Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Asparkam - what is it?
The drug Asparkam is a drug with antiarrhythmic properties . Used as an additional source of potassium and magnesium, as well as to restore electrolyte balance (if it has been disturbed).
Pharmacodynamics
The therapeutic effects of the drug are determined by the properties of the aspartates included in its composition. Potassium and magnesium in this form easily penetrate into the intracellular space, replenishing the deficiency of potassium and magnesium and restoring the disturbed balance of electrolytes.
Asparkam reduces the conductivity and excitability of the heart, improves its metabolism and its sensitivity to cardiac glycosides and their toxicity. It has a moderate antiarrhythmic effect and helps improve coronary circulation .
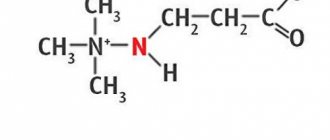
Mg2+ ions activate sodium-potassium ATP (adenosine triphosphatase). In this connection, the concentration of Na+ ions in the intracellular space decreases and the flow of K+ ions into the cells increases.
Due to a decrease in the concentration of Na+ ions inside the cell, the exchange of Ca2+ and Na+ ions in the smooth muscles of the vascular walls is inhibited, which leads to their relaxation. K+ ions stimulate the synthesis of adenosine triphosphatase, glycogen, acetylcholine, and proteins.
Penetrating into the cell, aspartate participates in metabolic processes, promotes the formation of amino sugars, amino acids, nitrogen-containing lipids and nucleotides, and also corrects impaired energy metabolism in ischemic heart muscle .
Pharmacodynamics
Absorption of the drug is rapid and complete. Metabolic products are excreted primarily by the kidneys. Serum concentrations of Mg and K reach peak values an hour or two after taking the medicine.
From the bloodstream, the drug enters the muscle cells of the heart in the form of Mg2+, K+ and aspartate ions and is included in metabolic processes there.
Potassium and magnesium
Cardiologists constantly talk about the importance of these microelements. There's nothing surprising about this
The rhythm of heart contractions is determined by the quality of the conduction system of the myocardium, in which impulses are generated independently and, passing through bundles of special nerve fibers, activate the periodicity of contraction of the atria and ventricles in a certain sequence. The normal conductivity of these fibers depends on the concentration of magnesium and potassium in them.
The heartbeat is normal, which means the person feels good, since each organ receives appropriate nutrition and oxygen on time and with a clear sequence. With a lack of magnesium, problems begin in the coronary vessels. They soften and become wide. As a result, the blood slows down, the organs begin to experience discomfort, and the patient begins to feel worse.
The opposite effect is observed with excess potassium: the coronaries become fragile and narrow. But this also brings nothing but trouble to the bloodstream, since blood cannot enter the main lines in normal quantities and be pumped to the organs. The loss of magnesium by cells, its release into the intercellular space entails the destruction of complex carbohydrates, and hyperkalemia occurs.
Magnesium takes part in all metabolic processes without exception. It is a catalyst for cell division, RNA synthesis, and provides the laying of hereditary information. But if its concentration decreases, the cell membrane becomes an insurmountable obstacle for the trace element. Magnesium Asparkam helps get into it with an additional amount of the element.
The concentration of potassium and magnesium in the cell is especially important during pregnancy. They ensure stable development and growth of the fetus
But Asparkam is prescribed to pregnant women with great caution, preferring German Panangin, a vitamin for the heart. Symptoms of overdose are fatigue and dysuria
Another nuance: a lack of potassium changes nervous excitability, and a deficiency of intracellular magnesium causes an imbalance in the generation and expenditure of energy, which stimulates convulsions, numbness of the limbs, and lethargy.
Indications for use of Asparkam: what are the tablets taken for and when should the d/i solution be prescribed?
Asparkam tablets - what are they for?
Wikipedia to the question “What are Asparkam tablets for?” answers that the medicine is intended to replenish the deficiency of Mg2+ and K+, including in cases of ischemic heart disease , acute myocardial infarction , CHF , arrhythmia (including those resulting from an overdose of cardiac glycosides ).
