Let's look at what fascia is and how to “release” it, while improving your posture and losing excess weight.
What is fascia - signs and causes of its tightness in humans
Imagine a peeled orange. Until the fruit is broken, it will not fall apart on its own. This is all thanks to the thin shell that covers each lobe and connects them to one another. Likewise, fascia, like a protective film, envelops all our organs, blood vessels, muscles, and nerves.
But this is not just a wrapper, but a reliable package of the body under a layer of skin. Fascia sets the position of the internal organs and ensures the sliding of muscles. It is elastic, strong, but at the same time elastic, and changes its position with any muscle contraction. Therefore, we are able to move smoothly, in different planes, and not like robots.
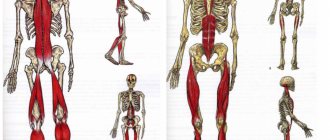
Superficial (cutaneous) fascia
Muscular fascia
Fascia is a dense, fibrous tissue. It consists of collagen and elastin intertwined. In terms of consistency, this fabric is plastic, “slime-like”, and can stretch and change shape if necessary. But this is what fascia looks like in perfect condition.
Unfortunately, many people face problems such as loss of elasticity of the fascia, its tightness, and tightness.
The following signs indicate deviations:
- Periodic pain, muscle spasms, especially after physical activity. 6 best ways to get rid of muscle pain after sports activities
- Poor mobility of muscles and joints, feeling of tightness. Deterioration of body flexibility. Accordingly, the chance of getting a dislocation or sprain increases.
- Poor posture, “distortions” in the body - for example, different leg lengths.
- Often fascial tightness causes radiculitis, migraines, herniated discs and even vascular problems.
Fascia becomes tight not only with age. It can lose elasticity even in a young person. The main reason for this is a sedentary lifestyle, or, conversely, excessive physical activity that does not correspond to the level of training of the body.
Injuries suffered also have a great influence: fractures, bruises, dislocations.
Frequent stress, emotional turmoil, negative thoughts and even lack of water affect the condition of the fascial tissue.
So what happens in practice?
Pumping is a special training method that allows you to achieve a burning sensation in the muscles, which indicates the depletion of glycogen and creatine phosphate reserves. As a result, the processes of aerobic energy supply to the muscles are launched. Oxygen begins to flow to them through the blood, therefore the muscles swell and the fascia stretches. You can build an entire workout around pumping, or add several approaches at the end of the session.
Below you will find several examples of techniques for achieving excellent pumping.
Superset
Supersets are a great way to add variety to your workouts. All we need is to perform two sets of antagonist muscles in a row, for example, biceps curls and triceps cable presses, horizontal pulldowns for the lats, dumbbell bench presses for the pecs, etc.
Complex sets
Complex sets - performing two exercises in a row, but for one muscle. For example, lifting a barbell for biceps and immediately after, alternately lifting dumbbells for biceps. Choose a weight that allows you to perform at least 12 reps on each set.
Dropsets
Dropsets – You will definitely need a partner to perform this type of exercise. The idea is to perform one set with a heavy weight for 10-12 repetitions, after which your partner slightly reduces the weight on the apparatus and you immediately do another 4-6 repetitions. This continues until the bar remains empty. Therefore, when you prepare the projectile, use light weight plates to make 4-5 phases of decreasing the load.
Stretching
Stretching is also one of the ways of mechanical impact on the fascia, but here we are not talking about the classic bending forward with straight legs.
We need to stretch the muscles after each approach and stretch them well at the end of the workout. However, it is very important to approach this issue wisely: you should not pull muscles after sets if you are doing a heavy workout with a lot of weight and a small number of repetitions. In this case, we weaken the natural spring from the fascia, which in the future can lead to injury.
Bodybuilding
Bodybuilding is a very long process that requires certain knowledge in the field of training methods, nutrition, etc., and there is no room for trifles. Working on stretching the fascia will undoubtedly help you achieve your goals faster and gain beautiful and defined muscles. Put the methods described above into practice and the result will not take long to arrive.
