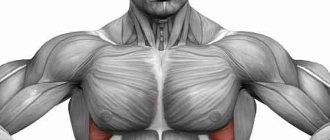
If you want to increase your strength
To become stronger, that is, to lift heavy weights to the limit of your capabilities, it is not enough just to build a mountain of muscle.
The fact is that our muscles are made of fibers, and not all of them tense at the same time to produce force. In order for you to lift really heavy weights, you need to train your nervous system to recruit as many muscle fibers as possible.
Heavy Why strength depends on more than muscle sets of 2–5 repetitions are suitable for this purpose. In this case, the weight should be 85-95% of your one-repetition maximum (1RM) - the weight that you can lift only once.
Despite the fact that such training is the best Differential Effects of Heavy Versus Moderate Loads on Measures of Strength and Hypertrophy in Resistance‑Trained Men, Effects of different volume‑equated resistance training loading strategies on muscular adaptations in well‑trained men. , what you can do to increase strength, you still shouldn’t practice them all the time. Especially when it comes to complex movements that involve many joints and muscle groups: squats, deadlifts, bench presses, snatches and clean and jerks.
Such exercises greatly tire the central nervous system (CNS), and working with heavy weights only increases the load.
As a result, you will have a long recovery time, and the accumulated fatigue can result in injury or overtraining. Even if your goal is to become strong, periodically insert lighter weights into your workout to relieve your muscles and brain.
Ten levels[edit | edit code]
Doing a lot of high-intensity reps is good. As discussed in Chapter 2, adding repetitions builds endurance but does not build strength or muscle. Strength and muscles are the main goal of the training process in prison and the meaning of the Training Zone. That's why each of the six Big Six movements consists of ten core exercises.
These ten exercises are called "Ten Levels". By performing them gradually and regularly, the athlete moves from easy to more complex, from beginner to professional level and ensures stable and long-term results. It should be noted that a different sequence of exercises will not lead you to your cherished goal - at least not in the foreseeable future.
The “Ten Levels” are variations on the Big Six core movements. For each of the Big Six movements—push-ups, squats, pull-ups, leg raises, bridges, and handstand push-ups—there are ten different types of exercises. In the second part, each type of movement and options for its development are described in detail in separate chapters. For example, the chapter on squats contains all the necessary information about this type of exercise and about ten variations of its implementation, which are ranked by level of difficulty, that is, from the simplest technique to the most complex. Level One, the Shoulderstand Squat, is the easiest variation of the squat, while Level Ten, the Single Leg Squat, is the most difficult variation of the exercise. Almost every athlete, even an untrained one, can do squats in a shoulder stand, but only a few can do squats on one leg without prior training. The main goal of such a structure is to show trainees how, without the help of a personal trainer and special equipment, they can learn to correctly perform a series of squats on one leg for 20 or 50 repetitions.
Once you can do the Level 10 strength exercises without too much effort, you can consider yourself a master of bodyweight training. You won't get that kind of strength lifting 180kg in the gym. That's a decent level of athleticism! Today, not all athletes have mastered old-school bodyweight training techniques and can perform this trick perfectly. Many, in an attempt to learn how to squat on one leg, have difficulty making one attempt, which seems impossible, because they do not know that the short path to perfection in this exercise lies through Ten levels. In modern gyms, these ten levels have been completely replaced with other exercises using free weights or using fancy equipment. However, the desired result still remains unattainable, and then steroids are used.
“Ten Levels” is the most important, revolutionary advantage of the Training Zone. If you learn to use these stages of strength building correctly, you can turn from a frail boy into a steel brute and fully realize your full physical potential inherent in nature. That is why the most effective techniques are kept secret by those who master them perfectly, because knowledge is power! Information about the method of increasing strength rarely left prison walls and, moreover, was never published anywhere. The book you are holding in your hands is the first to describe a training system using a complication system and is being presented to the general public for the first time. One thing is for sure: a lot of guys behind bars will hate me for giving away their secret.
