es_kula
Main types of postural disorders and their diagnosis
I would like to make a reservation right away: this is not a medical article, and its author does not claim professional competence in the matter.
In addition, I will not wrap up a universal “pill” that will help everyone without exception. The text, of course, will contain many simplifications and “straightenings” of a general educational nature. My task is to talk about the basic principles, what you need to know in order to be able to listen, feel, love and take care of your own body. Perhaps this is one of the most technically complex and term-rich parts of the story :)))
So, as the Great Schemer Ostap Bender used to say in moments of deep sadness: “Do you know that every person is pressed by an atmospheric column weighing 20 tons? This morning I felt its pressure more than ever.” It was the need to resist the pressure of this very pillar, while maintaining balance and a vertical position of the body, that gave our “axis of gravity” - the spine - the very shape that it has. Our spinal column has several NATURAL curves: cervical and lumbar lordosis, thoracic and sacrococcygeal kyphosis. Animals do not have such bends.
These curves (lordosis and kyphosis) in an adult, mature person may be excessive, but remember, if someone, looking at your back, sadly shakes their head: “Ah-ah, we have kyphosis here! We’ll fix it urgently!”, - this person, kick him in the neck, at least he doesn’t understand the terminology well enough :) Kyphoidosis and lordosis of the body serve for convenient “storage” of heavy internal organs.
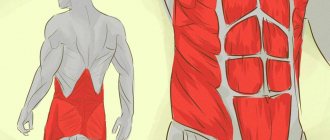
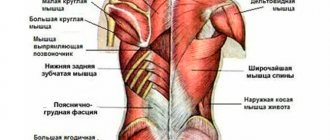
A very interesting comparison is given by Leopold Busquet - an orthopedist, sports doctor, osteopath - in his book “Muscular Chains”. He associates the human structure with. inflatable rubber doll. “We have many membranes: cutaneous, subcutaneous, superficial and deep (.) From the inside, these membranes are filled with organs, and muscles and bones give it all economical static.” After analyzing this ingenious system, the problems of a person who has lost weight, a person who quickly “deflates”, become clear.
The loss of elasticity of the membranes begins to be compensated by paravertebral (paravertebral) muscles, which are not at all adapted to perform this function. Therefore, a person who has dramatically lost weight experiences constant fatigue, pain in the area of muscle attachments and, as a result, tendinitis and periostitis (inflammation of the joints and tendons).
paravertebral (paravertebral) muscles
However, let's return to posture. Normal posture is one of the criteria that determines a person’s health status. But our body is a complex dynamic system, therefore the proportions, the ratio of the sizes and masses of its body are constantly changing throughout life. These changes depend on genetics, age, and are also influenced by the external environment.
Today, according to fitness statistics, for every 100 people with one or another type of postural disorder, there are only two people whose spine maintains an anatomically perfect position. Sad statistics. Even more sad are the statistics of age-related changes. Up to 60 years of age, scoliosis, thoracic kyphosis, cervical and lumbar lordosis are more often detected in women. With increasing age, the number of people with unchanged posture in a vertical position decreases sharply and the number of people with kyphotic posture increases. Torsion (twisting around its own axis) curvatures of the thoracic and lumbar spine are detected in more than half of practically healthy people of both sexes and are found more often with age.
So, the main types of deformities: Flat back (II) - an extremely rare and difficult to correct disorder (can be seen in representatives of Asian peoples, especially the Chinese and Japanese). The head is positioned straight, the neck is usually straight and long, the shoulders are noticeably lowered, “wing-shaped shoulder blades”, the stomach is retracted, the buttocks are flat. A flat back is characterized by poor development of normal curves of the spine, which results in functional inferiority of the muscles. With a flat back, the spring functions of the spine are least pronounced, which is fraught with adverse consequences during physical education and sports. Running, jumping, horse riding and cycling are especially dangerous. People with flat backs are predisposed to lateral curvatures of the spine, that is, to the formation of scoliotic posture or scoliosis. Many experts believe that the smoothness of physiological curves is the first stage of spinal osteochondrosis.
