Omega-3 fatty acids are extremely beneficial and essential for health. They are sometimes called “vitamins” for a reason.
(In the strict sense of the word they are not, but the term correctly emphasizes their important role: “vitamin” - important for life.)
In this article, we have prepared instructions on how to take omega-3 correctly. Let's talk about:
- how much omega-3 is needed per day (dosage);
- advantages of drugs in capsules compared to oily fish;
- who is at risk of omega-3 deficiency;
- how likely and dangerous a deficiency is in vegans and vegetarians;
- about the dangers of omega-3 in too large doses.
Main thoughts:
General recommendation for daily dose of omega-3: 500-2000 mg (in active forms EPA and DHA) or 2 times a week eating fatty fish
For optimal health, a balance between omega-3 and -6 fatty acids in the diet is important. The ideal ratio is 2:1 (omega-6: omega-3). However, statistics say that in the diet of the average Western person the balance is imbalanced and is approximately 15:1
Those who do not regularly eat fatty fish and other seafood are recommended to take additional omega-3 supplements in capsules
Vegetarians and vegans are recommended to take omega-3 supplements in capsules based on microalgae (phytoplankton): they are absorbed just as well and are just as beneficial as fish oil capsules
In the blood of vegans and vegetarians, the level of active forms of omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) is usually reduced, but a critical deficiency never develops due to an adaptation mechanism that increases the synthesis of omega-3 in the body
Omega-3 deficiency, which is dangerous for the function of important organs and tissues (brain, retina), can develop as a result of a lack of omega-3 in the diet over several generations. The result may be impaired vision and brain function in new generations
Children at risk for acute deficiency include those who were fed formulas deficient in active forms of omega-3 (DHA and EPA), as well as those whose parents, grandparents (etc.) did not consume them sufficiently
Omega-3s are considered relatively safe for health. However, too large doses of omega-3 per day (over 3000 mg) may be harmful because have a thinning effect on the blood and increase the risk of vitamin A overdose
A Brief Introduction to Omega-3s: What Anyone Considering Taking Omega-3s Needs to Know
Omega-3 fatty acids belong to the class of polyunsaturated essential fatty acids. “Irreplaceable” means that they must be present in the diet for the body to function properly.
Not all omega-3s are created equal.
There are three main forms of omega-3: ALA, EPA, DHA. ALA is the inactive form of omega-3 and must be converted into EPA and DHA within the body. The conversion efficiency is very low (~5%).
Therefore, omega-3 in the form of ALA should never be the sole source of these fatty acids.
Omega-3 in the form of ALA is found mainly in plant foods: flaxseed and oil, walnuts, chia seeds, soy.
EPA and DHA are the two active forms of omega-3s that are directly responsible for their beneficial properties. Their sources are fatty fish, fish oil, and krill oil, but they are initially synthesized by seaweed, which serve as food for marine life and, after absorption, become structural elements of tissues 1.
Omega-3s are active structural components of the body's cells, including some of the most important organs and systems: the brain, nervous tissue, eyes, sperm.
“Active” in this context means that they not only form the structure of cell membranes, but under certain conditions (stress in the form of inflammation or pain, for example) can leave them, performing useful functions.
So they participate in the formation of special signaling molecules (eicosanoids), which are very similar in structure to omega-3 fatty acids and have an anti-inflammatory effect, which explains many of the beneficial properties of omega-3 in the body (for cardiovascular, immune, endocrine, nervous systems), because Most diseases are accompanied by inflammatory processes.
We recommend : Read more about what omega-3 fatty acids are, their different forms and beneficial properties based on scientific research in the material What are Omega-3 fatty acids good for?
Scientific facts.
Salmon (4,023 mg per serving)
Salmon is one of the most nutritious foods on the planet.
It contains high-quality protein and a variety of nutrients, including large amounts of magnesium, potassium, selenium and B vitamins (,).
Research shows that people who regularly eat fatty fish such as salmon have a lower risk of developing diseases and conditions such as heart disease, dementia and depression (, , , ).
Omega-3 content : 4023 mg per half fillet (178 g) of cooked, farmed Atlantic salmon or 2260 mg per 100 grams ().
