A cramp is a sudden, involuntary, often painful contraction of a muscle. This happens to everyone from time to time: at night during sleep, during physical activity, and sometimes at rest. Spasm can occur in any part of the body - in the limbs, in the side, in the buttock, in the abdomen.
Often people have no idea why their muscles cramp. However, it is very important to find out the reasons for this, because a seizure can be both a physiological norm and a symptom of a serious disease. Let's look at this in detail.
Kinds
The disease is classified according to two factors: place of action and duration with varying degrees of severity. In the first case, doctors distinguish the following sudden contractions:
- Local - the phenomenon is observed in a single area. For example, it causes long-term cramps in the calf muscles, feet, shoulder blades, lower back, abs, and thighs.
- Unilateral - the process is fixed only on one side of the body (for example, on the left).
- General – muscles contract almost throughout the body (both front and back), which makes basic stretching, breathing, swallowing and other actions difficult. Problems with emptying the bladder and loss of consciousness are possible.
© bhakpong — stock.adobe.com
It is customary to classify seizures based on intensity and duration:
- Tonic - caused by physical work or bothering the back in the morning due to incorrect posture during sleep. Standard for athletes.
- Myoclonic - short-term, without systematic manifestations, contractions of the fingers, abdomen (often recorded in women during pregnancy), neck, shoulders and face that stop within a few minutes.
- Clonic – regular spasms of the body or an individual muscle.
- Tonic-clonic - the combined action of the previously noted types.
Causes of seizures in different parts of the body
Muscle spasm in a specific area of the body is caused by specific factors. Most often it occurs in the legs. The culprits may be overexertion (including due to intense training), varicose veins and hypothermia.
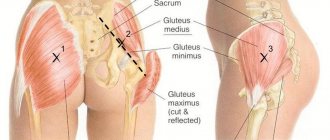
It can cramp not only the calf muscle, but also the femoral and even gluteal muscles. Sometimes the unpleasant sensation will spread throughout the entire leg.
Abdominal cramps are also common because most abdominal organs are composed of highly contractile smooth muscle cells. Most often, the organs of the digestive system spasm. This is how the well-known abdominal pain occurs. In women, contractions of the uterus (during menstruation, pregnancy or gynecological diseases) cannot be ruled out.
Muscle spasms in the back indicate diseases of the musculoskeletal system. This could be osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, degenerative changes in the spine.
Causes
Unintentional muscle contractions may be associated with a lack of water in the body, which is typical during running and other active sports, alcohol intoxication and intoxication. Another common cause is the effect of sub-zero temperatures, which impede blood flow to the extremities, which provokes cramps.
Problems with blood supply and muscle condition are a separate case. This is usually brought about by refusal of physical activity or, conversely, long hours of training without breaks (swimming, lifting weights, etc.).
A lack of calcium, magnesium and potassium (can be caused by taking certain medications) in the body has a bad effect on muscle contraction.
Excess weight, which affects metabolism and blood flow to tissues, can lead to seizures. When carrying a child, women often encounter problems caused by electrolyte deficiency.
Wear and tear of muscles and blood vessels due to age in the older generation is another possible reason.
How to overcome cramps and spasms during training?
Fatigue can be fought. You can also cope with a lack of attention. What if you have muscle spasms? When this happens, you start training through pain, which can only make things worse.
Cramps and spasms can appear not only in the abdomen, but also in any part of the body, from the thighs and calf muscles to the arm muscles.
Regardless of the type of exercise, anyone can experience cramps. If you don't know how to deal with them and how to prevent them, then your exercise may end there. Muscle spasms may go away on their own, but your motivation to continue exercising will decrease significantly.
Why is this happening?
Muscle cramps are painful, convulsive muscle contractions that occur involuntarily during or immediately after exercise.
The cause of seizures is not yet 100% understood and depends on various reasons. However, there are certain common reasons that determine why seizures occur.
Electrolytes
Your body's hydration status plays a key role in your likely occurrence of muscle cramps. Have you seen people drinking vitamin drinks at the gym? They do this for a reason.
These drinks contain a properly balanced concentration of sodium and potassium, which has a beneficial effect on the functioning of nerves and muscles.
When the balance of these electrolytes becomes imbalanced (as often happens when a person begins to sweat more), problems arise.
The same can happen if you start drinking a lot of water during exercise. Many people do a set, drink water, do another set, sip a little more, and so on. They think they are doing something better for their body. And since, as you know, three-quarters of the human body consists of water, you begin to sweat, and sodium is released along with sweat, which has nothing to replace.