People with such posture need to work on increasing the mobility of the lumbar and sacral spine (various twisting and twisting of the spine are recommended, including using a roller that can be placed under the lower back; rolling on the mat will not be amiss). The transverse abdominal muscle requires strengthening, but hyperextension, on the contrary, should be excluded. The legs (especially the quads) need to be stretched. It is worth including in your training plan any exercises that involve bringing your shoulder blades together, for example, on a crossover or with a shock absorber.
A round back is one of the most common, but at the same time, the most easily corrected postural disorders.
This is how it looks in particularly advanced cases. The spinous processes of the spine create an arc of curvature.
Causes of spinal curvature
Normally, people with correct posture have natural back curves. If they are located anteriorly, it is called lordosis, if posteriorly, it is called kyphosis. In healthy people, lordosis should be in the neck and lumbar region, in kyphosis - in the thoracic region and coccyx area.
The following congenital causes of poor posture are identified:
abnormal structure of various areas of the spine
due to gene mutation;
malformed vertebral arches
.
Separately, the causes of congenital scoliosis are distinguished:
formation of additional vertebrae;
congenital muscle weakness;
different distances between the vertebral arches.
Congenital causes are dangerous to the child's health. They are difficult to eliminate; in most cases, surgical intervention is resorted to. The consequences of spinal curvature affect the entire body, brain hypoxia and slow blood circulation appear.
The following types of acquired causes of spinal curvature are distinguished:
incorrect body posture while sitting is the main cause of poor posture (low head, shoulders shifted forward, excessive posterior protrusion of the thoracic spine);
incorrectly selected sizes of chairs and tables that a person uses for a long time during the day;
lack of change of position for a large amount of time;
incorrectly selected mattress and pillow;
flat feet, which changes the center of gravity of the body;
insufficiently active lifestyle, lack of physical activity and sports;
a decrease in the amount of muscle mass that often occurs during adolescence or old age, resulting in a lack of back support;
mechanical damage to the bones responsible for maintaining the spine;
wearing an incorrectly selected backpack (the cause of scoliosis in children in primary school);
rickets – insufficient calcium content in the bones, leading to their fragility, which is the main cause of poor posture in children under 3 years of age;
ankylosing spondylitis and other inflammatory diseases of the joints (cause of scoliosis in adults).
Unlike congenital causes of incorrect posture, acquired ones can be easily eliminated at the initial stage of formation.
Congenital pathologies appear in childhood. Acquired conditions can occur both in childhood and in adulthood. Most often, poor posture occurs in children in elementary school, when they begin to sit at a desk for a long time.
How to practice
If you're working your entire body in one workout, choose an exercise for each muscle group. If you prefer splits, take two exercises from each point and add them to your back day or deadlift day.
Some of the exercises described in the article pump up several muscle groups at once. Take this into account when creating your program. For example, you can choose one that will work both your upper and lower back well, or work these areas separately.
Select the weight of the equipment in such a way that the last repetitions in the approach are difficult, but without compromising the technique. The number of sets and repetitions will be indicated for each exercise.
How to do exercises for the latissimus dorsi muscles
These exercises will also help target the trapezius, rhomboids, infraspinatus, teres major, and teres minor muscles.
Upper pulley to chest
You can tilt the body back a little and lock it in this position. Fixation is of great importance: if you want to fully load your back, swinging must be eliminated.
Lower your shoulders and squeeze your shoulder blades together, pull the handle until it touches your chest, and then smoothly and under control return it to the starting position. There is no need to A Comparative Analysis and Technique of the Lat Pull-down raise your shoulders to your ears at the extreme point - keep them down and your shoulder blades retracted.
Perform 3-5 sets of 10-12 reps.
Pull of the lower block to the stomach
In addition to the lats, abdominal rows work well Variations in muscle activation levels during traditional latissimus dorsi weight training exercises: An experimental study of the middle trapezius and rhomboids. Therefore, if you want to pump up both the upper and lower back with one exercise, include this option in your workout.
