While maintaining a healthy lifestyle, people often forget about the most accessible form of body exercise – swimming. This sport is unique due to the development of all types of muscles, since almost the entire musculoskeletal system is involved when moving in water. Almost all muscles work when swimming, and the very presence of the human body in water trains the cardiovascular system and eliminates congestion in the lower extremities, which often happens with varicose veins and other unpleasant diseases. Which muscles work when swimming depends more on the swimming style, and we will talk about this in detail below.
Further:
Swimming styles
There are 4 sports styles in total:
- Front crawl (water style);
- Breaststroke (frog);
- Back crawl;
- Butterfly (butterfly, dolphin, butt).
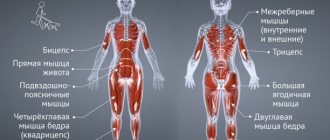
Regardless of which type you choose, the following muscle groups will be involved:
- Shoulders;
- Torso, abs;
- Back;
- Legs;
- Hands.
However, each style has a target group that works to a greater extent. For example, in crawl, the main load is placed on the arms and shoulders, and in breaststroke, the hips and buttocks receive the main load. Do you want to know which muscles work when swimming in different styles in the pool? Let's look at each one separately.
Why is swimming ineffective for those who want to gain weight?
First, let's start with the fact that this is aerobic exercise (like running, cycling, etc.). That is, the muscles do not work at the limit, as is sometimes necessary for their growth, but in a near-limit state. After all, their excessive tension only interferes with the coordination and free movements that a swimmer so needs. And this is not at all enough for muscle growth.
Secondly, only certain muscle groups are involved. Only that which is strained develops, and even then not much. Swimming is a “cyclical” sport that does not even increase working muscles.
Breaststroke
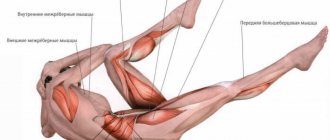
Breaststroke is a style in which all movements of the arms and legs are performed in a horizontal plane. This is the slowest type, but the most comfortable for long-distance swimming. The main engine that is mainly involved in propelling a swimmer forward is the legs. The hands work second, then the body.
Check out the muscles that move when swimming breaststroke in the pool:
- Quadriceps and hamstrings;
- Gluteus major, minor and medius;
- Calf;
- Hip adductors;
- Iliopsoas;
- Transverse and oblique abdomen;
- Latissimus dorsalis;
- Trapezoidal, large and small round, diamond-shaped;
- Deltoid muscles of the shoulders;
- Biceps, triceps, palm muscles;
- Brachioradial;
- Large pectoralis;
- Musculature of the foot.
We have listed which muscle groups work when swimming breaststroke; as you can see, almost the whole body is involved in the process. This is where the complexity of the impact of water sports on the human body is expressed.
Crawl on chest
Now let's list which muscles work during water style swimming. It is the most favorite among professional swimmers because it allows you to develop very high speeds. The style requires excellent physical shape, developed breathing and high endurance, since it is considered very energy-intensive. The main load in the front crawl is on the arms and shoulders, while the legs act as stabilizers in space.
So, check out the list of muscles that develop when swimming front crawl:
- Deltoid shoulders (anterior, middle, posterior bundles, as well as rotator cuffs);
- Dorsal: latissimus, trapezoid, large and small round, diamond-shaped;
- Triceps and biceps brachii;
- Brachioradial;
- Sternocleidomastoid;
- Anterior serratus;
- Oblique and straight abdomen;
- Gluteus maximus;
- Quadriceps and hamstrings;
- Calf;
- Anterior tibial and adductor magnus;
- The muscles of the palms and feet also work.
These are the muscle groups that are affected by water-style swimming on the chest in the pool; as you can see, the list is no less impressive. However, here the technique requires a higher tempo, so more energy is spent during the crawl. In other words, the muscles work harder.
Back crawl
Let's continue our review and move on to the next style. What muscle groups are affected by backstroke swimming in a pool? It is no secret that this type is considered the least energy-consuming. To increase the load, we recommend swimming quickly and without rest breaks. The work involves, first of all, the arms, then the legs.