Of course, you replace one released fluid with another, but without a key mineral component, muscle function deteriorates. In addition, if you practice in a very hot room, the process may become more difficult. Not only will you sweat more, but the heat will have a negative impact on your muscles, resulting in fatigue and weakness.
Calcium level
Another cause of cramps is low calcium levels in the body. When calcium levels decrease, the amount of extracellular fluid surrounding your nerves and muscles decreases. Nerve endings become overly irritated, which leads to spasms.
Muscle fatigue
After the muscles have tensed, a relaxation phase begins, which lasts longer than the contraction itself. However, this relaxation process is based on sensory feedback between the muscles and the spinal cord, which connects the neuromuscular spindles and tendons.
When muscles become tired, they tighten, which increases the work of the neuromuscular spindles and decreases the work of the tendons. When this happens at the same time, the process of proper compression and relaxation of the muscles is disrupted, after which a spasm occurs.
Large amount of carbohydrates
Muscle cramps can occur when a person on a low-carbohydrate diet eats a lot of carbohydrates. This may be due to your diet, so you should be aware that this can lead to muscle cramps. During this period, try to avoid unnecessary overexertion.
How to deal with cramps?
• As soon as you feel a cramp coming, start moving as much as possible. You may not be able to do this with full dedication, but if you force this muscle group to work, the neuromuscular spindles will return to normal and sensitivity to spasms will decrease. The movements should be smooth, so you can simply walk slowly or do light back-and-forth movements. • Drink fortified drinks rich in sodium and calcium before cramping begins. This will allow you to maintain the desired sodium-calcium concentration. • Increase the amount of exercise that strengthens the cardiovascular system. This way, your muscles will be better able to cope with fatigue. • Make sure you have enough calcium in your diet. The best way is to use a specific diet. For those who do not have a special diet, we recommend using vitamins. • Work on the right balance of physical activity. This improves the functioning of muscle proprioceptors (tendons and neuromuscular spindles) and your ability to cope with tension during various movements. For those whose work involves constant walking, we recommend taking vitamins with increased magnesium content. The mineral magnesium improves the body's ability to retain calcium in nerve endings. When the body loses magnesium, convulsions appear in the muscles, which leads to the appearance of the so-called. “tired legs” syndrome. To prevent this, take 250 to 500 mg of magnesium before bed. You can alternate beans, grains, nuts or dark chocolate into your diet, as they contain a lot of magnesium.
conclusions
Try some of the following methods to combat muscle spasms. Do not forget that each person has a unique body structure, and people have different reasons for the appearance of cramps.
Source: https://www.menslife.com/fitness/kak-pobedit-sudorogi-i-spazmy-vo-vremya-trenirovki.html
Symptoms
Muscle spasm is accompanied by pronounced symptoms that make it possible to distinguish it from other pathological conditions:
- cramps involving one or more muscle groups, causing acute pain and a feeling of tightness of the soft tissues;
- numbness in the fingers, spasms in the ribs, difficulty bending and straightening the knees and arms, curvature of the spine that limits freedom of action, uncontrolled throwing back of the head and tension in the neck;
- personality disorientation, irregular breathing rhythm, ignoring external stimuli;
- visual impairment, confusion of speech, problems with facial expressions;
- short-term inability to control the process of bowel movements.
Pathological nature of seizures
Involuntary contractions in the abdomen caused by diseases are often accompanied by a complex of unpleasant symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract.
Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract
Spasms and pain are observed in the following diseases:
- Gastritis. Spasms are most often localized in the left abdominal area and radiate into the chest. Less often, acute pain radiates to the back, and most often appears on an empty stomach.
- Stomach ulcer. Spastic pains usually appear after eating, and sometimes hunger cramps occur. The pain is located in the upper or middle abdomen and may radiate to the side. Antispasmodics do not help with such pain; special medications are required.
- Intestinal diseases. Spasms constantly accompany acute or chronic colitis, dysbacteriosis, and occur with intestinal obstruction. The muscles can contract in the left hypochondrium, on the right, below and on the side, because the intestines occupy a significant area of the abdomen. Additional symptoms include: acute pain, gas formation, bloating, nausea.
- Cholecystitis, pancreatitis and liver diseases. In this case, the pain is accompanied by spasms on the right or left, under the ribs. Symptoms are often associated with excessive production or stagnation of bile: sour taste, yellow tongue, rotten egg burps, changes in urine color and odor.