Sit on the machine, place your feet on the platform, and grab the handle. Lower and straighten your shoulders, straighten your back. As you exhale, pull the handle toward your stomach, then return it to the starting position and repeat.
Do not jerk your back or lean back: only your arms move throughout the entire exercise.
Do 3-5 sets of 10-12 reps.
Incline Pull-Ups
Another universal exercise that works well on almost all back muscles. Unlike regular pull-ups, it is suitable for any level of training: just change the position of the body and legs, and even a beginner can do a pull-up.
Find a low crossbar. If you work out at the gym, you can use a barbell on racks. Grasp it with a straight grip slightly wider than your shoulders: this position of the hands will more engage the latissimus dorsi and trapezius muscles. If possible, do inclined pull-ups on loops or rings - this will increase the load on your back Effects of hand-grip during the inverted row with and without a suspension device: An electromyographical investigation.
Hang on the selected apparatus, tighten your abs and buttocks, and stretch your body in one line. Lower your shoulders and squeeze your shoulder blades together, pull yourself up until your chest touches and lower back down.
You can simplify the exercise in two ways: find a higher bar so that your body is in a more vertical position, or bend your knees at a right angle and place your feet on the floor.
Incline pull-ups can be made more difficult by using elevation. Place your feet on the stand so that your body is in a horizontal plane.
Perform 3–5 sets of 15–20 reps.
Straight grip pull-ups
Grasp the horizontal bar, lower your shoulders and squeeze your shoulder blades together. Pull yourself up so that your chin goes beyond the level of the horizontal bar, lower yourself back down and repeat. When doing pull-ups, do not jerk or swing. At the top point, do not pull your chin up to reach the horizontal bar; at the bottom point, keep your shoulder blades retracted.
You can make the exercise more difficult by wearing a weight belt. Instead of simplifying, it is better to replace it with lat pull-downs or Australian pull-ups.
Perform 3-5 approaches at close range.
Bent-over barbell row
Grab the barbell with an overhand grip slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Bend your body slightly above parallel with the floor, bend your knees slightly, hold the barbell in your lowered hands, squeeze your shoulder blades together, straighten your back. As you exhale, pull the barbell toward your stomach, lower it, and repeat. Do not change your body position until the end of the exercise.
Do 3-5 sets of 8-10 reps.
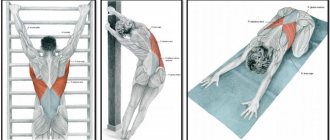
Exercises on the horizontal bar
What is kyphosis of the thoracic spine? causes, symptoms and treatment of back disease
This projectile can be of great benefit for the formation of beautiful posture. Today, there is a horizontal bar in any park, in many courtyards, and anyone can install it at home. Usually men are interested in such activities, but basic exercises will also be very useful for girls.
If necessary, the exercise can be complicated by swinging your legs and torso. Another option is to imitate walking by making appropriate movements with your lower limbs. For osteochondrosis, it is recommended to hang with your legs crossed at the ankles. But in this case, you should consult a doctor before exercising.
To strengthen the muscle corset and form a straight back, it is recommended to do pull-ups
It is important to perform the movement smoothly, synchronizing it with breathing. The grip should be firm, with the thumb pushed back
It is advisable to keep your elbows parallel to each other.
Thus, everyone can choose exercises in accordance with their level of training and their own taste. However, before starting classes, you should read the list of contraindications and consult with your doctor.
source
How to do exercises for the trapezius muscles of the back
Barbell row to the chin
Do 3-5 sets of 8-10 reps.
Reverse dumbbell swings lying on your stomach
Lie on your stomach on an incline bench, take dumbbells, turn your hands back to front. As you exhale, spread the dumbbells to the sides, while simultaneously turning your hands with your thumbs up. Lower back down and repeat.
Do 3-5 sets of 10-12 reps.
IYT climbs
Lie on your stomach on an incline bench, hold dumbbells in your hands. As you exhale, raise your arms above your head with the backs facing up and then lower them to the starting position.
Now raise your arms up diagonally so that your posture resembles the letter Y, with your palms facing upward with your thumbs. Lower to the starting position.
