Share:
Anyone who wants to build muscle mass is concerned with the question, how do muscles grow? Why do some look like “bulls”, others like “skinny deer”, although the only one working hard in the gym? To influence the process of muscle growth, you need to know physiology and properly organize training and rest.
A little physiology
Muscles are made up of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers. Muscles grow not while training occurs, but after it. During training, muscles are injured, strained and partially torn. After classes, a recovery process occurs. It is during the recovery process that muscle growth is observed. Healthy cells replace destroyed ones, and in increased numbers.
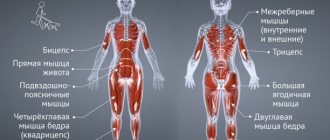
During training in the gym, a person trains skeletal muscles, consisting of myofibrils and sarcomeres. Together they form muscle fiber. A person has 650 skeletal muscles. They contract when a command is received from the motor neurons. Through nerve impulses, motor neurons “tell” the muscles that they need to contract. The better this connection is established, the more active the muscle fibers contract.
Interesting! A person’s physical power does not depend on the volume and mass of muscles, but on the body’s ability to stimulate motor neurons and better compress muscle fibers.
Operating principle
During active exercise, the number of nerve impulses that cause muscle contraction increases. Thus, the muscle tissue becomes harder, although it does not necessarily change in size in the early stages. It takes months of training for cells to grow.
Stimulation and recovery are two inextricably linked mechanisms that ensure muscle growth. During training in the gym there is stimulation. This is muscle compression and tension. When compressed, a microscopic rupture of muscle fibers necessarily occurs. Increasing the load each time, these microtraumas become constant companions of classes.
And after the impact on the muscles, rest is necessary. This is restoration. During the period that the cells are restored, new cells grow, and, consequently, the muscles themselves grow.
What is muscle fiber hypertrophy?
As a result of regular physical activity, a gradual increase in muscle mass is observed. This is called muscle hypertrophy. An increase in muscle volume requires special conditions and occurs if a person regularly increases the load, crossing the barrier to which the body has already managed to adapt.
There are different types of hypertrophy:
| View | Description |
| Myofibrillar hypertrophy | This is when muscle tissue thickens due to the density of myofibrils. Stiffness, strength in the arms and legs, and endurance appear. But the volume of muscle tissue itself remains the same. |
| Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy | This is when the cells themselves increase in cross section, but their strength remains the same and does not increase. But endurance increases. This makes it possible to exercise longer without getting tired. |
Testosterone production stimulants help create hypertrophy. But they will be useless without special nutrition, training and recovery. But there is no harm from these stimulants, unlike anabolic steroids.
Interesting! All the muscles of the body, especially the chest and abs, look much more beautiful with sarcoplasmic hypertrophy, which bodybuilders achieve. But athletes of other disciplines grinningly call this “empty muscles” because they have no strength.
Training FAQ
In this section we will answer frequently asked questions by novice athletes.
Question: What type of training promotes muscle growth?
Answer: In order for muscle fibers to increase in volume, strength training is necessary. The basis of training should be deadlifts, squats with a barbell, bench press, performed for 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions.
In addition to the “base”, you should do 2-3 isolation exercises for the target muscle group (3-4 sets of 12-15 repetitions). It is recommended to complete mass-building training with pumping loads (1-2 elements with a minimum weight for 2-3 sets of 15-20 repetitions).
Question: what should a vacation be like?
Answer: first of all, remember - muscles grow not during, but after training. Therefore, rest plays a vital role in building a powerful athletic body. Recovery time is from 1 to 3 days. During this period, healing of microtraumas received during strength training occurs.
In addition, bodybuilders should sleep well (8–9 hours), since it is at night that the hormone somatotropin is produced, which is responsible for the growth of muscle mass and the reduction of body fat.
Question: What is super compensation?
