To summarize
The two-handed kettlebell push is a basic exercise that came to CrossFit from kettlebell lifting. It perfectly develops the whole body without putting a separate load on the back muscles. With proper use and scaling of the load, you can strengthen the ligamentous apparatus, increase the strength of joints, and increase the strength of lagging muscle groups, especially deltoids. You should not chase the weights in this exercise, because... it is intended primarily to strengthen your ligaments and explosiveness, and violation of the technique due to its impulsive nature can lead to serious injury.
Author Yaroslav Khvatov
Training experience – more than 8 years. Winner and medalist of All-Russian powerlifting and deadlift tournaments. Candidate for Master of Sports in deadlift.
Kettlebell snatch: execution technique
The technique of performing a kettlebell snatch involves performing the exercise in several stages, each of which differs in the mechanics of the movement performed.
Starting position
To begin the snatch, the athlete must take the correct starting position. In the classic technique, you need to place your legs shoulder-width apart and place the weight in the middle, your legs should be slightly bent at the knees. The back is straightened, and there is a deflection at the lumbar level. One hand is placed on the weight, and the other is pulled back.
Executing the swing
The movement is performed by slightly extending the legs. The weight is lifted off the floor surface and carried between the legs with a straight arm to perform a jerk.
Detonation
To carry out the movement, it is necessary to apply a force in which the projectile moves sharply forward. It must be done when the weight returns to the lowest point between the feet. The jerk is produced through simultaneous movements - straightening the knees, raising the toes, raising the shoulders, straightening the body. In this case, the projectile rises by inertia on a straightened arm.
Performing a squat
When the weight reaches the top point, the athlete does not need to apply force. At this moment, he slightly bends his arm with the projectile and makes a squat. Bent elbows and knees should soften the impact of a heavy weight. The hand turns outward, the weight makes a movement about the arc.
Fixation moment
The arm and legs are fully straightened. Fixing the position is considered a completed jerk. It is recommended to hold the projectile in this position for several seconds, while trying to restore breathing.
Lowering the weight
To repeat the exercise, the projectile is lowered down, but not placed on the floor surface. You can do this with your arm straight or slightly bent at the elbow. In the first case, the exercise is easier to perform, since the muscles are resting at this moment. With the second option, the likelihood of hand injury is significantly reduced, but the benefit from the load on the muscles is significant. The subsequent movement is performed from the hang.
About exercising with kettlebells at home >>
Next, a small swing is made and the weight is intercepted with the other hand. The kettlebell push when performed with the other hand is performed in a similar manner. The main rule of performing a kettlebell push is that you need to prepare for fixation in advance, and not at the very end of the lift. It is important at this moment to fully straighten your arm. Fixation too early can result in injury to the shoulder joint or muscles.
Kettlebell snatch and jerk: how to breathe correctly?
Many novice athletes do not think about the need to breathe properly. Training with weights quickly causes oxygen starvation in the body. Errors in breathing lead to insufficient oxygen supply to the body, as a result, the muscles will quickly tire. Kettlebell lifting involves exhaling when applying force and exhaling at the stage of muscle relaxation.
When performing exercises with weights, it is recommended to adhere to breathing, consisting of 3 cycles:
- inhale when lifting the projectile and exhale when detonating;
- inhale when performing a squat and exhale when straightening the body and arms;
- inhale when the weight reaches chest level when lowering, exhale until the swing.
Results of studies on the effects of training with kettlebells on the body of the trainee
Finally, I would like to share with readers the results of a study of the impact of training with a kettlebell on the body of a trainee, which I conducted as part of the preparation of material for the republican scientific and practical conference “Management in the field of physical culture and sports: pedagogical, economic, legal, social and medical-biological aspects” .
