Author: Slauta Alexander - sports nutrition specialist and gym trainer | more details >> Graduated from: Belarusian State Pedagogical University named after M. Tank. Specialty: social work, pedagogy. Courses on health-improving fitness and bodybuilding at the Belarusian State University of Physical Culture, at the department of health-improving physical culture. Master of Masters in arm wrestling, 1st adult category in hand-to-hand combat. Prize-winner of the Cup of the Republic of Belarus in hand-to-hand combat. Prize-winner of the Republican Dynamyade in hand-to-hand combat.
Place in the ranking of authors:
3
(become an author)
Date:
2014-09-19
Views:
25,975
| All articles by the author >> | Medals articles >> |
Articles are loading...
Our body has many different tissues, hormones, enzymes that use amino acids as a substrate. I previously reviewed valine and leucine. Today we’ll look at isoleucine. Let us highlight its properties, functions in the body and describe its use in sports.
Isoleucine is an essential amino acid. This amino acid is not synthesized in our body. Getting it from food is necessary for the body for normal functioning and the functioning of many systems.
What role does the amino acid isoleucine play in the body?
Isoleucine is an essential amino acid with a branched side chain, which is not synthesized in the body independently, but only comes from food, is a component of many proteins and has anabolic properties, participating in energy metabolism.
Due to the special structure of the molecule, along with leucine and valine, the amino acid is part of the BCAA complexes (the abbreviation means “amino acids with branched side chains”).
If the body lacks leucine and valine, L-isoleucine is able to convert into these amino acids.
L-isoleucine is involved in the formation of red blood cells in the blood, energy metabolism and glucose utilization. The amino acid is metabolized in the muscles.
In medicine, L-isoleucine in drugs is used for:
- Treatment of asthenia.
- Preventing Parkinson's disease and cardiovascular diseases.
- Treatment of muscular dystrophy.
- Rehabilitation after injuries and operations.
- Treatment of inflammatory and acute bowel diseases.
Application in medicine
Preparations containing leucine are also used for therapeutic purposes. They are prescribed for severe liver diseases, dystrophy, polio, neuritis, anemia, and some mental health disorders.
As a rule, this compound is supplemented with medications containing glutamic acid and other amino acids to enhance the therapeutic effect.
The benefits of leucine for the body include the following effects:
- normalization of hepatocyte function;
- strengthening the immune system;
- reducing the risk of obesity;
- supporting proper muscle development;
- accelerating recovery after physical activity, increasing performance;
- beneficial effect on skin condition.
The amino acid is used to restore patients suffering from dystrophy; it is prescribed after prolonged fasting. It is also used in the treatment of cancer patients and patients with liver cirrhosis. Used to speed up recovery after injuries, surgical interventions, as well as in anti-aging programs.
What foods contain isoleucine?
Isoleucine is found in large quantities in animal foods:
- Poultry meat, including chicken meat.
- Pork, beef, rabbit.
- Sea fish.
- Liver.
- Chicken and quail eggs.
- Milk, sour cream, kefir, cottage cheese.
- Hard cheese.
The amino acid can also be obtained from plant sources:
- Almonds, peanuts, cashews, chickpeas.
- Lentils, hummus, corn, soybeans.
- Rye, buckwheat, rice.
- Cabbage, greens.
- Bakery products, including Borodino bread.
Leucine
One of the best essential amino acids for promoting muscle strength.
Helps regulate sugar levels and can prevent depression as it acts at the level of neurotransmitters in the brain. Plant sources include:
avocado, seaweed, peas, rice and sunflower grains, sesame, watercress, turnip greens, soybeans, beans, figs, raisins, dates, apples, blueberries, olives, pumpkin, bananas. Do not limit yourself to one food from this list, strive for variety during each meal.
Why is L-isoleucine used in sports?