Takei Hitoshi's fascia release method - a revolution in sports and medicine
Takei Hitoshi is a professor at the Medical University of Tokyo, a physiotherapist by training. He is engaged in scientific research in the field of orthopedic surgery and manual physical therapy. Thanks to scientific books and articles, appearances on radio and television, Takei Hitoshi is known not only in Japan, but throughout the world. The professor is called the “Doctor of Fascia.”
While studying fascia and its connection with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, Takei Hitoshi came up with a method for releasing fascia .
Many people at the end of the working day experience fatigue, heaviness in the body, and discomfort in the back. This occurs due to the prolonged presence of the fascia in an unnatural position and its compression. The same contractions are associated with the body's reaction to cold.
To release the fascia, it is necessary to regularly warm it up, fill it with energy and keep it in good shape. Special gymnastic exercises developed by the professor help any person free the fascia from cold, tightness and tightness .
Fascia under a microscope; this is how fascia envelops muscle fibers and organ walls
This theory is substantiated from the point of view of anatomy, physiology, and kinematics. In 2007, at a scientific conference at Harvard, a group of Japanese scientists used 3D visualization to show what the inside of the human body looks like if everything except fascial tissue is removed from it. The resulting image showed a three-dimensional mesh with many pockets, sections and processes. This means that fascia envelops every organ, every muscle from the outside and from the inside. When the fascia is pinched, it consequently compresses blood vessels, nerves, muscles, and impairs normal blood flow. The cells do not receive the normal amount of oxygen.
Try a little experiment: clench your fist tightly and hold it for a couple of minutes. After a while, you will notice that the hand of your clenched hand seems to be drained of blood.
This is exactly what happens with fascial tissue. When it is pinched, the blood in this tense area is squeezed out of the arteries and capillaries. Because of this, waste can accumulate in muscle tissue.
Why fascia needs special attention
Many factors in our daily lives, including poor posture habits, stress-induced muscle tension, injury and dehydration, and a sedentary lifestyle, lead to adhesions in the fascia and the muscles joining together, causing them to lose the ability to perform their individual functions. When muscles have to move together and work as a team, they become less efficient. The deeper layers of tissue, where adhesions and scars often occur, can be stubborn and require something more than your usual vinyasa flow to work out. However, other techniques that involve both muscle and fascia may be more effective. Massage, rolfing, self-massage with a roller and myofascial release are the most popular methods of influencing this tissue system. By using highly targeted fascial release techniques in our practice, we can initiate a process of fascial repair and remodeling to release tissue and increase range of motion that will last not only during, but also after, practice.
Rules for exercises to release fascia, contraindications, expected results
To release and restore the fascia, Professor Takei Hitoshi has developed 3 exercises that need to be performed every day.
This complex is especially suitable for office workers who spend a huge amount of time at their desks at the computer. But everyone else will notice the improvements too.
After 14 days of regular training, you can achieve the following results:
- Improved posture : a person will walk and sit with his shoulders back instead of slumped.
- Weight loss by improving blood circulation. The number of kilograms lost will depend on the person’s baseline data and nutrition. But the dynamics towards weight reduction will definitely happen.
- The body becomes more flexible.
- Muscle pain disappears if it periodically bothered a person.
- There is a feeling of energy in the body , as if the muscles were sleeping before, but after the gymnastics they woke up.
You can perform the exercises at any convenient time 1 or 2 times a day .
All movements are made smoothly , measuredly, slowly.
When performing exercises, you need to relax as much as possible and drive away negative thoughts.
If you have any diseases, it is better to first check with your doctor whether such exercises will cause harm.
But the obvious contraindications for gymnastics are:
- Exacerbations of many chronic diseases.
- Presence of a fracture, dislocation, post-traumatic condition.
- Pulmonary tuberculosis.
Layers of fascia
The thoracolumbar fascia is divided into 3 main layers. Almost all the muscles in the back are attached to the fascia. The entire muscle group runs from the first longitudinal vertebra to the very bottom:
1. The layer that is located at the back starts from the twelfth vertebra and stretches to the very bottom. Along the way, this layer has the internal oblique muscle and the abdominal muscle. In this case, the fascia connects the muscles of the back and the peritoneum.