You can learn more about the benefits of salmon for the human body on this page - Salmon: benefits and harm to the body.
How to take omega-3 fatty acids correctly
There are two ways to meet your daily requirement of omega-3 fatty acids: omega-3 rich foods and dietary supplements.
Often, expert recommendations on how to properly take omega-3 boil down to a simple rule: eat fatty fish at least twice a week 33.
The healthiest types of fish in terms of omega-3 content are salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, and sardines. For detailed information about natural products rich in omega-3, follow the link below in the material Which products contain omega-3 (table).
The omega-3 content of fish is determined by the food it is fed with. This is why farmed salmon (aquaculture) and wild salmon contain different amounts of omega-3: farmed salmon usually has a little more than 2.3. Why? Because there are more of them in the food.
Very low omega-3 content in beef and other meat and dairy products. However, if animals are raised in natural free-range conditions on pastures, their meat contains more than 4 omega-3 fatty acids.
Today, many food manufacturers fortify their products with omega-3 in the form of DHA. We are talking about eggs, yogurt, milk and soy products. Naturally, it is better to give preference to them.
We recommend : The benefits and harms of fish for human health: the result of an analysis of more than 40 scientific studies
Daily requirement
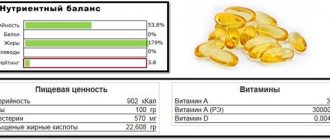
The daily norm of Omega 3 for women is 1-1.5 grams or 1000-1500 mg. The minimum daily dosage of Omega 3 for women is 250 mg (0.25 g). During pregnancy, menstruation, lactation, heavy physical activity, the dose can be increased to 5-6 g. You should not consume more than 7-8 g per day. You should take 3-4 capsules after meals.
Omega-3 dosage per day
It is necessary to understand that the recommended daily dose of omega-3 is a very relative value , which is a natural consequence of the ambiguity of the results of scientific studies of their effectiveness: very often, when using the same dose, scientists obtain different results, or in some experiments the effect can be positive with small doses , in others - at large ones. For an illustration, see What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are Good For. Scientific research.
This fact is manifested in particular in the significant difference in the daily doses of omega-3 recommended by leading health organizations: it is in a fairly wide range from 250 to 2000 mg per day 5,6:
Share with us your experience of losing weight or gaining muscle mass!
- World Health Organization - 2000 mg per day ;
- US Department of Health - 500 mg per day .
At the same time, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) calls the safe limit (maximum dose) 3000 mg per day 6.
Important: we are talking about the active forms of omega-3 DHA and EPA.
For pregnant and nursing mothers, it is recommended to increase the daily dose of omega-3 by at least 200 mg (in the form of DHA) on day 9, because they are very important for fetal development.
It is also important to keep in mind that the dose of omega-3 is determined largely by how much omega-6 is in the diet: the more of the latter, the more omega-3 you need.
General recommendation for daily dose of omega-3: 500-2000 mg (in active forms EPA and DHA) or 2 times a week eating fatty fish
Instructions for use of liquid fish oil
In liquid form, fatty acids are now used less and less, but some, in the old fashioned way, prefer to take them in the form of a solution. The oily liquid should be taken with meals so as not to cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract. An adult (regardless of whether he is a man or a woman) needs to take 1 tablespoon once a day. The duration of the course of treatment and dose adjustment are carried out by the doctor depending on the indications for use and possible restrictions.
Interestingly, the modern pharmaceutical industry has learned to produce a liquid without a fishy smell. And even flavored, for example, with the smell of lemon.
Omega-6s in your diet affect the amount of omega-3s you need
One study found that when the proportion of omega-6 rich foods in the diet increases, the blood trigylceride-lowering benefits of omega-3, which is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, are significantly reduced.
The same fish with the same levels of the health-promoting omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, but a different ratio of omega-6 to omega-3, has different effects on cardiovascular disease risk factors: blood triglyceride levels (blood clots) and inflammatory processes 10,11.
The average Westerner's diet contains 10-15 times more omega-6 fatty acids than omega-3 fatty acids . The source of omega-6 is mainly refined vegetable oils, which are added to processed foods (sunflower, palm, etc.) 12,13.
Experts say this ratio should not exceed 2:1 (omega-6:omega-3) 14.
