Is cellulite a cosmetic defect or a disease? There is no clear answer to this question. Many physiologists believe that this is just a manifestation of secondary sexual characteristics, because cellulite only affects women. However, in the medical literature there are many synonyms for “orange peel”: small tuberous lipodystrophy, liposclerosis, edematous fibrosclerosis, dermapanniculitis. And they don't sound harmless at all. What is cellulite, why does it occur and how does it manifest? We are looking for answers.
Types of cellulite
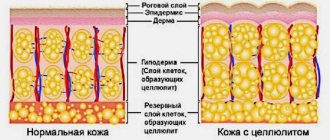
Cellulite (gynoid lipodystrophy or liposclerosis) is a pathological change in the structure of subcutaneous fat. The pathology is caused by circulatory disorders, as well as the outflow of lymph from tissues. As a result, toxins are not removed from the body, fat cells grow and become deformed.
Experts classify pathology according to various parameters. Depending on the clinical varieties, the following types of cellulite are distinguished:
- nodular, which is characterized by single or multiple nodules of varying consistency;
- plaque, in which fatty nodes unite into large foci with an uneven surface and a sunken, atrophic center.
According to the characteristics of the integument, liposclerosis is divided into:
- hard – with dense “balls” connected to the skin that do not change when changing body position. Stretch marks may be present. This look is typical for young, athletic girls;
- soft (flaccid) is distinguished by such signs as: muscle weakness, softness of the epidermis to the touch. The dermis trembles during movement, the tubercles shift when the patient gets up or lies down. It develops more often in women over 40 years of age who lead a sedentary lifestyle;
- edematous – caused by the accumulation of fluid in the legs. A distinctive feature is the formation of dents when pressing on the problem area. The skin becomes thinner, the limbs feel heaviness and discomfort.
Doctors classify mixed lipodystrophy, which is a combination of different types of disease, into a separate category. This is the most common form of the disease.
What is cellulite and its causes?
Cellulite is a stagnant phenomenon in subcutaneous adipose tissue, which leads to its degeneration. This structural change is responsible for the accumulation of fat, weakening of capillaries and the occurrence of edema. The phenomenon of cellulite development has not yet been thoroughly studied; it is only known that the cause of stagnation in the subcutaneous fat layer may not be one factor, but a combination of them.
Factors influencing the occurrence of cellulite:
- hormonal disorders;
- heredity;
- poor nutrition;
- ethnic characteristics;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking and alcohol;
- anatomical features of the skin;
- age.
Cellulite affects not only obese women, but also thin women
It has been established that in approximately 10 cases out of 100, cellulite first appears during puberty, in 20 cases - during pregnancy and after it, 25 women out of 100 noticed the first signs of “orange peel” during menopause. As we can see, most often changes in subcutaneous tissues appear during hormonal surges.
Smoking has a significant impact on the condition of the skin. Cigarette smoke has a detrimental effect on the metabolism in skin cells, disrupting blood supply and collagen formation. All this causes weakening of the connective tissue.
A clear genetic predisposition has also been noted. If the mother had obvious signs of cellulite, then there is a high probability that it will not keep her daughter waiting long.
There is an opinion that Asian women do not develop cellulite. This is wrong. It is also known to them, but due to natural thinness, thin bones and dietary culture, it is not so often found on representatives of the yellow race. In addition, the “orange peel” is not so clearly visible on dark skin.
Among women, cellulite occurs in almost 90% of cases
Development mechanism
Doctors diagnose four degrees of cellulite. Each of them is characterized by certain disturbances in the structure of the integument:
- First, the permeability of the vascular walls increases, blood circulation and lymph outflow worsen. Water begins to fill the intercellular space.
- During the transition to the second stage, dense lymphatic stagnation is formed, the disorder spreads to large veins, deposits become denser, and the tissue of the connecting septa changes.
- Vascular disorders progress, blood seeps into the surrounding fibers, and hematomas appear on the body. Swelling is increasing. The connective tissue receives less oxygen and nutritional components, grows, thickens, and fat cells swell.
- At the last stage, not only the septa are sclerotized, but also the fat cells. The lobules are united into nodes (macronodules). In addition to the damage to veins and arteries, compression of nerve fibers is added.
The first and second stages of lipodystrophy are classified as cosmetic defects. At these stages, the development of the disease can be stopped and the natural structure of the dermis can be restored. Third and fourth degrees are a serious disease that requires qualified therapeutic or surgical treatment.
Stages of the disease
For most women, unsightly bumps under the skin do not form in a day or two, but over a long period of time. Sometimes “sedentary” work reduces the time for the appearance of “orange peel” to a year or less.
Modern cosmetology distinguishes two scales of cellulite stages. One of them is used by specialists. It describes in detail the main forms with intermediate stages. Complex medical terms will provide little clarity to a wide range of readers.
