The human muscular system consists of approximately 650 large and small muscles responsible for the mobility of various parts of the skeleton. All muscles require regular training to maintain them in normal functional condition. Particular attention is paid to strengthening those on which the ability to maintain correct posture depends, thereby reducing the load on the spine and ensuring its normal functional state. These muscles include the back muscles, including the rhomboids.
Exercises for rhomboids
Below are exercises that involve the rhomboid muscle.
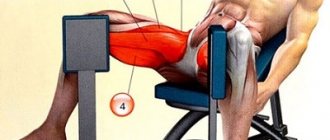
Lower block row to the waist while sitting
This exercise will allow you not only to increase the mass of your back muscles, but also to “draw” them.
Working muscles:
- Diamond-shaped
- Lat
- Middle and lower trapezius
- Rear delta
Exercise technique:
Sit on the seat. Take the handle in your hands and rest your feet on the stops. Knees slightly bent. The body is vertical. There is a deflection in the lower back. As you inhale, lean forward slightly with your lower back arched. As you exhale, pull the handle toward your lower abdomen, returning your torso to an upright position.
Important details:
During the exercise, you should actively move your shoulders back and squeeze your shoulder blades together as much as possible. The elbows go along the sides along the body. It is with this technique that the muscles of the upper and lower back will work as much as possible.
Upper pulley to chest
This exercise imitates pull-ups on a horizontal bar and will allow you to effectively work out the latissimus muscle and use the rhomboid muscle.
Working muscles:
- Lower trapezius
- Rear delta
- Diamond-shaped
- Latissimus
Exercise technique:
Take the handle of the exercise machine with a straight wide grip and sit on the seat. As you exhale, pull the handle toward your upper chest, slightly tilting your torso back. As you inhale, return to the starting position.
Important details:
As you row, push your chest out to meet the movement of the handle. The shoulders should move back and down, the shoulder blades should be brought together. Pay very close attention to the technique so that exactly the muscles that are supposed to work, namely the back muscles.
Pull-ups on the horizontal bar with a straight wide grip
An excellent exercise for training the rhomboid muscle on any sports field.
Working muscles:
- Rear delta
- Diamond-shaped
- Lower trapezius
- Latissimus
Exercise technique:
Grasp the bar with an overhand grip, much wider than shoulder width. Without straining your biceps and squeezing your shoulder blades, pull yourself up, trying to touch the bar with your upper chest. Pause a little at the top and return to the starting position.
Important details:
When pulling up, bend your back and look straight up.
Bent-over barbell row
One of the most effective exercises for pumping the latissimus muscle and engaging the rhomboid muscle.
Working muscles:
- Trapezoidal
- Diamond-shaped
- Latissimus
- Rear delta
Exercise technique:
Grasp the barbell with an overhand grip, slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Bend your legs slightly and lean your torso forward. The tilt should be significant, with the torso almost parallel to the floor. Arms straight. There is a deflection in the lower back. Inhale, and as you exhale, powerfully, while remaining bent over, pull the barbell until it touches your lower abdomen. As you inhale, slowly return to the starting position.
Important details:
At the top of the movement, move your elbows and shoulders back as far as possible and bring your shoulder blades together.
Options:
The T-bar row is almost identical to the bent-over barbell row, except that one end of the bar is attached to the floor or frame of the machine. As a result, it is possible to achieve less harmful tension in the lower region of the spine.
Bent-over dumbbell row
An excellent basic exercise for developing the central and upper back.
Working muscles:
- Latissimus
- Diamond-shaped
- Trapezoidal
- Rear delta
- Biceps
Exercise technique:
Place your left knee on the bench. Then bend over and place your hand on it. The body is almost parallel to the floor. There is a deflection in the lower back. The right foot is on the floor. With your right hand, hold the dumbbell with a neutral grip. As you exhale, pull the dumbbell to your lower abdomen by contracting your back muscles. As you inhale, slowly lower the dumbbell to the starting position.
Important details:
Try to perform the movement using your back muscles, not your arms. To do this, raise your elbow high and do not move it too far to the side. Keep your back horizontal and don't round it. Don't rotate at the waist. It is in this position of the body that the back muscles are maximally used.