Why is the amino acid so popular in sports and used in BCAA complexes? This is because the amino acid is involved in the synthesis of new muscle fibers, which means it has anabolic properties. Due to the fact that the amino acid is broken down within 20-30 minutes and goes directly to the muscles, which need rapid recovery after heavy physical activity, and not to the liver. This explains why BCAAs, including L-isoleucine, are needed after and during exercise to further muscle growth and prevent catabolism.
Benefits of amino acids
- Participates in the production of hemoglobin, affects blood quality, normalizes blood pressure.
- Promotes the growth and formation of new muscle fibers.
- Reduces blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
- Participates in energy metabolism, serves as a source of energy for muscles and brain.
- Prevents the destruction of muscle fibers.
- Regenerates damaged tissues.
- Increases endurance.
- Stimulates the work of the central nervous system and PNS.
- Increases immunity by producing hormones and enzymes.
- Promotes detoxification of the body.
Properties of isoleucine
1. STRENGTHENS THE OUTER LAYER OF THE SKIN (EPIDERMIS) - for the normal condition of the skin, intercellular fluid circulates, it is a mixture of lymph and blood, so that the metabolic process occurs as quickly as possible, essential amino acids are used, incl. isoleucine.
2. STABILIZES ENERGY POTENTIAL - the absorption of isoleucine begins in muscle fibers, which accelerates the rate of muscle recovery due to the synthesis of alanine, due to which glucose is produced from protein.
3. CONTROLS SUGAR LEVELS - a very important function of isoleucine is that it is directly involved in the formation of insulin, in simpler terms, it affects the activity of hormones, which in turn prevents sugar levels from rising in the blood.
4. PROMOTES HEMOGLOBIN SYNTHESIS - proteins in our body are attached to oxygen molecules, isoleucine helps attach more oxygen molecules to hemoglobin, thereby improving the transport of useful substances and the synthesis of hemoglobin itself. The result of all this will be better muscular endurance of the entire body.
Isoleucine is actively used in strength sports and helps arm wrestlers, powerlifters, bodybuilders, it increases strength endurance, ensures faster recovery, and also reduces the level of cortisol and catabolic processes in general.
Side effects and harm
- In rare cases: allergic reactions - eczema, dermatitis, conjunctivitis.
- Amino acid intolerance: nausea, vomiting, sleep disturbance, headache, fever.
- An overdose of the substance causes nausea, vomiting, organic acidemia, a specific smell of sweat and urine, convulsions, respiratory and heart rhythm disturbances, and renal failure.
- Apathy, blood thickening, increased ammonia levels and general poisoning of the body are possible.
Deficiency and excess: what are the dangers
Isoleucine deficiency causes symptoms in the body similar to hypoglycemia. A deficiency of the amino acid can result in headaches, dizziness, fatigue, depression, confusion, irritability, weakened immunity and muscle wasting. By the way, many people suffering from mental and physical disorders are diagnosed with insufficient levels of isoleucine.
Excess isoleucine is no less dangerous for humans. An amino acid in a particularly high concentration can, at best, manifest itself as a banal allergy. But there are also more serious consequences. For example, the so-called “sticky blood” (too thick), an increase in the concentration of ammonia and free radicals are also consequences of excessive saturation of the body with amino acids.
Contraindications
- Impaired excretion of isoleucine.
- Acidosis.
- Chronic kidney diseases.
- Diseases of the cardiorespiratory system and heart rhythm disturbances.
When taking isoleucine, it is prohibited to take vitamin B9 (folic acid), the amino acid reduces the concentration of B9 in the blood.
Although there is information that drugs with isoleucine are harmless to pregnant women and the fetus, it is still necessary to take any drugs strictly as prescribed by the doctor!
How to take in bodybuilding
The norm of isoleucine for a person is calculated by the formula: 50-70 mg per kilogram of weight.
BCAA contains isoleucine in an average amount of 1-2 grams per serving. The complex must be taken according to the instructions, without exceeding the maximum dosage.
When doing bodybuilding, the need for isoleucine increases to 4-6 grams per day.
- It is recommended to take one serving of BCAAs before training, half an hour or during, and a second serving immediately after completing the load.