- Appendicitis. Inflammation of the appendix of the cecum is difficult to confuse with other diseases, because the pain in this disease is unbearable, accompanied by high temperature, spreading to the hips, back, and sternum. There is a concept of chronic appendicitis, in which inflammation is accompanied by moderate spasms and the absence of suppuration (due to fatty foods, spicy dishes, stress or alcohol).
- Helminths. The symptoms combine a whole group of unpleasant symptoms; they can manifest themselves as spasms and a sensation of movement, pain appears when large parasites move. Symptoms of acute intoxication are observed, and sometimes skin rashes occur.
- Inflammation of the spleen. The pain is on the left side. When combined with inflammation of the stomach or pancreas, the symptoms “move” to the right side.
Spasms can also appear with severe food or chemical poisoning.
Stomach cramps caused by pathologies rarely remain without additional symptoms. You can suspect the disease by nausea, fever, acute pain that does not go away for more than 1-2 days, heartburn, belching, and bad breath.
Gynecological factors in women
Abdominal cramps may be associated with inflammation of the uterus and appendages. Usually accompanied by intense pain, sometimes the temperature rises, and spotting appears:
- Adnexitis - develops due to inflammation or infection, can appear on one or both sides.
- Ectopic pregnancy - the fertilized egg does not reach the uterus, remains in the tube, spasms intensify over time and cause unbearable pain.
- Apoplexy (damage to blood vessels) of the ovary - most often observed during ovulation as a result of too active sexual activity or physical activity, the girl loses strength, may faint, and the bleeding is quite severe.
- Endometriosis – pain is localized in the area just below the navel, but can radiate to other parts of the abdomen.
- Adhesive processes - develop due to the gluing of organs after surgery or prolonged inflammation. The pain is similar to that that develops before menstruation and is accompanied by digestive disorders.
- Inflection of the cyst - occurs after physical activity. The pathology is accompanied by weakness, swelling of the ovary and pain, nausea, and fever.
Pain and cramps can be observed due to kidney disease, prolapse, inflammation or the appearance of stones (sand). With cystitis, pain occurs during urination, and cramps appear in the very lower abdomen.
Diseases caused by muscle spasms
| Name of the disease | Characteristics |
| Tetanus | There are sudden contractions of the muscles of the face and jaw, spreading to other parts of the body up to the feet and hands. Convulsions are possible on a constant basis, accompanied by acute pain. |
| Viral diseases | Spasms due to high temperature, which can lead to cerebral edema. |
| Diabetes | Disorders affect the lower extremities due to the leaching of microelements involved in maintaining the normal condition of the muscles. |
| Epilepsy | Teenagers suffer from limb cramps during sleep. Men and women experience prolonged attacks that combine different types of spasms, caused by lack of sleep or the effects of alcohol. |
| Spasmophilia | Muscle contractions in children interfere with breathing and movement. May cause cardiac arrest. |
| Hysterical form of neurosis | The spine takes on an arched shape, attacks are accompanied by screams, moans and crying. |
| Osteochondrosis | Cramps during sleep, localized in the legs and back. |
| Hypoparathyroidism | Contractions lasting several minutes, covering most of the body. The feet and hands are most often affected. |
| Hypertension | Muscles contract unintentionally when the brain swells during a hypertensive crisis. |
| Hypomagnesemia | Magnesium deficiency causes problems with control of the neck, back and limbs. |
Why do muscles cramp?
The reasons can be divided into two groups. The first includes those that do not have any underlying diseases. So, if the calf or gluteal muscles cramp in a dream, there is no physiological pathology in this. The seizure in this case is a parasomnia, that is, a phenomenon associated with sleep. Spasms that occur during increased physical activity also do not indicate an abnormality.
In other cases, such discomfort may be caused by:
- neurological disorders;
- compaction of muscle fibers against the background of physical inactivity;
- metabolic disorders;
- micronutrient deficiency;
- dehydration;
- poisoning (including cramps from a hangover).
There is also a disease called hypoparathyroidism. It is characterized by a convulsive syndrome that immediately affects muscle groups. This condition is caused by hypofunction of the parathyroid glands.
Should I see a doctor?
There is no need to worry about a one-time muscle contraction, but regular repetition of cramps can be considered a signal of the progression of a particular disorder. The problem may be related to the functioning of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system or central nervous system, thyroid gland. You must make an appointment with a doctor in the following cases:
- monthly monitoring of the problem;
- convulsions generate severe pain;
- the cause is not physical activity;
- the condition does not change after massage and relaxation.