The manufacturer's annotation lists the following indications for the use of Asparkam in tablets:
- heart failure;
- post-infarction conditions;
- arrhythmias provoked by electrolyte imbalances (mainly ventricular);
- conditions that are accompanied by hypomagnesium or hypokalemia (including overdose of saluretics ).
The use of Asparkam in tablets also enhances the effectiveness and improves the tolerability of cardiac glycosides. therefore, the drug is often prescribed as a supplement to them.
cerebrovascular pathology ( subarachnoid hemorrhage , cerebral hemorrhage , cerebral infarction is significantly reduced .
In all of the above cases, the drug is prescribed as part of complex therapy.
Monotherapeutic use is indicated for hypomagnesemia and hypokalemia of any origin (including after repeated vomiting, taking laxatives, corticosteroids and non-potassium-sparing (“loop” and thiazide) diuretics). It is advisable to take the drug until the concentration of K+ and Mg2+ ions in the blood normalizes.
Asparkam solution: what is the injection form of the drug used for?
The d/i solution has the same indications for use as the tablet form of Asparkam. It is used as an addition to the main treatment for arrhythmia , heart failure , and MI.
Use of cardiac glycosides during therapy allows minimizing the risk of developing their inherent side effects and overdose of the latter.
Asparkam: what is this medicine used for in sports?
The instructions indicate that Asparkam is intended for the treatment of people with pathologies that are a consequence of K and Mg deficiency. In this case, the question naturally arises: “Why do they drink it in sports?”
According to Sport-Wiki, Asparkam in bodybuilding (and other strength sports) is taken to maintain the heart muscle during prolonged intense physical activity, arrhythmia , neurocirculatory dystonia , as well as maladaptation (conditions that are a consequence of overtraining).
The need to use the drug in athletes is due to the fact that the latter are often susceptible to the development of hypokalemia, which manifests itself in the form of seizures, muscle weakness, and cardiac arrhythmia .
One of the reasons for the loss of potassium in athletes is dietary habits, namely a high-protein diet: the breakdown of proteins also produces toxic substances that heavily “load” the kidneys and liver and for the removal of which the body must receive as much fluid as possible.
At the same time, not only toxins are excreted in the urine, but also inorganic ions (including K+ ions).
The second reason for the development of this condition is the loss of K+ and Mg2+ ions in sweat during intense exercise.
Thus, in bodybuilding, when, due to the characteristics of the diet, athletes cannot always consume a sufficient amount of potassium-rich food, the use of Asparkam is often the only way to compensate for the body’s needs for this mineral element.
With the use of Asparkam, the heart rate decreases, and the pulse during exercise does not exceed the permissible level. In addition, K+ and Mg2+ ions promote muscle relaxation, relieve excessive tension and cramps (the drug is often prescribed for leg cramps), and, therefore, the athlete can achieve better results during training.
As a result, the condition of the heart muscle , as well as its productivity and preparedness for high loads. All this helps reduce the risk of sudden death from cardiac arrest during intense exercise.
Many athletes take the drug in combination with Riboxin .
Indications for use
What does Asparkam help with? Indications for use of Asparkam are as follows:
1. When treating heart diseases in combination with other therapeutic drugs:
- ischemic pathology;
- insufficient heart function;
- after a heart attack;
- arrhythmia;
- tachycardia;
- digitalis intoxication.
2. If the level of potassium is insufficient - hypokalemia.
3. With a lack of magnesium.
Insufficient potassium-magnesium levels can occur with frequent vomiting or diarrhea, after taking diuretics and laxatives, artificial adrenal hormones.
4. For athletes during active training, neurocirculatory dystonia and cardiac arrhythmias.
Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated in:
- hypersensitivity to its constituent substances;
- acute renal failure and chronic renal failure;
- oliguria , anuria ;
- hypocorticism;
- hypermagnesium or hyperkalemia ;
- acute metabolic acidosis;
- cardiogenic shock (when systolic pressure does not exceed 90 mm Hg);
- atrioventricular block (AVB) of II-III degree;
- myasthenia gravis;
- hemolysis;
- dehydration.