Check out the list of muscles used when swimming the back crawl in the pool:
- Deltoids;
- Musculature of the forearm;
- Biceps and triceps of the arms;
- Muscles of the palms;
- Latissimus, major and minor round, diamond-shaped and trapezoidal backs;
- The core and abs muscles work as stabilizers;
- Large pectoralis;
- Sternocleidomastoid;
- Quadriceps and hamstrings;
- Calf;
- Gluteus maximus.
This style of swimming strengthens the muscles of the arms and core, while using the legs to a lesser extent. Its technique is similar to the front crawl, but here the athlete does not need to practice breathing techniques with his face immersed in the water.
Well, we have analyzed 3 swimming styles available to any beginner. We hope that the question “is it possible to build muscles by swimming in a pool” is no longer in front of you. Next, we move on to the most complex and most energy-consuming style, which is extremely difficult to master on your own.
Butterfly
This type is the most difficult technically, but the most spectacular and effective for pumping muscles and losing weight. It requires enormous effort and excellent physical preparation. The style allows you to develop high speed of movements. The main muscles that are pumped by butt swimming are located in the area of the upper shoulder girdle. The back also receives a high load, and the legs receive a secondary load.
Here is a complete list of muscles that are trained when swimming butterfly:
- Front, middle and rear beams of shoulders;
- Biceps and triceps of the arms;
- Brachioradialis and palm muscles;
- Dorsal: trapezoid, latissimus, rhomboid, large and small round;
- Press;
- Large pectoralis;
- Quadriceps femoris;
- Calf;
- Musculature of the feet;
- Gluteus maximus.
It is these muscles that are trained by butt swimming, but the level of load that is placed on them is several times higher than, for example, in breaststroke. The style requires high coordination and perfect execution technique. Swimmers work long and hard, honing their movements and increasing their speed. Amateur athletes rarely choose this style of training as their main one.
Swimming training and breathing
When swimming, due to the fact that a person learns to overcome oxygen starvation, not only overall muscle tone improves, but also the functioning of the circulatory system and even the brain (swimming is believed to help fight stress). It is also important that swimming develops the heart, the most important muscle in the body, without which life is impossible to function properly.
Regular swimming training optimizes the functioning of the respiratory system and increases the useful volume of his lungs, as a result of which the chest gradually expands - this is what becomes a key factor in creating a classic swimmer's figure. The second factor, as we mentioned above, is regular strength training and pullover strength exercises.
How to make a swimmer's figure?
On the one hand, swimming enlarges the chest and broadens the shoulders, due to which the figure takes on a characteristic triangular shape. But, on the other hand, most swimmers combine swimming with strength training in the gym, alternating between them - in this case, swimming acts as an active recovery tool.
This is what ensures comprehensive muscle development - endurance and strength through swimming and an increase in volume through strength exercises. Not to mention drawing muscle definition or losing weight - let us remind you that losing weight with swimming alone is almost impossible, since control over the diet is also required. In fact, swimming itself only increases your appetite.
Swimming is one of the best ways to strengthen the heart and respiratory system, work the internal muscles of the back and spine, as well as expand the shoulders and chest. However, even regular swimming only increases muscle strength and endurance, minimally affecting weight gain, muscle growth or weight loss processes.
How to pump up your body while swimming?
Well, we found out whether it is possible to get pumped up by swimming in the pool, and we even listed which muscles work during it. Now let's talk about how to organize this process correctly. Below are tips to help with this issue:
- Correct adherence to technique is of great importance. Yes, even if an athlete swims incorrectly, his muscles work. However, in this case, the spine receives unnecessary and, at times, dangerous load. If the technique is incorrect, the swimmer does not work as productively as required - he gets tired faster, moves more slowly, and often experiences pain after exercise.
- Muscle work during swimming is more effective with a correctly designed training schedule. The main rule in this matter is sufficient time for rest and regular exercise. In other words, classes must take place strictly according to schedule, without failures or long breaks. During training, the athlete works at full strength and even a little more, and after that, he allows the body to rest. The optimal mode for visiting the pool is every other day.