Leg cramps during pregnancy. What to do?
In most cases, spasm of the calf muscles in pregnant women occurs from the second semester. There are two main reasons for this. First: the weight of the expectant mother increases and creates additional stress on the leg muscles. Second: a woman’s need for additional microelements and vitamins.
And if such a problem arises, the algorithm for providing first aid will be identical, but you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. The specialist will examine the patient, prescribe a number of necessary tests and select the most effective vitamin complex. In addition, the woman will be advised to reconsider her diet, daily routine and allocate more time for rest.
What to do if your muscles are cramped: first aid
In order to get rid of the feeling of discomfort, you should
- Avoid actions that may cause unintentional reductions.
- Proceed with a gentle massage of the area where the problem is localized.
- Avoid sharp turns, bends and other movements immediately after getting rid of the unpleasant sensations - they can cause a recurrence.
- If pain persists even after the cramps have stopped, you should apply ice to the muscle or use an elastic bandage. Compresses will help eliminate hardness and tension in the area in severe cases.
In a situation where the calf muscle is cramped, you need to pull the toe of the foot towards you.
Action when reducing the calf muscle. © Paolese — stock.adobe.com
Convulsive contraction of leg muscles
Leg muscle cramps are one of the most common seizure conditions that many people experience, regardless of age. The reasons for their occurrence are usually associated with nervous strain, wearing shoes that cause discomfort, and prolonged exposure to the cold.
Muscle spasms caused by these reasons do not require treatment, since they are not pathological. In such cases, it is enough to simply eliminate the provoking factor, and the condition will be completely normalized.
But if you are concerned about frequent and prolonged leg muscle cramps, especially at night, you should definitely visit a doctor to determine the true causes of their occurrence.
If the trigger for the development of convulsive syndrome is a lack of potassium, magnesium or calcium in the blood, then therapeutic measures will be aimed at the inflammation of these minerals. Appropriate drug therapy will be prescribed, in addition to which recommendations on diet will be given. This treatment will allow you to achieve a positive result in a short time.
The child has
Children, unlike adults, usually suffer from generalized seizures that affect the entire body. Between the ages of six months and 5 years, contractions caused by excessively high temperatures are considered common. They pass after the fever and febrile state in general are eliminated, without posing a danger to life and health.
If febrile seizures occur once, there is a high risk of encountering this problem later. It is important to prevent the development of fever with the help of medications and avoid using injections in those parts of the body where spasms are localized.
The occurrence of disturbances even at normal temperatures may be evidence of:
- heart problems;
- water and electrolyte imbalance;
- early stages of epilepsy;
- hormonal imbalance.
What to do in this case?
If a muscle “stagnates” in an unpleasant way during training, you need to give it rest and take some time. Usually the cramp gradually releases, returning the muscle fiber to its original state. This will take up to a minute (in extreme cases, no more than 5). At the same time, there are several techniques that will help you do this more smoothly.
- It is necessary to stop moving, stand comfortably or sit down to maintain balance (if this concerns the leg muscles);
- Using superficial light movements, stroke the spasmed muscle, slightly stretching it to the sides.
If after a minute the cramp does not release the muscle, it is recommended to cool it with ice or apply a special rubberized bandage.
The significance of this phenomenon should not be underestimated. Most likely, the body is giving a signal that it is not ready for such stress or the organization of the lesson was carried out incorrectly. It is worth thinking about the functional redistribution of physical activity and alternating it with sufficient rest.
Diagnostics
Only clinical studies will help to accurately determine the cause of seizures. At the first stage, general and biochemical blood tests are taken. Then it is necessary to establish the condition of internal organs and systems using ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography, and electroencephalogram of the brain.
MRI. © Olesia Bilkei — stock.adobe.com
Causes of convulsive muscle contractions in children
In children, convulsive syndrome occurs much more often than in adults; this occurs due to the immaturity of various brain structures and an incompletely formed thermoregulation center. One of the most common causes of seizures in children is hyperthermia.
In addition, muscle cramps in children can develop as a result of a number of reasons, among which it is worth highlighting:
- diseases of viral or bacterial origin;
- traumatic damage to the meninges;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- poisoning of the body with toxic substances or decay products of pathogenic microorganisms;
- metabolic disorders that increase the likelihood of developing pathologies of the nervous system;
- hereditary predisposition;
- bleeding disorders;
- epileptic syndrome.
