Collagen is present in almost all tissues of the human body (cartilage, muscles, skin).
The function of the substance is to maintain the strength and elasticity of bones and epidermis, as well as provide restorative properties.
These properties make it indispensable in nutrition for athletes.
What is collagen?
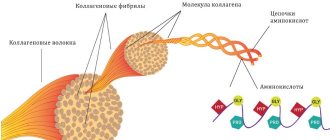
Collagen is primarily a fibrillar (thread-like) protein; in fact, it forms the connecting tissue of all organs of our body and is its framework, its basis. Its role is especially important for such an organ as the skin; collagen makes up 70% of the total protein found in it. It is also part of joints, ligaments, muscles and, of course, bones.
In the skin, it is located on the 3rd layer along with the protein elastin; together they create the framework of the skin, on which its external and internal structure, as well as quality, completely depend. Elasticity, strength, and firmness also depend 90% on collagen.
It is capable of being produced by the body in full until 25-30 years of age, after which its production is greatly reduced. Previously intact collagen bonds lose their former integrity and elasticity. In the entire mammalian body, the percentage of collagen is up to 35%, so you can understand how much worse the body will develop if it is deficient.
Having studied the chemical composition of this protein, you can find out that the propine contained in it, with the participation of vitamin C, is oxidized into hydroxypropine, which helps to preserve and create a stable collagen structure, which gives the protein special strength. Therefore, vitamin C intake is extremely important for the condition and quality of skin structure.
Reception scheme
For prevention purposes and for normal functioning of the body, it is enough to take 3-5 g of collagen per day. Its reception does not require any special actions or conditions. For people with active physical activity, the daily dose of collagen is 6 g. In the presence of joint diseases (osteochondrosis) and injuries, the dosage is increased to 10 g per day.
The use of the supplement can be divided into several times. Foods containing large amounts of protein are better absorbed in the morning, so collagen supplements are recommended to be taken in the morning on an empty stomach.
IMPORTANT ! The degree of stress, the presence of joint pain, and injuries should be taken into account before prescribing the dosage.
Collagen in the skin structure
As already mentioned, this protein makes up 70% of the structures of the skin, being responsible for their quality (firmness, strength, elasticity). It is located just below the epidermis, in the dermis. It should be taken into account that collagen production after 30 years decreases by 1-3% per year and this deficiency should be compensated for externally or internally.
But not only does a person lose collagen with age, there are many other reasons for this, such as:
- Active facial expressions.
- Smoking.
- Psychological stress.
- Poor nutrition.
- Alcohol consumption.
- Exposure of the skin to large quantities of sunlight.
- Environmental pollution.
But we must remember that this aggravates not only the quantity of collagen, but also its quality, which is important.
The synthesis of this protein is carried out in fibroblasts by creating peptide bonds from amino acids (hereinafter referred to as AMK), further spiralization and the formation of a tertiary (active) structure. With proper production, the skin becomes elastic and smooth.
It should be clarified that a wrinkle is a groove in the framework of which the collagen structure is destroyed.
What causes collagen destruction?
We have already discussed the functions, benefits and properties of collagen. Now it's time to discuss why many people lack collagen in their bodies. Despite the fact that we consume a lot of protein products throughout the day, a huge number of people still experience a deficiency.
So what are the causes of collagen destruction? There are several reasons, and we encounter most of them every day.
The main factors for the destruction of collagen compounds
- ultraviolet radiation
- stress
- smoking
- temperature changes
- hormonal fluctuations
- poor diet, large amounts of sugar and simple carbohydrates
The skin receives the first and maximum impact from these factors. Wrinkles appear, the elasticity and quality of the skin decrease.
In childhood and adolescence, this is not a problem, since there is virtually no stress, and the body itself produces enough collagen for its needs.
Over the years, as already mentioned, protein production gradually decreases. Collagen compounds are destroyed, and the body no longer has time to replenish protein reserves to replace them. In the future, various kinds of troubles arise, cracking in the joints, decreased muscle tone and problems with the vascular system.