Answer: supercompensation is a period characterized by a higher level of performance of the athlete compared to the initial one. This phase occurs during moments of rest, when the body has restored damaged tissues and replenished energy losses. It is at this moment that it is recommended to conduct the next strength training session.
Scientists have proven that supercompensation manifests itself on the second or third day after exercise (subject to high-quality recovery). This means that to achieve results in increasing body weight, you need to do 2-3 workouts per week.
Question: do muscles grow from pumping?
Answer: There is no scientific evidence to support the benefits of pumping for increasing muscle size. It is believed that high-repetition work with light weights is ineffective, since it has virtually no impact on stimulating growth.
On the other hand, some professional athletes include pumping exercises in their training. They explain this by the fact that pumping elements make it possible to increase micro-tears resulting from power loads and improve the supply of nutrients to the muscles. As a result, in their opinion, better hypertrophy occurs.
Question: do muscles grow from athletics?
Answer: no, they don’t grow. More precisely, not for everyone. A slight increase in muscle mass can only be observed in sprinters, as they perform the most intense and short races. In such athletes, as a rule, the leg muscles increase, but the upper body remains underdeveloped.
Of course, at world competitions you can see physically strong black runners who look like gym goers. But this “form” is associated with genetic characteristics.
Question: do muscles grow from static exercises?
Answer: an increase in muscle volume occurs due to the healing of micro-tears in the fibers. Such damage appears only when performing amplitude exercises with heavy weight.
Static loads cannot create the necessary tensile effect. The main functions of such elements are the development of strength and endurance of muscles and ligaments. Therefore, “statics” cannot be used as the basis for mass-gaining training.
Question: is it possible to build “lean” muscles and burn subcutaneous fat at the same time?
Answer: theoretically, yes. But to achieve this state, it is necessary to combine strength and aerobic training. The combined regimen is suitable only for trained athletes who have been training for at least 1 year and already have a shortened recovery period. Beginners are not recommended to combine different types of training, as this can lead to the development of symptoms of overtraining and stop progress.
Beginning bodybuilders who are overweight, first of all, need to lose weight. The more subcutaneous fat an athlete has, the lower his testosterone level and the worse he will perform at strength training. We recommend starting with simple running or even walking. After the amount of subcutaneous fat drops to at least 23-25% of the total body weight, you can begin strength training.
Question: how do you know that muscles are growing?
Answer: the most accurate indicators are a change in the reflection in the mirror and an increase in the numbers on the scales. To more accurately determine the results, take control measurements 2 times a month using a soft measuring tape. Keep a diary in which you will write down the parameters. This will allow you to track the dynamics of progress and will once again motivate you.
It is believed that muscle pain is an indicator of muscle growth. In fact, pain only means that the fibers received microtrauma during training. The increase in volume will depend on how the athlete rests and eats. It is important to distinguish muscle pain from injury, and if the latter occurs, take measures for recovery.
Question: How fast do muscles grow?
Answer: for each athlete the result is individual and depends on several factors (discussed in the previous section). As a rule, beginners who train “naturally” can gain up to 18–20 kg in the first year. In this case, 8–10 kg will be muscles, and the rest will be water and fat. This is considered a very good result.
With each subsequent year, the number of kilograms gained will decrease. This is due to the gradual adaptation of muscle fibers to strength training. Therefore, it is necessary to frequently change programs and regularly increase weight loads.
Question: Why do some muscles grow quickly and others slowly?
Answer: depends on the ratio of different types of fibers. The more fast glycolytic (white) thread-like structures in a muscle bundle, the stronger the muscle and the faster it increases in size. The degree of loading of the fibers also affects growth. For example, the calf and soleus muscles support an athlete's body weight every day. Therefore, they have a high endurance threshold and because of this they grow extremely slowly.
How to make muscles grow?
In order for muscles to grow, it is necessary to increase the number of myofibrils in muscle fibers. Muscle growth is impossible without special amino acids that affect the formation of myofibrils. Amino acids, in turn, are obtained from proteins of animal origin. It is a building material for muscles. This means that the first condition for their growth is a diet rich in proteins. Proteins are what makes muscles grow.