Abdominal thrust while sitting on a machine
Abdominal rows on the machine combine well the strength load with the safety of the workout.
Working muscles:
- Rear delta
- Trapezoidal
- Diamond-shaped
- Latissimus
Exercise technique:
Sit on the seat of the exercise machine and rest your feet on the supports. As you exhale, pull the handles of the exercise machine towards your stomach, straightening your chest and moving your elbows back. As you inhale, slowly return to the starting position.
Important details:
Do not use inertial force. Movements should be slow and controlled.
Problems
The rhomboid muscle is prone to weakness, usually on both sides at once. In such cases, the shoulders shift forward, resulting in stooping. When the fibers are weak, the pectoralis minor muscle begins to shorten. This allows for even greater shoulder displacement. The pectoral muscle in a shortened state can put pressure on the neurovascular bundle. Because of this, there is a feeling of goosebumps in the hands. Another sign of shortening is the rotation of the hands with the back area forward in a standing position with the upper limbs lowered. A weakened one will also displace the scapula, and subsequently the entire shoulder girdle. Following it, the neck and head will move forward, since the extensor muscle is the first to attach to the upper vertebrae of the thoracic region. Due to muscle weakness, it cannot function normally.
Exercises to develop the muscles of the middle back
Both machines and exercises with free weights are suitable for developing the muscles of the middle back. However, it is the simulators that will provide the greatest targeting. Although free weights should not be neglected.
T-bar row
Here, both the lower deltas and the rhomboid muscle are developed. The weight should be selected in such a way that you can perform 8 to 10 repetitions with the maximum range of motion. Moreover, without cheating.
This is a basic exercise that perfectly “gets” to the deepest muscles of the back.
If a T-bar is not available, you can build a similar one yourself by attaching a spacer to the end of a regular bar. Some athletes additionally wrap the spacer, for example, with elastic bandages to ensure the stability of the entire structure.
Row of two dumbbells to the waist from a bent over position
Starting position: the body is tilted parallel to the floor, legs are bent, dumbbells are held in lowered hands. Pull the dumbbells up to your waist and make sure that your elbows do not spread out to the sides. Try to exclude the biceps from the work, and perform exclusively with the efforts of the back. At the top point, pause for 10-20 seconds and slowly return the dumbbells to their original position.
This exercise should be performed with two dumbbells, not one. As for the weight, it should not be too heavy so that you can properly feel the entire movement and perform a static stop at the top peak point for at least 10 seconds.
You can perform this exercise not standing, but lying face down on a horizontal or inclined bench.
Lower block row on the simulator
The muscles of the middle back are worked very well. At the bottom point of the trajectory, you need to try to lower the weight as much as possible, you can even tilt your body and bend your legs. This way you can achieve maximum stretching of the back muscles. When moving up, you need to squeeze your shoulder blades together as much as possible and pull your shoulders back. The number of repetitions is from 10 to 12.
Crossover
This is an arm raise on a machine. When performing this exercise, you need to keep in mind that: if your hands are placed in front of your chest, then the rear deltoid muscle is activated. Therefore, it is better to spread your hands behind your head. The arms are straightened as much as possible, providing tension to the back muscles. Naturally, you need to delay for a few seconds - do not forget about static voltage. Then the weight slowly returns to its original position. The number of repetitions per set is from 10 to 15.
The really important thing here is not to “throw” the weight, but to monitor its controlled lowering
Symptoms of inflammation of the trapezius muscle
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the trapezius muscle are interrelated, therefore, before prescribing treatment, the specialist determines the nature of the manifestations.
A typical clinical picture includes the following signs of inflammation:
- constant pain in the neck, shoulders, between the shoulder blades,
- headaches localized in the back of the head,
- restriction of movements of the arms, head, neck,
- increased pain when palpating,
- feeling of muscle tension,
- decreased concentration.
Weakness, local fever, stiffness, and poor sleep may also be observed.
Why you need to strengthen your back
The spine is a core in the body that performs (together with the bones of the chest and ribs) not only the protective role of all internal organs from external physical influence, but also fixes their location in the appropriate locations.