Additional contraindications for parenteral use of the drug are childhood, severe liver failure , risk of edema, metabolic acidosis .
Asparkam should be used with caution in pregnant and lactating women, with urolithiasis (associated with impaired metabolism of ammonium phosphate, Ca2+ and Mg2+), hypophosphatemia, and grade I AVB.
Side effects
Side effects with the use of Asparkam rarely develop.
When taking tablets, the following are possible:
- disorders of the digestive system, which manifest themselves in the form of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, burning sensation in the epigastric region, pain and discomfort in the abdomen, bleeding into the lumen of the stomach, small or large intestine, ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa, dry mouth;
- cardiovascular disorders , manifested in the form of decreased blood pressure, AVB, myocardial ;
- disorders of the nervous system (usually paresthesia , convulsions, hyporeflexia );
- hypersensitivity reactions (itching, rash, redness of the facial skin);
- symptoms of hypermagnesemia (respiratory depression, feeling hot).
of hyperkalemia ( paresthesia , diarrhea, nausea, vomiting) and/or hypermagnesemia ( hyporeflexia , facial redness, feeling of heat, convulsions, respiratory depression) may occur
Instructions for use of Asparkam
Asparkam tablets: instructions for use
Asparkam tablets are taken orally after meals. The daily dose for an adult is 3-6 tablets. It should be divided into three doses.
The duration of the course depends on the nature and course of the disease.
Asparkam solution: instructions for use
The solution is intended exclusively for intravenous administration. For drip infusion, 10-20 ml of Asparkam (contents of 2-4 ampoules) are diluted in 50-200 ml of isotonic glucose solution. Infusion rate - 25 drops/min. The highest single dose of Asparkam is 20 ml. If necessary, administration of the drug is repeated after 4-6 hours.
When using a jet infusion, the infusion rate should not exceed 5 ml/min. The infusion solution is prepared by dissolving 10 ml of the drug in 20 ml of isotonic glucose solution or sterile water for injection.
The duration of the course is 5 days.
How should athletes take Asparkam tablets?
Athletes are recommended to take the medicine three times a day, 1-2 tablets. Sometimes the tablets are taken immediately before training (about an hour before it starts). Single dose - 2-3 tablets. It is believed that in this way it is possible to compensate for the loss of potassium through sweat).
How to take Asparkam with Riboxin to prevent hypokalemia?
If Asparkam is used in combination with Riboxin , both drugs are taken three times a day. The dosage of Asparkam is one tablet, Riboxin is two tablets for each dose.
The course of use of each drug individually or their combination can be repeated every 90 days.
Instructions for use of Asparkam for children: indications for use in pediatrics
In pediatrics, Asparkam is used to replenish potassium deficiency in children over 12 months of age.
If, based on the results of a blood test for ions, hypokalemia , then, regardless of the reasons that led to the development of this condition, the child is prescribed Asparkam tablets.
Parenteral administration of the drug is allowed only in case of a threat to life.
Signs of hypokalemia in children are:
- drowsiness;
- lethargy;
- drop in blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- arrhythmia;
- muscle weakness.
In infants, hypokalemia may be indicated by increased formation of gases in the intestinal lumen, poor breastfeeding, dry skin, frequent regurgitation and/or vomiting.
The causes of hypokalemia in a child can be:
- diarrhea for at least 24 hours;
- repeated vomiting;
- severe liver/kidney pathologies;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- intravenous administration of solutions of proteins, glucose, salts without potassium;
- use of GCS;
- use of non-potassium-sparing diuretics .
If the child has recently been exposed to the above factors of hypokalemia , it is recommended to conduct a study of the electrolyte composition of the blood and determine the serum potassium concentration.
If it turns out to be low or corresponds to the lower limit of the norm, the child is prescribed a course of treatment with Asparkam in an individual dosage.
In pediatric practice, the drug is also used to relieve arrhythmia caused by inflammatory damage to the myocardium , which developed as a complication of a bacterial or viral infection.