This doesn't mean you need to eat more than usual or increase your calories. You need to eat in the same usual amount. The ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates should be optimal: 30\10\60.
The rate of muscle growth is largely determined genetically. However, it is possible to interfere with nature. Factors that influence muscle growth potential include:
- thickness of transverse muscle fibers;
- fiber type (slow or fast twitch);
- number of muscle fibers;
- the amount of fluid that is in the muscles;
- the amount of sarcoplasm present;
- the number of blood vessels in the muscles.
You cannot influence what a person is already born with. But it is quite possible to correct the potential inherent in nature. In this case, you need to take into account the type of body structure.
There are types such as:
- endomorph (short limbs and wide body);
- mesomorph (body parameters are relatively harmonious);
- ectomorph (thin people with problems building muscle).
Individual nutrition and training are selected for each body type.
Rest time between workouts and its role
Merely eating meat and other proteins is not enough without a proper exercise and relaxation routine. Periods of work and rest should be alternated correctly. Training is the determining factor for muscle growth and hypertrophy. When the body feels that it lacks the physical potential to complete a given task, it resorts to hypertrophy.
Training solves several problems at once - not only promotes the growth of muscle tissue, but also helps to grow up if a person is not yet 25 years old. A person can grow 5-6 centimeters in a year. And training also helps launch the mechanism for the formation of amino acids - important components of proteins.
Without going into complex medical terms, you just need to understand that after training it is extremely important to get proper rest . And even during the workout itself, you need to take 3-5 minute breaks. The optimal pause between active training is a day. Or even better – 48 hours. That is, you need to study in a day or two.
Note! Of course, you need to follow expert advice, but you shouldn’t ignore your own feelings: the body itself will tell you when to add rest and when to add exercise.
The fact is that for muscle growth the body needs to overcome physical fatigue. If there is not enough recovery time between workouts, fatigue will accumulate and muscle growth will stop. The body will spend energy on maintaining vital functions, and not on increasing muscle volume.
Important! Muscles grow when the rate of recovery exceeds the rate of muscle protein breakdown.
The effect of muscle tension on muscle growth
Muscle tension is one of the factors for muscle growth. Therefore, weight lifting is often used in classes. When muscles tense, chemical processes in muscle tissue are activated, affecting cell growth. In order for muscles to increase in volume, it is necessary to give the body such a load to which it has not yet had time to get used.
Interesting! Painful sensations after exercise almost completely disappear after a year of training. The pain dulls over time, the person no longer feels it.
The role of hormones in the process
Do muscles grow due to additional hormone production? Certainly. During training, testosterone levels increase, and it stimulates the response to growth hormone. This process begins at the moment when a person is unable to lift a projectile or do push-ups. This is called muscle failure. This condition causes a shock to the body, which is why an additional portion of hormones is produced.
Athletes additionally take artificial hormones to speed up results. But according to many doctors, it is better not to get carried away with this. In order for growth hormones to reach the muscles and not be destroyed by the liver, hydrogen ions are needed. Hydrogen ions should be no more and no less than necessary. With a deficiency or excess, muscle growth will be inhibited. Hormonal balance is maintained by the correct regime of exercise and rest.
The role of amino acids
Amino acids are part of protein compounds, and without them muscle growth cannot be achieved. There are 22 types of amino acids in the body. Our body produces 4 of them itself, and another 8 come to us with food.
To the list of essential amino acids you can add:
- leucine – protects muscles from destruction;
- isoleucine – increases muscle endurance and promotes their rapid recovery after microtrauma;
- valine – affects the speed of muscle tissue construction;
- methionine is an important amino acid for muscle growth and the synthesis of creatine and adrenaline.
Most essential amino acids are found in plant and animal products, namely in proteins.