Without a developed muscular corset, pathological changes in the spinal canal will not be long in coming. A person will be diagnosed with spinal curvature, disc displacement, and protrusion.
Consequences:
1. Various types of pinching and compression of adjacent organs, disruption of their blood supply:
- There will be general imbalances in blood flow and lymphatic flow in various parts of the body. The result is the formation of zones of oxygen starvation and pockets of stagnation.
- The reflex and conduction functions of the spinal cord, an organ of a single part of the central nervous system, will not be performed properly. The consequence is a violation of motor skills, facial expressions, and diction; problems with impulse transmission at the cellular level.
2. External manifestations that have a repulsive effect on surrounding people:
- Slouch.
- Gibbosity.
- Lameness.
3. Decrease in the overall level of human quality of life. A physically developed person (including one with a trained back) has a number of advantages when performing all kinds of power actions.
Don't miss the most popular article in the section: Body drying for girls. Training program, detailed nutrition menu for the month by day.
Trapezius muscle: anatomy and functions
The trapezius muscle is a superficial muscle that occupies the upper back and back of the neck.
In appearance, it resembles a triangle: its base is attached to the spine, and its apex to the shoulder blade. There are 2 such muscles in the body, located on both sides of the spine.
Reference. Together, these two structures form a trapezoid-shaped muscle mass.
The anatomy of the trapezius muscle has a complex structure consisting of 3 sections:
- upper - attached to the occipital bone, cervical vertebrae and collarbone,
- middle - attached to 1-4 vertebrae of the thoracic spinal column and scapula,
- lower - located at the level of 5-12 vertebrae of the thoracic segment and attached to the scapula.
These muscles have important functions: movement, support and stabilization of the spinal column and shoulder blades.
Also, this muscle mass allows a person to perform such actions as:
- raising of hands,
- tilts and turns of the head,
- slight increase in the respiratory capacity of the lungs,
- adduction and dilation of the shoulder blades,
- movement of the shoulder blades up and down.
When damaged, muscle tissue no longer provides the required range of movements. Pain causes physical and mental discomfort to a person and requires immediate treatment.
Physical exercises in the gym to strengthen the rhomboid muscle
- Movement of the block from the floor to the lower back from a sitting position. This exercise helps to significantly strengthen all back muscles as a whole. Sit on the simulator and take the handle of the projectile in your hands, while resting your feet on the special racks. In this position, the knees are bent and the body is vertical to the floor. The position of the lower back becomes similar to a deflection. Now you need to take a deep breath, and as you exhale, pull the handle of the exercise machine towards you all the way to your lower abdomen and return your body to a vertical position. For the greatest effect, it is necessary to bring the shoulder blades as close as possible to each other during the exercise.
- Movement of the block to the chest. This exercise is analogous to pull-ups on a horizontal bar, which allows you to make maximum use of the rhomboid back muscle. To perform this exercise, take the handle of the machine and sit on a special seat. Then, as you exhale, pull the block towards you to the point of the upper part of the sternum, slightly tilting your body back. As you inhale, you need to return to the starting point. While pulling the projectile towards you, move your chest towards the handle, and bring your shoulders behind you as much as possible.
- Pull-ups on the horizontal bar involve many back muscles, which is very effective for strengthening the rhomboid muscle, which is involved along with the rest. To perform this exercise, you need to grab the bar so that your hands are much wider than the ends of the shoulder part of the body. Next, you need to pull yourself up, trying to get your chest to touch the bar of the horizontal bar. Having achieved your goal, you need to return to the starting point. When pulling up, your back should arch slightly and your head should look up.
- The bent over movement with a dumbbell is good for strengthening the central and upper torso. To perform this exercise, you need to place your left kneecap on a bench or any support, and then rest your hand there, with your torso positioned almost parallel to the floor. In this pose, a deflection of the lumbar back is formed, and the right leg stands on the floor. Next, with your right hand, as you exhale, pull the projectile to the lower abdomen, and while inhaling, return to the starting point. For greater effect, you should try to perform the exercise using your back muscles, not your arms.