Then spread your arms out to the sides with your thumbs up so that your body resembles the letter T. Lower to the starting position. This was one approach.
Do the same 3-5 times for 4-5 repetitions.
Changing the pattern size
If the size of the model does not correspond to your size, you still take it as a basis and then adjust it to the size you need, carefully studying all the instructions that follow. The pictures show how to go from one size to another (for example, from 44 to 46), following the diagonal.
Care should be taken to ensure that the corresponding size changes will be made diagonally, running at an angle of 45 degrees in the drawing. To do this you need to use a ruler and a square. The ruler must be placed completely straight (for example, on the edge of the table), the long side of the square rests on the upper edge of the ruler (see figure).
You need to use a 45 degree square. The figure shows the offsets with the corresponding ones for restructuring the pattern by one size (for a larger size it should be multiplied by two or three, etc.). This method is suitable for both reduction and enlargement. Once the size you want is determined, check all measurements carefully before cutting your fabric.
Skirt - front and back panels: increase by 0.5 cm on each side. Lengthen or shorten if necessary.
Bodice-back : increase the middle of the back by 0.2 cm and along the edge by 0.7 cm, increase the outer shoulder point by 0.5 cm, raise the neckline by 0.4 cm.
Front : increase by 0.3 cm in the middle of the front and by 0.8 cm along the edge. Shoulders and neckline, same as for the back. Depending on the need, it should be lengthened or shortened.
Sleeve - raise the armhole by 0.5 cm to the hem, widen the front and back by 0.8 cm. Lengthen or shorten if necessary.
Pants - front half: increase along the outer and inner edges by 0.5 cm, raise the waistband by 0.5 cm. Back half: increase along the edge and raise the waistband by 0.5 cm, increase the middle of the back half (step cut) by 0 .6 cm. Increase or shorten as necessary. For sizes larger than 44, change the waistband line by measuring the length of the inseam and raising it to the required distance.
How to do back extensor exercises
These two best exercises are Trunk muscle activity during stability ball and free weight exercises; Muscle activation during various hamstring exercises for the back extensors work well on the entire posterior chain, including the glutes and hamstrings.
Deadlift
Stand over the barbell with the bar over the laces of your shoes. Push your hips back, bend over with a straight back, and grab the barbell with an overhand grip slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
As you exhale, straighten your hip and knee joints, keeping your back straight. Bring the barbell close to your shins, almost touching them. Lower it to the floor and repeat.
Perform 3-5 sets of 6-8 reps.
Hyperextension on GHD
This exercise is often used at the beginning of a workout to warm up and strengthen the back, buttocks, and hamstrings.
Place your feet under the rollers of the GHD machine and place your hands behind your head. Lower your body and then return to the starting position. At the top, rise above the parallel of your back with the floor and look forward. Perform smoothly and under control, without rocking or jerking.
Do 3-5 sets of 15-20 reps.
Hold it to failure for as long as you can. Perform 3 sets.
Anatomy of the spine
A formed spine performs one of the main functions in the body - it provides balance in space and the ability to hold the body in an upright position while minimizing the load on muscles, bones and ligaments.
Signs of correct posture
Normal posture is a straight back with well-defined physiological curves. In a standing position, the vertical axis stretches from the middle part of the skull to the ligament of the Chopart joint, at the edge of the dorsal surface of the heel. At the same time, it conditionally runs along the posterior edge of the lower jaw, touches the cervical lordosis, crosses the lumbar lordosis, the middle part between the heads of the femurs, and passes in front of the knee joints.
With normal posture, all parts of the body are located symmetrically, relative to the spine. The head occupies a strictly vertical position. The tragus of the ears are located at the same level as the lower line of the eye sockets. The chin is slightly raised. The shoulder line is horizontal, the shoulder blades do not protrude, the chest is raised, the stomach is drawn in.
Signs and treatment of round-concave back
A round-concave back is a postural disorder that is characterized by an increase in all curves of the spine, including the thoracic, sacral, lumbar and cervical. In this case, there is a significant shift in the center of gravity, which greatly affects a person’s gait. The peculiarity of this pathology is that a patient with this diagnosis begins to bend his legs in a standing position.