Physiology of skeletal muscle hypertrophy[edit | edit code]
The physiology of skeletal muscle hypertrophy examines the role and interactions of satellite cells, immune system responses, and growth factors.
Satellite cells (Satellite cells)
Functions of satellite cells:
- Facilitation of growth;
- Life support;
- Restoration of damaged skeletal (non-cardiac) muscle tissue.
The cells are called satellite cells because they are located on the outer surface of the muscle fibers, between the sarcolemma and the basal lamina (the top layer of the basement membrane) of the muscle fiber. Satellite cells have one nucleus, which occupies most of their volume. These cells are usually in a resting state, but are activated when the muscle fibers receive any type of injury, such as from strength training. The satellite cells then multiply and the daughter cells are attracted to the damaged muscle area. They then fuse with the existing muscle fiber, donating their nuclei, which help regenerate the muscle fiber. It is important to emphasize that this process does not create new skeletal muscle fibers (in humans), but increases the size and amount of contractile proteins (actin and myosin) within the muscle fiber. This period of satellite cell activation and proliferation lasts up to 48 hours after injury or after a strength training session[2].
The number of satellite cells depends on the type of fiber. Type I or slow twitch fibers
, typically have five to six times more satellite cells than type II (
fast-twitch fibers
), due to increased blood supply and a greater number of capillaries. This may be due to the fact that type 1 muscle fibers are used most frequently, and thus more satellite cells may be required for ongoing minor muscle injuries.
Researchers at the University of Rochester Medical Center found[3] that loss of muscle stem cells is a major driver of muscle loss in older adults. Their finding challenges the existing theory that age-related muscle contraction is caused primarily by the loss of motor neurons.
Immunology
As previously described, strength exercise causes skeletal muscle injury. The immune system responds with a complex sequence of reactions leading to inflammation[4]. The goal of the inflammatory response is to contain the injured area, repair the damage, and cleanse the injured area.
The immune system initiates a sequence of events in response to damage to skeletal muscle. Macrophages involved in phagocytosis (the process by which certain cells engulf and destroy microorganisms and waste products from damaged cells) move to the site of injury and release cytokines, growth factors and other substances. Cytokines are proteins that act as “conductors” of the immune system. They are responsible for connections between cells in the body. Cytokines stimulate the arrival of lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes and other cells at the site of injury to repair tissue [5].
The three most important cytokines related to exercise are interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). These cytokines mediate most of the inflammatory response and are therefore called “inflammatory or proinflammatory cytokines” [6]. They are responsible for breaking down proteins, removing damaged muscle cells, and increasing the production of prostaglandins (hormone-like substances that help control inflammation).
Growth factors[edit | edit code]
Growth factors are highly specific proteins, including hormones and cytokines, which are very actively involved in the phenomenon of muscle hypertrophy [7]. Growth factors stimulate the division and differentiation (acquisition of one or more characteristics different from the parent cell) of a particular cell type. Growth factors of particular interest in connection with skeletal muscle hypertrophy are insulin-like growth factor (IGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). These growth factors work in combination with each other to cause skeletal muscle hypertrophy.
Insulin-like growth factor
IGF is a hormone that is secreted in skeletal muscle. It regulates insulin metabolism and stimulates protein synthesis. There are two forms, IGF-I, which causes satellite cell proliferation and differentiation, and IGF-II, which is responsible for satellite cell proliferation. In response to overload, IGF-I levels increase, leading to skeletal muscle hypertrophy [8].
Fibroblast growth factor
FGF is found in skeletal muscles. FGF has nine forms, five of which cause satellite cell proliferation and differentiation, leading to skeletal muscle hypertrophy. The amount of FGF released into skeletal muscle is directly proportional to the degree of muscle injury[9].
Hepatocyte growth factor
HGF is a cytokine with various functions in the cell. Specific to skeletal muscle hypertrophy, FRG activates satellite cells and may be responsible for the migration of satellite cells to the injured area.