- The movement of the block to the stomach occurs on the simulator from a sitting position. The load is pulled as you exhale. At this moment, you need to straighten your chest and point your elbows back. As you inhale, we return to the starting point. The main thing with this exercise is that the movements are smooth, without sudden lunges.
- Exercise with a barbell. You need to grab the barbell with your hands, wider than your shoulders, and lean forward slightly with your legs bent. As you inhale, reach the barbell to your lower abdomen, and as you exhale, return to the original position.
Some exercises can be performed in the gym, and it is better to do them under the supervision of a trainer who will prevent incorrect movements.
For athletes who train muscles professionally, for example, bodybuilders, it is necessary to devote as much time as possible to stretching exercises for the back muscles in order not to overload them. , as well as for the prevention of problems with the rhomboid muscles, since such people are most susceptible to such pathologies.
How to relieve PBMC tension
If, after maintaining an uncomfortable static posture for a long time, a person is bothered by pain in the PBMC area, indicating a disruption in its normal activity, it is necessary to quickly relieve excessive tension, leading to weakening of the muscle, as quickly as possible. This can be done at home in several ways.
- Lie on your back on a hard, flat surface (the floor), placing a thin pillow under your head. Place a small round object (ball) under your back between your shoulder blades, focusing on your own sensations: the ball should lie so as to press on the area of the back where the greatest pain is experienced. You need to spend 2-3 minutes in this position. It is important to completely relax, breathe evenly and deeply.
- Sit on a chair, leaning forward and lowering your head. Lie with your chest on your feet. Cross your arms so that you grab your left knee with your right hand and your right knee with your left. You need to stay in this position for about 20 seconds.
- Boat. Lie on your stomach, raise your shoulders and head, bringing your shoulder blades together. At the same time, move your arms back, stretching them along the body, and slightly raise your straightened legs. Maintaining the position, rock up and down, then lower your limbs and head, relaxing your shoulders. When it is not possible to perform a boat while lying down, you can sit or stand and bring your shoulder blades together several times.
With the help of simple exercises that are accessible to people with almost any level of physical fitness, it is possible to temporarily get rid of unpleasant sensations. However, to prevent them from occurring in the future, it is necessary to seriously engage in strengthening the spinal muscles.
Exercises at home
It's not easy to train your back at home. This is due to the anatomy of movements. It is not possible to repeat them without weighting or a special load. And those exercises that allow you to load your back using your own body without special equipment are ineffective when it comes to serious loads. Let's look at some basic back exercises at home.
- Pull-ups. A serious complex exercise that can be performed even without a horizontal bar. It is enough to have a strong door that can support your weight. You can also use any other similar devices.
- Boat. A good exercise that develops the rhomboid and latissimus dorsi muscles. The technique is extremely simple: lie on the floor, slightly raise your outstretched arms and legs.
- Bridge. A static exercise with your own weight that perfectly develops back extensors without injury. Suitable for recovery or maintenance training. It is recommended for anyone who wants to develop not only strength, but also flexibility of the back muscles.
- Farmer's Walk. This exercise is in the home category because it can be performed with any home weight. All you need to do is take 2 thick bags, fill them evenly with books and get started. Develops all muscle groups with an emphasis on the trapezius muscles. There are options in the form of lunges, which additionally load the leg muscles.
Symptoms of inflammation of the trapezius muscle
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the trapezius muscle are interrelated, therefore, before prescribing treatment, the specialist determines the nature of the manifestations.
A typical clinical picture includes the following signs of inflammation:
- constant pain in the neck, shoulders, between the shoulder blades,
- headaches localized in the back of the head,
- restriction of movements of the arms, head, neck,
- increased pain when palpating,
- feeling of muscle tension,
- decreased concentration.
Weakness, local fever, stiffness, and poor sleep may also be observed.
Exercises to develop back muscles
Muscles can always be developed and that's great. Since every organism needs their volume and elasticity. And the best thing that can help you with this is, of course, training and exercises.
However, it is important to remember that you need to choose exercises individually. It's best to do this with a trainer.
But there are still basic and common exercises that can give excellent results.
