[edit] History of creation
The date of birth of the Kettlebell Hand Row as a new strength movement can be considered July 29, 2014, when in Russia in Tolyatti the REGIONAL PUBLIC ORGANIZATION OF THE SAMARA REGION “SPORTS ORGANIZATION OF KELLY KELLY RELATIONSHIP” was founded and registered with the Ministry of Justice.
The creator and founder of the Kettlebell Hand Traction can be considered Fedorov S.A., who is the president of KTG. Under his leadership, KTG received competitive development; already 4 months after the founding of the Sports Organization, the first Open City Tournament was held, in which athletes from various sports (athletics, boxing, wrestling, powerlifting, extreme strength) took part. Over the past 3 years, competition rules have been developed and implemented, which were finalized during this time, 11 Tournaments were held, in particular, city, regional, participation in two All-Russian Spartakiads “Invincible Power (Martial Arts Spartakiad)”, holding two international Tournaments[ 1] within the framework of the World Armlifting Championship (Armlifting APL[2]).
Since October 2020, to motivate athletes participating in CTG competitions, sports standards from the third category up to and including Master of Sports have been developed and introduced. As of June 2017, 8 discharge athletes, 5 Candidates for Master of Sports, 4 Masters of Sports in Kettlebell Hand Pull have been trained.
Recommendations for implementation
For men
It will not be possible to perform this exercise in the usual mass-gaining or strength mode, since deadlifts on one leg are impossible with small repetitions with a large weight. And to improve the definition of the muscles of the back surface, 14-16 repetitions with a light weight of 4 sets will be enough.
For girls
It is enough to improve the shape of the gluteal and hamstrings with 20-25 repetitions on each leg, 3-4 approaches. The main thing is to hone your technique, concentrating on the working muscles.
[edit] Rules for the Kettlebell Carpal Row competition
According to the nature of the competition, they are divided into personal and personal-team. In personal competitions, only the participant’s personal result is counted and, in accordance with this, his place in the competition is determined.
In individual-team competitions, the results of one participant and the team as a whole are counted separately. And in accordance with this, the personal places of participants and teams are determined. Competitions are held with weights: 24 kg, 28 kg, 32 kg, 40 kg, 44 kg. The winners are determined in each weight category based on the greatest number of lifts. If several athletes lift the same number of lifts, the advantage goes to:
- a participant who has less body weight before the performance;
- in case of equal weight, the one who was first in the draw wins.
Age of participants
Athletes aged 18 years and older are allowed to compete.
Weight categories
Competition participants are divided into the following weight categories:
- Up to 80 kg - compete with 24 kg and 28 kg weights.
- Up to 100 kg - compete with 28 and 32 kg weights.
- Over 100 kg - compete with 32 and 40 kg weights.
- Absolute category - compete with a 44 kg kettlebell.
Athletes can apply to participate in two categories.
The participants' performance uniform is sports.
For athletes, the time interval is 10 minutes. During this time, the participant must complete the greatest number of lifts.
It is prohibited to use any devices that make the exercise easier (wristbands, elastic bandages on the wrists, gloves on the palms, etc.). Before going on the platform, the athlete can use magnesium on the arms and on the kettlebell.
Representatives and team captains:
- an organization participating in individual-team competitions must have its own representative;
- a team representative may be present at the weigh-in of the members of the team he represents;
- If the members of a team do not have a representative, his duties are performed by the team captain.
[edit] Rules for performing the exercise
2 minutes before the start of the performance, the participant is invited to the performance. During this time, the participant must go to the platform to the apparatus and prepare to perform the exercise. The athlete takes the starting position (goes down to his knees, presses his forearms to the platform, puts his elbows at shoulder level, places the weight on his side, grabs the handle of the weight with his hands so that all five fingers clasp the handle, the thumb rests on top). Five seconds before the “Start” command, the control time is counted: 5, 4, 3, 2, 1. And at the “Start” command, the participant begins lifting the weight, placing it on the handle, with the bottom vertically up. Each lift performed is accompanied by a score from the judge on the platform. During the lifting process, the participant can stop the exercise when the weight is in a vertical position on the handle to rest, holding it in this position. The exercise is considered completed when the weight is in a horizontal position for more than 5 seconds, and the “Stop” command is given. During the exercise, a slight separation of the elbow is allowed when lowering the weight to the lower position.