The dosage of Asparkam for children is selected depending on age. The course usually lasts from 7 to 14 days.
Children under 12 months of age should be given ¼ tablet/day. (the entire dose is taken at one time), children from one to 3 years old - ½ tablet/day, from 3 to 6 years old - ½ tablet. twice a day, from 7 to 10 years - ½ tablet. three times a day.
Dose for children 11-12 years old - 1 tablet. once or twice a day, for children 13-16 years old - 1 tablet. twice a day. From the age of sixteen, the drug is prescribed to take one tablet three times a day.
The dosages indicated are approximate. In each specific case, the treatment regimen is selected by the doctor taking into account the characteristics of the child.
For children taking non-potassium-sparing diuretics or corticosteroids, the doctor also prescribes Asparkam in addition to them to avoid the development of hypokalemia . Recommendations on how to take Furosemide with Asparkam or Prednisolone with Asparkam in a given case can only be given by your attending physician.
How to take Asparkam in combination with Diacarb?
The combination of Asparkam and Diacarb is one of the most frequently prescribed to children.
Diacarb is a drug with a diuretic and anti-edematous effect , which is used to treat glaucoma , mountain sickness , epilepsy , and edema syndrome .
as a diuretic , much more often it is prescribed for cardiopulmonary insufficiency , which develops against the background of a number of lung diseases (for example, emphysema ), for intracranial hypertension (including children under one year old), for an acute attack of glaucoma , which is accompanied by severe headaches, as well as to eliminate the consequences of brain injuries .
Dr. Komarovsky notes that indications for prescribing the combination of “Asparkam and Diacarb” to infants are also some forms of hydrocephalus .
The use of Asparkam allows you to compensate for the side effects of Diacarb , which, according to the instructions, can manifest themselves in the form of muscle weakness, decreased K concentration in the blood serum, tinnitus, paresthesia, skin hyperemia, convulsions, metabolic acidosis , hematuria , nephrolithiasis , hemolytic anemia , disorientation , agranulocytosis , drowsiness, disturbances of touch, leukopenia , allergic reactions .
By supplying cells with potassium and the energy necessary for their normal functioning, Asparkam reduces the increased alkalinity of the blood and minimizes the risk of developing severe adverse reactions.
Since the diuretic effect of Diacarb quickly decreases with long-term use, this drug is prescribed to be taken in short courses (usually 2-4 days) at intervals of several days. Children under one year of age are given the medicine ¼ tablet/day. (the tablet is given to the child in the morning, before meals). Asparkam in the dosage recommended by the doctor (usually ¼ tablet) is given on the day of taking Diacarb.
Reviews from mothers and doctors indicate that treatment according to this regimen is the most effective way to remove excess fluid from the body without complications. If necessary, it can be lengthy.
How to take the drug for a hangover?
Since alcohol helps remove fluid from the body, it therefore also removes the substances it needs. In particular, potassium and magnesium. Mg deficiency leads to saturation of the blood with calcium, and this, in turn, causes chills, increased nervous excitability, the development of muscle weakness, and heart problems.
To eliminate hangover symptoms, take 1-2 Asparkam tablets after meals.
To provide drug treatment at home, it is justified to use the drug only in the complex treatment of alcohol intoxication. It has no value as an emergency treatment.
Composition of Asparkam
You can purchase Asparkam in the form of flat tablets or a solution for injection in ampoules of 5 and 10 ml.
It contains only two active ingredients:
- Potassium, which ensures the conduction of nerve impulses, has a diuretic effect and contracts muscles.
- Magnesium is involved in enzymatic reactions, in the movement of ions, as well as in cell growth processes.
The tablets contain 175 mg of each component. In addition, the composition contains corn starch, polysorbate-80 , talc and calcium stearate.
The principle of action of the drug is based on the ability of magnesium and potassium ions to penetrate inside and participate in metabolism. The dosage of the drug depends on age, symptoms of the disease and course of treatment. Most often it is determined by a doctor.
The medicine is also used for children. In this case, the drug is prescribed from the age of three. You should not self-medicate or prescribe it yourself, especially to a child.