Basic exercises include:
1. Pull-ups on the bar. This exercise works a large number of muscles in the arms and back.
Pull-ups are one of the universal exercises for developing the muscles of the back and waist. By “playing” with grip width, direction and amplitude, a person can easily redirect the load to those places that he wants to develop, and these are mainly the back muscles, deltoid and biceps.
2. Pull-ups in the simulator are a great way to develop the latissimus dorsi muscles, as well as the shoulder muscles.
3. If we talk about a more complex basic exercise, then the deadlift takes pride of place. To perform this exercise, you will have to use many different muscle groups, and this in turn will make it possible to moderately develop not only your back, but also other parts of the body, such as limbs. No matter how paradoxical it may sound, this exercise is still recommended for beginners, as it is a comprehensive approach for the whole body.
But this exercise is also important for experienced athletes.
4. Bent-over barbell row – This exercise is the best for building the lats. In this exercise, the movement of the barbell towards one or another part of the body plays an important role. For example, if the barbell is raised to the chest, the impact will be on the upper muscles. And if the barbell is near the stomach, then the lower ones.
5. Bent-over dumbbell rows have a beneficial effect on the rhomboid back muscles. When performing the exercise, you need to balance the strength and heaviness of the dumbbell. To perform the exercise, you need to take a comfortable position and fix the upper back. You need to pull the dumbbell by bending your arm at the elbow, but remember not to get carried away with repeated repetitions.
6. Pullover with a dumbbell - has a wonderful effect on the latissimus muscles. This exercise will bring benefits when lying on your back. You need to take a deep breath and try to keep your abs tense. Trying not to change the position of the body, move the dumbbell behind the head. It is necessary to ensure that the back does not arch too much, otherwise there will be no effective impact on the latissimus muscles.
Causes of pain in the trapezius muscle
The causes of pain are many and varied. The most common ones are:
- Constant tension - affects not only intense loads, but also frequent stay in the same position (sedentary work).
- Injuries and bruises are common among athletes. Pain occurs after a hematoma has formed.
- Constant traumatization - monotonous movements provoke the development of stereotypical chronic overexertion. Typically for dancers, gymnasts, tourists.
- Stretching is the result of lack or insufficient warm-up before physical activity, sudden movements, or lifting weights.
- Hypothermia - provokes the development of severe muscle spasms or an inflammatory process - myositis of the trapezius muscle.
- Stress – frequent stressful situations and emotional overload cause muscle tension, which subsequently leads to the development of pain.
- Spinal pathologies – kyphosis, scoliosis, intervertebral hernia.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system – tendonitis, myogelosis.
Also, pain often occurs due to an unsuccessfully chosen sleeping position.
How to quickly correct your posture
In order to correct your posture, you need more than just strength exercises to straighten your back or regularly hang on the horizontal bar. Unfortunately, the gym more often spoils your posture than improves it. For example, latching onto your head instead of your chest is a fast track to chronic pain in the neck, lower spine, and shoulder joints. Just like training your arm muscles with too much weight.
Improving posture is, first of all, increasing the flexibility of the body with the help of special stretching exercises borrowed from yoga. It is known that regular yoga classes not only have a positive effect on a person’s overall well-being and stress level, but are also extremely useful for straightening the back - primarily by developing mobility in the thoracic spine and eliminating stooping.
The advantage of straightening your back is that it can really increase your height and make a person 3-5 cm taller. Performance in strength exercises will improve (especially for the leg muscles - for example, squats), having a positive effect on the development of muscles throughout the body. In addition, strengthening the muscles of the core, back and abs will undoubtedly help to remove belly fat and significantly improve the overall tone of the body.
What is posture?
Posture is the ability of the core and pelvic muscles to maintain the most effective position of the spine. It is correct posture that allows the internal organs of the body to function optimally and the muscles to work at their full strength. Poor posture, in turn, leads to an imbalance in the muscular system, overstrain in work areas and the development of chronic pain. Especially neck pain.
To feel correct posture and a straight back:
- Stand up straight
- Place your feet narrower than shoulder width
- Take a deep breath
- Straighten your shoulders while squeezing your shoulder blades together and slightly moving your shoulders back and down
- Push your chest forward, take another breath and exhale through your diaphragm.