- On rest days, you can take a serving of BCAAs in the morning, and a second during the day between meals.
Top 3 L-Isoleucine Supplements
- Olimp Bcaa Xplode 1000 grams - one serving of powder supplement (10 g) contains 1500 mg of isoleucine, 3000 mg of leucine, 1500 mg of valine in a 2:1:1 ratio, as well as 1000 mg of glutamine and 2 mg of vitamin B6. The product contains 100 servings.
- Optimum Nutrition BCAA 1000 – one serving (2 capsules) contains: 500 mg leucine, 250 mg isoleucine, 250 mg valine in a 2:1:1 ratio. Take 1 serving 3 times a day.
- Scitec Nutrition BCAA Xpress - powder form in a ratio of 2:1:1 (leucine - 2500 mg, isoleucine - 1250 mg, valine - 1250 mg). One serving is 7 grams - half a scoop. The portion is diluted in water or juice.
Isoleucine is an essential amino acid that must be supplied with food. Isoleucine is found in proteins in small quantities.
Isoleucine is one of three branched amino acids, so named for the specific structure of the molecule.
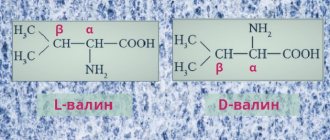
Isoleucine is one of the hydrophobic amino acids, because has a hydrocarbon side chain, the characteristic feature of which is its chirality (another such amino acid is threonine).
Isoleucine is a non-polar hydrophobic amino acid.
Based on the structure of the compounds resulting from the cleavage of the carbon chain of proteinogenic amino acids, glucoplastic (glucogenic) and ketoplastic (ketogenic) amino acids are distinguished. Isoleucine is glucoplastic and ketoplastic.
Isoleucine is 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic or α-amino-β-methylvaleric acid.
Isoleucine ( Ile, Ile , I ) is an aliphatic α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH (NH2) CH (CH3) CH2CH3.
Isoleucine was discovered by F. Ehrlich in 1904 in the breakdown products of the fibrin protein. It was first obtained synthetically in 1905.
daily need for isoleucine is 3-4 grams.
Physical properties
Isoleucine is a colorless crystalline powder. Isoleucine is highly soluble in water, hot acetic acid and aqueous solutions of alkalis, poorly soluble in ethanol, and insoluble in diethyl ether. Melting point 2860C (dec.).
Main functions
Reduces weight by reducing appetite and accelerating metabolism. Increases a person's physical and mental endurance.
Provides muscle tissue with energy. Promotes the flow of biochemical processes that produce energy. Prevents feelings of restlessness, anxiety, fear.
Reduces excessive sweating. Prevents an increase in insulin levels in the blood. Stabilizes blood sugar levels and energy supply processes.
Promotes the restoration of muscle tissue. Effective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Plays a key role in the production of hemoglobin.
metabolism occurs in muscle tissue.
Biological role
Isoleucine, like all other compounds related to amino acids, is involved in the creation of protein molecules.
Due to its branched structure, isoleucine is involved in energy metabolism occurring in the body.
Isoleucine promotes rapid tissue healing, regulates blood glucose and cholesterol levels, and allows muscles to recover after physical activity.
Isoleucine is an obligatory participant in energy metabolism. This amino acid is a source of energy for muscle cells.
It also prevents the overproduction of serotonin in the brain by limiting the availability of tryptophan.
Isoleucine is necessary for many mental illnesses.
Isoleucine is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin.
Isoleucine is very necessary for athletes - BCAA (valine, leucine and isoleucine), as it increases endurance and promotes the restoration of muscle tissue.
A sufficient amount of this amino acid in the body ensures normal muscle mass gain and effective functioning of the immune system, prevents body tissue from destruction, and enriches the muscles and brain with the necessary energy resources.
Natural springs
Isoleucine is found in lactalbumin (whey protein), casein, meat proteins, egg whites, and hazelnut proteins.