If you are going to pump up your stamina and health
If you don't need bench and squat records and prioritize health and endurance, choose 15+ reps with light weights—about 30-50% of the weight you can lift once.
This intensity is good for beginners, injured and older people, as well as those returning to strength training after a long break.
By working with light weights, you reduce the risk of injury due to errors in technique and reduce stress on your joints and spine.
Strength work 20-25 times per set increases Aerobic Endurance Training Strategies muscle endurance - the ability to work longer without fatigue. And it pumps up intermuscular coordination—your body’s ability to tense and relax the right muscles in a timely manner. This helps improve performance and reduce the risk of injury in endurance sports.
Many people think that working with light weights excludes building muscle mass. This is wrong. In fact, by doing high reps you can build muscle just as effectively as using a heavier barbell. But only under certain conditions.
Large excess weight: why it should be taken into account when thinking through a training program
A lot of excess weight is a big burden. On the heart, joints, and not only the knees, about the possible problems with which doctors so persistently remind fat people, but also the hip, ankle, lumbar spine , veins - overweight people often develop varicose veins .
“Large excess weight is generally accompanied by many diseases,” says Yanina Sabirova , master of sports in bodybuilding, personal trainer at the Janinn Fitness fitness club. — Hypertension, diabetes, arthrosis... This bunch of problems can affect middle-aged men and women, and even young ones. And all this must be taken into account when thinking through a training program. Ideally after consultation with a therapist and/or a fitness club doctor.”
If you want to build muscle
To build muscle equally Pumping iron: Lighter weights just as effective as heavier weights to gain muscle, build strength, Strength and Hypertrophy Adaptations Between Low- vs. High-Load Resistance Training: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. 2–6 heavy repetitions per set work well, and 6–2 times with medium weights, and even 20–25 with light weights.
The main factor for muscle growth is not the number of repetitions and weight, but the fatigue of muscle fibers.
In other words, you must tire your muscles so much on each set that you come close to muscle failure—the state in which you can't do a single rep. With a heavy weight, five times will be enough for this; with a light barbell you will have to suffer longer, but this does not change the essence. There is fatigue - there will be growth.
However, in bodybuilding, sets of 8-12 reps are considered the gold standard. And they really work great. The fact is that our body constantly adapts to stress. Today, five squats with a 50 kg barbell will tire your muscles enough to trigger their growth, but after 1-2 weeks this load will not be enough.
The muscles will adapt, and you will need to increase the volume again - increase the weight, the number of repetitions or approaches. And here the average number of repetitions has its advantages.
It is difficult to increase volume by working 2-5 times with heavy weights. Strength does not grow so quickly, but the load on the joints and central nervous system is simply enormous. By inadequately assessing your capabilities, you risk injury or burnout.
It is not so easy to increase volumes when working with light weights: too long approaches will become exhausting and waste a lot of calories. As a result, it will be more difficult to gain muscle mass.
By performing 8-12 reps at 75-85% of your 1RM, you can increase volume easier and safer, without the risk of injury or the prospect of spending three and a half hours in the gym.
If you want to build muscle, don't have joint problems, and aren't looking for strength, 8-12 reps per set will work best for you.
However, this does not mean that other training intensities will be useless. You can mix them together to avoid stagnation and improve all aspects of your fitness. Here are some examples of how you can do this:
1. Within one workout . For example, do a heavy squat for 2–6 reps, dumbbell presses and dips for 6–12 reps, and dumbbell flyes for 15–20 reps.
2. By splits . One day work on upper body strength (2-6 reps with 85-95% of 1RM), the second day - on lower body strength, third day - on upper body volume (8-12 repetitions with 75-85% of 1RM), the fourth - for the volume of the lower one.
3. According to training cycles . 2-4 weeks work on strength (2-6 repetitions), the next 2-4 weeks on muscle size (8-12 repetitions), and 2-4 weeks on endurance (15 or more repetitions).
Listen to your body, track your progress and decide what works best for you.