When all lordosis and kyphosis increase, which is what happens with a round-concave back, the center of gravity shifts, which is expressed in increased pressure on the pelvic area and leg joints. Therefore, over time, this pathology leads to arthrosis, displacement of internal organs, and changes in gait.
The severity of symptoms will depend on which part of the spine is affected the most. For example, with increased thoracic kyphosis, the patient may experience symptoms such as:
- Difficulty breathing.
- Chest deformity.
- Violation of heart activity.
- Pain in hands.
At the same time, the signs of a round-concave back disappear when a person assumes a horizontal position. This is due to the fact that the muscle corset is able to support the spine in the only correct physiological position for it.
Types of deviations
Normal posture is characterized by a flat back, a straight line of the shoulder girdle, a retracted stomach and a vertical head posture.
If the body position does not correspond to these parameters for a long time, one of the following deviations can be stated:
- Round or round-concave back - shoulders tilted forward and down, increased deflection of the thoracic, lumbar and cervical spine, increased flexibility of the spinal column, with rare lateral curvatures, slightly bent knees and a head bent forward. Some researchers describe a type of round back with kyphosis and lumbar spine too;
- Flat or flat-concave back - weak deflections of the entire spine, flattened chest, retracted stomach. The compensatory functions of the spine are reduced to a dangerous level, which leads to damage from minor mechanical impacts and lateral curvatures;
- Slouched back - the chest deflection is clearly pronounced, the bends of the other sections are only outlined. Often accompanied by scoliosis of varying severity and direction.
Some deviations indicate only a slight weakening of the muscle corset and poor self-control, while others may be the result of serious disorders.
Therefore, you need to pay attention to this and possibly identify one of the violations at an early stage in order to take measures to eradicate it.
How to correct pathology
The most important thing when treating a round-concave back is to correct all existing pathological curvatures of the spine. Today, corsets and therapeutic exercises are increasingly used for these purposes. Moreover, exercises should be selected very carefully, because their main task is to eliminate the existing spasm of skeletal muscles.
The first thing to start with is to stand near a wall several times a day and rest your shoulders, the back of your head, and your buttocks against it. It is advisable to draw in your stomach as much as possible. This exercise helps to form correct posture, so you need to do it regularly. The duration can be from a minute to three. After this, you must definitely walk around the room, trying not to bend your back, but keep it in the same position as near the wall.
The second exercise for a round-concave back is performed as follows. In a horizontal position, you need to inhale and draw in your stomach as much as possible, and as you exhale, sit down on your heels. After this, kneel down and inhale again. The number of repetitions can be from 8 to 10.
The third exercise is performed in a standing position. To do this, you need to cross your fingers behind your back and change their position every 10 seconds. This exercise helps to get rid of lateral scoliosis if it is present. Each time you should perform 4–6 repetitions.
When diagnosed with a round-concave back, it is very important to train not only the thoracic, lumbar and other parts of the spine, but also the abdominal muscles. The easiest way to do this is with the following exercise: first take a shallow breath and draw in your stomach, then straighten your chest as you exhale. The number of exercises should not exceed 4 - 6 in one approach.
Treatment of a round back in a child
In childhood, it is easiest to correct the pathology; the skeletal system is not yet formed and can be easily corrected. When treating poor posture in a child, it is important to follow the following principles:
- Provide favorable conditions for the functioning of the spinal column.
- Strengthen the muscle corset and improve the child’s physical capabilities.
Therapy begins with compliance with a general hygienic regime, which involves:
- A balanced diet containing all important vitamins and minerals.
- Frequent walks in the fresh air.
- A good night's sleep on an orthopedic mattress and pillow.
- Compliance with the study and rest regime.
- Carrying out hardening procedures.
Doctors often recommend wearing corsets to correct a round back, but they give the desired effect, but it disappears immediately after you stop wearing it. This can be explained by the fact that correctors and corsets deprive muscle fibers of the ability to stabilize the spine during movement; they take over this function.