The study was conducted over a month in a study group consisting of 6 people, whose average age was 22 years. A feature of the study was the periodization of training – once a week. The reason for this was the need to study the effects of training with kettlebells on the human body in the absence of the possibility of more frequent training. The only equipment for training were weights, the weight of which varied based on the physical capabilities of the subjects. Performing a control set of exercises using kettlebells was included in the main part of the lesson and was carried out using the circuit training method. The complex used special physical training exercises in classical kettlebell lifting (kettlebell swings, etc.), as well as some modified exercises consisting of several components (thrusters - squats with a kettlebell on the chest and subsequent “shvung” of the kettlebell, etc.). To monitor functional data, the pulsometry method was used. Measurements were carried out in the preparatory, main and final parts of the lesson. Based on the measurement results, a graph of changes in indicators was constructed (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Dynamics of changes in the heart rate of trainees during the control period
The objective of the study was to study the dynamics of the heart rate of exercisers after performing a set of exercises during a control period of 1 month. As a result of the research, it was found that in the first lesson, the heart rate of the trainees after completing the complex averaged 170 beats/min. It turned out that after the first lesson, it took an average of 3-4 days for the participants to restore their well-being according to subjective indicators.
Studies of these indicators over the course of a month have revealed positive dynamics: a gradual decrease in the maximum heart rate of those involved with an increase in the volume of work and the weight of weights by an average of 25%. The period of recovery of well-being according to subjective data was also shortened.
In addition, training with kettlebells has a beneficial effect on improving metabolism in the body and also speeds up the fat burning process. But I repeat, all of the listed properties are characteristic only with proper planning of the training process and the technical literacy of the trainer.
Description of the exercise
This exercise is competitive in kettlebell biathlon. According to the competition rules:
- The arms at the top should be fully straightened
- It is forbidden to place the weight on the floor until the exercise is completed.
- The weight should be lifted to the top in one movement (jerk).
- It is forbidden to press the weight at the top.
- You can only change hands once. If the weight breaks out of your hands, the exercise stops.
- 10 minutes are allotted to complete the exercise.
- Competitions are held with kettlebells weighing 16, 24 and 32 kg.
Nuances and errors
1. To avoid tearing calluses, do not grab the arch with your whole palm. At the bottom you need to lower the bow of the weight onto your fingers, and at the top you need to thread the hand as deep as possible into the bow. So that the bow is on the bone, and not in the palm.
2. You don’t need to let the weight go far away from you when swinging. Otherwise, in the end it will fly not only up, but also back. You need to undermine it so that it flies up and closer to the body. It should also be omitted. That is, you do not need to jerk with a straight arm. The arm should only be straight at the bottom at the beginning of the swing.
3. Do not lean on your leg with your free hand. It is forbidden. It should hang freely from the side and just act as a counterweight.
4. When lowering the weight down, you need to not only tilt your back, but also slightly bend your knees. According to the rules, this is not necessary, but bending your legs will make it easier and more efficient to swing.
5. The swing should occur mainly due to the muscles of the back, buttocks and legs. At the end of the swing, you need to jerk your shoulder upward with the trapezoid to give the weight a flight path. The hand should simply catch the weight at the top. That is, your hands should work as little as possible.
6. To strain your forearms less, you need to screw your hand as deeply as possible into the arch of the weight at the moment the weight flies.
7. Don't lower the weight too low. This will increase the amplitude and you will expend more energy. Lower it as little as possible so that it fits between your legs.
8. When swinging back, you can tear off your toes to remove the center of gravity on the heels and make the swing stronger.
Two kettlebell push technique
- Place your feet hip-width apart (not too wide or narrow), with your toes turned slightly to the sides.
- Grasp the handles of the weights with your hands, tilt your back straight and swing your arms, swinging the weights back and forth.
- Through a squat, throw the weights in front of you, bend your elbows in the middle of the amplitude and take the starting position - your elbows are pressed as close to your body as possible and lie on your stomach, above your pelvis.
- Hold the weights with their arms facing each other. Straighten your knees, move your pelvis slightly forward, and tilt your back back - this will make it possible to rest your elbows on your stomach without straining your arm muscles.
- Next, push the weights through the squat, bend your knees, lift your heels off the floor as much as possible and push your elbows out using the push of your pelvis and the strength of your quadriceps. The weights should fly up, but not through the strength of the arms, but only from the hips.
- When pushing the weights up, bend your knees while straightening your arms above your head, and exhale in the top position. Hitting the floor with your heels provides the energy and momentum to fully straighten your arms. Thus, without overloading the knee joint. After fixing the weights at the top point, straighten your knees completely. The inner sides of the hands are turned forward.