The role of hormones in skeletal muscle hypertrophy[edit | edit code]
Hormones are chemicals that organs secrete to initiate or regulate the activity of an organ or group of cells in another part of the body. It should be noted that hormonal function is influenced by nutritional status, food intake, and lifestyle factors such as stress, sleep, and general health. The following hormones are of particular interest in skeletal muscle hypertrophy.
A growth hormone
Growth hormone is a peptide hormone that stimulates immunoenzymatic reactions in skeletal muscle, promoting satellite cell activation, proliferation and differentiation[10]. However, the observed muscle growth effects of GH supplementation studied in groups receiving growth hormone and performing strength exercises may be less due to increases in contractile proteins and more due to fluid retention and connective tissue accumulation.
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone (a hormone that is steroid-based and can pass through the cell membrane without a receptor) that is produced in the adrenal cortex. It is a stress hormone that stimulates gluconeogenesis, that is, the formation of glucose from other sources such as amino acids and free fatty acids. Cortisol also inhibits the uptake of glucose by most cells in the body. It initiates protein catabolism, thereby releasing amino acids that will be used to create various proteins that may be needed during times of stress.
From a hypertrophy perspective, increased cortisol is associated with increased protein catabolism. Thus, cortisol breaks down muscle proteins, inhibiting skeletal muscle growth[11].
Testosterone
Testosterone is an androgen, or male sex hormone. The main physiological role of androgens is to promote the growth and development of male organs and characteristics. Testosterone affects the nervous system, skeletal muscles, bone marrow, skin, hair and genitals. In skeletal muscle, testosterone, which is produced in much greater quantities in men, has an anabolic effect. This contributes to the gender differences observed in the body weight and build of men and women. Testosterone increases protein synthesis, which induces hypertrophy [12].
Necessary conditions for muscle growth
In order for the body to acquire the long-awaited forms, the following conditions must be created:
- Repeating basic movements such as squats, bench presses, deadlifts.
- It is recommended to eat small and frequent meals – at least 6 times.
- The diet should consist mainly of proteins. You also need vitamins, minerals, and mineral water.
- You need to sleep enough. It is during sleep that the muscles completely relax, and this is important for their growth.
Another important point is the connection between muscle growth and the central nervous system. To start the process of muscle growth, you need to influence the central nervous system with firm beliefs, self-hypnosis, and a great desire to achieve your goal. And also create stressful conditions for the central nervous system in the form of additional load during training, increasing time for exercise, changing the training schedule.
How can you tell that muscles are growing? If all three directions are set correctly - nutrition, training and rest, then the muscles will definitely grow. It is best to check monthly with a flexible meter how much muscle tissue has increased.
What should you eat to grow muscles?
The main food should be carbohydrates. But these are complex carbohydrates. The menu should include:
- rice, buckwheat, other cereals, as well as potatoes and pasta;
- fats, but mainly vegetable ones (found in nuts, avocados);
- chicken, chicken proteins, cottage cheese, as well as nutritional supplements.
Vitamins are required. The most popular among vitamin complexes are:
Athletes use special nutrition rich in protein and proteins. Including protein drinks that can be used during forced fasting.
The following will help speed up the process of muscle fiber growth:
- creatine – it increases blood flow and thus breaks muscles under the pressure of blood flow;
- carnitine increases calorie content by burning subcutaneous fat, increasing performance, and therefore stamina in performing activities;
- protein shakes supply the body with protein;
- l-arginine affects the formation of protein in muscles, that is, promotes their growth;
- curcumin is similar in action to l-arginine;
- Nitrogen donors activate the healing of microcracks in muscle tissue, which means you can quickly start new activities.
You also need to eat small meals. The more often a person eats (of course, in small portions), the faster the metabolism, the metabolism accelerates, fat tissue melts, and muscle tissue builds up.
Another important condition is to drink enough water. Precisely water, not juices and tea. You should drink at least 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day. But not in one sitting, but divided into 5-6 servings. And drink half an hour before meals and two hours after meals.