There are different forms of the drug, for example Asparkam Avexima.
Overdose
In case of an overdose of Asparkam, symptoms of hyperkalemia (diarrhea, nausea, the appearance of a metallic taste in the mouth, paresthesia of the extremities , abdominal pain, weakness, bradycardia , muscle paralysis , disorientation) and symptoms of hypermagnesemia ( hypotension, thirst , redness of the facial skin, nervous disorders) may theoretically develop. -muscle transmission, hyporeflexia , arrhythmia , convulsions, respiratory depression).
The ECG can record:
- expansion of the ventricular complex;
- low P wave voltage;
- high T wave voltage.
If signs of overdose appear, treatment with Asparkam is stopped, and the patient is prescribed an injection of calcium chloride (dose - 100 mg/min) and, if necessary, hemodialysis peritoneal dialysis can be performed as an alternative ).
Interaction
Use in combination with ACE inhibitors, potassium-sparing diuretics , Cyclosporine and beta-blockers can cause the development of hyperkalemia and an increased inhibitory effect on intestinal contractility.
Asparkam slows down the absorption of oral medications tetracyclines , sodium fluoride and iron salts (a three-hour interval must be maintained between doses of these medications).
Potentiates the effects of drugs that stimulate trophic processes in the heart muscle ; prevents the development of hypokalemia during the use of corticosteroids, saluretics , cardiac glycosides ; reduces the severity of the cardiotoxic effects of cardiac glycosides .
In combination with peripherally acting muscle relaxants ( Dexamethonium , Atracurium , Suxamethonium ), an increase in neuromuscular blockade is noted, while with general anesthetics ( Ketamine , Ftorotan , Hexanal , etc.) the central nervous system is depressed .
Mg preparations reduce the effectiveness of Polymyxin B , Neomycin , streptomycin and Tetracycline . Asparkam in combination with Calcitriol helps to increase the serum concentration of Mg; in combination with calcium preparations, a decrease in the effect of Mg ions is observed.
There are no data on incompatibility for the injection form of the drug.
Interaction of Asparkam with other drugs
When taking some drugs simultaneously with asparkam, there may be incompatibility.
Asparkam and potassium-sparing drugs can lead to the accumulation of potassium in the blood.
“Asparkam” and glycosides – decreased sensitivity of the heart muscle.
“Asparkam” with sodium fluoride and tetracycline reduces the therapeutic effect of these drugs on the body.
"Asparkam" and drugs for cardiac activity - increases their therapeutic effect.
special instructions
In patients receiving the drug for a long time, it is necessary to monitor ECG data, as well as serum concentrations of K and Mg.
Rapid intravenous administration of the parenteral form of the drug is contraindicated, since this can provoke the development of hyperkalium and hypermagnesemia and, as a consequence, life-threatening arrhythmia .
With rapid injection into a vein, skin hyperemia may develop.
When taking the drug, it is recommended to take vitamin B6 , since Mg is absorbed in the body only in its presence.
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Magnesium Orotate
Magnerot
Panangin
Analogues of Asparkam are the drugs Aspangin , Asparkam-L , Potassium and magnesium asparaginate Berlin-Chemie , Potassium and magnesium asparaginate , Asparkam-Ferrein , Asparkam-UBF , Panangin , Panangin Forte .
Which is better Asparkam or Panangin?
Panangin, like Asparkam, is a potassium and magnesium preparation. One Panangin contains 140 mg of anhydrous Mg aspartate and 158 mg of anhydrous K aspartate. The concentration of K+ in 1 ml of solution is 10.33 mg, Mg2+ - 3.37 mg.
That is, the differences between Panangin and Asparkam, which may affect the choice of a particular drug, are:
- dosage of active and composition of auxiliary components;
- release form (Panangin tablets are coated, which makes them lighter and also prevents damage to tooth enamel);
- price ( Panangin is a more expensive analogue of Asparkam; it is produced by the company Gedeon Richter).