- Lean your body back slightly and drop the weights to the starting position on your elbows. Relax your hands. When dropping weights, also do a squat, unloading the knee joint and taking the projectile onto your stomach again using the strength of your hips.
- Repeat pushing out as many times as necessary.
- After completing the exercise, relax your arms and tilt your body, placing the weights on the floor at the end of the movement.
Benefits of exercise
Training plays an important role in the physical development of an athlete. If you follow the technique of execution, then it is available not only for men, but also for women. Performing this exercise brings a variety of benefits:
- Strength, elasticity, mobility of ligaments and muscles improves.
- The voluminous and beautiful muscles of the body are harmoniously formed.
- The level of coordination and the ability to correctly combine the action of various muscles, their inclusion in work and relaxation increases.
- Due to increased heart rate and increased breathing, a high load on the cardiorespiratory system is ensured.
- Performing a snatch helps develop strength and general endurance.
- There is an improvement in speed performance.
- High loads during the kettlebell snatch help burn excess fat in the body.
Performing a snatch contributes to the development of strength and general endurance, the formation of beautiful and voluminous muscles
Regular exercise allows you to improve the strength, elasticity, mobility of ligaments and muscles
Due to increased heart rate and increased breathing during the jerk, a high beneficial load on the cardiorespiratory system is provided
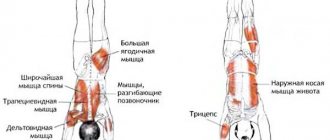
What muscle groups work?
Despite the fact that the kettlebell push develops all major muscle groups, the main profile is the development of the triceps and medial deltoids, which bear the greatest load.
| Muscle group | Movement phase | Load type |
| Upper chest bundle | Primary push impulse | Pulse dynamic |
| Triceps. Lateral head | Kettlebell extension | Basic dynamic |
| Deltas - upper beam | From lifting the weight to the final static tension in the fixation | Basic dynamic |
| Deltas - anterior beam | First phase of pushing movement | Pulse dynamic |
| Biceps hamstrings | Keeping your legs straight while changing your body | Static constant |
| Quadriceps | Setting an impulse to the body | Pulse |
| Biceps flexor arm | Stabilization during the stage of lowering the weight to the shoulder | Static stabilizing |
| Wrist muscles | Hold the kettlebell throughout all stages | Static |
| Trapezius muscles | Holding the weight on your shoulder at the correct angle | Dynamic secondary |
| Rhomboid muscles | Transmission of primary impulse from quadriceps + core stabilization | Pulse + static |
| Psoas muscles | Core stabilization throughout the exercise | Static stabilizing |
| Gluteal muscles | Creating additional momentum when pushing with two hands | Pulse dynamic |
As can be seen from the table, despite the involvement of large muscle groups, the main dynamic load is taken by the muscles of the shoulder and forearm. Thanks to this, kettlebell complexes perfectly work out the small muscles of the arms, which are lagging behind in people who practice exclusively basic movements.
Crossfit complex
The two kettlebell snatch is a popular exercise that is often used in CrossFit. The following is a complex that is suitable for an athlete with a high level of physical fitness. If you are at an intermediate level, you can reduce the number of repetitions in each exercise.
Only 1 round at a time, do not change exercises.
- Mach 53
- 200 m of penetration with two weights on outstretched arms;
- 53 sumo row to the chin;
- 150m penetration with two weights on outstretched arms;
- 53 Snatch of two weights;
- 100m penetration with two weights;
- 53 Kettlebell Extensions;
- 50m penetration with weights.
The average execution time for athletes is 30-45 minutes, depending on preparation.
Kettlebell push with one hand
This technique is recommended for beginners to learn; only after mastering the push of one kettlebell, proceed to a more complex version. Start working with a small weight of the kettlebell, work out precise technique, learn how to properly push the kettlebell out without overloading the shoulder girdle. Also start practicing the technique with two kettlebells with a light weight.
- Take a stable starting position – feet not wide, slightly turn your toes apart.
- Grasp the handle of the weight with one hand and swing the weight across your chest, resting your elbow on your stomach. The body is slightly tilted back and the pelvis forward.
- From a squat, using the strength of the pelvis and legs, push the weight of the weight and straighten the elbow, also fixing the arm on bent knees, after which the legs are straightened. Keep your other hand loose.