Only a qualified specialist can say exactly why a child has muscle cramps and what to do in such a situation, after conducting all the necessary tests.
Convulsive contraction can affect any muscles: respiratory, facial and laryngeal, and spasms of the masticatory muscles can also be observed. But no matter what kind of convulsions you have encountered, you should not neglect medical advice, since such a condition may indicate the presence of quite serious diseases.
Everyone is familiar with the unpleasant and painful feeling of muscle strain. Seizures occur for a variety of reasons. Most often they occur during active sports and have mild and severe forms.
Treatment
The exact treatment program can be chosen only after determining the disease that underlies the sudden muscle contractions. In the case of regularly recurring seizures of a local or general nature, at first it is necessary to use pharmaceutical solutions that can eliminate the symptoms and improve the general condition:
- With a high potassium content (Panangin and Asparkam). Restore normal functioning of muscle tissue and block the development of spasms.
- With a high content of magnesium (Magnelis and Magvit). They help to establish water-electrolyte metabolism and eliminate the deficiency of microelements in the body.
- Creams and ointments, the effect of which can reduce pain and relieve tension in certain areas of the body (Venoflebin and Troxevasin).
special instructions
For the treatment of neuralgia, osteochondrosis and other neurological diseases, a complex of the above drugs is used, but they all have contraindications and side effects:
- Muscle relaxants cause bradycardia and a decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, and reduce the speed of reactions. Therefore, they are prescribed with caution for work that requires increased attention, or prescribed at night.
- Antispasmodics can cause a decrease in blood pressure. Hypotension and bradycardia are absolute contraindications for use.
- NSAIDs have an ulcerogenic effect on the gastrointestinal tract. They are prescribed with caution for gastrointestinal diseases. NSAIDs must be taken after meals, preferably with milk.
Features of prescribing drugs for the treatment of muscle spasms
- For mild pain, local medications are prescribed in the form of ointments (Nurofen, Nise, Ketonal, Voltaren), or patches (Nanoplast, Voltaren, Dorsaplast, Versatis)
- For osteochondrosis, muscle relaxants are prescribed in combination with NSAIDs and vitamins.
- For pain that is not relieved by oral and local medications, injections of muscle relaxants, NSAIDs and vitamins are used. Drug provocation leads to pain relief.
- Often muscle spasms require the prescription of drugs that help normalize blood circulation (Actovegin, Cerebrolysin, Cavinton).
Prevention of seizures in athletes
Follow these simple tips to avoid seizures:
- Do a warm-up and cool-down. This improves blood circulation, prepares the body for stress and recovery.
- Increase your training volume gradually, starting strength training with the lightest weights
- Take a vacation. During recovery, the muscles “digest” the load and adapt to it. Relax your muscles with a massage, bath, sauna
- Don't forget about restoring your nervous system. Get enough sleep, take complete rest days from training
- Stay hydrated - drink water or isotonic water. In hot weather over long distances, try to drink mineral water (still), isotonic water or take salt capsules
- Make a competent training plan that will lead you to your goal. Gradually adapt your muscles to the loads, be sure to do strength training. For example, if you are going to run a marathon in the heat, it is not enough to train for 5 km in cool weather.
Always monitor your body and pay attention to the conditions under which cramps occur. It could be hot weather, increased sweating, or some specific load. Then you will know the weak points of your body and work on them.
How to fight?
First aid and treatment
As a rule, symptoms disappear on their own and do not require special treatment. But in order to stop the convulsive contraction, you must do the following:
- Stop performing the movement that causes the spasm;
- Slowly stretch and massage the cramped part of the body;
- Try to relax and rest for a few minutes;
- If the pain remains, you can apply ice or apply an elastic bandage;
- If possible, do not strain the muscle for a while.
If these actions do not give the desired result, you should immediately call a doctor and begin treating the cause of the painful contractions.
Prevention
The most effective exercise remains stretching the entire body. A thorough warm-up reduces the likelihood of cramps by up to 80%. Moreover, you need to warm up your muscles both before and after training.
A relaxing massage is also a good preventative measure. It is better to use oils when rubbing. They will not only make the process more enjoyable, but will also enrich the muscles with microelements. After the procedure, you need to apply something warm to the painful part of the body.
Warm milk (rich in calcium) before bed is good for abdominal cramps. It is necessary to increase the consumption of foods rich in magnesium and calcium.
This will strengthen connective tissue. Using herbal tea helps. Sometimes the reason for frequent contractions lies in nervous tension, and herbal decoctions relieve it.