- Tighten your abs, making sure your tailbone is pointing down
- Consciously stretch the top of your head up
- Take three full breaths and relax
Most people will find this posture not only completely uncomfortable, but also quite difficult to maintain. However, this position is only the starting point of any yoga pose, called tadasana. A beginner with minimal knowledge can learn to perform this exercise even at home.
Let us note that the internal muscles of the body and the deep muscles of the spine are primarily responsible for the formation of correct posture. These muscle groups consist predominantly of slow fibers, so training them requires static exercises performed without significant force tension - primarily, the abdominal vacuum exercise and the plank exercise.
Causes of pain in the trapezius muscle
The causes of pain are many and varied. The most common ones are:
- Constant tension - affects not only intense loads, but also frequent stay in the same position (sedentary work).
- Injuries and bruises are common among athletes. Pain occurs after a hematoma has formed.
- Constant traumatization - monotonous movements provoke the development of stereotypical chronic overexertion. Typically for dancers, gymnasts, tourists.
- Stretching is the result of lack or insufficient warm-up before physical activity, sudden movements, or lifting weights.
- Hypothermia - provokes the development of severe muscle spasms or an inflammatory process - myositis of the trapezius muscle.
- Stress – frequent stressful situations and emotional overload cause muscle tension, which subsequently leads to the development of pain.
- Spinal pathologies – kyphosis, scoliosis, intervertebral hernia.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system – tendonitis, myogelosis.
Also, pain often occurs due to an unsuccessfully chosen sleeping position.
Exercises with non-standard equipment
If you have a chest expander, fitball or rubber band (rubber loop) on hand, choose the appropriate one from the exercises presented. They will significantly diversify your load and allow you to work your muscles at a more natural angle. Suitable for both home and hall.
- Reduction of shoulder blades with a chest expander. A unique exercise that simultaneously works the rhomboid and latissimus dorsi muscles. It is considered one of the heaviest. It has the maximum natural amplitude for a person.
- Pull your own weight using a rubber band. A lightweight version of pull-ups and a complete analogue of the overhead pull-down.
- Horizontal pull-ups with a tourniquet. Analogous to the thrust of a horizontal block. One side of the tourniquet is tied to the battery (door handle, etc.), the further task is to sit on the floor and pull your body towards the projectile, completely raising your body and without bending your legs at the knee joint.
- Hyperextension on a fitball.
Consequences
As a result of disturbances in the activity of the rhomboid muscle, the pectoral muscles suffer. It begins to shorten. It is worth saying that the pectoralis minor muscle is fixed on the coracoid process of the scapula and 3-5 ribs. If its operation is disrupted, many problems arise. First of all, the pectoral muscle is a respiratory muscle. Due to its shortening, 3-5 ribs are fixed, the mobility of 3-5 vertebrae becomes limited. As a result, the duration of inspiration decreases. The muscle pulls the ribs up. Because of this, the chest is always in a state of inhalation. The rhomboid muscle is responsible for exhalation. The complex set of changes associated with stooping is called upper cross syndrome.
Let's sum it up
The rhomboid muscle of the back performs the most important functions, therefore, if pathologies concerning it occur, a person loses the opportunity to live fully. For this reason, it is necessary to get rid of the causes of diseases as early as possible. This will be helped by physical exercise and the simultaneous use of medications that will help relieve pain and muscle tension. If the treatment is carried out correctly, under the supervision of a specialist, then you will be able to forget about pain and problems with movement forever.
Why do defined muscles make a person attractive? From an aesthetic point of view, the beauty of the body implies physical health.
Strong back muscles provide powerful protection to the spinal column, a complex organ that ensures the normal functioning of internal organs and is sensitive to disruptions in their functioning.
The strong rhomboid back muscle is located under, and thanks to it a person can freely maintain a beautiful straight posture. Antagonists are the pectoral muscles.
A weak rhomboid muscle leads to gradual shortening of the pectoral muscle. And then it’s very close to problems with the spine.