- Relax your shoulder girdle, leaning back slightly, and drop the weight to the starting position - elbow on your stomach.
- After completing the exercise, place the kettlebell on the floor and change hands.
What muscles are involved?
This workout is complex. Accordingly, the athlete works out different parts of the body. What muscles work during a snatch:
- abdominal muscles (oblique and rectus);
- gluteal;
- brachialis clavicular muscle;
- infraspinatus
The deltoids, calves, latissimus muscle, and forearms actively participate in the movements. If you hold the sports equipment closer to the body, the load on the muscles will be reduced. As this distance increases, more effort will be required to complete the movement. When mastering the technique, it is preferable to use the first of these options; for a more experienced athlete, the second method of execution may become attractive.
Snatching not only makes your muscles stronger, but also helps develop their endurance. The trapezius and deltoid muscles receive maximum load, contributing to the active development of the shoulder girdle. Performing a snatch has a positive effect on the development of the entire group of spinal extensor muscles and the muscle corset as a whole.
In order for this exercise to be as effective as possible, it is important to strictly follow the movement technique.
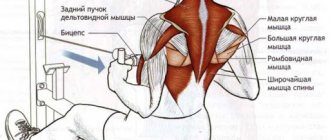
Working muscles and joints
During the kettlebell push, a large number of different muscle groups work, the main ones being the legs, long back muscles, anterior deltoid, pectoralis major, triceps, biceps and forearm. Some muscles work more, some less, which, in particular, depends on the technique of performing the push, but, nevertheless, the push allows you to work almost the entire body. Dynamic work is primarily performed by the triceps, legs and deltoids, while the biceps, forearms and long back muscles act as stabilizers. Pay special attention to the work of the long muscles, since they control the position of the spine, so if you have them poorly developed, they should be worked in deadlifts or reverse hyperextensions.
Since the exercise involves a large number of muscle groups, it goes without saying that the push also involves a large number of joints, which share the load among themselves. However, since the kettlebell jerk is not only a multi-joint, compound exercise, but is also a multi-joint exercise, different joints are worked at each stage. If during the bench press the load is distributed permanently between the elbow and shoulder, then, for example, the knee joint in the push sometimes works, sometimes it doesn’t work. That is why it is especially important to practice coordination of movements, their synchronization and sequence, so as not to get confused and not cause injury to yourself.
What muscles work?
It may seem that the work of the arms in the snatch is significant, but this is not at all the case; for the most part, only the forearms are used in the arms. The main muscles involved in the snatch are the muscles of the back and legs, especially the core.
The entire muscular frame is connected to work in the snatch, and if we take into account that it should not be crudely mechanical, but coordinated and technical, it turns out that along with their strength, muscle coordination and dynamics also develop.
Particularly valuable is the load on the postural muscle layers, also known as deep skeletal muscles.
This is not to say that the snatch “explodes them,” but with regular practice of this exercise and progression in it, the increase in their power will not take long to come.
Exercise technique
How to do a classic kettlebell jerk, and how does it differ from a competitive one? Not only by changing the technique, but also by the muscles involved. So, during training, the emphasis is shifted to the deltoids and triceps, but the correct competitive version primarily uses the legs. The technique of lifting a kettlebell in the jerk style is quite simple, but requires extreme attention to detail. First you need to decide on the weight of the projectile. This can be determined in two main ways:
- The athlete's net muscle weight. Typically, the first weights with a total weight should be no less than a third of the athlete’s weight and no more than half. Those. For a person weighing 70 kilograms, both 16 and 24 kg weights are suitable. And for an athlete weighing over 90, you can safely start working with 32-kilogram weights.
- Indicators in the push-up and military press. The weight of the kettlebell should be 25-30% less than the working indicator. That is, if you work in the military press with weights of about 50 kg, then the weights should be no more than 16 (i.e., the total weight of the shells should not exceed 35 kg).
How to properly push a kettlebell so as not to injure your back and arms:
- Pick up the projectile by throwing it onto your shoulders.
Important: the projectile should lie on the shoulders, not on the chest, and not rest on the side of the elbows.
- Prepare for the pushing movement. To do this, you need to slightly bend your legs.
- Sharply throw the weight up, creating maximum impulse movement through the muscles of the back and legs.