During the exercise, it is prohibited to lift the body, move the body forward and backward (swinging the body in time with the movement), hitting the weights on the floor, which can make it easier to perform this exercise.
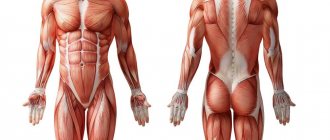
What muscles work during single leg deadlifts?
Both when performing the exercise on two legs and on one, the target muscles are the gluteal and hamstrings. If we compare the exercise with a deadlift on straight legs, where the hamstrings are subject to greater load and stretching, then in a deadlift on one leg, the load will be accentuated on the gluteal group, and all its muscles: large, middle, small.
In addition, an important difference from the classical execution is the connection of stabilizer muscles, which are responsible for maintaining balance and stabilizing the skeleton in an unstable position. Therefore, while maintaining balance, the adductor muscles of the thigh are additionally activated. Quadriceps and shins also act as stabilizers in the exercise. In addition to the muscles of the lower extremities, spinal stabilizers are included: transverse, rectus and oblique abdominal muscles, lumbar extensors, as well as muscles that stabilize the shoulder blades and thoracic region when holding equipment in the hands. thigh biceps, then in the one-leg deadlift the load will be accentuated on the gluteal group, and all its muscles: large, middle, small.
Pros of Single Leg Deadlifts
- Allows you to effectively work out the gluteal muscles and hamstrings even with a light load.
- It has several execution options, allowing you to select the exercise individually at different stages of physical training.
- Develops coordination, balance, strengthens stabilizer muscles, developing the functionality of the body.
- Shapes the buttocks and the peak of the hamstrings, suitable for both men and women.
- Accelerates metabolic processes in the body, allows you to burn subcutaneous fat.
Disadvantages of the technique option
- Not suitable for beginners, as untrained muscles are not able to maintain balance.
- The incidence of injury is increased, again, when performed by an untrained athlete and non-compliance with the technique.
- The difficulty of the technique lies in the instability due to performing on one leg, which initially causes difficulties in maintaining balance.
- It is difficult to concentrate on target muscles until the stabilizers for balance are strengthened.
[edit] Sports standards
From October 1, 2016, ROOSO “Sports Organization of Kettlebell Hand Pull” introduces rank standards for assigning sports ranks up to Master of Sports. Athletes fulfill the standards at competitions in a 10-minute time interval according to the Rules. Weight category:
Up to 80 kg (weight 28 kg):
- MS – 300 lifts
- KMS - 250 lifts
- I category - 200 lifts
- II category - 150 lifts
- III category - 100 lifts
Up to 100 kg (weight 32 kg):
- MS – 230 lifts
- KMS - 180 lifts
- I category - 130 lifts
- II category - 90 lifts
- III category - 50 lifts
Over 100 kg (weight 32 kg):
- MS – 250 lifts
- KMS - 200 lifts
- I category - 150 lifts
- II category - 100 lifts
- III category - 60 lifts
Exercise options
Depending on which segment of the lats you want to focus on, bent over rows can be performed in different ways. Among the most effective and common are the following:
- straight grip barbell row;
- reverse grip barbell row;
- explosive bent-over barbell row;
- barbell row in the Smith machine;
- barbell row lying on your stomach on a bench;
- pulling the barbell to the chest.
Rows with forward and reverse grip
Bent-over barbell rows with a straight grip load the entire array of latissimus muscles and are the main tool for building a wide and sculpted back.