A large amount of isoleucine is found in milk and dairy products (especially hard cheeses, cottage cheese, feta cheese), and seafood (fish, red and black caviar). Isoleucine is found in meat and poultry.
Among foods of plant origin, soybeans, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, lentils, beans, as well as nuts (cashews, almonds), and cereals are richer in isoleucine. Isoleucine is also present in small quantities in cereals and pasta. Examples of food sources: almonds, cashews, chicken, chickpeas, eggs, fish, lentils, liver, meat, rye, most seeds, soy proteins.
deficiency results in loss of muscle mass. Since it plays a significant role in obtaining energy through the breakdown of muscle glycogen, a lack of isoleucine also leads to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), resulting in lethargy and drowsiness.
Areas of use
Application of BCCA (leucine, valine, isoleucine)
Strenuous training entails wear and tear of some contractile proteins. Additionally consuming BCAAs (leucine, valine, isoleucine), athletes recover faster after hard training.
Muscle fatigue occurs due to depletion of muscle glycogen stores. As these stores dwindle, the liver begins to remove BCAAs from the bloodstream and sends them to the muscles being trained to support their energy needs. The higher the intensity of training, the faster glycogen is consumed, the more significant the role that BCAAs play as an alternative source of “fuel”.
The process of fatigue is accelerated in the event of a sharp depletion of glycogen reserves and insufficient intake of carbohydrates from food. Therefore, supplementation with BCAAs is especially important for athletes on a low-carbohydrate diet (such as bodybuilders preparing for competition).
BCAAs can not only provide muscles with building material and energy, but also slow down the catabolism (destruction) of muscle protein.
This statement most applies to leucine, which serves as a substrate of muscle metabolism during periods of cellular energy depletion.
Working out takes a toll on your muscles, and they need some time to recover in order to continue to grow. For different people, this process takes approximately 40 to 96 hours. And if there is not enough time to rest, the negative effects will only accumulate.
Muscle mass does not grow and training does not bring satisfaction. In this case, BCAAs will help, as they create the basis for building muscle mass and accelerate metabolic processes, which ultimately leads to a reduction in the recovery period.
Another benefit of BCAAs is the fact that they can not only prevent fatigue and muscle breakdown, but also smooth out hormonal fluctuations caused by intense exercise.
First of all, you should not take each amino acid from BCAAs separately from the other. Their optimal ratio is 2:1:1, otherwise an imbalance of amino acids will occur.
Some people take BCAA capsules before and after training. Taking BCAAs before training can protect muscles if there is insufficient glycogen in the liver. And their direct use afterwards can quickly restore the energy potential of the cells.
In this case, the most optimal time to take amino acids will be the first 30 minutes.
Professional athletes take BCAAs in very large quantities, up to 30 grams per day. For the average jock, this amount can be reduced to 5-10 grams.
Thus, if you need to build more muscle mass and protect your body from the breakdown of muscle protein and provide it with new energy, you need to take BCAAs regularly. Combined with training, branched-chain amino acids are an essential prerequisite for muscle growth.
dietary supplements
There are biologically active food supplements containing isoleucine. In this case, it is necessary to maintain the correct balance between isoleucine and two other branched amino acids - leucine and valine. The most effective combination of branched amino acids is approximately 1 mg of isoleucine for every 2 mg of leucine and 2 mg of valine.
Anticatabolan Mega Caps are a unique composition of specially selected components. Ingredients: L-valine, L-leucine, L-isoleucine, acetyl-L-glutamine, L-arginine pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6). Excipients: magnesium stearate, gelatin.
Leucine, isoleucine and valine are essential for muscle tissue, but they are most quickly broken down by protein catabolism (breakdown). When taken continuously in the form of dietary supplements, they quickly penetrate into the muscles and inhibit the activity of catabolic enzymes.
Difference between BCAA and other amino acids
These are the only amino acids that are metabolized primarily in skeletal muscle and to a much lesser extent in the liver. BCAA amino acids can be considered “fuel” for skeletal muscles.
Amino acids
Classification of amino acids