The fact is that both types of fatty acids seem to compete with each other: they require the same enzymes to be converted into their active form: the more omega-6, the smaller the share of enzymes goes to omega-3 15,16.
Or in other words, if the diet is very high in omega-6, then a higher dosage of omega-3 is needed.
It also works in the opposite direction: reducing the amount of omega-6 reduces the required amount of omega-3.
For optimal health, a balance between omega-3 and -6 fatty acids in the diet is important. The ideal ratio is 2:1 (omega-6: omega-3). However, statistics say that in the diet of the average Western person the balance is imbalanced and is approximately 15:1
We recommend : Mercury in fish: risks. Scientific research
If you think what we do is important, support our project!
YES!
Is it worth taking?
Omega-3 is an absolutely necessary supplement, the role of which is increasing every year. The quality of food regularly deteriorates and today it is almost impossible to get the daily requirement of healthy fats from ordinary foods. To do this, the fish must be freshly caught, without freezing or heat treatment. Moreover, in most countries, sea fish (especially salmon) are grown on special farms and there is much less omega-3 in them than in ordinary sea fish. In such cases, taking the supplement is highly preferable for all people who want to improve their health, and also necessary for those who are determined to progress in any sport.
How to take omega-3 capsules. Omega-3 doses in capsules
Omega-3 supplements are another good alternative source of the health-promoting active forms of omega-3 EPA and DHA.
Most scientific studies highlighting the benefits of omega-3s use dietary supplements.
The best omega-3 capsules are those made from fish oil, krill oil, and cod liver oil. For vegetarians, there is a worthy alternative - omega-3 preparations based on algae.
Both contain omega-3s in the active forms EPA and DHA and are very well absorbed.
The average fish oil capsule weighs 1000 mg and contains approximately 180 mg EPA and 120 mg DHA. However, doses of omega-3 vary widely among products from different manufacturers 17.
Pay attention to the difference in the mass of the omega-3 capsule and the fatty acids in it: when purchasing, it is very important to pay attention to the mass content of EPA and DHA in each capsule . Sometimes the manufacturer may indicate the weight of fish oil per capsule, which is NOT equivalent to the weight of omega-3 fatty acids.
In addition to omega-3, cod liver oil contains fairly large doses of vitamins A and D. On the one hand, this is good. On the other hand, it is important to always keep this in mind to avoid an overdose: an overdose of vitamin A can be dangerous to health.
Today, many types of fish have high levels of contamination with toxins and heavy metals. In particular, mercury and lead. One of the undoubted advantages of omega-3 preparations is that, as a rule, they are purified of toxins and heavy metals during the production process 18.
For more information about omega-3 preparations, their varieties, advantages and disadvantages based on scientific research, read the material Which omega-3 preparations (capsules) are the best: how to choose and what to buy.
Those who do not regularly eat fatty fish and other seafood are recommended to take additional omega-3 supplements in capsules
We recommend : Which vitamins are better to take: synthetic or natural from products?
Daily intake of omega-3 for children
Polyunsaturated acids are important for the child’s body, but even more important for the embryo developing in the womb. Without fatty acids, proper intrauterine development of a child is impossible.
How much omega-3 should children of different ages consume per day? The daily dose is:
- for children from 6 months to 3 years – 70 mg;
- for children from 3 to 6 years – 100 – 120 mg;
- for children from 6 to 12 years old – 200 – 250 mg.
It is advisable to agree on the dosage and course of administration with your pediatrician.
What omega-3 supplements should vegans/vegetarians take?
Despite the fact that the list of products containing omega-3 in fairly large quantities includes many vegetable products (flax seeds and oil, chia, walnuts, sesame, etc.), as already mentioned, all of them are a source of the inactive form of omega-3 - ALA - whose effectiveness is very low, as are its beneficial properties.
Most omega-3 preparations in pharmacies are made from fish, so they are not suitable for strict vegetarians (vegans).
But for vegetarians, there is a wonderful alternative - omega-3 preparations based on phytoplankton (algae) - the same one from which omega-3 fatty acids enter the body of fish and shellfish, including krill.
Such preparations are an excellent and probably the only plant source of effective forms of omega-3 DHA. In terms of their beneficial properties and degree of absorption, they are close to fish oil 19-22.