Another scale clearly describes the stages of cellulite:
- 0 – absence of unesthetic signs, normal skin tone;
- 1 – violation of fat breakdown is easy to detect. Grab a small area of the body measuring 5-10 cm with your fingers, squeeze lightly - tubercles form on the surface;
- 2 – manifestations of cellulite are visible even without squeezing the skin, there is no pain;
- 3 – the bumpy relief is clearly visible, squeezing the affected areas causes pain.
How to determine the stages of cellulite
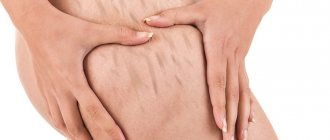
Many girls know how to determine whether they have cellulite. But, unfortunately, changes are already detected in rather advanced forms. Meanwhile, specific symptoms are observed at all stages of lipodystrophy development, including the earliest.
Stage 1 - pre-cellulite
At this stage, negative changes are almost invisible. In a relaxed state, the integument looks smooth and even. If you squeeze and palpate the fold of the dermis, lumps are felt in it. The fat layer is soft.
The affected areas (usually the thighs, buttocks) slightly increase in volume due to slight tissue swelling. Scratches take longer to heal, minor injuries cause bruises.
Stage 2 - initial
Swelling increases; with compression of the epidermis or muscle tension, an inconspicuous lumpiness is visible. In a static state, small “waves” are noticeable.
The subcutaneous tissue hardens when palpated. After pressing, dents remain that are not immediately smoothed out.
Stage 3 - micronodular
The “orange peel” remains in a calm and tense state. The swelling volume of the thighs increases. Tubercles appear on the surface of the skin in areas of overgrown fat lobules, and pits appear in the area of connecting septa. On palpation, small nodules are detected.
Spontaneous hematomas appear on the integument. The skin turns pale, dries out, and becomes cool to the touch due to a decrease in local temperature. A venous pattern appears in problem areas.
Stage 4 - macronodular
Pronounced large numerous bumps are formed in a static position (for example, standing or lying down). The integument is bluish, cold areas alternate with hyperemic ones. The venous network is clearly visible.
Patting or trying to make a fold of skin causes pain. During palpation, large painful nodes are clearly felt. The epidermis is rough, with severe swelling.
In addition to those listed, some experts also identify the fifth and sixth stages of liposclerosis. They differ from the fourth in the large area of affected areas and the redistribution of deposits in parts of the body that are uncharacteristic for them.
The first stage is the restoration of microcirculation
At the beginning of each stage 1 procedure, we must first perform a main vascular puncture (capillary mesotherapy), using the combined drug “GAG Complex DVL Capyl” - based on gingo biloba extract and troxerutin. Based on its composition, it is a vascular drug that specifically affects microcirculation. But, if we also need pronounced drainage properties, then we can add a couple of ml of drugs to the syringe with this drug - “Artichoke” or “Rutin + melilot extract”.
Examples of drugs –
The main vascular puncture is done along the lines along the spine, including paravertebral lines, as well as along the legs, i.e. along the lateral outer and inner surfaces of the thighs and legs (stripe technique), in increments of 1.5 cm. Usually we need 5.0 ml of the drug for this. Our goal is to activate metabolism, microcirculation and lymphatic drainage not only locally, but throughout the entire body. After this, we move on to working with local problem areas.
Working with problem areas - the optimal preparation for this is “GAG Complex DVL E”, which, in addition to gingo biloba extract and troxerutin, also contains artichoke with yohimbine. Artichoke has drainage properties, relieving interstitial edema, and yohimbine is a lipolytic with combined action. Yohimbine simultaneously affects alpha-adrenergic receptors of fat cells, thereby reducing lipogenesis, as well as beta-adrenergic receptors, activating lipolysis in fat cells.
Thus, this drug will allow us in areas with cellulite to improve microcirculation with lymphatic drainage, relieve swelling, as well as activate lipolysis and suppress lipogenesis in fat cells. Problem areas (for example, buttocks and thighs) are pierced in a checkerboard pattern in increments of 1.5 cm. For stages 1-2 of cellulite, we can take about 8-10 ml of the “GAG Complex DVL E” drug for injection in local areas, and for stages 3 -4 stages – use from 10 to 15 ml of this drug.
All procedures are carried out once a week. The total number of procedures at this stage of treatment for stages 1-2 of cellulite is 4-6 procedures. It turns out that if you only need cellulite prevention, or you only have stage 1 of cellulite (in the absence of an increased body mass index), you can limit yourself to stage 1 of treatment. If you have stage 1 against the background of an increased body mass index, or you already have stages 2-3-4, in any case we move on to the second stage of treatment, i.e. active lipolysis.
Treatment at every stage of cellulite
Therapy for lipodystrophy, regardless of the stage of development of the pathology, is aimed at:
- stimulation of fat breakdown;
- normalization of lymphatic drainage;
- improved blood circulation;
- improvement of blood vessels;
- muscle toning;
- strengthening the epidermis, increasing its firmness and elasticity.
At any stage of cellulite, treatment begins with nutritional correction. You will have to give up:
- semi-finished products;
- fatty, fried foods;
- heavy cream desserts;
- pickles;
- marinades;
- sweets;
- smoked meats;
- flour;
- sausages.