Functional Features
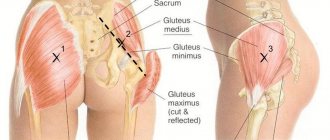
The rhomboid muscle received its name for its resemblance to a geometric figure. In the area between the shoulder blades on either side of the spine, muscle fibers stretch left and right, ending at the lower edge of the shoulder blades.
The muscle consists of 2 parts: the large rhomboid muscle covers the area from 1 to 5 thoracic vertebrae, the small muscle stretches from the 6-7 cervical vertebrae.
The large muscle pulls the shoulder blades toward the midvertebral line, and the small muscle rotates the lower corner of the shoulder blade inward during movements. These are their main functions.
Exercises for the rhomboid muscle group include many basic combinations that also involve other spinal muscles.
These muscle fibers are to some extent independent, since any efforts aimed at strengthening the muscular frame of the back simultaneously have an indirect effect on the rhomboid muscles.
A weak rhomboid muscle causes spinal pathologies in the thoracic region. The back hurts in this area due to the fact that the stretched muscle fibers no longer provide support to the vertebrae, the pressure on which increases.
With increased physical activity, a gradual flattening of the intervertebral discs occurs - and develop.
The problem is aggravated by the fact that the body compensates for the “powerlessness” of the rhomboid muscle by gradually shortening the pectoral muscle fibers.
And then, when a person tries to straighten his back, he cannot completely straighten his shoulders and involuntarily arches his back in the lower back, which is also subject to unnecessary stress.
Thus, a weakened rhomboid muscle becomes the cause of pathologies of the spine in its various parts. To properly pump these muscle fibers, you can perform a wide variety of exercises to strengthen the back muscles.
What movements should you perform?
The anatomy of the rhomboid muscle is designed in such a way that it is involved in almost all back strengthening exercises. You can choose movements that are simple in technique, but very effective. For example, these:
- I.p. – sitting, legs slightly apart. You need to sit at some distance from the back of the chair, bend your elbows. Elbows point down. The shoulder blades move towards each other. Having brought them to the closest possible distance, you need to linger for a few seconds.
- Good training also occurs when performing this exercise: from i.p. – sitting, legs bent at the knees – place your hands on your knees in opposite directions. The left hand lies on the right knee, the right hand on the left. Make a slight tilt with your body forward, tilt your chin slightly down. Hold for a few seconds.
- Other effective exercises for strengthening the rhomboid muscle include movements that involve the shoulder blades. Bringing them together and spreading them, fixing the chosen position is a good training exercise for the specified muscle group. Fortunately, there are a lot of such variations and it will not be difficult to choose the most suitable ones for yourself.
Before starting training, it would be a good idea to stretch your muscles with simple movements: walking with moderate swinging of your arms, stretching them, spreading them to the sides, lowering them down - warming up has a tonic, general strengthening effect. When the rhomboid muscles are warmed up, you can begin the main exercises.
Trapezius muscle: anatomy and functions
The trapezius muscle is a superficial muscle that occupies the upper back and back of the neck.
In appearance, it resembles a triangle: its base is attached to the spine, and its apex to the shoulder blade. There are 2 such muscles in the body, located on both sides of the spine.
Reference. Together, these two structures form a trapezoid-shaped muscle mass.
The anatomy of the trapezius muscle has a complex structure consisting of 3 sections:
- upper - attached to the occipital bone, cervical vertebrae and collarbone,
- middle - attached to 1-4 vertebrae of the thoracic spinal column and scapula,
- lower - located at the level of 5-12 vertebrae of the thoracic segment and attached to the scapula.
These muscles have important functions: movement, support and stabilization of the spinal column and shoulder blades.
Also, this muscle mass allows a person to perform such actions as:
- raising of hands,
- tilts and turns of the head,
- slight increase in the respiratory capacity of the lungs,
- adduction and dilation of the shoulder blades,
- movement of the shoulder blades up and down.
When damaged, muscle tissue no longer provides the required range of movements. Pain causes physical and mental discomfort to a person and requires immediate treatment.