Vegetarians and vegans are recommended to take omega-3 supplements in capsules based on microalgae (phytoplankton): they are absorbed just as well and are just as beneficial as fish oil capsules
Mackerel (4107 mg per serving)
If you're wondering which foods have the most omega-3s, look no further than a familiar fish called mackerel.
Mackerel is a small, fatty fish.
In Western countries, it is usually smoked or eaten in a pickled form.
Mackerel is incredibly rich in nutrients - a 100-gram serving contains 200% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) of vitamin B12 and 100% of selenium ().
In addition to the fact that this fish is very healthy, it also tastes delicious.
Omega-3 content : 4107 mg in one piece (80 g) of salted mackerel or 5134 mg for every 100 grams ().
You can learn more about the benefits of mackerel for human health on this page - Mackerel: benefits and harm to the body.
Omega-3 deficiency. Symptoms. Risk of acute deficiency in vegetarians and vegans
Scientists note that if there is a lack of omega-3 in active forms (DHA and EPA) in the diet of vegetarians, complete depletion of their content in the blood does not occur, because the body adapts and increases the production of active forms of omega-3 (DHA and EPA) in the liver from inactive forms (ALA) found in many plants 23,24.
Also, during periods of poor nutrition or dieting, when an energy deficit is created, the body begins to use fat stored in fat stores for energy, while simultaneously releasing omega-3 25.
Read us on the networks
As the amount of omega-3 (DHA and EPA) in the diet increases, their synthesis by the body decreases. This is an adaptation mechanism, which probably explains the fact that a critical omega-3 deficiency that is dangerous to health is almost never observed.
In the blood of vegans and vegetarians, the level of active forms of omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) is usually reduced, but a critical deficiency never develops due to an adaptation mechanism that increases the synthesis of omega-3 in the body
However, animal experiments have shown that acute deficiency of omega-3 (DHA) in important organs (retina and brain) is possible after restricting them in the diet for several generations , which manifests itself in impaired vision and brain function in offspring 26-28.
Omega-3 deficiency, which is dangerous for the function of important organs and tissues (brain, retina), can develop as a result of a lack of omega-3 in the diet over several generations. The result may be impaired vision and brain function in new generations
With a lack of omega-3 (DHA) in the diet, their concentration in the brain drops by 30%-50% (the lower limit corresponds to a diet high in plant omega-3 (ALA), the upper limit is low) 29.
This omega-3 depletion occurs with prolonged dietary omega-3 deficiency from 18 months to 5 years and is further accelerated by alcohol intake 30,31.
We recommend : Protein and cancer: Animal protein is one of the main causes of cancer. Interview with a leading expert
Symptoms of acute omega-3 deficiency 32:
- roughening of the skin;
- dermatitis;
- a drop in the level of omega-3 in the form of DHA in the blood and tissues.
We recommend
Omega-3 krill oil and fish oil capsules can be purchased at iHerb.com. The iTested option on the left side of the panel allows you to display additives tested for quality in an independent laboratory.
Groups at risk for omega-3 deficiency
As noted above, omega-3 deficiency as such is a very rare phenomenon 32 due to the body's adaptive mechanism and its ability to synthesize active forms of omega-3 (DHA, EPA) from inactive ones (ALA), as well as releasing them from fat stores.
Therefore, the only people at risk for omega-3 deficiency are those whose parents did not consume enough omega-3 (in the form of DHA) or, even worse, several previous generations of whom had a lack of these fatty acids in their diet .
Also at risk for omega-3 deficiency are children who were fed infant formulas deficient in active forms of omega-3 (DHA and EPA). An example is soy infant formula, in which omega-3s are present in the form of ALA.
Children at risk for acute deficiency include those who were fed formulas deficient in active forms of omega-3 (DHA and EPA), as well as those whose parents, grandparents (etc.) did not consume them sufficiently
We recommend : The benefits and harms of milk: expert reviews
Walnuts (2,542 mg per serving)
Walnuts are very nutritious and rich in fiber. They also contain high amounts of copper, manganese, vitamin E and important plant compounds ().
When consuming them, the peel should not be removed, as it contains a large amount of phenolic antioxidants, which have important beneficial properties.
