save money, you should pay attention to tablets. They are cheaper and easy to use.
Dosage and regimen
Adults can safely take 500 to 1000 mg (1-3 tablets) of amino acid per day. For children, the dose is determined by the doctor. Tyrosine should be consumed 20-30 minutes before meals, washed down with sweet and sour (apple or orange) juice. The duration of therapy is from three weeks to 3 months.
Table 4 - Tyrosine dosage for healthy adults depending on exercise intensity
| Conditions | Daily requirement for the substance, g |
| Passive pastime | 0,8-2 |
| Active lifestyle | 1,5-5 |
| One-time dose after a short exercise (1-2 times a week) | 3-6 |
| Severe mental workload (exams, leadership position) | 3-7 |
| Regular exercise | 3-5 once a day before training |
For any of the conditions, the dose should not be exceeded 12 mg per day. In case of digestive problems, the daily dose of the drug is divided into 3-4 doses.
Daily norm
The body should receive from 1 to 5 g of tyrosine per day. In the form of a dietary supplement, the permissible norm is 12 g. The exact dosage is determined by gender, age, diet and is prescribed by a doctor. With a deficiency or excess of amino acids, various pathological conditions are observed. Increasing the dosage is recommended for people who are overweight, have poor memory, have problems with the functioning of the thyroid gland, are prone to depression, or are overly active.
Interesting fact: The amino acid is better absorbed when taken on an empty stomach with B vitamins and (for example, tyrosine with orange juice). The combination with St. John's wort, lemon balm, chamomile, and valerian has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous system.
Side effects and allergies
If you use the nutritional supplement correctly, there is no need to worry about side effects, although the possibility of their occurrence cannot be completely excluded. In rare cases, patients complain of nausea, heartburn, headache and fatigue . Older people develop arthralgia. In case of individual intolerance to the substance, allergic reactions often appear in the form of redness of the skin, rash, and itching.
Another side effect of the amino acid may be an increase in thyroxine levels. An increase in hormone concentration can complicate the course of hyperthyroidism and weaken the effectiveness of the therapy used. Therefore, people with an overactive thyroid gland should not take the supplement without consulting a doctor.
Side effects
Taking tyrosine as a supplement can cause a number of unpleasant side effects. People with an overactive thyroid gland should take this substance with particular caution.
- Anxiety.
Unexplained anxiety may be a side effect of taking tyrosine. This amino acid affects cognitive abilities and also acts as a stimulant of the central nervous system. And taking a pharmaceutical analogue of tyrosine can increase the frequency of impulses in the brain several times. An increased sense of fear and panic is a possible result of regular use of the substance.
- Digestive disorder.
Tyrosine in dietary supplement form has been shown to benefit the health of the digestive system. First of all, its not the best effect is felt by the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. Irritation from the amino acid causes stomach discomfort. If there is blood in your stool, you should immediately stop taking tyrosine and consult a doctor.
After the “chemical” tyrosine enters the digestive system, reflux can develop. Due to the effects of the amino acid, the sphincter in the digestive canal relaxes and allows stomach contents back into the esophagus, causing heartburn and other discomfort.
- Migraine.
Migraine in severe and prolonged form is one of the side effects of long-term use of the amino acid. In this case, you should stop taking the drug containing tyrosine and replenish its reserves exclusively from natural foods.
- Tachycardia.
Chest fluttering can be caused by tyrosine, which, by stimulating the central nervous system, speeds up and intensifies the heartbeat.
- Nervousness.
Influencing the nervous system, it can cause the development of nervousness, which arises seemingly for no reason. In fact, there is a reason - the body does not accept a drug containing an amino acid.
Overdose
With prolonged use of tyrosine preparations, the possibility of overdose increases. Medical sources indicate that with an excess of amino acids, the heart rhythm is disturbed, the acidity of gastric juice increases up to the development of gastric ulcers, and appetite worsens. A person also suffers from headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, or vice versa, increased excitability and aggressiveness. In severe cases, hyperthyroidism may develop.