Bent-over barbell rows with a reverse grip place more load on the lower segment of the latissimus dorsi muscles, due to which the back muscles become more prominent and proportional. It is this variation of the bent-over row that creates that very V-shaped silhouette that the vast majority of gym goers are chasing.
Explosive bent over row
Explosive Bent Over Row – The motion vector is about the same as a regular Bent Over Row, but after each repetition we must place the barbell back on the floor and pause for one to two seconds. You can work with any grip convenient for you. This exercise perfectly develops the explosive power of all the muscles of your torso and increases your grip strength. It should be performed with moderate weight, without using an athletic belt or straps.
Smith machine row
Bent-over barbell rows on a Smith machine allow you to better focus on peak contraction of your back muscles. Due to a short pause and “squeezing” the working muscles in the upper position, the back visually becomes more lumpy and developed.
Barbell row lying on a bench
The barbell row lying on a bench is a more isolated exercise for the back muscles, representing a kind of T-bar row with emphasis on the stomach. Can be performed on both a horizontal and an inclined bench. In this exercise, there is virtually no axial load on the spine, so it can be performed by athletes who have medical contraindications to performing bent-over barbell or dumbbell rows.
Bent over row
The bent-over row of the barbell shifts most of the load to the rear deltoid muscles and the back of the trapezius, while the latissimus dorsi muscles act as a kind of assistant in the movement. It is recommended to perform this exercise with a light working weight and try to concentrate as much as possible on contracting the muscles we need. Remember that the middle and rear delts like maximum isolation work, light weights and high repetitions.
[edit] Links
- “Prosport 63” - Information portal of the Samara region
- “Prosport 63” - Information portal of the Samara region
- “Prosport 63” - Information portal of the Samara region
- Tolyatti online – Sports news
- Without format - News of the city of Togliatti
- Without format - News of the city of Togliatti
- TLT.ru - City information portal of Tolyatti
- Sports portal Tolyatti
- TLT.NEWS - Information server
- TLT.NEWS - Information server
- August Radio – August radio FM 102.3
- Vesti Tolyatti
Pulldowns with a medium reverse grip
This version of the exercise works the lower bundle of the latissimus muscles, it does not allow you to emphasize the load on the top, this is not necessary. Many athletes choose heavier weights for reverse grip deadlifts, but this is wrong. It turns out that the load goes to the biceps. It is better to take medium resistance or weight and pull the block, as if meeting the handle of the machine with your chest.
Correct technique
- The grip is shoulder-width apart, not narrower; a narrower hand position requires a special handle with double symmetrical handles to maintain healthy shoulders;
- On a regular handle, grab the notch in the middle, or, if there is none, the handle with gloved hands;
- The palms should be directed towards the athlete's face;
- They sit on the machine bench when the grip is already set and the fingers tightly clasp the handle;
- Then the arms seem to stretch upward, the shoulder blades are assembled towards the spine, the body is tilted back;
- By contracting the latissimus dorsi muscles, the athlete brings the handle of the exercise machine to the top of the chest;
- In this case, the forearms move along the body, the elbows move towards the floor;
- You should not put your elbows behind your back, as well as excessively contract your biceps;
- The reverse movement consists of gradually relaxing the back and moving the handle back;
- The arms are fully extended at the top point of the exercise.
Reverse grip lat pulldown: execution technique
Watch this video on YouTube
Technical errors
- A grip error is holding the handle on your fingertips. This leads to overload of the forearms and a shift in emphasis to them. The forearms become clogged and the athlete cannot complete the required number of approaches and repetitions;
- It is technically incorrect to pull exclusively with the biceps, as if taking the back out of the range of work. From the outside it looks as if the athlete is pulling the handle with his hands and bringing it to his shoulders by bending his arms at the elbow joint;
- You can’t turn on the press too much; this usually happens due to the incorrectly chosen weight of the burden, and the tendency to twist forward, as it were, and pull the lower ribs towards the pelvic bones. This movement helps unload the back muscles, so it is unacceptable