Bodyweight strength exercises[edit | edit code]
Table of bodyweight exercises for various muscle groups
The idea for this book came to me while I was serving time in Angola. It was the sixth year of my eight-year sentence, and I had already trained many guys. As a result, I ended up with a pile of notes, ideas, and sketches of training programs that I kept in a thick folder. In fact, the idea to write a book was suggested to me by a security guard whose name was, say, Ronnie.
Ronnie, a big and powerful black man, was respected by all the prisoners. He was a local high-ranking powerlifter and not only looked like a tank, but also had the same remarkable strength. He always spoke softly and confidently. And just as gently and confidently he broke the hands of the offenders. I got along with Ronnie - we had a common interest. Sometimes in the evenings at the end of his rounds he would stop at my cell to talk about certain strength exercises or listen to interesting facts about the history of iron sports. And then one day, when we were talking about the nuances of the hand press, Ronnie said: “You know, you should write all this down. No one knows anything about this in the wild. Everything was lost." After sifting through tons of magazines and books in the prison library, I came to the conclusion that Ronnie was right.
Over the course of several years, I brought all my notes into divine shape. I can’t say that it was difficult - the system was already written, since I had been training with it for several years. But transforming the text into a real tutorial required a lot of effort. Gradually I found the right way to present the material, fortunately I had plenty of time.
This book, The Training Zone, is my creation, the result of my labors and rethinking. For your convenience and to better understand my bodyweight training technique, I will first describe the structure of the book, highlighting the key points of each chapter.
Explosive push-ups for bodyweight training
Part I. Preparation[edit | edit code]
In the first part you will find the origin story of the Training Zone. It contains an introduction, a chapter on old school bodyweight training, a chapter on the benefits of the system compared to modern methods, and an "About This Book" chapter. These four parts contain everything you need to provide you with the theoretical knowledge of my training system, its main characteristics and benefits. You will learn about the traditions of physical training in prisons, the origin and history of the Training Zone. Moreover, this part of the book gives first-hand accounts of prison training, which can be extremely helpful for those who have misconceptions about the subject.
Part II. Big Six[edit | edit code]
The second part of the book is called The Big Six: Movements of Power. This part is the basis of the system. As the name suggests, the system is based on six basic types of body movement - the Big Six.
There are thousands of exercises for training muscles, as any more or less competent trainer will confirm, but in fact, only a few basic exercises are needed for everyday training. The human body is made up of more than five hundred different muscles that have evolved as a single unit during evolution. That is why, by working only one muscle group, you upset the balance in the body’s work and destroy the instincts inherent in nature, such as coordination. That's why the best method of daily training is to perform several strength exercises that work all muscle groups at the same time and allow you not only to maintain physical fitness, but also to constantly build strength and endurance.
Without fatigue there is no development
The famous fitness scientist Brad Schoenfeld has repeatedly made similar conclusions in his studies - hypertrophy is similar, and strength grows better from heavy weights than from high repetitions [18, 19, 20].
A completely logical question may arise - why do we walk every day, supposedly, a lot of repetitions, but our legs don’t grow? We bring our hand with a spoon to our mouth a lot and often, but our biceps don’t grow? Another outstanding professor Vladimir Mikhailovich Zatsiorsky, who wrote a lot of educational literature in the field of muscle biomechanics, whose works are fundamental in higher educational institutions in the field of physical education, said something like the following: “A muscle fiber that is involved in work, but is not tired, does not develop .”
And here we are talking about those very “stimulating repetitions” [21]. That is, even if we “move the cabinet” once, our muscles will not grow either, although it seems to be heavy.
When lifting more weight, the first few repetitions will be “idle”; there is no particular benefit from them, because metabolic stress has not set in, the body has not yet realized that it cannot cope, and there is no need for it to attract “additional forces” and stimulate the growth of new muscles. By lifting less weight, we have even more “idle” repetitions, and only towards the end will the body begin to “stress.”
Thus, working to “failure” in itself is not a prerequisite for hypertrophy, but the key repetitions are those that are as close to failure as possible !