The diet should be balanced. It should be filled with plenty of fruits, vegetables, herbs, seafood, dairy products, poultry (it must be cooked without skin), and beef. Food must be stewed, boiled or steamed. It is permissible to use cereals as side dishes for meat and fish dishes. It is better to replace sugar with honey, and limit salt consumption.
Why does this happen?
Among the many factors that are direct or indirect causes of lipid metabolism disorders and, consequently, the development of cellulite, the main ones can be confidently identified:
- hormonal imbalance, primarily ovarian dysfunction, accompanied by an increase in estrogen levels in the blood;
- thyroid diseases and other endocrine disorders;
- disorders of protein metabolism, in particular a decrease in the level of albumin protein in the blood;
- hereditary factor;
- violation of proper diet;
- physical inactivity, i.e. sedentary life;
- chronic stress;
- chronic fatigue, etc.
Habits that will help you get rid of cellulite
To stop the development of lipodystrophy, you need to change some habits:
- reduce your coffee consumption to one small mug in the morning. The rest of the time, drink green tea, natural (not packaged) juices, fruit drinks, herbal decoctions with diuretic properties;
- if you want to drink alcohol at the holiday, you should give preference to dry red wine (no more than 150 g);
- quit smoking;
- do not consume a lot of fatty dairy products (ice cream, yogurt, cottage cheese);
- include sea fish and fresh vegetables in your diet;
- do not wear high-heeled shoes or tight clothing every day;
- change body position more often, get out of the habit of sitting cross-legged.
A good way to remove cellulite on the butt is to stop using the elevator and walk up the stairs home.
Prevention at an early stage
The main role in preventing the formation of “orange peel” on the legs, buttocks or stomach is played by a balanced diet combined with regular physical activity.
To maintain a beautiful figure, you need to:
- spend more time outdoors;
- get a good night's sleep;
- do exercises every day;
- When going outside in the summer, apply sunscreen to your body;
- use anti-cellulite cosmetics;
- develop stress resistance;
- take a contrast shower every day, rinse problem areas;
- balance your drinking regime (drink at least two liters of water per day).
Weight needs to be lost gradually. Dramatic weight loss will only make the skin sagging and the bumps will become more noticeable. Constant jumps in body weight will lead to the final loss of firmness and elasticity of the integument.
Lipodystrophy in the early stages is a cosmetic defect that can and should be combated. Otherwise, it will turn into a pathological form, and the reverse process will no longer be possible. It is better if the patient’s question of how to get rid of cellulite is answered by a doctor. A qualified specialist will help you choose the most effective creams and develop a special diet and set of exercises. The main thing is that measures to combat the “orange peel” are consistent and regular. Exercising “occasionally” and constant disruptions in nutrition will not only not bring the desired result, but will also accelerate the development of the disease.
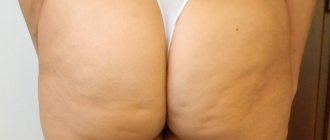
Cellulite can be felt under the skin: what’s wrong with my body, what should I do?
Cellulite can be felt under the skin.
Doctors have long developed a classification of cellulite as a disease. It can be of different types, but they all have a similar feature: any type of cellulite affects women more often than men. If cellulite can be felt under the skin, this is a reason to talk to a specialist. Below we will briefly look at the characteristics of the problem and some methods for solving it. Cellulite can be felt under the skin - what’s wrong with my body, what should I do?
If the fat is already palpable, then complications have appeared, which are called hard cellulite.
- This type of disease most often occurs in young women and is one of the first external signs of hard cellulite.
- The skin becomes dense and grainy, sometimes with dimples similar to an orange peel.
- The appearance of the affected skin does not change when walking or moving. The skin appears to be firmly attached to the muscle.
Vulnerable areas:
- The buttocks and upper thighs are often located around the back and behind the knees.
Age:
- It starts already in adolescence.
- Without early treatment, hard cellulite will never be eliminated.
Appearance:
- The skin is dimpled or pitted, but the affected areas are permanent and do not change position when the body moves.
Texture:
- The skin appears too tight and may be sore or sensitive to the touch.
What to do? Treatment:
- Steps to resolve the problem must be taken immediately.
- One of the most effective treatment methods is mesotherapy. The procedure involves injecting customized combinations of medications, vitamins and natural extracts into the mesoderm layer where they target the problem below the surface.
- Cosmetic creams have also worked well and should be applied twice a day at the beginning of treatment, followed by long-term “maintenance” applications.
- Endermological and cosmetic procedures using special devices that help “break up” and “tear” cellulite from the muscles can be effective and safe in solving the problem.
It is important to remember: When cellulite appears, especially in adolescence, you should not be scared or worried. This can aggravate the problem, and the girl will begin to “eat up” her experiences, which can even lead to obesity.
It should be understood that every woman has such fat deposits, and this is due to a special hormonal background that only women have. Men rarely experience cellulite due to the presence of male hormones in the body.