2. The middle layer is the broad dorsi muscle; it acts as a support for the body and helps to move the body weight freely. This layer begins directly from the thoracolumbar fascia.
3. The front layer helps to bend the body and calmly hold any upright posture.
Oddly enough, back pain can occur not only in adults, but even in the youngest. Intense pain can lead to a person’s disability.
Just three exercises every day to release fascia and lose weight
Exercise No. 1
- Starting position: left hand raised above your head, right hand behind your back. The arms are relaxed, half-bent.
- Bend your elbows at right angles and move your arms clockwise. At the same time, you need to feel how your shoulder blades tense. We freeze for 5 seconds with our arms extended as far as possible.
- We return to the starting position and change hands: now the right one is raised up above the annual one, and the left one is behind the back.
- Again, bend your elbows at a right angle and move your arms clockwise. We freeze for 5 seconds.
The number of approaches for overweight and elderly people is 4-6 times (2-3 times per arm). For everyone else, you can double the number of approaches.
Exercise No. 2
- Starting position: standing in front of a table or window sill, we put our right leg forward, with the knee slightly bent. Left leg in a straight position. Feet pressed firmly to the floor. We place the left hand on the table (window sill).
- We raise our right hand up, pull it towards the ceiling, without lifting our feet off the floor. We freeze in this position for 20 seconds.
- We swap arms and legs: now the left leg is in front, and the right hand is on the table. We pull our left hand up and freeze in this position for 20 seconds.
The number of approaches for overweight and elderly people is 8-10 times (4-5 times for each hand). All others, accordingly, can double the number of approaches.
Exercise #3
- The starting position is the same as in exercise No. 2. The right leg is in front, the knee is slightly bent. The left hand lies on the table. Pull your right hand up.
- We turn our body to the right, and we also try to turn our right hand to the right. We freeze for 20 seconds.
- Bend the left elbow, the forearm should lie on the table or windowsill. The right hand is still up. Hold the position for 20 seconds.
- We change places of the arm and leg, do the same, only now we turn the body to the left.
For older people, it is enough to perform this exercise once on each side. But, if blood pressure is increased, it is better to cancel exercise No. 3 until the pressure stabilizes.
People who are clearly overweight can perform 2-3 approaches in each direction. The rest double this amount.
Fascia connects our body into a single whole. It is closely interconnected with the muscular, circulatory, nervous and other systems.
Today, athletes, fitness enthusiasts and simply people who care about their bodies should train not only their muscles and joints, but also their fascia.
Pumping and stretching
To achieve the result we need, we can use two methods: pumping and stretching. As mentioned above, fascia always tightly envelops the muscles, but it can stretch, because if it did not have this ability, then aerobic methods of energy supply to the muscles would be difficult. You've undoubtedly noticed how your muscles swell after intense work with high repetitions and light weights. This process is especially noticeable in the case of the arm and pectoral muscles.
This pumping effect becomes possible because the muscle is washed with blood, which is necessary during prolonged muscle work, since creatine phosphate and glycogen have already been used, and the body begins to look for alternative sources of energy. After training, this effect subsides and the muscles gradually return to their normal state.
The fascia also tightens and tightly envelops the muscles. This means that fascia is capable of changing its size. We need to not only stretch the fascia during training, but also ensure that at the end of the training they maintain a stretched state. How realistic is this? Absolutely real! However, this is a rather complex process, and the body will only become involved in it if you create the necessary conditions for it.
Main functions of fascia
It is worth noting that fascia is primarily an inelastic support that allows you to properly hold the pelvis, torso and all limbs, and also allows you to freely distribute the entire load throughout the body. Let us consider in detail what functions the lumbothoracic fascia performs:
- While the muscles in the abdomen begin to activate, the fascia begins to restrict the movement of the pelvic bones, and the work of the iliac joints improves.
- When horizontal muscle tension occurs, the transverse abdominal muscles begin to contract in the peritoneum and thereby stabilize the pelvis.
- The muscles that are connected to the fascia allow you to balance tension and force the group of muscles that are responsible for this to straighten the spine.
Most often, pain occurs in the lower back.