Reviews from patients indicate that the drugs do not differ in effectiveness, but Panangin , according to subjective sensations, is less likely to provoke drowsiness.
Therapeutic effect of "Asparkam"
The effect of Asparkam is determined by the potassium and magnesium included in the drug. The medicine is the primary source of ions of these substances. It eliminates potassium-magnesium deficiency and normalizes metabolic reactions, since potassium-magnesium ions act in numerous chemical reactions in organs and tissues.
Once in the cells, potassium activates the synthesis of adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP), proteins, acetylcholine and glycogen. ATP is for the body like gasoline in a car. The substance is necessary for the course of all processes and normal cellular activity. Potassium optimizes ATP production and fills the cell with the necessary energy potential. With this energy, cells can perform various functions.
Activation of glycogen synthesis ensures the creation of a reserve in the cell, which, in case of deficiency, can be converted into ATP. Potassium helps cells produce supplies for future energy release. Interfering with protein production allows the cell to swap out old molecules that don't do their job well with new ones that can function well and quickly. This process is reminiscent of replacing worn parts in any mechanism. Of course, with new spare parts, any device improves its performance. Potassium ions promote cellular function and allow the cell to store useful energy.
About 300 enzymes involved in metabolic processes and ensuring the activity of body cells need magnesium saturation. Magnesium is involved in ATP synthesis and affects potassium levels. The interaction of potassium-magnesium ions helps maintain the polarization of cell membranes. This is necessary to separate the internal and external environments of the cell contents. As a result of this division, the cell is protected from foreign agents, and the results of metabolic reactions freely flow beyond its boundaries. Aspartate serves as a transporter of potassium and magnesium ions into the interior of the cell. Once in the cell, potassium and magnesium are released from the binder with aspartate, the latter, in turn, is included in the metabolic reaction. Aspartate has a positive effect on the synthesis of acids, nucleotides for DNA and lipids. It improves the disrupted process of energy exchange in the heart due to hypoxia during ischemia, atherosclerosis and other diseases.
“Asparkam” produces similar effects in any tissues and organs, but these effects are most noticeable in the heart area. That is why the drug is popular for heart diseases. The effect of Asparkam on the heart:
- eliminates potassium deficiency in the blood;
- improves metabolic reactions in the heart;
- reduces arrhythmia;
- increases the tolerability of cardiotonic and antiarrhythmic drugs;
- makes the heart stronger and able to cope with unlimited amounts of work.
Asparkam during pregnancy
data on the negative effects of potassium and magnesium aspartate on the fetus/child. The use of tablets during pregnancy and lactation is possible if the doctor considers that the benefit to the mother’s body outweighs the risk to the fetus/child.
The drug is not used for preventive purposes in pregnant women, as this can cause an imbalance of ions in the blood and severe complications of pregnancy (including pregnancy loss).
With high blood pressure and fluid retention in the body, it is advisable to use Furosemide and Asparkam. The first is a potent diuretic and is very effective in edematous syndrome , but it also removes potassium from the body, which is necessary to ensure its normal functioning. Asparkam prevents the loss of potassium.
If a woman suffers from frequent vomiting or diarrhea, the doctor may recommend taking Asparkam in short courses (lasting 7 to 14 days). Typically, one tablet is taken three times a day for 7 days after two episodes of vomiting.
If it is necessary to use Asparkam during lactation, it is necessary to resolve the issue of stopping breastfeeding.
Reviews about Asparkam
Reviews about Asparkam on forums, as well as reviews from doctors, are positive in almost 100% of cases. The medicine is excellent for treating conditions caused by a deficiency of magnesium and potassium in the body. In particular, it promotes faster recovery after a concussion, eliminates leg cramps, and normalizes heart function.
The main part of the reviews concerns the use of the drug for cardiac diseases . Patients who took Asparkam for organic and functional heart lesions note that during treatment their tolerance to emotional and physical stress significantly increased, manifestations of tachycardia and a number of other unpleasant symptoms disappeared, and laboratory parameters normalized.
The drug allows people with functional disorders of the cardiovascular system of the heart muscle for high loads.