What are the benefits of collagen?
The helices of this protein allow the connective tissues of the human body to remain in working condition; they have such good strength that they are practically not stretchable.
The main functions and tasks of the “protein of youth”:
- Protective. Protects body tissues (for example, muscles) from mechanical damage.
- Restorative. Regenerates cells.
- Support. Strengthens the structures of organ forms.
- Provides elasticity of structures.
- Inhibition in the development of melanomas (these are skin tumors).
- Stimulation of the development of new cell membranes.
Collagen is an excellent raw material for the structure of epidermal cells, ligaments and joints. Thanks to this feature, it is often used by bodybuilders. But besides this, of course, you should not underestimate it as a skin and hair care product. One important property of this protein is that it can bind water molecules (like gelatin, which is a derivative of collagen), due to this property in creams, in addition to a source of amino acids, it is a transport system for liquid.
Benefits of the substance
Several beneficial properties of protein for the human body should be noted:
- Maintaining healthy skin appearance. Most women who use collagen creams or supplements report a smoothing of wrinkles and cellulite. With prolonged use of cosmetics and protein-based drugs, the changes will be more noticeable.
- Loss of body weight. The effect is due to the fact that collagen accelerates metabolism and promotes faster absorption of food. Glycine in collagen supplements ensures that sugars from food are converted into energy rather than stored fat.
- Normalization of the gastrointestinal tract. This fact has not been scientifically proven, but many people have noted an improvement in their condition after consuming protein supplements. Theoretically, it is believed that this effect is achieved by restoring damaged intestinal cells and accelerating metabolism.
- Maintenance of bone and muscle apparatus. The human skeleton contains its own collagen, the level of which decreases with age. Protein-based supplements allow people not only to tolerate intense physical activity, but also to prevent bone destruction associated with age-related changes in the body.
- Improving athletic performance. The risk of injury has been found to be reduced in athletes who regularly consume collagen. The substance protects ligaments and muscles from stretching and tearing by increasing their elasticity. This property is very important for people involved in sports, since professional injuries have a bad impact on their career.
- Improved sleep quality. It has been experimentally revealed that people taking collagen do not feel daytime lethargy and are completely restored within 5.5-7.5 hours of sleep at night.
Read more about the benefits and harms of sports nutrition in our article.
Importance of Collagen
Collagen for the skin is something like springs for a mattress - it helps the dermis return to its original position. It maintains the functionality of the epidermis layer and participates in the interaction of skin levels.
Collagen is the main element that restores damaged skin or muscle and renews cells in this area. The importance of this protein is enormous.
No matter how hard you try to preserve collagen in the skin and body, changes cannot be stopped and the aging process cannot be reversed.
The consequence of a decrease in the amount of protein in the body is:
- Loss of skin elasticity, appearance of wrinkles.
- Malaise and frequent illnesses.
- Rapid fatigue.
- Periodic pain in all muscles of the body.
- Thinning and fragility of blood vessels.
- Severe overstrain of the body's muscles.
- Unintentional decrease in activity level.
- Worsening of the average condition of the body.
- Weakening and brittleness of bone tissue.
- Lathyrism (disease).
How is collagen formed?
Like all proteins, the formation of collagen occurs from ANA, most of this protein consists of:
- glycine (about 33%);
- proline (12%);
- alanine (11%);
- glutamic acid (8%) and others.
It is these AMCs that form its primary structure.
In our body, collagen is formed from procollagen by breaking its peptide bonds. The resulting collagen has 3 subunits that twist in a spiral. They are stacked in such a way that the three-helix structure has no limited dimensions and is not interrupted by anything.
Collagen synthesis specifically in the skin includes 8 stages (5 in fibroblasts, 3 extracellular). Synthesis is greatly influenced by adrenal hormones and vitamin C.