- Muscles tend to get used to the load. To prevent this from happening, regularly increase their task. As soon as you feel that the distance is easy for you, increase it. Move at a faster pace, alternate between different swimming styles. Let the muscles work to the limit of their capabilities, this is the only way to pump them up quickly.
Can muscles hurt after swimming?
Important! If after the pool the muscles of your back, shoulders, and neck hurt, it means that you performed the swimming technique incorrectly. Correctly performed exercise is the key to health.
Pros of visiting the pool:
- All muscle mass develops effectively. Training activates and develops our entire body;
- water has a beneficial effect on the body’s recovery after injury;
- Thanks to exercise in water, the muscles become elastic and take on an elastic shape. For muscles, the pool is an ideal option to remain in the same condition and maintain tone;
- swimming allows you to get rid of diseases such as asthma;
- excess fat is intensively burned in water, which has a beneficial effect on the body as a whole;
- water hardens the body;
- for a person, swimming in a pool produces a positive effect on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and the body’s muscles restore their functions;
- for pregnant women, visiting the pool allows you to maintain muscle tone, and after childbirth you can quickly return to your previous appearance;
- every muscle mass is hardened and massaged;
- an opportunity to lift your spirits and recharge yourself with positive energy.
Disadvantages of visiting the pool:
- Do not overuse training.
- The water in the pool contains many harmful microbes. However, if you have good immunity, then this will not create any special problems for you.
- Chlorine, which is used to purify water, negatively affects the condition of the skin and worsens the hair. May lead to the development of allergic reactions to this component.
If physical exercise is contraindicated for you, then water exercises are perfect for you. Water resistance will have a beneficial effect on good muscle function, and this will lead to the disappearance of subcutaneous fat.
Special treatment sessions are often organized in the pool
How long does it take to work out to get pumped up?
Please note that when swimming in the sea, the same muscles work as in the pool. The type of body of water does not affect the group of muscles involved. However, the natural reservoir and natural conditions often have an impact on the load. For example, a strong current makes progress difficult, forcing the swimmer to increase effort as he swims backwards. Sea water better holds the body on the surface, reducing the load on the muscles responsible for balance and balance.
During training in deep water, the athlete is influenced by wind, sun, bottom quality, waves, etc. Classes in an artificial environment are easier to plan and control.
In conclusion, let's talk about how much and how to swim correctly to strengthen the muscles of the back, legs and arms.
- Follow your schedule and don’t miss classes;
- Control the load;
- Use complex swimming (alternating styles);
- Keep an eye on your technique.
On average, after just a month of active training you will feel and notice the first results. You will clearly understand whether the abdominal muscles work when swimming by seeing the outlines of the desired cubes. Of course, if you are overweight, it will take much more time. However, a month later the volumes will definitely become smaller and the weight will decrease. Of course, subject to stable training, proper nutrition and proper rest, including night time.
Well, we found out which muscles benefit from swimming in the pool, and also which of them work more actively in each of the 4 styles. Based on this information, you can safely draw up a lesson plan. I wish you a beautiful body and high sports results!
Swimming training - what is the benefit?
Without a doubt, swimming is one of the best types of physical activity for muscle development: strengthening the cardiovascular system, increasing muscle strength and performance. Thanks to regular training in the pool, ligaments and tendons acquire both strength and elasticity, and the muscles of the whole body become significantly more resilient.
At the same time, swimming has the greatest positive effect on the figure in adolescence - training in the pool helps not only to develop a broad back and strengthen the core muscles, but also promotes elongation in height due to a comprehensive improvement in posture. In other words, for teenagers, swimming lays the foundation that will help them build muscle and get pumped up quickly in the future.
Speaking about professional sports, we note that the rules of sports standards for swimming say that the title of candidate for master of sports can be obtained at the age of 10, and the title of master of sports - at 12 years. Due to such age limits, in practice, youth swimming categories are practically not registered - children involved in swimming can receive adult categories as early as 8 years old.