The medicine helps with leg cramps (including in pregnant women) and muscle strain, and also helps reduce the severity of unpleasant PMS symptoms.
Some women leave reviews about using Asparkam for weight loss. The pills, of course, do not reduce the volume of body fat, but they minimize the negative effects of diuretics, which are used for weight loss. In addition, Mg preparations have the ability to reduce cravings for sweets, which can also benefit your figure.
A separate group of reviews are reviews of Asparkam and Diakarb for children. The combination is used to treat neurological disorders in children of the first year of life. Indications for its use are ICP, consequences of brain injuries , cysts in the ventricles of the brain , hydrocephalus , glaucoma , etc.
Most mothers note that after using Diacarb, the child very quickly (within 20-40 minutes) calms down and falls asleep peacefully. Asparkam reduces the risk of developing side effects typical of diuretics and serves as an additional source of K and Mg in the body.
Analogues and prices
There are quite a lot of Asparkam analogues sold on the market from different factories: from Hungary to Ukraine. Naturally, depending on what kind of plant it is, the price will also change. Complete analogues, including in composition, are Asparkam Pharmak, Asparkam-Health and Panangin. These are Russian, Ukrainian and Hungarian factories. Of these, the Hungarian drug has the highest price. In general, the cost of a domestic drug is from 7 rubles.
Also as analogues we can name:
- Mexarithm (active ingredient - mexiletine):
- Rhythmocard (active ingredient - propafenone)
Their number is quite large, and prices sometimes differ significantly.
In addition, unlike Asparkam, whose effect has been proven by a huge number of clinical studies, the effect of such drugs is not nearly as noticeable according to patients. Therefore, when purchasing any product, it is best to focus on independent sources of data - articles in specialized medical journals and partly reviews of other people.
Asparkam price
The price of Asparkam tablets in Russia is from 50 rubles. You can buy a solution for an average of 75 rubles.
In Ukrainian pharmacies the price of Asparkam in tablets is from 7.25 UAH, solution - from 13 UAH.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Asparkam-l solution for intravenous administration amp 5 ml No. 10 PAO Biosintez
68 rub. order - Asparkam tablets 20 pcs. Pharmstandard-Leksredstva OJSC
42 RUR order
- Asparkam tablets 50 pcs. LLC "FC "Zdorovye"
45 rub. order
- Asparkam tab. 50 pcs. JSC Medisorb
59 RUR order
- Asparkam-L solution for intravenous administration. 10ml 10 pcs. PAO Biosintez
103 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Asparkam tablets No. 50 5x10Health/Ukraine
47 RUR order
- Asparkam (tab. No. 56)Updating PFC CJSC
101 rub. order
- Asparkam (tab. No. 50)Health/Ukraine
44 RUR order
- Asparkam Avexima (tab. No. 56) Irbitsky Chemical Plant
95 rub. order
- Asparkam (tab. No. 50) Medisorb
60 rub. order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Asparkam No. 50 tablets PAT "Khimfarmzavod" Chervona Zirka", Kharkov, Ukraine
12 UAH. order - Asparkam 10 ml N10 injection solution PAT "Galichfarm", Ukraine
31 UAH order
- Asparkam 20 ml No. 10 injection solution PAT "Farmak", Ukraine
74 UAH order
- Asparkam 5 ml No. 10 solution PAT "Galichfarm", Ukraine
20 UAH order
- Asparkam 10 ml N10 injection solution PAT "Farmak", Ukraine
44 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Asparkam ampoule Asparkam injection solution ampoules 20ml No. 10 Ukraine, Farmak OJSC
84 UAH order
- Asparkam tablet. 0.5 No. 50 Ukraine, Health LLC
13 UAH order
- Asparkam ampoule Asparkam injection solution ampoules 10ml No. 10 Ukraine, Farmak OJSC
48 UAH order
- Asparkam solution d/in. amp. 10ml No. 10 Ukraine, Galichfarm JSC
37 UAH order
- Asparkam tablet. 0.5 No. 10 Ukraine, Red Star JSC
3 UAH order
show more