Inside the cell
- First stage. Synthesis of preprocollagen on ribosomes.
- Second phase. Formation of procollagen on fibroblast EPS.
- Third stage. Oxidation of AMK residues under the action of enzymes and ascorbic acid.
- Fourth stage. Transfer of BUNs such as glucose and galactose to procollagen.
- Fifth stage. Complete formation of molecules.
Outside the cage
- First stage. Penetration of tropocollagen into the environment between cells. Uncoupling the links.
- Second phase. Formation of an insoluble molecule by "crosslinking" the ends.
- Third stage. The connection of molecules in the second stage to form inextensible fibers.
Salmon is one of the foods that stimulates collagen production.
Literature[edit | edit code]
- Pearson, David. "Gelatin found to reduce joint pain in athletes"
- https://raypeat.com/articles/articles/gelatin.shtml
- wai, K.; Hasegawa, T., Taguchi, Y., Morimatsu, F., Sato, K., Nakamura, Y., Higashi, A., Kido, Y., Nakabo, Y. and Ohtsuki, K. (2005). "Identification of food-derived collagen peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates." Journal of agriculture and food chemistry 53 (16): 6531–6536.
- Barnett ML, Kremer JM, St Clair EW, Clegg DO, Furst D, Weisman M, Fletcher MJ, Chasan-Taber S, Finger E, Morales A, Le CH, Trentham DE: Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with oral type II collagen. Results of a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 1998 Feb;41(2):290-7.
- Ausar SF, Beltramo DM, Castagna LF, Quintana S, Silvera E, Kalayan G, Revigliano M, Landa CA, Bianco ID: Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by oral administration of bovine tracheal type II collagen. Rheumatol Int. 2001 May;20(4):138-44.
- Bagchi D, Misner B, Bagchi M, Kothari SC, Downs BW, Fafard RD, Preuss HG: Effects of orally administered undenatured type II collagen against arthritic inflammatory disease: a mechanistic exploration. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 2002;22(3-4):101-10.
- Matsuda, N.; Koyama, Y., Hosaka, Y., Ueda, H., Watanabe, T., Araya, T., Irie, S. and Takehana K. (2006). "Effects of ingestion of collagen peptide on collagen fibrils and glycosaminoglycans in the dermis." Journal of nutritional vitaminology 52: 211–215.
- Shigemura, Y.; K Iwai, F Morimatsu, T Iwamoto, T Mori, C Oda, T Taira, EY Park, Y Nakamura and K Sato (2009). "Effect of prolyl-hydroxyproline (Pro-Hyp), a food-derived collagen peptide in human blood, on growth of fibroblasts from mouse skin." J Agric Food Chem 57(2):444–449.
- Matsumoto, H.; Ohara, H., Ito, K., Nakamura, Y. and Takahashi, S. (2006). "Clinical effects of fish type I collagen hydrolysate on skin properties." ITE Letters 7(4): 386–390.
- Nomura, Y.; Oohashi, K., Watanabe, M. and Kasugai (2005). "Increase in bone mineral density through oral administration of shark gelatin to ovariectomized rats." S Nutrition 21(11-12):1120–1126.
- Moskowitz, R. (2000). "Role of collagen hydrolysate in bone and joint disease". Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism 30 (2): 87–99.
Types and Sources of Collagen
Collagen is found in food, but, unfortunately, in very low concentrations. There are not enough of them for any effect to be noticeable in humans. It would be good to add gelatin-rich foods to your diet, but the choice is limited.
That is why you need to use dietary supplements and medications that contain collagen. The source of this protein can be the tendons, skin and joints of cattle, as well as wheat or fish dermis, as a result of which we can say that collagen is divided into 3 types (types), by the way, it directly depends on the type of collagen cosmetic effect.
Animal collagen
This is the cheapest type of collagen, which is why it is the most common. It is used in inexpensive cosmetics (less often in more expensive ones). This type of protein comes from the top layer of livestock hides.