- At the top point, fix the weight on your fully extended arm.
- Lower the weight, lightly cushioning the knee joint.
With breathing in the exercise, everything is simple: we exhale during the push, inhale between the pushes.
History and facts
Equipment resembling weights was made in Ancient Greece and was used for training by Olympians.
But with the advent of the Dark Ages, the cult of a healthy body disappeared and there was no mention of this projectile for a long time. In modern times, weights were used only as measures of weight in trade.
By the 19th century, they began to be used again to develop the body, but there was no talk of serious sport: kettlebells were mainly used by circus performers who entertained the public.
Only towards the end of the same century, exercises with kettlebells received official recognition, began to be actively included in athletes’ training programs and were a type of weightlifting.
And in the middle of the last century, kettlebell lifting became an independent discipline. Thus, in the USSR in 1948, the first All-Union Strongman Competition was held.
Although the rules of this competition were regulated rather vaguely, it was significant, because it significantly popularized kettlebell lifting and gave it light both as a professional discipline and as an amateur means of physical education.
The modern rules of kettlebell lifting were finally formed by the early 90s.
The world record holder in the one-arm kettlebell snatch weighing 16 kg is Sergei Trifanov. In one hour he did 1501 repetitions.
Program
In order to understand how to increase the number of kettlebell pushes, you need to remember that results in any exercise are achieved by combining work with an exercise according to the program and auxiliary exercises.
A classic combination is suitable as a program for developing strength endurance:
- Full cycle push of the kettlebell with both hands.
- Alternate kettlebell jerk with one hand.
- An attempt to lift a weight in failure mode (the weight of the weight must be greater than 1 RM).
If this does not help, you should use additional auxiliary exercises:
| Exercise | Working muscles |
| Kettlebell Snatch | Triceps, deltoids, back |
| Kettlebell Squat | Legs + deltoids on hold |
| Kettlebell press | Deltoids + triceps + pectorals |
| Army press | |
| Kettlebell row with straight legs | Legs + back |
| Smith machine squat | Legs |
| Farmer's Walk | Back + deltoids + legs |
| Leg press | Legs |
| Swing dumbbells to the sides | Deltas - especially the upper beam. |
| Dips | Deltoids + triceps + pectorals |
| Incline Barbell Press | |
| Push ups |
Kettlebell selection
For exercises, sports equipment weighing 16 kg, 24 kg or 32 kg is used. Choosing the right kettlebell should depend on the athlete's skill level. If we are talking about a beginner, then he should start with the smallest weight. To master the correct execution of a snatch, you need to conduct preliminary training and study the technique. For an athlete with a sufficient level of training, the choice of weight depends on the tasks facing him. The greatest benefit will be obtained if a weight is used that best matches the athlete's fitness level.
A 16 kg kettlebell can be used for preparatory exercises at the stage of mastering the technique. When choosing sports equipment, you can also check how suitable its weight is for a person. To do this, it is enough to do the bench press several times (for example, 10). If possible, then such a kettlebell is suitable for training. If the test can be done for different weights, choose the maximum one.
Typically, sports equipment weighing 16, 24 or 32 kg is used to perform a snatch - the choice depends on the athlete’s level of training
Standards in kettlebell lifting
As in other sports, kettlebell competitions have their own standards that determine the athlete’s stage of development. Depending on the fitness and experience of the athlete, different degrees of severity in kg are selected. The standards described below are used for a load weighing 16 kg. The third junior category provides from 50 to 80 points per exercise, the 2nd junior category provides 75 - 125 points, the 1st junior category even more - 110 - 170 points. A weight weighing 24 kg is already used in adult standards . The snatch standards for a 24 kg kettlebell do not differ much and are also divided into weight categories, as is the case with a 16 kg load.
3rd category from 50 to 100 points, 2nd category 70 – 130, and 1st category provides from 90 to 160 points.
A 16 kg kettlebell is the weight that is best for a beginner to start with. Even if the person who decided to engage in kettlebell lifting is 25–30 years old and weighs 70 kg or more, it is still better to start with light weights. This will give you the opportunity to work out a clear technique for jerking the projectile and prepare your muscles for working with larger weights.