Diagnostics
When muscle activity is disrupted, pain occurs. They are localized in the area of the scapula, along its inner edge. However, pain does not always occur when moving. It can often be felt at rest. It is worth noting that more than one rhomboid muscle is involved in the formation of pain. However, to feel it, it is necessary to eliminate stress points in the infraspinatus, trapezius fibers and the structure responsible for raising the shoulder blades. If crunching, clicking, or pain occurs when moving the latter, this may indicate a malfunction of the rhomboid muscle. An accurate diagnosis must be made by a doctor. Experts do not recommend delaying visiting a doctor.
Main complex
The gradual increase in strength training is carried out in two ways: extensive and intensive. The extensive path involves an increase in the total number of movements. The intensive method involves the use of auxiliary devices.
Universal exercises without machines
These classes can be carried out at home or on nearby sports grounds:
- lifting the body from a lying position with fixing the legs;
- pull-up with a wide wrist grip;
- pulling up by the head;
- push-ups with the widest grip possible.
Such elementary techniques are part of standard sports training complexes. For beginners, it is recommended to increase the frequency of movements over a fixed time, for example, within 1 minute. Sufficient physical fitness allows you to begin quantitative approaches.
Exercises with weights
To develop the rear part of the body, weights reduced by 10–20% are recommended, the emphasis is on the completeness of the exercise. Too heavy weights reduce the range of motion and create constant muscle tension.
At the end of the exercises, the muscles should be pleasantly tired, pain is unacceptable. Overload, such as stress, must be short-lived, otherwise its positive impact is lost. To put it in simple terms, do everything you can and then a little more.
Using a variety of weights (vests, belts, cuffs), you can build muscle mass in a short time, reducing the speed of execution, while simultaneously increasing concentration on the working muscle.
- Pull-ups with weights from 5 kg. Wide straight, reverse grip “behind the head” - for the back muscles, narrow - for the chest.
- Rotations of the body with dumbbells extended forward/arms with weights.
- Lifting - lowering dumbbells/arms with weights in the lateral plane
- Bent-over rows.
- Torso bends.
- Shoulder shrugs (shrugs) with a barbell or dumbbells; a curved neck will help avoid some inconveniences
- Deadlift. In the phase of gaining muscle mass and increasing strength, this is certainly one of the most necessary exercises.
You also need to pay attention to your breathing while performing the action. Inhale - tension, exhale - relaxation, mentally direct energy into the muscle group being trained
The greater the weight, the more important the technique of performing movements.
Exercises for back width in the gym
For back strength training, which should be done regularly two to three times a week, you will need special equipment.
- Vertical block trainer. “Pullover”, rows with a wide and reverse grip. It is the reverse grip that maximally develops the latissimus muscles, giving the body the desired V-shape.
- T-bar. Traction in the safest mode.
- Horizontal block exercise machine. Traction similar to the movements of rowing athletes.
Text neck syndrome [edit | edit code ]
The load on the cervical spine increases significantly if the head tilts forward and down. For example, at a tilt angle of 15 degrees, the load on the spine is approximately 12 kg, at a tilt angle of 30 degrees, the load increases to 18 kg, and at a tilt angle of 60 degrees, the load increases to 27 kg. A similar increase in load occurs when reading books, using smartphones and other devices, and prolonged overload of the spine in turn leads to spondylosis, disc degeneration, osteochondrosis and irreversible curvature of the spine. In the medical community, the position with a large tilt of the head is called “text neck.”
.
According to a medical specialist at New York Spine Surgery and Rehabilitation Medicine, this problem became epidemic in 2020 [1]. Statistics show that the average user spends 2 to 4 hours a day in this position. Violations are detected in 58% of users. This problem is especially relevant for schoolchildren. In addition to disorders in the cervical spine, changes in the natural curvature are also observed in other parts of the spine. This also entails additional complications.
: decreased lung capacity up to 30%, headaches, depression and cardiovascular disease.
Recommendations:
Try to always keep your head straight, looking down at the screen only. Warm up your neck systematically. Use arm resistance from the front, back, and sides to train. Other exercises that help correct posture will also be useful. In order not to forget about the correct posture while reading and writing, it is recommended to make yourself a reminder (on your phone screensaver and desktop).