There are nuances here: this species differs in composition from the human one, as a result of which it may not penetrate the cells of the dermis or simply cause allergies. With proper processing, even such collagen can retain useful substances such as polysaccharides, hyaluronic acid and others.
Peculiarities
- Allergic.
- Poor penetration into cells.
- Small amount of nutrients.
- Cheap.
Marine collagen
This type of collagen is also called “fish” collagen for good reason (produced from the skin of marine fish). It is very close in structure to the protein produced in the human body, therefore it is incapable of causing addiction, penetrates perfectly into cells, and, most importantly, promotes the production of collagen by the body. But there are nuances here too: production is possible only at low temperatures, which complicates the task.
Peculiarities
- May cause allergies.
- Good penetration into cells.
- Not addictive.
- Promotes the production of natural collagen.
- Difficulties in production (consequence - price).
- Sterility is required.
Plant collagen
This is not exactly collagen, it is made from wheat proteins, despite this, it includes collagen-containing substances that act on the skin, improving its firmness and elasticity. Any collagen is a protein, but not any protein is collagen, so it will be clearer.
Protein, which is obtained from wheat or other plants, has enormous vitamin and general nutritional value, but, unfortunately, the production of this type is extremely expensive. This is why prices for products with plant collagen seem incredibly high.
Peculiarities
- It cannot be called collagen, but the structure is similar.
- Hypoallergenic.
- Positively affects the structure of the skin.
- Well absorbed by human skin.
- Complex production.
- Very high price.
Collagen products:
- Meat, animal tongue, liver.
- Whole grains containing iron, green apples.
- Egg white (rich in sulfur).
- Red vegetables.
- Black currants, kiwis, and citrus fruits contain vitamin C, which helps produce collagen.
Collagen in food
Properties and structure of collagen
A distinctive property of collagen from other proteins found in the dermis is its unusual AMC composition. The position of the polypeptide chains and the unique electron microscopic structure are very striking; all this shows the uniqueness and irreplaceability of this protein.
An important difference in the AMK composition is the content of a third (or 33%, as mentioned above) of glycine, a high content of proline and hydroxyproline. This compound can be qualitatively determined by its content of oxylysine and hydroxyproline.
The structure of collagen, like all proteins, is divided into:
- primary;
- secondary;
- tertiary;
- quaternary
A characteristic difference in the primary structure from other proteins is the alternation of regions consisting of non-polar AMK residues with regions consisting of polar residues.
The secondary and tertiary structures have no distinctive features, and a fibril with a collagen micromolecule is formed on the quaternary structure.
Use in cosmetology
It is used in cosmetology in two cases:
- To stimulate collagen synthesis in the skin.
- For technological applications.
In cosmetology, different types of collagen are used, but, as already mentioned, animal collagen is most often used:
- External use. Included in anti-aging gels, creams, masks. It must be taken into account that large molecules are not able to penetrate the stratum corneum, so it can temporarily fill microcracks. The effect mainly arises from the fact that collagen is hygroscopic, but given that this effect is only superficial, it cannot be called extremely effective. The downside is that collagen creates a film and prevents liquid from leaving the pores; this effect can be compared to “moisturizing” your hands with latex gloves. If the composition contains any other useful substances, for example, microelements, vitamins, then a positive effect will be observed.
- In the form of fillers , which are also called fillers, they are used for injections, contouring, mesotherapy (together with hyaluronic acid), and are produced on the basis of human collagen (or bovine) in the form of gels. Stimulates the production of your own collagen. Moisturizing and the effect of them appear literally immediately and are observed within 6-12 months (in rare cases, a little more than this period)
- In dietary supplements in different types and forms of release (capsules, powders, etc.)
Dietary supplement Collagen Ultra plus glucosamine
In addition to the main active ingredient, the dietary supplement Collagen Ultra plus glucosamine includes useful extracts of five types and a vitamin complex. Essential oil is present as an additional component.