It is more effective to strengthen your own muscle frame, therefore the following are shown:
- Massage.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Physiotherapy.
Exercises for a round back can be used as follows:
- Stand straight, put your hands on your shoulders. Bend your torso forward and backward. The back should be straight.
- Squats, holding a gymnastic stick in your hands in front of you.
- In a standing position, inhaling, lift the stick up, and exhale, return back.
- In a standing position, bend your hands back on your waist, arching your back, and pull your elbows back.
- Lying on the floor, on your stomach, raise your upper body, bending at the lower back.
Parents should understand that the result of therapy depends on the regularity and correct execution of exercises.
Basic Rules
When treating round-concave back with exercises, several important rules must be followed. Strength and range of motion should be increased gradually from session to session. If pain occurs in the spine while performing one or another exercise, you need to stop exercising, consult a specialist and choose another, more gentle complex for yourself.
Many exercises for this postural pathology train not only the back muscles, but also many other muscles that are in close proximity. However, to achieve this, you must perform all the exercises regularly and correctly.
If you have a strongly protruding abdomen, you need to choose those exercises that could only affect the abdominal muscles and would not affect the lower back muscles in any way.
Treatment methods
To treat the disease, orthosis (wearing orthopedic corsets) is first prescribed. They allow you to remove muscle tension and “synchronize” the muscles on both sides of the body. To relax the muscle corset, 2 methods are used:
- Regulatory;
- Physical.
The regulatory method of treating round-concave back involves prescribing tranquilizers that relax the muscle corset. Antidepressant medications help relieve the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. If pain occurs due to pathology, doctors prescribe muscle relaxants and painkillers.
The physical method involves daily gymnastic exercises prescribed by an orthopedic traumatologist.
Nishi Method
Before performing exercises to correct a flat-concave back using the Nishi method, you should relax. For this:
- Wear loose clothing;
- Remove jewelry and metal objects;
- Create silence in the room;
- Take a comfortable position;
- Optimize your breathing;
- Stay still for 10 minutes and think about something pleasant.
There are other relaxation techniques. They are used to relieve muscle tension before performing gymnastics.
Bragg Field Method
Plano-concave back in children and adolescents is treated according to Paul Bragg. This therapy has the maximum effect when the spinal column is flexible during active vertebral growth.
Therapeutic gymnastics by Paul Bragg for poor posture in children
- Elimination of straightened kyphosis, neck and head position is achieved by daily performing the following exercise. Stand with your back to the wall. Try to keep your head, shoulders and buttocks in close contact with it. Pull your stomach inward to reduce the gap between the vertical plane and the lower back;
- To strengthen your abdominal muscles, lie on your stomach and turn left and right. Repeat the gymnastics 9-10 times;
- To relieve residual tension from the muscles, sit on the floor and rest your hands on it with your hands behind you. Raise your pelvis as high as possible. Hold the position for 2 minutes and lower down;
- Wrap your arms around your knees while sitting on the floor. Raise your head and touch your chin to your chest. Try to move your buttocks up as much as possible and at the same time move your head back. This exercise trains the lumbar muscles of the back. You need to repeat it 2-4 times daily.
Treatment of a plano-concave back requires diligence, regularity and precision when performing gymnastics. If these requirements are met, then in an average of 2-3 months the spinal axis can be returned to its physiological position.
Prevention
Prevention of such a pathology as round-concave back is based on the exclusion of provoking factors. This can be a general improvement of the body, an individual approach or social preventive actions.
General wellness includes measures to reduce the load on the spine and correct movements, as well as eliminating certain consequences of spinal disease that can lead to a deterioration in general condition.
Individual prevention includes measures that will help a person reduce the provoking effects of those factors that affect the curvature of posture. This can be either regular gymnastics or hardening, as well as proper nutrition with plenty of vegetables and fruits.
Social prevention is aimed at improving working conditions, and with a round-concave back it is very important to create an optimal work and rest regime that would help prevent the further development of the pathology itself and become a factor that would help protect a person from all kinds of complications.