Similar exercises
- Swing kettlebells alternately
- Swing kettlebells overhead
- Sandbag Snatch
- Dash into a standing position from the explosion site
Rate the material: rate
Found an error in the article? Select it with the mouse and press Ctrl + Enter. And we will fix it!
| SHARE | SUBSCRIBE |
- Individual selection of a set of exercises
- Training program for beginners – girls
- Workouts at home, or how to pump up at home
- Calorie consumption counter
- Training Plan for Beginners - Men
- Daily calorie consumption calculator
- A set of exercises for weight loss
- Women's diet for weight loss
- Weight loss exercise program for men
- Workouts for girls on relief with emphasis on the hips and buttocks
- Snatch deadlift from a low start: technique and nuances
- Snatch lift with detonation: technique and nuances
- Snatch grip squats: technique and nuances
- Jerking exits: technique and nuances
What weights are used?
Today, three weight categories of projectile are widely used - 16, 24 and 32 kg. The snatch with the smallest weight is used by athletes when passing the GTO standards. The task is to lift the projectile as much as possible within 4 minutes. Not everyone manages to meet the established standards, since they require quite serious physical training. For example, men under the age of 40 must snatch a weight of 16 kg at least 40 times to be able to receive a gold GTO badge.
Before approaching training with kettlebells, it is recommended to go through a preparatory period, including deadlifts and push-ups using the military press technique in the program.
You should always aim for the same number of repetitions with both hands. If one hand turns out to be weaker than the other, then classes should begin with it. To train strength and endurance, it is recommended to include exercises in the program for 10 minutes, during which the maximum number of repetitions should be performed.
Rank standards and records
The long cycle kettlebell jerk is a challenging competitive exercise. Below are the category standards for men and women, as well as Russian records among men with a 32 kg kettlebell.
TABLE OF DIFFERENT STANDARDS FOR MEN:
DC push (number of weight lifts in 10 minutes)
| Weight category (kilogram) | MSMK kettlebell 32kg | MS kettlebell 32kg | KMS kettlebell 32kg | I weight 24kg | II kettlebell 24kg | III kettlebell 24kg | I(u) kettlebell 16kg | II(u) kettlebell 16kg | III(u) kettlebell 16kg |
| 48 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 40 | 35 | 30 |
| 53 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 48 | 42 | 36 |
| 58 | — | — | — | 55 | 45 | 35 | 55 | 48 | 40 |
| 63 | 59 | 44 | 35 | 60 | 49 | 39 | 61 | 51 | 42 |
| 68 | 72 | 56 | 45 | 65 | 54 | 43 | 66 | 56 | 46 |
| 73 | 76 | 62 | 48 | 70 | 58 | 46 | 71 | 61 | 51 |
| 73+ | — | — | — | — | — | — | 74 | 64 | 54 |
| 78 | — | — | — | 74 | 62 | 50 | — | — | — |
| 85 | 82 | 69 | 55 | 79 | 66 | 54 | — | — | — |
| 85+ | 88 | 75 | 58 | 90 | 75 | 60 | — | — | — |
TABLE OF DIFFERENT STANDARDS FOR WOMEN:
DC push (number of weight lifts in 10 minutes)
| Weight category (kilogram) | MSMK kettlebell 24kg | MS kettlebell 24kg | KMS kettlebell 24kg | I weight 16kg | II kettlebell 16kg | III kettlebell 16kg |
| 63 | 59 | 44 | 35 | 60 | 49 | 39 |
| 63+ | 72 | 56 | 45 | 65 | 54 | 43 |
Records of Russia. Men (long cycle) - kettlebell 32 kg.
| Weight category | Last name, first name | Region | Result | Year of establishment |
| 63 | Ryabkov Alexey | Tyumen region | 74 | 2015 KR |
| 68 | Usoltsev Alexander | Tyumen region | 80 | 2015 CR |
| 73 | Belyaev Ivan | Belgorod region | 87 | 2014 World Cup |
| 78 | Chuev Pavel | Belgorod region | 84 | 2017 CR |
| 85 | Vasiliev Denis | Saint Petersburg | 91 | 2014 World Cup |
| 95 | Balabanov Sergey | Rostov region | 93 | 2017 KR |
| St. 95 | Denisov Ivan | Chelyabinsk region | 110 | 2014 World Cup |