The complex composition is designed to significantly improve the condition of the musculoskeletal system in the treatment of various diseases. In addition to this drug, it is recommended for use as a prophylactic agent.
Daily dose – 8 grams per day during or after meals. The optimal course duration is 1.5 months. The number of courses is at least twice a year. The drug can be bought at a pharmacy without a prescription. Cost – from 360 rubles.
Use of collagen in medicine
Basically, of course, it is used as a dietary supplement to improve the structure of skin, hair, tendons, but after the appearance of collagen from the skin of carp fish, its use moved to a new level. This protein is closest to natural human protein. It is able to maintain its protein structure outside(!) the body in an environment whose temperature is below +28 degrees, without the use of preservatives.
This collagen is capable of:
- improve the human immune system;
- slow down aging;
- reduce biological age;
- remove toxins and much more.
They also produce separately preparations for external use in the form of creams and gels, which are needed to strengthen joints and ligaments and, of course, for cosmetic purposes, which were described above.
Hydrolyzed (active) collagen is indicated during sports, as well as in the postoperative period.
Use of collagen in cosmetology
How to restore your skin's own collagen
Stimulation of this process occurs in several ways:
- Hardware techniques (such as ultrasound or diamond peeling, laser dermabrasion, myostimulation, thermolifting, electroporation and many other procedures).
- Using contour plastic surgery and mesotherapy (using injections with vitamin-protein complexes or hyaluronic acid).
- Microneedling (occurs with the help of a mesoscooter; it is possible either with a cosmetologist, or in a clinic, or at home).
- The use of dietary supplements containing proteins, vitamins (in particular vitamin C), amino acids that stimulate collagen production.
- Diets with a high content of foods rich in amino acids, vitamins, minerals, as well as omega-3; these diets should contain eggs (yolk), cereals, fatty fish, citrus fruits, and vegetables. It should be noted that many of these foods can increase estrogen levels.
- Taking herbal hormonal drugs (estrogen, testosterone). Do not take without consulting a doctor.
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and using cosmetology methods, even in old age you can maintain a beautiful and well-groomed appearance. The most effective method is collagen injections; they not only maintain the firmness and elasticity of the skin, but also help remove existing wrinkles.
If you decide to have an injection at a clinic, you must conduct a trial test, which the clinic must organize itself. Once every 2 weeks, a dose of collagen is injected into the forearm area; if an allergic reaction is not observed after 4 procedures, then injections can be made. This is necessary in order to determine whether animal collagen is causing your allergies.
In addition to cosmetic procedures, you should not forget to consume more rose hips, kiwi and citrus fruits to increase your vitamin C levels.
Clinically Effective Collagen Dosage
You probably have a question: “How much and how to take collagen?”
There is no clinically effective dose for type I collagen, as it is currently unknown whether the product has any benefit. However, if you want to try it, take 2.5 to 3 g per day.
For type II collagen, the clinically effective dosage is 10 to 40 mg per day to improve joint health.
Yes, this is a fairly large dosing range, but it is based on studies using different doses (it is not known for sure whether the rule of thumb applies in this case). The experiments clearly show that 10 mg is effective, but increasing the dosage by 2 –4 times does not necessarily mean an improvement in the effect.
Regarding your dosage regimen, follow the recommendations provided by the manufacturer of the product you choose.
Conclusion
Collagen is the most important protein in our body; its deficiency should be treated with trepidation. Eat the right foods and use the right cosmetics. It is necessary to exclude harmful environmental factors; this can help maintain beautiful and elastic skin until old age, as well as maintain the condition of bones and tendons at a high level. You need to use dietary supplements, this is especially important when leading an active lifestyle and playing sports.
There is no need to neglect such an important thing as the “protein of youth”, because such expressions are true. The most important thing is to determine whether you are allergic to anything, then even in old age you can look great. Collagen is the most important element of human health.