Omega-3 content : 2542 mg per 28 gram serving, equal to approximately 7 walnuts ().
You can learn more about the benefits of walnuts for human health on this page - Walnuts: benefits and harm to the body.
Omega-3 harm: too large doses of omega-3 per day can be hazardous to health
According to the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), a dose of omega-3 per day of 3000 mg is safe 6.
According to the European equivalent of the FDA - EFSA - daily doses of omega-3 up to 5000 mg are not harmful to health.
What is the basis for setting an upper limit?
Too much daily dosage of omega-3s can thin the blood , causing excess bleeding from open wounds or certain medical conditions.
This is why very often doctors recommend excluding omega-3s from their diet to patients who are undergoing surgery several weeks before it.
Another reason for limiting the dose of omega-3 is the high probability of overdose of vitamin A , which is included in many preparations based on fish oil and cod liver oil, an overdose of which can be hazardous to health.
In scientific experiments to study the benefits and harms of omega-3, doses of omega-3 exceeding 5000 mg are almost never used.
Omega-3s are considered relatively safe for health. However, too large doses of omega-3 per day (over 3000 mg) may be harmful because have a thinning effect on the blood and increase the risk of vitamin A overdose
Contraindications and side effects
In general, omega-3 has no contraindications or side effects. These are absolutely essential substances for the body. However, it is important to avoid overdoses, which can lead to various bleeding and other individual reactions (in rare cases, rash or allergic reactions).
When consuming omega-3, you must strictly adhere to the indicated dosages. The maximum permissible daily allowance is 4 g for men and 3 g for women. The optimal amount is considered to be 2-3 grams/day.
Table of Omega-3 acids content in 3 products
Data on the amount of essential omega-3 PUFAs in popular foods are shown in the table.
| Product | What acid does it contain? | Content per 100 g of product, mg | Additionally |
| Mackerel | EPA+DHA | 5 134 | 100 g of mackerel contains 200% of the daily value of vitamin B12 and 100% of selenium |
| Salmon | EPA+DHA | 2 260 | Contains high-quality protein, large amounts of magnesium, potassium, selenium and B vitamins |
| Herring | EPA+DHA | 1 729 | 100 g of herring contains 400% of the daily value of vitamin D, 200% of vitamin B12 and 50% of selenium |
| Oysters | EPA+DHA | 672 | Oysters contain more zinc than any other food - 600% of the daily value per 100 g, as well as 200% copper and 300% vitamin B12 |
| Sardines | EPA+DHA | 1 480 | 100 g of sardines contain 150% of the daily value of vitamin B12 and 75% of selenium |
| Tuna | EPA+DHA | 1 664 | 100 g of tuna contains 180% of the daily value of vitamin B12 and 65% of selenium |
| Anchovies | EPA+DHA | 2 113 | Product rich in vitamin B3, selenium and calcium |
| Red and black caviar | EPA+DHA | 6 789 | High content of vitamins B4 and B12 |
| Flax-seed | ALC | 2 2813 | Very rich in fiber, vitamin E, magnesium |
| Chia seeds | ALC | 17 552 | High level of minerals: calcium, manganese, phosphorus |
| Walnuts | ALC | 9 079 | Contains a lot of fiber, copper, manganese, vitamin E |
| Soya beans | ALC | 1 443 | Source of potassium, magnesium and vitamins B2, B9, K |
| Brussels sprouts | ALC | 173 | Source of vitamins C and K |
Summarize
- When taking omega-3 fatty acid supplements, always follow the directions on the label.
- However, keep in mind that omega-3 requirements vary from person to person. Some people may need more than others.
- The recommended intake level for alpha-linolenic acid is 1.6 grams per day for men and 1 gram per day for women.
- In contrast, there are no official guidelines regarding long-chain omega-3 supplementation. However, medical organizations generally recommend a minimum of 250 mg and a maximum of 3,000 mg of combined EPA and DHA per day, unless your doctor instructs otherwise.
Tags: Omega-3
- Related Posts
- Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG): properties, dosage, side effects
- Transglutaminase (meat glue): what is it and is it safe?
- 6 Side Effects of Vitamin D
« Previous entry