If unpleasant symptoms appear or your health worsens, you should stop taking supplements and consult a doctor immediately. To reduce the negative impact of the substance, you can take activated carbon or another absorbent before going to a specialist.
Reviews about the application
To leave a review, fill out the special form below:
| Leave your review | |
| 1 2 3 4 5 | |
| Send Cancel | |
Send your review
Tyrosine
Average rating: Number of reviews: 0
Most of the positive reviews about tyrosine are related to the treatment of the thyroid gland. Buyers note a rapid improvement in well-being, a decrease in the severity of symptoms, restoration of physical strength and good mood. Those who took the weight loss supplement are also satisfied. The drug reduces appetite and cravings for sweets.
Elderly people using the nutrient to increase mental abilities not only improved memory and attention, but also restored coordination of movements and the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. Many people experienced increased stamina, normalized sleep, and a decrease in the amount of gray hair in their hair.
But there are also negative responses to the drug: some patients did not notice any results from its use, others developed allergies and discomfort in the stomach.
Jarrow Formulas, L-Tyrosine, 500 mg, 100 Capsules
★★★★☆
from 639 ₽
More details
Drug interactions
The instructions for use indicate that L-tyrosine cannot be combined with hormonal drugs for the treatment of hypothyroidism and antidepressants used in psychiatry. And combined use with MAO inhibitors (Pyrazidol, Incazan, Aurorix, Befol) can provoke an increase in blood pressure, cause a stroke or heart attack.
It is not advisable to use tyrosine together with the drug Levodopa, prescribed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The interaction of these drugs will reduce the effectiveness of therapy and increase adverse reactions. With caution, tyrosine is prescribed with amino acids such as Glycine, Tryptophan and Valine.
Vitamin B6 and ascorbic acid, taken simultaneously with the amino acid, accelerate the synthesis of hormones.
Contraindications
Dietary supplements are not drugs, but still have their own specific effects on the body. Tyrosine is a fairly active amino acid, so there are a number of restrictions.
- It should not be used by people with individual intolerance to the components.
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is also necessary to avoid taking this drug, since there is no need for excess stress on the child’s fragile body.
- It is forbidden to take tyrosine with other antidepressants. Most representatives of this group of drugs belong to the group of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. They additionally affect the rate of dopamine metabolism in the brain.
- In case of schizophrenia, taking the drug is also contraindicated, since the main basic therapy necessarily includes drugs that affect the metabolism of dopamine in the brain.
- It is recommended to limit use to those under 18 years of age.
Based on reviews of the use of L-tyrosine, side effects usually occur when instructions for use are not followed or the amino acid is overdosed. This can be caused by taking capsules against the background of active intake of the product with food. Overdose has the following side symptoms:
- allergic manifestations: itching, urticaria, hyperemia;
- headache;
- fatigue;
- insomnia;
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- epigastric pain.
It is worth remembering that uncontrolled use of even a harmless biological additive without prior consultation with a doctor can provoke a cascade of pathological processes that are difficult to treat.
Analogs
Not only L-tyrosine can cope with a bad mood and resist stress. There are other supplements with similar effects. Among them are:
- 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), which is a precursor to serotonin;
- L-Carnitine, which improves the synthesis of norepinephrine and acetylcholine;
- L-Theanine, which is used to combat nervousness and stress.
The supplements considered, like the amino acid, normalize behavioral reactions, help cope with insomnia, save you from overthinking, and correct the emotional sphere.
Tyrosine has many indications for use. The drug relieves fatigue and drowsiness, normalizes metabolism, improves memory and attention, and supports the health of the thyroid gland. However, despite all the beneficial properties, the amino acid should not be taken without consulting a doctor. If used incorrectly, it can provoke adverse reactions and worsen health in diseases of the endocrine system.
Did you like the article? Share it on social networks.